IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Recently, the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) denied the rumours of irregularities in the Assistant Provident Fund Commissioner (APFC) Examination.
Background:-
- The Assistant Provident Fund Commissioner (APFC) Examination was conducted in July.
- Following the exam, some images of question paper portions were allegedly uploaded on social media, which led to speculations about potential irregularities.
About Union Public Service Commission (UPSC):-
- The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) is the central recruiting agency in India.
- It is an independent constitutional body.
- The provisions regarding the composition of UPSC, the appointment and removal of its members and the powers and functions of UPSC are provided in Part XIV of the Indian Constitution under Article 315 to Article 323.
- Parallel to the UPSC at the Centre, there is a State Public Service Commission (SPSC) in the state.
- The provisions regarding the composition of SPSC, the appointment and removal of its members and the powers and functions of SPSC are provided in Part XIV of the Indian Constitution under Article 315 to Article 323.
Constitutional Provisions:-
- Article 315: Constitution of Public Service Commissions (PSC) for the Union and for the States of India.
- Article 316: Appointment and term of office of members of UPSC as well as SPSC.
- Article 317: Removal and suspension of a member of both the UPSC or SPSC.
- Article 318: Power to make regulations for the conditions of service of members and staff of the Commission.
Composition of Union Public Service Commission:-
- Appointment of Members: The Chairman and other members of the UPSC are appointed by the President of India.
- Term of Office: Any member of the UPSC shall hold office for a term of six years or till the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- Reappointment: Any person who has once held the office as a member of a Public Service Commission is ineligible for reappointment to that office.
- Resignation: A member of the Union Public Service Commission may resign from his/her office by submitting a written resignation to the President of India.
- Removal/Suspension of Members: The Chairman or any other member of UPSC shall only be removed from his/her office by order of the President of India.
- The President can suspend the Chairman or any other member from his/her office in respect of whom a reference has been made to the Supreme Court.
- Conditions for Removal: The Chairman or any other member of UPSC may be removed if he/she:
- is adjudged
- engages during his/her term of office in any paid employment outside the duties of his/her office.
- is, in the opinion of the President, unfit to continue in office by reason of infirmity of mind or body.
- Regulating the Conditions of Service: In the case of the UPSC, the President of India shall:-
- Determine the number of members of the Commission and their conditions of service.
- Make provisions with respect to the number of members of the staff of the Commission and their conditions of service.
- Expenses of UPSC: The expenses of the UPSC including salaries, allowances and pensions of the members or staff of the Commission are charged to the Consolidated Fund of India.
- Submission of Reports: The UPSC shall present an annual report to the President of India containing the work done by the Commission.
MUST READ: Finance Commission
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following organizations/bodies in India: (2023)
- The National Commission for Backward Classes
- The National Human Rights Commission
- The National Law Commission
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
How many of the above are constitutional bodies?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2). Consider the following statements: (2023)
- The Attorney General of India and Solicitor General of India are the only officers of the Government who are allowed to participate in the meetings of the Parliament of India.
- Accotrding to the Constitution of India, the Attorney General of India submits his resignation when the Government which appointed him resigns.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) in the National Capital Region (NCR) has announced a revision in the existing Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP).
About Graded Response Action Plan:-

IMAGE SOURCE: Hindustan Times
- Formulated in 2016.
- It was officially notified in 2017 for Delhi and the National Capital Region (NCR).
- The plan was formulated after several meetings were held by Environment Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority (EPCA) with state government representatives and experts.
- These are institutionalized measures to be taken when air quality deteriorates, hence work only as an emergency measure.
- GRAP includes the measures, which will be taken by different government agencies to prevent the worsening of the Air Quality of Delhi-NCR and prevent PM10 and PM2.5 levels to go beyond the ‘moderate’ national Air Quality Index (AQI) category. (Air pollution)
- If air quality reaches the severe+ stage, GRAP talks about shutting down schools and implementing the odd-even road-space rationing scheme.
- The plan requires action and coordination among 13 different agencies in Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana and Rajasthan (NCR areas).
Measures announced-
Moderate to poor- (when PM2.5 is in the range of 61-120 or when PM10 is in the range of 101-350.):-
- Heavy fines for garbage burning.
- Close/enforce pollution control regulations in brick kilns and industries.
- Mechanised sweeping on roads with heavy traffic and water sprinkling.
- Strictly enforce a ban on firecrackers.
Very Poor- (PM2.5 is in the range of 121-250 or PM10 is in the range of 351-430):-
- Stop the use of diesel generator sets.
- Enhance parking fee by 3-4 times.
- Increase bus and Metro services.
- Apartment owners to discourage burning fires in winter by providing electric heaters during winter.
- Advisories to people with respiratory and cardiac conditions to restrict outdoor movement.
Severe- (PM 2.5 over 250 or PM10 over 430):-
- Close brick kilns, hot mix plants, and stone crushers.
- Maximise power generation from natural gas to reduce generation from coal.
- Encourage public transport, with differential rates.
- More frequent mechanized cleaning of roads and sprinkling of water.
Severe+ or Emergency- (PM 2.5 over 300 or PM10 over 500 for 48+ hours):-
- Stop entry of trucks into Delhi (except essential commodities).
- Stop construction work.
- Introduce odd/even schemes for private vehicles and minimise exemptions.
- Task Force to decide any additional steps including shutting of schools.
Revised GRAP:
- The revised GRAP will come into force from 1st October 2023 and will be applicable to the entire NCR.
- The key revisions include the enforcement of the National Green Tribunal or Supreme Court’s order on overaged diesel and petrol vehicles and as per extant statutes during ‘Poor’ Air Quality.
- In the case of ‘Very Poor’ Air Quality, remedial measures need to be intensified for the predominant sectors contributing to adverse air quality in each of such hotspots.
- During ‘Severe’ Air Quality, NCR State governments will impose strict restrictions on plying of BS III petrol and BS IV diesel Light Motor Vehicles (LMVs) in Delhi and in the districts of Gurugram, Faridabad, Ghaziabad, and Gautam Buddh Nagar.
- If air quality reaches ‘Severe ’, then NCR State governments might take a decision on discontinuing physical classes even for classes sixth to ninth, class 11th, and conduct lessons in an online mode.
About the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM):-
- Establishment: 2020.
- It was formed by an ordinance in October 2020.
- HQ: Delhi. (CAQM)
- The commission replaces the Environment Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority (EPCA).
- EPCA: it is a Supreme Court-mandated body tasked with taking various measures to tackle air pollution in the National Capital Region.
- It was notified in 1998 by Environment Ministry under Environment Protection Act, 1986.
Objectives of CAQM:-
- For Air Quality Management in National Capital Region and Adjoining Areas. ( Delhi and Air Pollution)
- For better co-ordination, research, identification and resolution of problems surrounding the air quality index and
- For matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
Powers of the CAQM:-
- The rulings by the Commission on air pollution will override anything contained in any other law.
- The powers of the Commission will also supersede that of any other body in matters of air pollution.
- Therefore, in cases where conflict may arise between orders or directions issued by the other State governments, State Pollution Control Boards or even the Central Pollution Control Board, the orders of the Commission will prevail.
- The Commission will have the power to take measures, issue directions and entertain complaints “for the purpose of protecting and improving the quality of air in the National Capital Region”.
- It will also coordinate action taken by states on air pollution and will lay down parameters for air quality and emission or discharge of environmental pollutants.
- It will also have powers to restrict industries in any area, carry out random inspections of any premises including factories and be able to close down an industry or cut its power and water supply in case of non-compliance.
- It will also be monitoring the measures taken by the States to prevent stubble burning.
Merits of CAQM:-
- Effective Mechanism to tackle Pollution: The permanent Commission envisages a multi-sectoral, public participatory, multi-state dynamic body for combating pollution on a war footing.
- More Teeth: It will now be binding on state governments to follow the directions of the Commission regarding air quality management.
- It will also have powers to restrict the setting up of industries in vulnerable areas and will be able to conduct site inspections of industrial units.
- Consolidated Approach: The commission will have the power to coordinate with relevant state and central governments on the multi-sector plan including industry, power plants, agriculture, transport, residential and construction.
- Penal Powers: The penalty for non-compliance shall be imprisonment of up to five years or a fine up to Rs 1 crore, or both.
- Relieves Supreme Court: The Centre seeks to relieve the Supreme Court from having to constantly monitor pollution levels through various pollution-related cases.
- Participatory Democracy: the Commission would function under the oversight of the elected representatives with regular reports to the Parliament.
MUST READ: Initiatives and Measures for Prevention of Air Pollution
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following: (2023)
- Aerosols
- Foam agents
- Fire retardants
- Lubricants
In the making of how many of the above are hydrofluorocarbons used?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) In the context of WHO Air Quality Guidelines, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The 24-hour mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 15 ug/m3 and annual mean of PM2.5 should not exceed 5 ug/m3.
- In a year, the highest levels of ozone pollution occur during periods of inclement weather.
- PM10 can penetrate the lung barrier and enter the bloodstream.
- Excessive ozone in the air can trigger asthma.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1 and 4 only
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1 and 2 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: The government has decided to merge Project Tiger with Project Elephant.
Background:-
- The merger was announced in April 2023.
- However, there is still no clarity on how the finances would be split between the conservation projects.
About Project Tiger:-
- Launched: 1973.
- Launched at Jim Corbett National Park, Uttarakhand.
- Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Implementing Agency: National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
- HQ of NTCA: New Delhi.
- Project Tiger is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
Objectives of Project Tiger:-
- To ensure the survival of India’s tiger population for scientific, economic, cultural, and aesthetic reasons.
- To identify and mitigate factors causing tiger habitat loss through appropriate management practices.
- To preserve areas of such biological importance as a national heritage for the benefit of education and enjoyment of the people at all times. (Saving the Tiger)
- The preservation of endangered species. ( Importance of Tiger Conservation)
- To safeguard the rights of tribals and local people living near tiger reserves.
Conservation Status of Tiger:-
- Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List: Endangered.
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES): Appendix I.
Tiger reserves under Project Tiger:-
- Tiger reserves are designated areas for the protection of tigers and their prey.
- They are governed by Project Tiger.
- On the recommendation of the National Tiger Conservation Authority, the State Government shall declare an area a tiger reserve.
Achievements of Project Tiger:-
- The number of tigers in India has increased. (Tiger Estimation)
- India met its goal of doubling the wild tiger population by 2022 in 2018.
- As hunting was banned to save tigers, the population of many other animals started increasing.
About Project Elephant:-
- Launched: 1992.
- Launched at Jim Corbett National Park, Uttarakhand.
- Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Project Elephant is a Centrally-sponsored scheme
- It completed 30 years in 2022.
- States receive both financial and technical assistance to help them achieve the Project’s goals.
Objectives of Project Elephant:-
- Provide financial and technical support to wildlife management efforts, and ensure long-term survival.
- Support research on the ecology and management of elephants. ( Elephant Conservation)
- Create awareness of conservation among local people.
- Provide improved veterinary care for captive elephants.
Asian Elephants:
- The Asian elephant is the largest land mammal on the Asian continent.
- Distribution: They inhabit dry to wet forest and grassland habitats in 13 range countries spanning South and Southeast Asia.
Conservation Status:-
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix I.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I.
MUST READ: Project Re-Hab
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following makes a tool with a stick to scrape insects from a hole in a tree or a log of wood? (2023)
- Fishing cat
- Orangutan
- Otter
- Sloth bear
Q.2) With reference to Indian laws about wildlife protection, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Wild animals are the sole property of the government.
- When a wild animal is declared protected, such animal is entitled to equal protection whether it is found in protected areas or outside.
- Apprehension of a protected wild animal becoming a danger to human life is sufficient ground for its capture or killing.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the Government has approved Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP).
About Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP):-
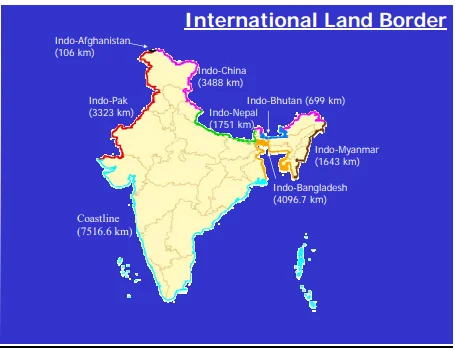
IMAGE SOURCE: IASBABA.COM
- Launched:2023.
- It was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 (to 2025-26).
- Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Objective: to create sufficient incentives for people to stay in the selected villages.
- Coverage: It will cover the border areas of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim and Ladakh.
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.( The India-China border flare-up)
Salient Features of Vibrant Villages Programme:-
- The programme envisages focused areas of interventions in the select villages for the creation of opportunities for livelihood generation.
- This would be done through the promotion of tourism & cultural heritage, skill development & entrepreneurship.
- It works for the development of cooperative societies including agriculture/horticulture, cultivation of medicinal plants/herbs etc.
- It also includes providing road connectivity to unconnected villages, housing & village infrastructures, energy including renewable energy, television & telecom connectivity.
- It focuses on the comprehensive development of villages of blocks on the northern border.
- It will provide funds for the development of essential infrastructure.
- It will lead to the creation of livelihood opportunities in 19 Districts and 46 Border blocks 4 states and 1 UT along the northern land border of the country.
- It will help in achieving inclusive growth and retaining the population in the border areas.
Significance of Vibrant Villages Programme:-
- Strengthening the Security: It is aimed at strengthening the security grid on the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- Infrastructure development: Infrastructure will be improved in states like Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, and Arunachal Pradesh. ( Significance of border infrastructure)
- Under the programme, residential and tourist centers will be constructed.
- Connectivity and Energy resources: It will also provide for improvement in road connectivity and the development of decentralized renewable energy
- Educational outreach: Apart from that, direct access to Doordarshan and education-related channels will be provided.
- Livelihood Support: help and support will be provided for the livelihood of the people.
MUST READ: Challenges to Secure India’s Land Borders
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following countries: (2023)
- Bulgaria
- Czech Republic
- Hungary
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Romania
How many of the above-mentioned countries share a land border with Ukraine?
- Only two
- Only three
- Only four
- Only five
Q.2) Consider the following countries: (2022)
- Azerbaijan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Tajikistan
- Uzbekistan
- Turkmenistan
Which of the above has borders with Afghanistan?
- 1, 2 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
- 3, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: As per recent data, National Coal Index showed a decline of 33.8 % in May 2023.
Background:-
- The National Coal Index combines coal prices from all sales channels, including notified prices, auction prices and import prices.
- It serves as a reliable indicator of market dynamics, providing valuable insights into coal price fluctuations.
- The National Coal Index (NCI) has shown a significant decline of 33.8% in May 2023 compared to May 2022, which suggests significant reduction in coal prices.
- This indicates a strong supply of coal in the market, with sufficient availability to meet the growing demands.
About National Coal Index:-
- Launched: 2020.
- Ministry: Ministry of Coal.
- Developed by: Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata. (India’s Transition away from Coal)
- It is a price index, which reflects the change in the price level of coal on a particular month relative to the fixed base year.
- Objective: to have an index that will truly reflect the market price.
- Base year: 2017-18.
- This price index combines the prices of coal from all the sales channels– Notified Prices, Auction Prices and Import Prices.
MUST READ: Economy
SOURCE: NEWS ON AIR
Circular Economy
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: Resource Efficiency Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC) was recently launched on the side-lines of the fourth G-20 Environment and Climate Sustainability Working Group (ECSWG) and Environment and Climate Ministers’ meeting.
About Circular Economy:

- A Circular Economy is the one where products are designed for durability, reuse and recyclability and thus almost everything is reused, remanufactured, and recycled into a raw material or used as a source of energy.
- It includes 6 R’s – Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Refurbishment, Recover, and Repairing of materials.
Need for Circular Economy:
- CE focuses on minimising waste while maximising utilisation and calls for a production model aiming to retain the most value to create a system that promotes sustainability, longevity, reuse, and recycling.
- Though India has always had a culture of recycle and reuse, its rapid economic growth, growing population, impact of climate change and rising environmental pollution, the adoption of a circular economy is more imperative now.
- CE can lead to the emergence of more sustainable production and consumption patterns, thus providing opportunities for developed and developing countries to achieve economic growth and inclusive and sustainable industrial development (ISID) in line with the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Significance of Circular Economy:
- Protection of the environment: Circular economy benefits the environment by consuming fewer natural resources, and thus reduces ecological footprint.
- It helps lower the emissions and produces less polluting waste.
- It helps in preservation of biodiversity, as there is less pressure on natural resources like forests.
- Benefits for the local economy: There is emphasis on promoting production models that rely on reuse of nearby waste as raw material.
- Drives employment growth: Circular Economy fosters the development of a new, more inventive, and competitive industrial model, resulting in higher economic growth and more employment opportunities.
- Promotes resource independence: Reusing local resources can reduce reliance on imported raw materials.
- It can help in achieving self-sufficiency.
- Enhanced Food Security: The circular bio economy can contribute to improved food security by using agricultural residues and waste as feedstock for bio-based products instead of diverting them from food production.
Challenges of the Circular Economy:
- Infrastructure and Technology: Developing and upgrading recycling and waste management infrastructure, as well as adopting advanced technologies for resource recovery, can be a major challenge.
- Behavioural Change: Encouraging a shift in consumer behaviour towards responsible consumption, product reuse, and recycling requires effective communication and behavioural change campaigns.
- Regulatory Framework: Ensuring effective and harmonized policies, regulations, and incentives to support circular economy practices across different sectors is challenging.
- Financial Investment: Circular economy projects often require significant upfront investments.
- Attracting private and public investment to fund these initiatives can be challenging.
Government Initiatives to promote CE
- E-Waste Management Policy: Electrical and electronic waste, including both whole and unfinished discarded equipment from their manufacture and repair processes, is referred to as “e-waste” and “electrical and electronic equipment.
- Plastic Waste Management (Second Amendment) Rules, 2022: The Union Environment Ministry has launched this policy to mandate to increase in the thickness of plastic carry bags to over 120 microns and the phase-out of some single-use plastic products.
- Swachh Bharat Mission – Urban 2.0 (SBM-U2.0): It aims to achieve the objective of safe sanitation in urban areas by making all cities “Garbage Free,” guaranteeing grey and black water management in all cities.
- It also aims at making all urban local bodies open defecation free (ODF+) and those with a population of less than 1 lakh as ODF++.
- In order to effectively manage solid waste, the mission will concentrate on source segregation of trash, using the 3Rs (reduce, reuse, recycle) as a guideline, scientific processing of all sorts of municipal solid waste, and repair of former dumpsites.
- City Investments to Innovate, Integrate and Sustain (CITIIS) 2.0: The Government launched the City Investments to Innovate, Integrate and Sustain (CITIIS) 2.0 to promote circular economy in 18 smart cities to be selected through a competition.
- The total funding for the scheme will come from loans and a grant of Rs. 106 crore from the European Union.
- The programme starts this year and will run until 2027, with the support of the National Institute of Urban Affairs.
Way Forward:
India’s G-20 presidency has placed resource efficiency and circular economy at the centre of the global sustainability agenda. The ‘reduce-reuse-recycle’ model and circular economy strategies are essential in minimizing environmental impact and decoupling resource utilization from economic growth. Through its focus on circularity in the steel sector, Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), circular bio economy, and an industry-led coalition, India aims to drive the transition towards a more sustainable and resilient future.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Society) and GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Social Justice and Empowerment has called upon the Union government for failing to accurately estimate the population of Persons with Disabilities (PwDs).
About Persons with Disabilities (PWDs):
- As per United Nations Conventions on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities PWDs include those who have long-term physical, mental, intellectual or sensory impairments which in interaction with various barriers may hinder their full and effective participation in society on an equal basis with others.
- As per National Family Health Survey, India’s population of people with a disability has reduced to 1% between 2019 and 2021, from the 2.2% (26.8 million) estimated by the Indian census in 2011.
Constitutional Frameworks for Disabled in India:
- Article 41 of the Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP) states that State shall make effective provision for securing right to work, to education and to public assistance in cases of unemployment, old age, sickness and disablement, within the limits of its economic capacity and development.
- The subject of ‘relief of the disabled and unemployable’ is specified in state list of the Seventh Schedule of the constitution.
Current status regarding Persons with Disabilities:
- In India, there were around 26.8 million persons with disabilities, constituting 2.21% of India’s total population (2011 Census).
- There were 14.9 million men (2.41% of men) and 11.9 million women (2.01% of women) with disabilities. 69% (18 million) of persons with disabilities reside in rural areas.
- 20% of persons with disabilities in India have a disability in movement, 19% have visual impairment, 19% have a hearing impairment and 8% have multiple disabilities.
- Disabilities are highest in the age group 10-19 years (46.2 lakh people).
- At an all India level, 34% of the total disabled population is reported as ‘workers’. The proportion is highest in Nagaland (~52%) followed by Sikkim (49%) and Arunachal Pradesh (~45%).
Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act 2016
- The Act replaces the Persons with Disabilities (Equal Opportunities, Protection of Rights and Full Participation) Act, 1995.
- It fulfils the obligations to the United National Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), to which India is a signatory.
- Disability has been defined based on an evolving and dynamic concept.
- The types of disabilities covered are 21 and the Central Government has the power to add more types of disabilities.
- The Act provides for penalties for offences committed against persons with disabilities and violation of the provisions of the new law.
- Special Courts will be designated in each district to handle cases concerning the violation of the rights of PwDs.
Challenges faced by PWDs
- Social Stigma: The word disability is being seen as a social stigma, according to which parents feel ashamed of their children, and in fear, most of them feel uncomfortable in public upfront.
- Institutional Failures: Indian education system and Government institutions both are failing in deciding for the welfare for disabled persons to an extent.
- There should be proper seats for disabled persons at classrooms as well as at the exam centers.
- Illiteracy is particularly prevalent among disabled people and constitutes a double disadvantage. In addition to being disabled, they are isolated by illiteracy.
- Unemployment: Disabled persons are the ones who are scapegoats in being fired during recessions.
- They are first to be discharged from their services when cost cutting methods are adopted by the companies.
- Stress: The physically handicapped person is subjected to a lot of stress because of lack of social relations.
- In addition to increased physical and emotional stress, the crippled individual is condemned to a similar outcome in his social life.
Govt. schemes:
- Accessible India Campaign (Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan): Launched in 2015, this campaign aims to make public spaces, transportation, and information and communication technologies (ICT) accessible to PwDs.
- National Action Plan for Skill Development of Persons with Disabilities (NAP-SDP): This initiative focuses on enhancing the employability and skills of PwDs through vocational training, skill development programs, and creating inclusive employment opportunities.
- Deendayal Disabled Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS): The scheme provides financial assistance for various rehabilitation services, including education, skill training, healthcare, and assistive devices, to economically disadvantaged PwDs.
- Scholarship Schemes: The government offers various scholarship schemes for PwDs to support their education and skill development.
- These include the National Scholarship Scheme for Persons with Disabilities and the Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scholarship schemes.
- Accessible Education: The government has taken steps to promote inclusive education for PwDs, such as the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) and the Inclusive Education for Disabled at Secondary Stage (IEDSS) programs.
- Reservation in Government Jobs: PwDs are entitled to reservation in government jobs and public sector undertakings as per the provisions of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act.
Way Forward:
The Government has undertaken commendable initiatives for the welfare of the disabled and make them independent. However, they still face social exclusion driven by stigma and stereotypes about disability. The need of the hour is proper sensitization of the community towards the issues faced by PwDs, as well as to remove the social stigma attached to their integration into the society.
Source: The Hindu
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements with reference to India: (2023)
- According to the ‘Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006’, the ‘medium enterprises’ are those with
- Investments in plant and machinery between (15 crore and 25 crore).
- All bank loans to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises qualify under the priority sector.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) In the context of finance, the term ‘beta’ refers to (2023)
- the process of simultaneous buying and selling of an asset from different platforms ·
- an investment strategy of a portfolio manager to balance risk versus reward.
- a type of systemic risk that arises where perfect hedging is not possible.
- a numeric value that measures the fluctuations. of stock to changes in the overall stock market.
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Species | IUCN Status |
| 1.Asian Elephants | Endangered |
| 2.Cheetah | Vulnerable |
| 3.Tiger | Endangered |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Any person who has once held the office as a member of a Public Service Commission is ineligible for reappointment to that office.
Statement-II:
The President of India shall determine the number of members of the Commission and their conditions of service.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
National Coal Index is developed by the Indian Statistical Institute.
Statement-II:
The Base year is 2011-12.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) “With the growing recognition of the finite nature of many resources and the negative impacts of waste and pollution, the circular economy offers a more sustainable and resilient alternative to the traditional linear model of economic growth”. Critically analyse (250 words)
Q.2) What measures have been taken by the government to create a conducive environment for the disabled community? Discuss various reasons for limited impact of such initiatives. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 29th July 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 28th July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – b











