IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Ongoing avian influenza outbreaks in animals are raising concerns about the potential risks to humans, according to a joint statement issued by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the World Health Organization (WHO), and the World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH).
About Avian Influenza:-
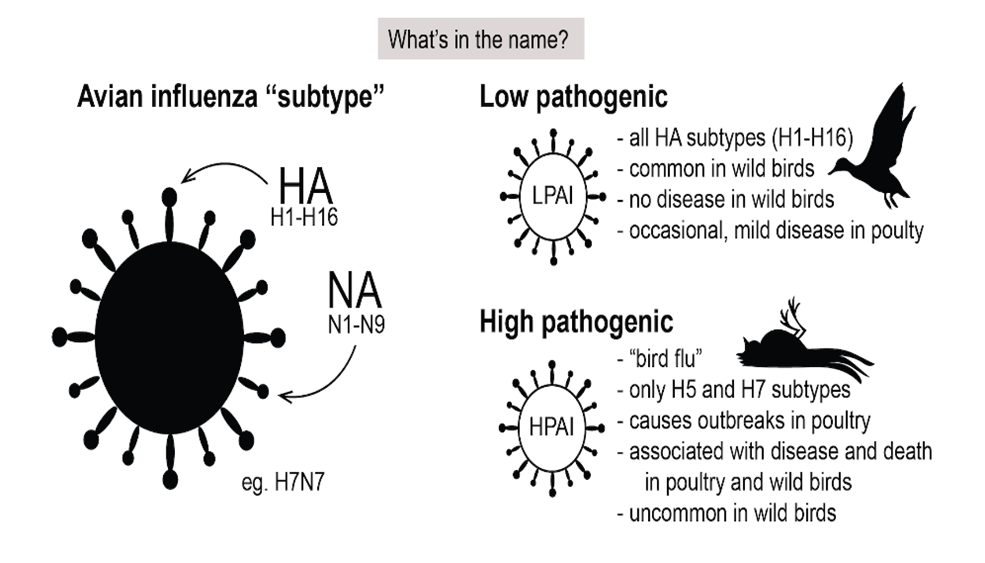
IMAGE SOURCE: The Conversation
- Avian influenza or bird flu refers to the disease caused by infection with avian (bird) influenza (flu) Influenza A viruses. (UPSC CSE: Bird flu)
- Influenza viruses
- There are four types of influenza viruses: types A, B, C and D.
- Influenza A viruses: infect humans and many different animals.
- Influenza B viruses: circulate among humans and cause seasonal epidemics.
- Influenza C viruses: can infect both humans and pigs but infections are generally mild and are rarely reported.
- Influenza D viruses: primarily affect cattle and are not known to infect or cause illness in people.
- Influenza A viruses are the only influenza viruses known to cause flu pandemics.
- These are divided into subtypes based on two proteins on the surface of the virus: hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N).
- These subtypes include: A(H5N1), A(H7N9), and A(H9N2).
- H5N1 virus occurs mainly in birds and is highly contagious among them.
- HPAI Asian H5N1 is especially deadly for poultry.
- Avian influenza is a highly contagious viral disease.
- It can infect domestic poultry and other bird and animal species.
- Avian influenza viruses do not normally infect humans.
- However, sporadic human infections with bird flu viruses have occurred.
- Risk: The primary risk factor for humans is exposure to infected live or dead poultry or contaminated environments, such as live bird markets.
Prevention:-
- Controlling the disease in the animal source is critical to decreasing the risk to humans.
- Travelers to countries and people living in countries with known outbreaks should avoid poultry farms, entering areas where poultry may be slaughtered, and contaminated with faeces from poultry or other animals.
- Quality surveillance in both animal and human populations, thorough investigation of every human infection and risk-based pandemic planning is essential.
Treatment:-
- Antiviral drugs: Neuraminidase inhibitors like oseltamivir, and zanamivir, can reduce the duration of viral replication and improve prospects of survival.
- Treatment period: recommended for a minimum of 5 days but can be extended until there is satisfactory clinical improvement.
Vaccination:-
- No vaccine for the prevention of avian influenza infections in humans is commercially available. (UPSC CSE: Vaccine Development for COVID-19)
MUST READ: AB-PMJAY and COVID treatment
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Serum Institute of India produced a COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using an mRNA platform.
- Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using a vector-based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen-based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above is correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under the Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy: (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for pre-school children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with a special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the 120th anniversary of the Indian Government Mint was celebrated in Hyderabad with commemorative souvenir coins.
Background:-
- These souvenir coins were crafted of silver, copper, and serve as a tribute to the rich legacy and contributions of the Indian Government Mint in the field of coinage and minting.
- Security Printing and Minting Corporation of India Ltd (SPMCIL) Chairman and Managing Director SK Sinha released the commemorative coins.
About Security Printing and Minting Corporation of India Ltd (SPMCIL)
- It is a wholly owned Schedule ‘A’ Miniratna Category-I company of t Government of India.
- Establishment: 2006.
- Ministry: Ministry of Finance.
- Objectives To be a leader in the manufacturing of currency, coins and security products through process excellence and innovation.
- Functions::-
- Conducting printing and minting activities of the Government of India.
- Developing state-of-art currency, coins and diversified security products in a transparent, cost-effective and efficient manner.
- Constantly focusing on benchmarking, process automation, applied R & D, indigenization and the triple bottom line people, planet and profit.
- Ensuring Employees, Customers and Stakeholders’ delight.
- Production of Currency and Bank Notes, Security Paper, Non-Judicial Stamp Papers, Postal Stamps & Stationery.
- It also includes producing Travel Documents viz. Passport and Visa, Security certificates, Cheques, Bonds, Warrants, Special Certificates with security features, Security Inks, Circulation & Commemorative Coins, Medallions, Refining of Gold & Silver, and Assay of Precious Metals.
About India Government Mint:-
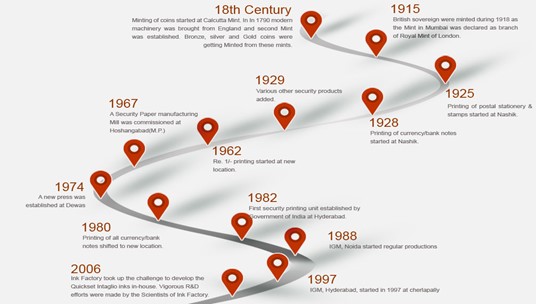
IMAGE SOURCE: https://www.spmcil.com/en/about-us/#history
- India Government Mints (IGM) the units of Security Printing and Minting Corporation of India Ltd (SPMCIL).
- There are four such units:-
- India Government Mints (IGM) Mumbai: it was established in 1829, and is one of the oldest mints in India.
- India Government Mints (IGM) Hyderabad: The present mint started in 1997 at Cherlapally.
- India Government Mints (IGM) Kolkata: The new mint was established in 1952 and became a unit of SPMCIL during corporatization in 2006.
- India Government Mints (IGM) Noida: it is the only Mint established in the post-independence era.(UPSC CSE: Kushans and Coins in India)
- IGMs offer a comprehensive range of services covering every stage of the minting process – from planning to the finished products.
- They utilize advanced technology, innovation, quality and reliable delivery methods.
- They strictly follow global laboratory standards. (UPSC CSE: India’s Digital rupee: CBDC)
MUST READ: Binance
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the context of finance, the term ‘beta’ refers to (2023)
- the process of simultaneous buying and selling of an asset from different platforms ·
- an investment strategy of a portfolio manager to balance risk versus reward
- a type of systemic risk that arises where perfect hedging is not possible
- A numeric value that measures the fluctuations of a stock to changes in the overall stock market.
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I:
Switzerland is one of the leading exporters of gold in terms of value.
Statement-II:
Switzerland has the second-largest gold reserves in the world.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
Context: As per recent reports, the Maputo Protocol contributed towards Africa’s progress in gender equality.
Key findings of the report:-
- There has been some progress on gender equality in African countries due to the Maputo Protocol, but it has been uneven, according to a new report.
- The Protocol has a target of universal ratification in Africa by 2028.
- However, with just five years until the target year, there are still 12 countries that are yet to ratify this important legal instrument.
- There is an urgent need for Botswana, Burundi, Central African Republic, Chad, Egypt, Eritrea, Madagascar, Morocco, Niger, Somalia and Sudan to renew their commitments and ratify the Maputo Protocol in order to deliver on their promises to the women and girls in their countries.
- Significant efforts have been made to promote gender equality under all the provisions of the Maputo Protocol, which include advancing reproductive health and rights, facilitating equal access to and participation in political processes, promoting economic empowerment and ending violence against women.
- In the past two decades (2003-2022), in nearly all countries, women’s labour force participation rate (LFPR) as compared to that of men has remained low.
- In 24 countries, the share of women in the labour force has decreased. (UPSC CSE: Women Employment)
- Women’s economic rights and opportunities and access to social welfare and protection are significantly affected by external factors such as conflict, COVID-19, the pandemic and climate change.
- The ripple effects of the COVID-19 pandemic have undone the progress towards ending child marriage.
- The pandemic had also strained and pressured the existing public health systems.
- There has been an improvement in women’s participation in the political and decision-making processes.
About Maputo Protocol:-
- It is an International human rights document for the protection of women and girls in Africa.
- Adopted: July 2003.
- Adopted in Mozambique.
- Adopted by: African Union (AU).
- Ratification: Of the 55 member states, 44 have ratified or acceded to the Protocol.
- Objective: The Protocol requires the African States to eliminate all forms of discrimination and violence against women in Africa and to promote equality between men and women.
- Significance:-
- It is a comprehensive legal framework that holds the African government to account in the event of a violation of women’s rights.
- It also gives women the right to take part in political processes, social and political equality with men, improved autonomy in their reproductive health decisions, and an end to female genital mutilation.
- The Protocol is considered one of the world’s most progressive legal frameworks for women’s rights.
- It is one of the most ratified instruments in the AU. (UPSC CSE: India-Africa: Challenges & Way Ahead)
MUST READ: Global Gender Gap Report 2021
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following countries have been suffering from decades of civil strife and food shortages and was in the news in the recent past for its very severe famine? (2023)
- Angola
- Costa Rica
- Ecuador
- Somalia
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
The ‘Stability and Growth Pact’ of the European Union is a treaty that
- Limits the levels of the budgetary deficit of the countries of the European Union.
- makes the countries of the European Union share their infrastructure facilities
- enables the countries of the European Union to share their technologies
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only· two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Massive ‘shelf cloud’ formation was spotted in Haridwar, Uttarakhand recently.
Background:-
- Video featuring clouds that resemble a majestic snow-covered mountain has sparked curiosity about this extraordinary weather phenomenon.
About Shelf Cloud:-
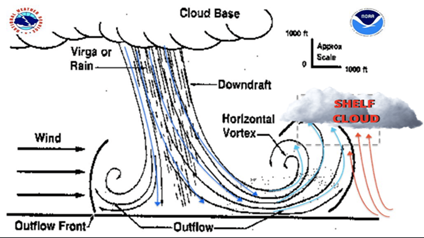
IMAGE SOURCE: mprnews.org
- Shelf clouds are a type of Arcus cloud characterized by a low-lying, horizontal formation.
- Arcus cloud: a low, horizontal cloud formation, usually appearing as an accessory cloud to a cumulonimbus.
- They appear as a wedge-shaped structure beneath the main cloud base and typically form on the leading edge of a storm. (UPSC CSE: Cloudbursts)
- They resemble a shelf hanging from the sky.
- It is a wide, low cloud that appears before a big storm.
- They are usually dark and ominous-looking due to the condensation and the presence of rain or hail within the storm.
- Shelf clouds produced by thunderstorms are always preceded by a rush of dry and cold air ahead of the cloud, with rain arriving after the shelf cloud has passed overhead.
Formation of shelf clouds:-
- Shelf clouds are formed when a mass of cold, dense air forcefully interacts with a warmer air mass.
- When warm, moist air is lifted rapidly by an advancing thunderstorm or cold front Shelf clouds are formed.
Safety concerns:-
- Shelf clouds are typically found in conjunction with thunderstorms, which can bring strong winds, heavy rainfall, and lightning. (UPSC CSE: Lightning)
- Their presence often suggests the potential for severe weather conditions, prompting the need for caution and preparedness.
MUST READ: Cloud Wars
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the Earth’s atmosphere, which one of the following statements is correct? (2023)
- The total amount of insolation received at the equator is roughly about 10 times that received at the poles.
- Infrared rays constitute roughly two-thirds of insolation.
- Infrared waves are largely absorbed by water vapour that is concentrated in the lower atmosphere.
- Infrared waves are a part of the visible spectrum of electromagnetic waves of solar radiation.
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- High clouds primarily reflect solar radiation and cool the surface of the Earth.
- Low clouds have a high absorption of infrared radiation emanating from the Earth’s surface and thus cause a warming effect.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: Recently, India voted in favour of a draft resolution tabled in the UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC) condemning “public and premeditated” acts of desecration of the Holy Quran.
Background:-
- UN Human Rights Council adopted the draft resolution ‘Countering religious hatred constituting incitement to discrimination, hostility or violence’, with 28 members voting in favour, seven abstentions and 12 nations voting against.
- The resolution was strongly opposed by the United States and the European Union, who say it conflicts with their view on human rights and freedom of expression.
About UN Human Rights Council (UNHRC):-
- It is an inter-governmental body within the United Nations system. (UPSC CSE: United Nations Human Rights Council)
- Objective: it is responsible for strengthening the promotion and protection of human rights around the world.
- Establishment: 2006.
- The Council was created by the United Nations General Assembly in 2006.
- It replaced the former United Nations Commission on Human Rights.
- HQ: Geneva, Switzerland.
Membership:-
- Current members: 47 Member States.
- These are elected by the majority of members of the General Assembly of the United Nations through direct and secret ballots.
- The Council’s Membership is based on equitable geographical distribution.
- Seats are distributed as follows:
- African States: 13 seats
- Asia-Pacific States: 13 seats
- Latin American and Caribbean States: 8 seats
- Western European and other States: 7 seats
- Eastern European States: 6 seats
- The term of each seat is three years.
- No member may occupy a seat for more than two consecutive terms.
India and UN Human Rights Council:-
- 2019: India was elected to the Council for a period of three years.
- 2020: India’s National Human Rights Commission submitted its mid-term report to the Council as a part of the third round of the Universal Periodic Review (UPR) process.
- 2021: India was re-elected to the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) for the 2022-24 term.
- It vowed to continue to work for the promotion and protection of human rights through “Samman, Samvad and Sahyog”. (UPSC CSE: Pakistan gets re-elected to the UNHRC)
MUST READ: Moscow’s Suspension from U.N. Human Rights Council
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- Recently, all the countries of the United Nations have adopted the first-ever compact for international migration, the ‘Global Compact for Safe, Orderly and Regular Migration (GCM)’.
- The objectives and commitments stated in the GCM are binding on the UN member countries.
- The GCM addresses internal migration or internally displaced people also in its objectives and commitments.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Consider the following statements about G-20: (2023)
- The G-20 group was originally established as a platform for the Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors to discuss international economic and financial issues.
- Digital public infrastructure is one of India’s G-20 priorities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently visited the Bastille Day Parade.
Background:-
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Bastille Day visit adds to the significance of the India-France relationship.
- It is expected that this meeting will set the tone for the next 25 years.
About Bastille Day Parade:-
- Location: Paris, France.
- Began in 1880.
- It is an annual event.
- It has been held on the morning of 14 July each year.
- It is a French military parade.
- It is also known as the 14 July military parade.
- It is also one of the oldest regular military parades in the world.
Historical Background:-
- July 14 is one of the most important days in the history of France, it marks the fall of the Bastille, a military fortress and political prison, then considered a symbol of the monarchy and armoury.
- This day is marked as the National Day of France.
Significance:-
- Honouring Unity and Freedom: A national holiday in France, Bastille Day honours the independence and unification brought forth by the French Revolution.
- Celebrating French Identity with Cultural Pride: The French people experience a high sense of national pride during the Bastille Day festivities.
- Promoting Global Solidarity: Celebrations of Bastille Day take place all around the world and offer an opportunity for nations to unite and build global solidarity. (UPSC CSE: India-EU ties)
Indo-French strategic partnership
- Defence Collaborations:-
- Purchase of Rafale aircraft: India and France inked a ₹59000-crore deal for 36 Rafale jets in 2016.
- Construction of Scorpene class submarines by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited in collaboration with Naval Group, France. (UPSC CSE: India and France relations)
- Adoption of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism (CCIT) in the UN.
- Following the Pulwama attack in 2019, France nationally listed the Pakistan-based Hafiz Saeed as a ‘global terrorist’.
- France has also supported India’s requests to block attempts by Pakistan to enlist innocent Indian citizens under the UNSC 1267 sanctions Committee based on fabricated charges.
- UNSC 1267: a list of terrorists is a global list, with a United Nations Security Council’s (UNSC) stamp.
- Bilateral military exercises:-
- Navy: Exercise Varuna
- Army: Exercise Shakti
- Air Force: Exercise Garuda
MUST READ: EU’s Sustainability Push on India
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the recent years Chad, Guinea, Mali and Sudan caught international attention for which one of the following reasons is common to all of them? (2023)
- Discovery of rich deposits of rare earth elements
- Establishment of Chinese military bases.
- Southward expansion of Sahara Desert
- Successful coups
Q.2) In the Indian context, what is the implication of ratifying the ‘Additional Protocol’ with the ‘International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’? (2018)
- The civilian nuclear reactors come under IAEA safeguards.
- The military nuclear installations come under the inspection of IAEA
- The country will have the privilege to buy uranium from the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
- The country automatically becomes a member of the NSG.
India-France Ties
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: The recent visit of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to France on Bastille Day celebrations in Paris as the guest of honour coincides with 25 years of the oldest among India’s almost 30 strategic partnerships around the world.
About India-France Relations:
- The two countries commenced their strategic partnership, India’s first, immediately after India’s nuclear tests.
- France was the first country to recognise the strategic importance of India after the nuclear tests in 1998.
- The signing of an agreement for the supply of 36 Rafale aircraft in September 2016, and an industrial agreement in March 2018 to build six European pressurized water reactors (EPR) at the Jaitapur site are directly linked to this partnership.
Climate agreements:
- Recently, India and France signed a Road Map on Green Hydrogen, which aims to bring the French and Indian hydrogen ecosystems together to establish a reliable and sustainable value chain for a global supply of decarbonised hydrogen.
- In 2022, they signed a Road Map on the Blue Economy and Ocean Governance.
Economic Cooperation
- France has emerged as a major source of FDI for India with more than 1,000 French establishments already present in India.
- France is the 11th largest foreign investor in India with a cumulative FDI stock of USD 9.83 billion from April 2000 to March 2021, which represents 2 % of the total FDI inflows into India.
- There are more than 150 Indian companies operating in France (including sub-subsidiaries).
- India’s exports to France were valued at USD 5.6 billion, down by 22.9%.
- French exports to India decreased by 20.95% during the same period to USD 5.1 billion.
- Trade with France constitutes only 1.41% of India’s total international trade.
- A joint announcement was also signed for setting up of a FAST-TRACK system for French companies in India and Indian companies in France.
Defence:
- France has emerged as a key defence partner for India, becoming the second largest defence supplier in 2017- 2021.
- France has emerged as a major strategic partner for India with crucial defence deals and increased military to military engagement.
- Induction of the French Scorpene conventional submarines, being built in India under technology transfer agreement of 2005, and the Indian Air Force having received 36 Rafale fighter jets.
- The Tata group has also tied up with Airbus to manufacture C-295 tactical transport aircraft in Vadodara, Gujarat.
- Military Dialogues and Regularly held Joint Exercises: Varuna (navy), Garuda (air force), and Shakti (army).
Road Map on Green Hydrogen:
- The two sides also cooperate closely on climate change initiatives.
- Recently they signed a Road Map on Green Hydrogen, which aims “to bring the French and Indian hydrogen ecosystems together” to establish a reliable and sustainable value chain for a global supply of decarbonised hydrogen.
Indo-Pacific:
- “Joint Strategic Vision of India-France Cooperation in the Indian Ocean Region” presents a blueprint for a strengthening of ties like Franco-Indian joint patrolling in the Indian Ocean.
- India and France agreed to set up an Indo-Pacific Trilateral Development Cooperation Fund that will support innovative solutions for countries in the region.
- The two partners have formed a trilateral grouping with the United Arab Emirates to ensure security from the east coast of Africa to the far Pacific.
Significance of the India France relationship:
- Securing the Indo-Pacific: India will require the support of France for maintaining the stability and security of the Indo-Pacific region and countering the growing Chinese aggression.
- The Indian Ocean holds importance for France as it controls the Reunion Islands.
- Both countries have concluded a Joint Strategic Vision for cooperation in the Indian Ocean Region in 2018.
- High Degree of Trust: France has stood by India through thick and thin, beginning with 1998 when India conducted nuclear tests.
- Both nations share a high degree of mutual trust that allows them to cooperate on bilateral and multilateral issues.
- Entry to Key Organizations: France’s support will be crucial to India’s entry into the UNSC and the NSG.
- Tackling Climate Change: The cooperation between them can be helpful to achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement and in implementing the Glasgow Climate Pact.
- Global Stability: Cooperation between the two can help in checking Russia’s assertiveness in Europe and China’s assertiveness in Asia, thereby ensuring global stability and world order.
Challenges:
- Stalled Projects: Many projects that have been negotiated between the countries have not been operationalized.
- For instance, the Jaitapur nuclear project has been stalled and is facing a lot of domestic impediments.
- Free Trade with EU: Despite having good relations, France and India don’t have a free trade agreement between them.
- Further, no progress is being made on the India-EU Broad based Trade and Investment agreement (BTIA) as well.
- Stand on Russia Ukraine conflict: France has openly criticized the Russian invasion. India has a more restrained stance on the conflict.
- The difference in the response hasn’t impacted their bilateral relationship till now.
- However if the conflict gets prolonged, then it might impact the India France relationship as well.
Way Forward:
India’s partnership with France is built on common values and goals. Both have underlined the importance of maintaining strategic autonomy with a shared understanding of global risks in many domains. There is a high-level India-France political dialogue that is ongoing in defence, maritime, counterterrorism and the Indo-Pacific. In the marking of a long strategic partnership, a common interest in enhancing strategic autonomy and improving resilience, there is much ground ahead for further collaboration.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently, the Supreme Court has asked the Enforcement Directorate (ED) Director to resign four months before his third extension ends in November 2023.
About ED:
- The Directorate of Enforcement is a multi-disciplinary organization mandated with investigation of offence of money laundering and violations of foreign exchange laws.
History of ED:
- 1956: The Enforcement Unit was founded within the Department of Economic Affairs of the Ministry of Finance.
- 1957: The Enforcement Unit was renamed as the Enforcement Directorate.
- 1960: The administrative control of the Enforcement Directorate was transferred to the Department of Revenue.
- Post-Liberalization Era: The nature of the Enforcement Directorate changed as India underwent economic liberalization.
- FERA 1973 was repealed, and the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA), came into operation on June 1, 2000.
- The Present Mandate of ED: Presently, the ED deals with four laws
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA)
- The Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA)
- The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018 (FEOA)
- Conservation of Foreign Exchange and Prevention of Smuggling Activities Act, 1974 (COFEPOSA)
Powers of ED:
- Admissibility of Statements: Statements recorded before an ED investigation officer (IO) are admissible as evidence in court under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA).
- Non-Bailable Offences: All offences under the PMLA, which the ED deals with, are classified as non-bailable.
- Custody Procedures: Individuals in ED custody are sent to the nearest police station’s lock-up, irrespective of its status.
- Challenges in Property Attachment: Once the ED attaches properties belonging to an accused, it can be a lengthy and challenging process to retrieve those assets.
- Burden of Proof on the Accused: Unlike regular criminal law, under the PMLA, the burden of proof lies with the accused rather than the prosecutor.
- Accused individuals are required to furnish proof in their defense, making it harder to deal with the ED’s investigations.
The High-Level Committees for Extensions of Service:
For the ED Director:
- The panel consisted of a five-member committee comprising the Central Vigilance Commissioner and Vigilance Commissioners.
- They were responsible for recommending whether an ED Director should receive an extension in service.
- The committees were required to provide written reasons supporting their recommendations.
For the CBI Director:
- The High-Level Committee for the CBI Director included the Prime Minister, Opposition Leader, and the Chief Justice of India.
- This committee was responsible for recommending whether a CBI Director should be granted an extension in service.
- Like the ED Director committee, this committee also had to provide written reasons to support their recommendations.
Recent Developments:
- 2018: SK Mishra is appointed as the Enforcement Directorate (ED) Director for a two-year term.
- 2020: The original appointment of the ED Director is retrospectively amended to extend the tenure to three years.
- 2021: The Supreme Court (SC) directs the government to stop granting extensions to the ED Director.
- 2021: Amendments are enacted to the Central Vigilance Commission Act and the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act.
- These amendments allow a maximum of three annual extensions (totalling a term of five years) to the Directors of the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) and ED, based on the recommendation of High-Level Committees.
Criticism of the ED:
- Being Used for Ordinary Crimes: PMLA is pulled into the investigation of even “ordinary” crimes and assets of genuine victims have been attached.
- Lack of Transparency and Clarity: The Enforcement Case Information Report (ECIR) – an equivalent of the FIR – is considered an “internal document” and not given to the accused.
- The ED treats itself as an exception to the principles and practices and chooses to register an ECIR on its own whims and fancies on its own file.
Recent Supreme Court Ruling:
- On Tenure Extension: The Supreme Court declared the consecutive service extensions granted to ED Director in 2021 and 2022 as illegal.
- As a result, the court ordered the present ED Chief to resign by July 31, facilitating a smooth transition to a new chief.
- On 2021 Amendments: Regarding the amendments made to the Central Vigilance Commission Act, 2003, and the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946, the Supreme Court upheld their constitutionality.
Way Forward:
At a time when there is a cloud of suspicion over the misuse of government agencies against political opponents, the Court’s endorsement of a tenure extension system designed to undermine their independence is not conducive to the rule of law.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Shelf clouds are characterized by a low-lying, horizontal formation.
Statement-II:
They are formed when a mass of cold, dense air forcefully interacts with a warmer air mass.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Bastille Day Parade is held twice a year in France.
Statement-II:
This day is marked as the National Day of France.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following pairs:
Exercise Countries
- Exercise SAMPRITI India and Maldives
- Exercise Garuda India Malaysia
- Exercise SAMUDRA SHAKTI India and Indonesia
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- None
Mains Practice Questions:
Q.1) India’s partnership with France is built on common values and goals. In recent times, France has emerged as a key defence-trading partner of India. Discuss (250 words).
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 15th July 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 14th July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – b
Q.3) -b











