IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
Context: The evidence of a Bizarre’ bird-like dinosaur Fujianvenator prodigiosus has enthralled scientists recently.
Background:-
- Scientists reported to have unearthed the fossil of a Jurassic Period dinosaur they named Fujianvenator from the Fujian Province. (Dinosaur footprints in China)
- It is a creature that sheds light on a critical evolutionary stage in the origin of birds.
About Fujianvenator prodigious:-
- Distribution: southeastern China. (Abnormal’ dinosaur egg in India)
- Fujianvenator is a member of a grouping called avialans.
- This group includes all birds and their closest non-avian dinosaur
- Survival: Despite their modest beginnings, birds survived the asteroid strike 66 million years ago that doomed their non-avian dinosaur comrades.
- Diet and lifestyle: The Fujianvenator fossil, discovered lacks the animal’s skull and parts of its feet, making it hard to interpret its diet and lifestyle.
Physical Description: –
- It was a pheasant-sized and bird-like dinosaur.
- It had elongated legs and arms built much like wings.
- It had a puzzling anatomy suggesting it either was a fast runner or lived a lifestyle like a modern wading bird.
- Its lower leg bone – the tibia – was twice as long as its thigh bone – the femur.
- It also had a long bony tail.
- The forelimb is generally built like a bird’s wing, but with three claws on the fingers, which are absent from modern birds.
- It cannot be determined whether it could fly or not
MUST READ: Dinosaur eggs
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1Consider the following fauna: (2023)
- Lion-tailed Macaque
- Malabar Civet
- Sambar Deer
How many of the above are generally nocturnal or most active after sunset?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) The word ‘Denisovan’ is sometimes mentioned in media in reference to (2017)
- fossils of a kind of dinosaurs
- an early human species
- a cave system found in North-East India
- a geological period in the history of the Indian subcontinent
Syllabus
- Prelims –Government Scheme
Context: The government recently approved ₹3,760 crore for viability gap funding of up to 40% of total capital cost to set up a 4,000 MWh battery energy storage system in the country.
Background:-
- The entire ₹3,760 crore viability gap funding (VGF) will be borne by the central government.
- The VGF will be released in five tranches till 2030-31.
- Viability Gap Finance: It means a grant to support projects that are economically justified but not financially viable.
- It aims to reduce the levelized cost of storage (LCoS) to ₹5.50-6.60 per kilowatt-hour (kWh), making storage a viable option to manage peak power demand.
- It will help in the creation of 4,000 MWh storage across the country.
- The selection of BESS developers for VGF grants will be carried out through a transparent competitive bidding process, promoting a level-playing field for both public and private sector entities.
About Battery energy storage systems:-
- A battery energy storage system is a type of energy storage system that uses batteries to store and distribute energy as electricity.
- These are often used to enable energy from renewable sources, like solar and wind, to be stored and released.
Types of Battery energy storage systems:-
- Residential BESS: for homes
- Commercial BESS: for businesses
- Utility-scale BESS: for large-scale energy storage.
Benefits:-
- BESS will enhance renewable energy integration into the grid. (Sustainable Energy)
- It will reduce wastage, and minimize infrastructure upgrade costs.
- It will reduce peak demand and associated costs.
Challenges:-
- It has High initial costs. ( Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) for 1000 MWhourproject)
- Recycling and disposal of batteries issues.
- Regulatory and grid integration issues.
MUST READ: Solar Energy in India
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I:
Carbon markets are likely to be one of the most widespread tools in the fight against climate change.
Statement-II:
Carbon markets transfer resources from the private sector to the State.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q.2) “R2 Code of Practices” constitutes a tool available for promoting the adoption of (2021)
- Environmentally responsible practices in the electronics recycling industry
- Ecological management of ‘’Wetlands of International Importance” under the Ramsar Convention
- Sustainable practices in the cultivation of agricultural crops in degraded lands
- ‘’Environmental Impact Assessment’’ in the exploitation of natural resources
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, India’s first UPI-ATM was unveiled.
Background:-
- India’s first UPI-ATM was launched recently as a White Label ATM (WLA) by Hitachi Payment Services in collaboration with the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) in order to enable “seamless cash withdrawals”.
- It offers an experience that allows customers of certain banks to enjoy “QR-based cashless withdrawals”.
About UPI-ATM:-
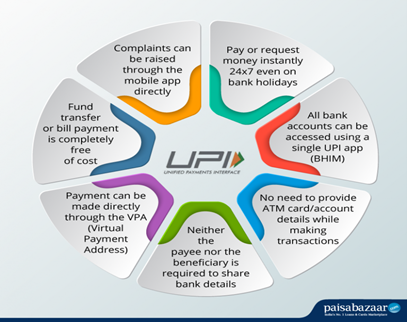
IMAGE SOURCE: Paisabazaar.com
- The UPI-ATM service is also known as Interoperable Cardless Cash Withdrawal (ICCW).
- It offers a convenient way for customers of participating banks who are using UPI to withdraw cash from any ATM that supports UPI-ATM functionality, without the need for a physical card.
- India’s first UPI-ATM was launched recently as a White Label ATM (WLA) by Hitachi Payment Services in collaboration with the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI). (UPI and NPCI Regulation)
Working Mechanism:-
- When a customer selects the ‘UPI cash withdrawal’ option at the ATM, they will be prompted to enter the desired withdrawal amount.
- Once the amount is entered, a unique and secure dynamic QR code will appear on the ATM screen.
- To complete the transaction and obtain cash from the ATM, the customer simply needs to scan this QR code using any UPI app and authorize the transaction with their UPI PIN on their mobile device.
Features of UPI-ATM
- Compatible with various systems.
- Transactions without the need for a physical card.
- Transaction limit of up to ₹10,000 per transaction, aligned with existing UPI daily limits and issuer bank’s UPI-ATM transaction limits.
- Allows cash withdrawals from multiple accounts via the UPI app.
Benefits:-
- It will eliminate the need to carry physical ATM cards.
- It allows users to obtain cash from multiple accounts using the UPI app.
- It will prevent issues such as card skimming.
- Card skimming: a type of financial fraud where devices are installed at ATMs or point-of-sales terminals to gather card information such as PIN and card number to siphon off cash.
MUST READ: India’s UPI Push
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the context of finance, the term ‘beta’ refers to (2023)
- the process of simultaneous buying and selling of an asset from different platforms
- an investment strategy of a portfolio manager to balance risk versus reward
- a type of systemic risk that arises where perfect hedging is not possible
- a numeric value that measures the fluctuations. of stock to changes in the overall stock market.
Q.2) With reference to Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), consider the following statements: (2022)
- They enable the digital representation of physical assets.
- They are unique cryptographic tokens that exist on a blockchain.
- They can be traded or exchanged at equivalency and therefore can be used as a medium transaction. of commercial
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
Context: The Ministry of Tourism in collaboration with the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), unveiled the G20 Tourism and SDG Dashboard recently.
Background:-
- Union Tourism Minister G Kishan Reddy launched the dashboard in a virtual ceremony.
- The virtual launch witnessed participation from G20 member countries, invited countries, international organizations, various states and Union Territories, and industry stakeholders.
About G20 Tourism and SDG Dashboard:-

IMAGE SOURCE: SDG
- Launched: 2023.
- Developed by: the Ministry of Tourism in collaboration with the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO).
- The G20 Tourism and SDG Dashboard showcases the best practices, case studies, and insights from G20 countries.
- These all are modeled for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). (sustainable Development Goals (SDG) India Index)
- It serves as a comprehensive online public platform, amalgamating the collective knowledge of the G20 Tourism Working Group.
- It consolidates the GOA Roadmap, survey results, case studies, and best practices from G20 countries.
- It offers insights into sustainable tourism practices.
- It also provides a platform for knowledge exchange, collaboration, and growth.
- It offers a wealth of knowledge and showcases best practices, aimed at steering the tourism industry towards greater sustainability, resilience, and inclusivity.
Significance:-
- This dashboard is a lasting legacy of India’s G20 Presidency.
- It reflects its dedication to global collaboration and sustainable growth in the global tourism industry.
MUST READ: Top Three SDGs & India
SOURCE: NEWS ON AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements about G-20: (2023)
- The G-20 group was originally established as a platform for the Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors to discuss international economic and financial issues.
- Digital public infrastructure is one of India’s G-20 priorities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to green hydrogen, consider the following statements : (2023)
- It can be used directly as a fuel for internal combustion.
- It can be blended with natural gas and used as fuel for heat or power generation.
- It can be used in the hydrogen fuel cell to run vehicles.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Recently, the Supreme Court sought the views of the Centre and the states on the Justice Amitava Roy Committee report.
Background:-
- On August 29, the Supreme Court sought the views of the Centre and the states on the Justice Amitava Roy Committee report submitted on December 27, 2022, underlining that the correctional justice system is “evidently gender exclusionary”.
About Amitava Roy Committee report:-

IMAGE SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
- Formation: 2018.
- Formed by: Supreme Court of India.
- In September 2018, the Supreme Court formed a Committee on Prison Reforms chaired by former judge, Justice Amitava Roy.
- Objective: To examine the various problems plaguing prisons in the country, from overcrowding to lack of legal advice to convicts to issues of remission and parole.
Historical Background:-
- The decision was taken based on a letter from former Chief Justice of India R.C. Lahoti highlighting the overcrowding in prisons, unnatural deaths of prisoners, gross inadequacy of staff, and the lack of trained staff.
- The court asked the committee to complete the collection of data and information and submit the report in a year.
- The committee submitted the final report in December 2022.
Functions of the committee:-
- Examine the extent of overcrowding in prisons and correctional homes & and recommend remedial measures.
- Grant of remission, parole, and furlough.
- Reasons for violence in prisons and correctional homes.
- Recommend measures to prevent unnatural deaths.
- Assess the availability of medical facilities in prisons and correctional homes.
Key Findings of the Committee:-
- Globally, one in three prisoners are undertrials.
- In India, three out of four, or about 77% of the total prison population in 2021, were undertrials.
- Undertrials: people waiting for the completion of a trial or investigation.
- Women prisoners face far worse conditions than men in terms of access to basic facilities.
- Prisons only in Goa, Delhi, and Puducherry allow female inmates to meet their children without any bars or glass separation. (National Commission for Women)
- Less than 40% of prisons provide sanitary napkins to female inmates.
- Only 18% of female prisoners get exclusive women’s prison facilities.
- Prison authorities of only 13 states and two Union Territories have designated a ‘complaint officer’ to deal with complaints of violation of rights of transgender inmates in prisons.
- Majority of the states and Union Territories have not formulated welfare schemes for transgender prisoners.
- Suicide is a major cause of the 817 unnatural deaths reported in jails across the country between 2017 and 2021.
- Uttar Pradesh recorded the highest number of suicides at 101 during this period.
Key Recommendations of the Committee:-
- Speedy trials.
- Lawyer to prisoner ratio: There should be at least one lawyer for every 30 prisoners.
- Special courts should be set up to deal exclusively with petty offenses.
- Accommodative Transition: Every new prisoner should be allowed a free phone call a day to his family members to see him through his first week in jail. (Police & Prison Reform)
- Legal aid must be provided.
- Use of video-conferencing for trial.
- Modern cooking facilities and canteens to buy essential items.
- The Supreme Court should pass directions asking authorities to start the recruitment process against permanent vacancies within three months and the process should be completed in a year.
MUST READ: Inter-operable Criminal Justice System (ICJS)
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I:
In India, prisons are managed by State Governments with their own rules and regulations for the day-to-day administration of prisons.
Statement-II:
In India, prisons are governed by the Prisons Act, of 1894 which expressly kept the subject of prisons in the control of Provincial Governments.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-1 and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
Q.2) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Judicial custody means an accused is in the custody of the concerned magistrate and such an accused is locked up in a police station, not in jail.
- During judicial custody, the police officer in charge of the case is not allowed to interrogate the suspect without the approval of the court.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Art and Culture
Context: The Sculptures of Nataraja, Dancing Girl will be used greet delegates at Bharat Mandapam as per recent announcements.
About Dancing Girl:-
- Discovered in 1926.
- Discovered by: Ernest Mackay.
- Discovered at Mohenjodaro,
- The ‘Dancing Girl’ is a sculpture made of bronze.
- It is one of the highest achievements of the artists of Mohenjodaro.
- It belongs to the Indus Valley Civilization and dates back to circa 2500 BCE.
- It is 10.5 cm in height, 5 cm in width, and 2.5 cm in depth.
- Presently, it is on display in the Indus Valley Civilization gallery in the National Museum, New Delhi.
- The statue is named the ‘Dancing Girl’ owing to her posture, with her right hand on the back of her hip and the left hand resting on her left thigh.
- Her features are prominent with large eyes, curly hair, and a flat nose.
- She appears to be adorned by a necklace alongside some bangles.
- Her hair is plaited on the back and neatly tied in a bun.
- Her arms are unnaturally long which is a common feature of the artefacts of this time.
- Her head is tilted slightly backward.
- An interesting fact to notice is that the number of bangles in her hands differs.
- She has 24 bangles in one hand and 4 in the other.
- The sculpture was made using the ‘Lost Wax’ method.
- Lost Wax’ method: molten wax is poured into a mould to create a model.
- In the 1920s Daya Ram Sahni and D. Banerji began excavating in modern-day Harappa and Mohenjodaro.
About Nataraja:-
- It is the representation of the Hindu god Shiva during his form as the cosmic dance.
- It is represented in metal or stone in many Shaivite temples, particularly in South India. (Shore temple)
- It is an important piece of Chola sculpture.
Features of the Nataraja:-
- The upper right hand holds the drum: it signifies the sound of creation.
- All creations spring from the great sound of the
- The upper left hand holds the eternal fire: it represents the destruction. Destruction is the precursor and inevitable counterpart of creation.
- The lower right hand is raised in the gesture of Abhay Mudra signifying benediction and reassuring the devotee to not be afraid.
- The lower left hand points towards the upraised foot and indicates the path of salvation.
- Shiva is dancing on the figure of a small dwarf.
- The dwarf symbolizes ignorance and the ego of an individual.
- The matted and flowing locks of Shiva represent the flow of the river Ganges.
- This represents the fusion of male and female and is often referred to as
- A snake is wrapped around the arm of Shiva.
- The snake symbolizes the kundalini power, which resides in the human spine in the dormant stage.
MUST READ: Language in Indus Valley Civilization
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to ancient South India, Korkai, Poompuhar, and Muchiri were well-known as (2023)
- capital cities
- ports
- centers of iron-and-steel making
- shrines of Jain Tirthankaras
Q.2) The Prime Minister recently inaugurated the new Circuit House near Somnath Temple Veraval. Which of the following statements are correct regarding Somnath Temple? (2022)
- Somnath Temple is one of the Jyotirlinga shrines.
- A description of Somnath Temple was given by Al-Biruni.
- Pran Pratishtha of Somnath Temple (installation of the present-day temple) was done by President S. Radhakrishnan.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
India and ASEAN Relations
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: Recently the Prime Minister of India attended the 20th ASEAN-India Summit and the 18th East Asia Summit (EAS) in Jakarta, Indonesia.
About India and ASEAN Relations:
Political:
- India has been actively engaged with ASEAN in various regional forums and initiatives, such as the ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF), ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting + (ADMM+), and the East Asia Summit (EAS).
- In recent years, they share interests in cooperation in sectors, such as trade and investment, energy, infrastructure, and people-to-people contacts.
- India’s Act East Policy, which was formally enunciated in 2014, is a key pillar of its foreign policy and is focused on expanding its engagement with ASEAN and other countries in the region.
- Mission to ASEAN 2015 with a dedicated Ambassador to strengthen engagement with ASEAN and ASEAN-centric processes
- Delhi Dialogue hosted by India annually, traditionally inaugurated jointly by India and ASEAN at the Foreign Minister’s level, serves as the main Track 1.5 mechanism for our engagement.
Trade and Investment:
- India and ASEAN have signed an FTA that has boosted trade and investment between the two.
- ASEAN is India’s 4th largest trading partner.
- Total trade stood at $110.4 billion in 2021-22.
- ASEAN-India Business Council (AIBC) was set up in 2005 with the aim of fostering closer business linkages.
- India’s export to ASEAN stands at 28% of our total exports.
- ASEAN accounting for approximately 28% of investment flows into India since 2000.
Multilateral and Bilateral Engagements:
- Bilaterally, India has signed ‘strategic partnerships’ with four ASEAN countries, namely, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore and Vietnam.
- At the multilateral level, India is a member of multiple ASEAN-led fora, including the East Asia Summit, the ASEAN Regional Forum, and the ASEAN Defence Ministers Meeting.
Maritime cooperation:
- India’s flagship MILAN naval exercise, started in the 1990s, includes several ASEAN members.
- India also conducts bilateral coordinated patrols with several ASEAN countries, as well as exercises such as the Singapore-India Maritime Exercise, which completed 25 years in 2018.
Socio-cultural cooperation:
- India and ASEAN have promoted cultural exchanges to enhance people-to-people ties.
- Inviting ASEAN students to India each year for the Students Exchange Programme, Special Training Course for ASEAN diplomats, Exchange of Parliamentarians, ASEAN-India Network of Think Tanks, ASEAN-India Eminent Persons Lecture Series, etc.
- India has established the ASEAN-India Centre at the Research and Information System for Developing Countries (RIS) to promote research and studies on ASEAN-India relations.
Significance of ASEAN partnership for India:
- Significant market size: ASEAN constitutes the 3rd largest market in the world.
- This can help India utilize its export potential.
- Way for countering China’s influence: Strengthening relations with ASEAN countries can serve as a counterbalance to China’s influence in the region.
- Convergence with Indo-Pacific strategy: ASEAN is a crucial component of India’s “Act East” policy and its “Indo-Pacific” strategy, reflecting the convergence of interests in the region.
- Significance of rule-based order: ASEAN plays a central role in promoting a rules-based security architecture in the Indo-Pacific region, which is essential for the region’s stability and prosperity.
- Development of North East region: Connectivity initiatives with ASEAN can boost economic development in India’s northeastern states by positioning them as a hub for regional trade and commerce.
India – ASEAN challenges:
- Slow implementation of projects: The lack of time-bound implementation of projects, such as the India-Myanmar-Thailand trilateral highway and Kaladan multimodal project, which would enhance connectivity between India and the ASEAN region.
- Trade and economic ties remain low: Despite efforts to strengthen economic ties, India’s trade and economic ties with ASEAN are much below their potential.
- But China remains the largest trading partner of the regional grouping, followed by the European Union and the United States.
- Quadrilateral Security Initiative: ASEAN has not been very favourable to the rise of QUAD as a significant security institution in the region.
- It is neither willing to be entangled in the possible power transition taking place in the Indo Pacific.
- Low FDI: India’s FDI in ASEAN is also low in comparison to China, with China’s FDI to ASEAN standing at a much higher figure.
- Territorial disputes hindering the progress: ASEAN member states are enmeshed in territorial disputes with interested powers for a long time, which creates a challenge for maintaining peaceful relations.
- Wobbling geopolitics: The geopolitical tension in the Indo-Pacific is producing geoeconomics consequences where issues of trade and technology cooperation as well as supply chain resilience are at peak.
- This is happening at a time when ASEAN remains a divided organization internally on how to manage these challenges.
- Indo-Pacific rivalry: The rivalry between major powers in the Indo-Pacific region, such as China and the United States, threatens the underlying stability on which rested the regional growth and prosperity.
Way Forward:
While the two sides have made tremendous progress in the last few decades and built strong linkages with each other, the potential for further growth and connections is immense. There is a bright future ahead for the ASEAN and India relations. As with the US and China, the ASEAN member states will need to seek to balance and pursue their interests in the developing India-China dynamic in the region.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Environment)
Context: The Intergovernmental negotiating committee (INC) to develop an international legally binding instrument on plastic pollution, recently released a zero draft to end plastic pollution.
Highlights of the draft: The text is divided into four parts:
- Part I: It covers the objectives of the instrument and leaves placeholders, as requested at the second session of the committee from May 29-June 2 for elements that Members may wish to include but were not discussed at the second session.
- Part II: Elements in this Part are broadly structured around the life cycle of plastics and plastic products with the aim of addressing plastic pollution.
- It aims to collectively promote the sustainable production and consumption of plastics through product design and environmentally sound waste management, including through resource efficiency and circular economy approaches.
- Part III and IV: The third and fourth parts outline different options of measures aimed at collectively addressing the implementation of the instrument.
About plastics and its pollution:
- Plastics are a group of materials, either synthetic or naturally occurring, that may be shaped when soft and then hardened to retain the given shape.
- Plastics can be divided into two general categories–thermoplastics and thermosets.
- Thermoplastics are defined as polymers that can be melted and recast almost indefinitely.
- Thermosets is a polymer that irreversibly becomes rigid when heated.
- Plastic pollution occurs when plastic has gathered in an area and has begun to negatively impact the natural environment and create problems for plants, wildlife, and even the human population.
- This includes killing plant life and posing dangers to local animals.
- Plastic is an incredibly useful material, but it is not biodegradable.
Significance of Plastics:
- Properties of plastics such as resistant, inert, and lightweight offers many benefits to companies, consumers, and other links in society.
- This is all because of its low-cost and versatile nature.
- In the medical industry, plastics are used to keep things sterile.
- Syringes and surgical implements are all plastic and single use.
- In the automotive industry, it has allowed a significant reduction in vehicle weight, reducing fuel consumption and, consequently, the environmental impact of automobiles.
- Plastics protect our heads in the form of helmets.
- They keep us safer in our cars in the form of seatbelts, fuel tanks, windscreens and airbags.
Major Concerns with Plastic pollution:
- Pollution: Plastic waste is blocking sewers, threatening marine life and generating health risks for residents in landfills or the natural environment.
- Food and health: Invisible plastic has been identified in tap water, beer, salt and are present in all samples collected in the world’s oceans, including the Arctic.
- The transfer of contaminants between marine species and humans through the consumption of seafood has been identified as a health hazard.
- Financial costs of marine plastic pollution: According to conservative forecasts made in March 2020, the direct harm to the blue economy of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations will be $2.1 billion per year.
- Boats become entangled in abandoned or discarded fishing nets or their engines may become blocked with plastic debris.
- Coastal pollution: Residents of coastal regions suffer from the harmful health impacts of plastic pollution and waste brought in by the tides and are inextricably linked to the fishing and tourism industry for their livelihoods.
- Tourism: Plastic waste damages the aesthetic value of tourist destinations, leading to decreased tourism-related incomes and major economic costs related to the cleaning and maintenance of the sites.
- Climate change: Plastic, which is a petroleum product, also contributes to global warming. If plastic waste is incinerated, it releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, thereby increasing carbon emissions.
Govt of India’s initiatives to tackle plastic waste:
- The Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016: It clearly stipulates that urban local bodies (ULBs) should ban less than 50 micron thick plastic bags and not allow the usage of recycled plastics for packing food, beverage or any other eatables.
- It introduced the concept of EPR(Extended Producer Responsibility) to manage plastics in India.
- Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2022: The guidelines on EPR(Extended Producer Responsibility) coupled with the prohibition of identified single-use plastic items.
- It banned the manufacture, import, stocking, distribution, sale and use of carry bags made of virgin or recycled plastic less than seventy-five microns.
- Swachh Bharat Mission – Urban 2.0: Under this, every Urban Local Bodies (ULB) is required to adopt 100% source segregation of waste, and have access to a Material Recovery Facility (MRF) for sorting the dry waste (including plastic waste) into further fractions for recycling and/ or processing into value-added products.
- Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB): CPCB along with state pollution bodies, will monitor the ban, identify violations, and impose penalties already prescribed under the Environmental Protection Act.
- Plastic Parks: India has set up Plastic Parks, which are specialized industrial zones for recycling and processing plastic waste.
- Project REPLAN: REducing PLastic in Nature launched by Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) aims to reduce consumption of plastic bags by providing a more sustainable alternative.
Way Forward:
A comprehensive extended producer responsibility is also needed to ensure manufacturers are accountable for recycling, on the lines of rules for electronic waste. The whole world is mobilising efforts to decrease plastic footprint. Every country is reeling under this menace and there is a huge support system globally continuously created to tackle this menace.
Source: DTE
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Types of ATMs | Definition |
| 1.White Label ATM | In this type of ATM, the hardware and lease of the ATM are owned by the service provider but the cash management and connectivity to the banking network are provided by the sponsor bank. |
| 2.Brown Label ATM | ATMs that are used for agricultural transactions. |
| 3.Pink Label ATM | This type of ATM is solely made for women’s banking. |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
The dancing girl sculpture has 24 bangles in one hand and 4 in the other.
Statement-II:
The sculpture is made of Gold.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) With reference to Fujianvenator prodigiosus, consider the following statements:
- It survived the asteroid strike 66 million years ago that doomed its non-avian dinosaur comrades.
- It had wings and could fly.
- It inhabited southeastern China.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) Analyse the significance and challenges of ASEAN relationship with India as the ‘central pillar’ of India’s Act East Policy? (250 words)
Q.2) Plastic has become one of the most challenging environmental issues in the recent decades. Discuss the current status and the targets to be achieved pertaining to plastic waste management across the world. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 9th September 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 8th September – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – a











