IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Recently, the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) commemorated the success of the “SWAYATT” initiative.
About Start-ups, Women and Youth Advantage Through e-transactions (SWAYATT ):
- SWAYATT”, is an initiative to promote Start-ups, Women, and Youth advantage through e-Transactions on the Government eMarketplace (GeM).
- Ministry: Ministry of Commerce & Industry
- The initiative to promote “Start-ups, Women and Youth Advantage Through e-transactions” (SWAYATT) on GeM was first launched in February 2019.
- This will bring together the key stakeholders within the Indian entrepreneurial ecosystem to the Government e-Marketplace the national procurement portal.
About Self-Employed Women’s Association (SEWA-Bharat) :
- It is a federation of women-led institutions providing economic and social support to women in the informal economy.
- It is part of the national SEWA movement and was established in 1984.
- It emerged out of the need to address the SEWA movement’s challenges with geographical expansion and coordination.
- It is a family of SEWA organizations to further informal women workers’ rights, livelihoods, financial independence, education, health, and social security.
- SEWA organizes workers to achieve their goals of full employment and self-reliance through the strategy of struggle and development.
About National Cooperative Union of India (NCUI):
- NCUI was established in 1929.
- It is an all-India Co-operative Institutes Association and was re-named National Co-operative Union of India in 1961.
- It is an apex Cooperative organization representing the entire Indian Cooperative Movement established in 1929.
- The Cooperative Education Field Project was introduced in Nagaland in 2002 with its Head Office in New Delhi.
Objectives:
- to promote and develop the co-operative movement in India
- to educate, guide and assist the people in their efforts
- to build up and expand the co-operative sector
- NCUI membership is open to national and state-level co-operative organizations as well as multi-state co-operative societies.
- As of 30th June 2016, NCUI had 260 members, including, 17 National, 163 State, and 80 Multi-State Cooperatives.
About Small Farmers Agri Consortium (SFAC):
- Small Farmers Agribusiness Consortium (SFAC) is an Autonomous Society promoted by the Ministry of Agriculture, Cooperation and Farmers’ Welfare, Government of India.
- It was registered under the Societies Registration Act XXI of 1860 in 1994.
- The Society is governed by a Board of Management which is chaired, ex-officio, by the hon’ble Union minister for Agriculture and Farmers Welfare as the President and the Secretary, Department of Agriculture, Cooperation and Farmers Welfare, Government of India, is the ex-officio Vice-President.
- SFAC is implementing the central schemes of the Government of India namely VCA, and EGCGS for the economic inclusion of small and marginal farmers in agribusiness activities.
- Society is a pioneer in organizing small and marginal farmers such as Farmer’s Interest Groups, Farmer’s Producers Organizations, and Farmer’s Producers Companies for endowing them with bargaining power and economies of scale.
- It provides a platform for increased accessibility and cheaper availability of agricultural inputs to small and marginal farmers and for establishing forward and backward linkages in supply chain management.
- Recently the Society has been entrusted with the task of implementing the critically important Delhi Kisan Mandi and National Agriculture Market Scheme on an e-platform to progressively free agricultural trade and offer price discovery to farmers.
Source: PIB
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to foreign-owned e-commerce firms operating in India, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- They can sell their own goods in addition to offering their platforms as marketplaces.
- The degree to which they can own big sellers on their platforms is limited.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Private and public hospitals must adopt it.
- As it aims to achieve universal health coverage, every citizen of India should be part of it ultimately.
- It has seamless portability across the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
Context: The representatives of fugitive ‘godman’ Nithyananda’s self-proclaimed country, the United States of Kailasa (USK), attended a discussion conducted by the United Nations Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (CESCR) recently.
About United Nations Committee on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights:
- The Committee on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights (CESCR) is the body of 18 independent experts that monitors the implementation of the International Covenant on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights by its States parties.
- It was established under ECOSOC Resolution 1985/17 in 1985.
- All States parties are obliged to submit regular reports to the Committee on how economic, social, and cultural rights are being implemented.
- States must report initially within two years of accepting the Covenant and thereafter every five years.
- The Committee examines each report and addresses its concerns and recommendations to the State party in the form of “concluding observations”.
- The Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, which entered into force in 2013, gives the Committee competence to receive and consider communications from individuals claiming that their rights under the Covenant have been violated.
- The Committee meets in Geneva and normally holds two sessions per year.
Objectives :
- to carry out the monitoring functions assigned to the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) in Part IV of the Covenant.
- Drawing on the legal and practical expertise of its members.
- It also helps States in fulfilling their obligations under the Covenant by issuing specific legislative, policy, and other recommendations so that economic, social, and cultural rights are better protected.
It seeks to:
- develop a constructive dialogue with State parties
- determine whether the Covenant’s norms are being applied in State parties
- assess how the implementation and enforcement of the Covenant could be improved
MUST READ: United Nations Institute for Water, Environment and Health (UNU-INWEH)
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1.In which one of the following groups are all four countries members of G20? (2020)
- Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
- Australia, Canada, Malaysia, and New Zealand
- Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and Vietnam
- Indonesia, Japan, Singapore, and South Korea
Q.2. Which of the following is/are the indicator/indicators used by IFPRI to compute the Global Hunger Index Report?
- Undernourishment
- Child stunting
- Child mortality
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3 only
Q3. With reference to ‘The Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)’, consider the following statements : (2016)
- It is an organization of the European Union in working relation with NATO and WHO.
- It monitors the chemical industry to prevent new weapons from emerging.
- It provides assistance and protection to States (Parties) against chemical weapons threats.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy, International Relations
Context: Recently, the UK government reached a landmark deal with the European Union (EU) on post-Brexit trade rules that will govern Northern Ireland.
About Windsor Framework:
- The ‘Windsor Framework’ will replace the Northern Ireland Protocol, which had proved to be among the thorniest of Brexit fall-outs, creating problems both economic and political.
The Northern Ireland Protocol:
- The Northern Ireland Protocol is a trading agreement that was negotiated in 2020 between the U.K. and the E.U.
- Under the protocol, both the U.K. and E.U. agreed that the inspection of goods would be conducted between Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
- Northern Ireland remained in the EU single market, and trade-and-customs inspections of goods coming from Great Britain took place at its ports along the Irish Sea.
Issues related to the Northern Ireland Protocol :
- The protocol has led to political division in Northern Ireland.
- The checks made trade between Great Britain and Northern Ireland cumbersome, with food products, especially, losing out on shelf life while they waited for clearance. Some taxation and spending policies of the UK government could not be implemented in Northern Ireland because of EU rules.
- The sale of medicines, too, was caught between different British and EU rules.
Salient features of the Windsor Framework:
- The framework has two crucial aspects:
- Introduction of a green lane and red lane system – For goods that will stay in Northern Ireland and those that will go to the EU respectively.
- The Stormont Brake – it allows Northern Ireland lawmakers and London to veto any EU regulation they believe affects the region adversely.
- The two-lane system– British goods meant for Northern Ireland will use the green lane at the ports and will be allowed to pass with minimal paperwork and checks.
- Physical checks will be conducted if the goods are deemed suspicious, in place of the routine checks now.
- Goods destined for Ireland or the rest of the EU will have to take the red lane, with the attendant customs and other checks.
MUST READ: Post Brexit fishing tussle
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1. With reference to Trade-Related Investment Measures (TRIMS), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2020)
- Quantitative restrictions on imports by foreign investors are prohibited.
- They apply to investment measures related to trade in both goods and services.
- They are not concerned with the regulation of foreign investment.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as : (2016)
- G20
- ASEAN
- SCO
- SAARC
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Recently, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology launched the Grievance Appellate Committee (GAC) portal.
About Grievance Appellate Committee (GAC):
- The Grievance Appellate Committee (GAC) is established under the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021 [“IT Rules”], made under the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- The IT Rules and GAC aim to ensure a Safe & Trusted and Accountable Internet for Indian users.
- The GAC is an online dispute resolution mechanism.
- The GAC deals with the appeals of users (Digital Nagriks) aggrieved by decisions of Grievance Officers of social media intermediaries and other intermediaries on complaints of users or victims against violation of the IT Rules and any other matters pertaining to the computer resources made available by the intermediaries.
- The Committee will try to respond to the user’s appeal within 30 days.
- Within 24 hours of receiving the complaint, this official is required to acknowledge it and offer a resolution within 15 days.
- It is required that complaints connected to crimes against women be handled within 24 hours in specific situations.
About the GAC portal :
- It will be a virtual Digital platform that will operate only online and digitally
- The entire appeal process, from the filing of the appeal to the decision thereof, shall be conducted digitally through the new portal.
- The new portal lists detailed FAQs for the convenience of users.
- The appellants can track the status of their appeal through the Appellant Login window.
- GAC will upload its order on the portal, and the appellant will receive notification of the same by SMS and email.
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1. With reference to the funds under the Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLADS), which of the following statements is correct? (2020)
- MPLADS funds must be used to create durable assets like physical infrastructure for health, education, etc.
- A specified portion of each MP’s fund must benefit SC/ST populations.
- MPLADS funds are sanctioned on yearly basis and the unused funds cannot be carried forward to the next year.
- The district authority must inspect at least 10% of all works under implementation every year.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 4 only
Q.2. Rashtriya Garima Abhiyaan is a national campaign to (2016)
- Rehabilitate the homeless and destitute persons and provide them with suitable sources of livelihood
- Release the sex workers from their practice and provide them with alternative sources of livelihood
- Eradicate the practice of manual scavenging and rehabilitate the manual scavengers
- Release the bonded laborers from their bondage and rehabilitate them
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: A new report by the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) claims that India’s iron and steel sector can produce fewer emissions and increase its output at the same time.
About Decarbonizing India: Iron and Steel Sector report:
- The iron and steel sector is a hard-to-abate sector in terms of greenhouse gas emissions, but it is an equally critical contributor to the economic development of the country.
- India is the second-largest producer of crude steel in the world and plans to almost triple its production by 2030
- The report(Decarbonizing India: Iron and Steel Sector) was released by the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE).
- According to it India’s iron and steel sector can produce fewer emissions and increase its output at the same time.
- The analysis shows that it is possible to bring down carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from our iron and steel sector drastically by 2030, while more than doubling India’s output of steel.
- emissions from crude steel production are estimated to grow to almost 2.5 times by 2030.
- This report provides a detailed insight into the GHG emissions of the iron and steel sector and its future emission scenarios for 2030 -the report provides, based on available information, unit and company-wise data on emissions, which will help design the road ahead.
- The report suggests a roadmap for the sector, highlighting the pathways for GHG emissions reduction. The assessment clearly finds there are huge opportunities to bend the carbon dioxide curve for this emission-intensive sector, but it will need planning, technology and adequate funds.
About Iron and Steel Industry in India :
- India surpassed Japan as the second top steel producer in 2019.
- India was the world’s second-largest steel producer.
- China remains the world’s largest crude steel producer .
- India is the largest producer of sponge iron in the world and the 3rd largest finished steel consumer in the world after China & USA.
- The Government has taken various steps to boost the sector including the introduction of the National Steel Policy 2017 and allowing 100 per cent Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the steel sector under the automatic route.
- The beginning of the Iron and steel industry was in 1907 with the setting up of the TISCO plant at Jamshedpur.
- The development of the Iron and Steel industry was envisaged during the first five-year plan (FYP), but it was during the second FYP that three integrated projects were started at Bhilai (with erstwhile USSR technical and financial support), Rourkela (with German assistance) and Durgapur (with U.K assistance)
- During the third FYP, the Bokaro steel plant was started (production started in 1972)
- Steel Authority of India (SAIL) Established in 1973, SAIL is a government undertaking and is responsible for the management of steel plants
Distribution of Iron ores:
- The Chota Nagpur plateau is home to all of India’s major steel-making centres, which are spread across four states: West Bengal, Jharkhand, Orissa, and Chhattisgarh.
Major Steel Industries :
- TISCO -Jamshedpur, Jharkhand
- The Visvesvaraya Iron and Steel Plant -Bhadravati, Karnataka
- Bhilai Steel Plant – Chhattisgarh
- Rourkela Steel Plant-Odisha
- Durgapur Steel Plant- West Bengal
- Bokaro Steel Plant-Jharkhand
- Salem Steel Plant-Tamil Nadu
- Visakhapatnam Steel Plant- Andhra Pradesh
MUST READ: Iron Ore
Source: DOWN TO EARTH
Previous Year Questions
Q.1. Steel slag can be the material for which of the following? (2020)
- Construction of base road
- Improvement of agricultural soil
- Production of cement
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2. Consider the following minerals:
- Bentonite
- Chromite
- Kyanite
- Sillimanite
In India, which of the above is/are officially designated as major minerals? (2020)
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Recent studies talk about the inaccessibility of Proton beam therapy for many with cancer.
About Proton beam therapy treatment:
- Proton therapy is a type of radiation therapy, that uses high-powered energy to treat cancer and some noncancerous tumors.
- Proton therapy is a newer type of radiation therapy that uses energy from positively charged particles (protons).
- Proton therapy has shown promise in treating several kinds of cancer.
- It may cause fewer side effects than traditional radiation since doctors can better control where the proton beams deliver their energy.
- Proton therapy accurately targets very specific locations, which may result in less damage to surrounding tissues while conventional radiation therapy is less targeted, and more “normal” cells in the region of a tumor may be damaged.
- Proton beam therapy is not one single type of treatment, but rather there are different types and methods.
Advantages :
- Precise delivery with less long-term damage
- It may allow a ‘Higher Radiation Dose’
- It causes less damage to surrounding tissues and fewer long-term risks
- Proton Beams are easier to control
- It can be well tolerated
- It can be used for inoperable Tumors
Disadvantages
- It may miss cancer outside the radiation field.
- At the current time, proton beam therapy is roughly twice as expensive as conventional radiation therapy.
- Challenges with proton therapy include motion management and changes in anatomy that take place before and during treatment.11
- Limited availability of proton beam therapy centers.
Applications: Proton therapy is sometimes used to treat: Brain tumors, various cancer types including breast cancer, Lymphoma, Pituitary gland tumors etc.
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1. Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body? (2022)
- They protect the environmental allergens. body
- They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
- They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
- They protect the body from diseases caused by pathogens.
Q.2. In the context of hereditary diseases, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Passing on mitochondrial diseases from parent to child can be prevented by mitochondrial replacement therapy either before or after in vitro fertilization of the egg.
- A child inherits mitochondrial diseases entirely from the mother and not from the father.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science, and Technology
Context: Recent research announced that India’s first and only DNA vaccine for dengue has shown promising results.
About Dengue:
- Dengue is a vector-borne disease transmitted by the bite of an infected female Aedes Aegypti mosquito.
- The mosquito becomes infected when it feeds on the blood of a person infected with the virus.
- There are 4 serotypes of the virus that causes dengue. These are known as DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3, and DEN-4.
- Dengue cannot be spread directly from person to person.
- Most cases occur in tropical areas of the world, including the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, Southern China, Taiwan, the Pacific Islands, the Caribbean, Mexico, Africa, and Central, and South America.
Symptoms include: High fever, Headache, Vomiting, Muscle and joint pains, Skin Rash
- The diagnosis of dengue infection is done with a blood test.
- WHO estimates 39 crore dengue virus infections per year, of which 9.6 crore show symptoms.
About DNA Vaccines :
- DNA vaccines are often referred to as third-generation vaccines.
- They use engineered DNA to induce an immunologic response in the host against bacteria, parasites, viruses, and potentially cancer.
- The vaccines that are currently available to the global population include those for measles, mumps, rubella, seasonal influenza virus, tetanus, polio, Hepatitis B, cervical cancer, diphtheria, pertussis as well as several other diseases that are endemic to certain regions of the world.
Working :
- DNA vaccines induce an adaptive immune response.
- The basic working principle behind any DNA vaccine involves the use of a DNA plasmid that encodes for a protein that originated from the pathogen in which the vaccine will be targeted.
- More specifically, these vaccines expose the immune system to the target pathogen elements, which allows the immune system to develop antibodies that can recognize and attack this infectious agent if the vaccinated host encounters this pathogen in the future.
DNA Vaccine and COVID-19:
- In September 2021, India gave emergency authorization to the world’s first DNA vaccine for human use called ZyCoV-D.
- The vaccine was developed by the Zydus Cadila pharmaceutical company.
- It was approved for emergency use in adults and in children 12 and older.
Advantages of DNA Vaccine:
- They can be developed quickly.
- They are easy to transport and store.
- It’s less expensive to make and purify large amounts of DNA from viruses or bacteria than to create traditional vaccines.
Disadvantages of DNA Vaccines:
- Limited approvals: as of 2021, the FDA had approved the DNA vaccine only for use in certain animal diseases, such as West Nile Virus in horses and melanoma in dogs.
- More research into the use of DNA vaccines against COVID-19 and other diseases caused by viruses or bacteria is required.
- Scientists still do not properly understand much of the immune response caused by DNA vaccines. Limited data is available on their safety, possible side effects, and effectiveness.
MUST READ: Immunity and types of Immunities
Source: DOWN TO EARTH
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent the COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Serum Institute of India produced a COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using an mRNA platform.
- The Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using a vector-based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen-based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to recent developments regarding ‘Recombinant vector Vaccines’, consider the following statements: (2021)
- Genetic engineering is applied in the development of these vaccines.
- Bacteria and viruses are used as vectors.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: Recently, German Chancellor Olaf Scholz came to India on a bilateral visit.
Key outcomes of the bilateral meeting
Green and Sustainable Development Partnership (GSDP):
- GSDP is an umbrella partnership that provides political guidance and steer to robust ties in climate action and SDGs.
- Under this, Germany will place €10 billion in new and additional commitments under their development cooperation portfolio in India.
- India-Germany agreed on a vision statement to Enhance Cooperation in Innovation and Technology.
- Under the framework of the Inter-Governmental Agreement on ‘Cooperation in Scientific Research and Technological Development’, the two countries share a long history of cooperation in science and technology, research and innovation.
Cooperation in Green Hydrogen:
- For this, the Indo-German Green Hydrogen Task Force was constituted in September 2022.
Triangular Development Cooperation:
- India and Germany agreed to work on development projects in third countries.
- Both sides concluded agreements on “Digital Transformation, FinTech, IT, Telecom and Supply chains’ diversification”.
Indo – German Bilateral Relations:

- Germany is one of India’s most important partners in Europe owing to the strength of bilateral relations, as also Germany’s key role in the EU.
- India was among the first countries to establish diplomatic ties with the Federal Republic of Germany after the Second World War.
- On March 7, 2021, India and Germany marked the 70th anniversary of the establishment of diplomatic relations.
Trade and economic relations:
- Germany is India’s largest trading partner in Europe, with a total trade of USD 21.07 Billion in 2020-21, occupying 17.4% of share in European Market.
- Germany is the 7th largest foreign direct investor in India since April 2000.
- Germany’s total FDI in India from 2000 until 2019 amounted to US$ 11.9 billion.
- Germany has a Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA) with India via the EU.
Multilateral Cooperation:
- Germany and India support each other on UNSC expansion within the framework of the G-4.
- Germany joined the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) in February 2020 and participated in the first Governing Council meeting in March 2020.
- In April 2021, the German Federal Cabinet approved the signing of the amended framework agreement of the International Solar Alliance (ISA), and thereby Germany’s accession to the ISA.
Defence co-operation:
- India-Germany Defence Cooperation Agreement (2006) provides a framework for bilateral defence cooperation.
- Both the countries signed the Arrangement on Implementation of the Agreement, concerning Bilateral Defence Cooperation which enables both the countries to share classified information with each other
- Indian and German navy ships regularly conduct anti-piracy operations in the Indian ocean.
- The first ever Franco-Indian-German military exercise is expected to take place in 2024.
Science and Technology:
- Bilateral Science and Technology cooperation is implemented under an Inter-Governmental Agreement on ‘Cooperation in Scientific Research and Technological Development’ signed in May 1974.
- The Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF) are the nodal agencies for overall coordination.
- An apex Indo-German Committee on Science and Technology, established in 1994 coordinates the implementation of cooperation and joint review of activities.
Culture and Indian diaspora:
- The translation of Kalidas’s ‘Shakuntala’ in 1791 envisaged institution-based scientific research on sacred Indian texts for the quest of Indian philosophy and literature.
- Max Mueller was the first scholar of Indo-European languages to translate and publish Upanishads and Rigveda.
- There are around 03 lakh (December 2021) Indian passport holders and Indian-origin people (about 1.60 lakh NRIs/Indian Passport holders and around 43,000 PIOs) in Germany.
Issues associated with bilateral relations:
- Germany’s low trade: Germany’s trade with India is less than ten percent of its trade with china.
- Restrictive Policies: Germany has an advanced defence manufacturing comparable to that of France, but the defence exports are less than potential because of restrictive arms export policy
- Lack of a separate bilateral investment treaty between the two countries hampers the commercial potential between two countries.
- Germany is not confident about India’s trade liberalization measures; it bats for more liberal labour regulations.
Way Forward:
At present, in spite of various setbacks, the Indo-German relations have made a rapid stride. The ‘policy of benign neglect’ had changed into a more ‘vibrant partnership’. Indo-German cooperation should be based on a win win situation so that both countries can help each other in improving their economic, technological, defence and political position in the international arena.
This is not a difficult task as Germany are India are “natural allies”. While Germany has surplus capital, modern technology and a demographic deficit, India has a deficit of capital, lacks modern technology and has exportable human capital.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Geography)
Context: India is experiencing a colder winter than normal with the La Niña is going on for a record-breaking third consecutive year also known as the ‘Triple dip’ La Nina.
- Forecasts for the 2023 fall and winter are predicting that El Niño will occur with more than a 50% probability.
About the El Niño, La Niña and ENSO:
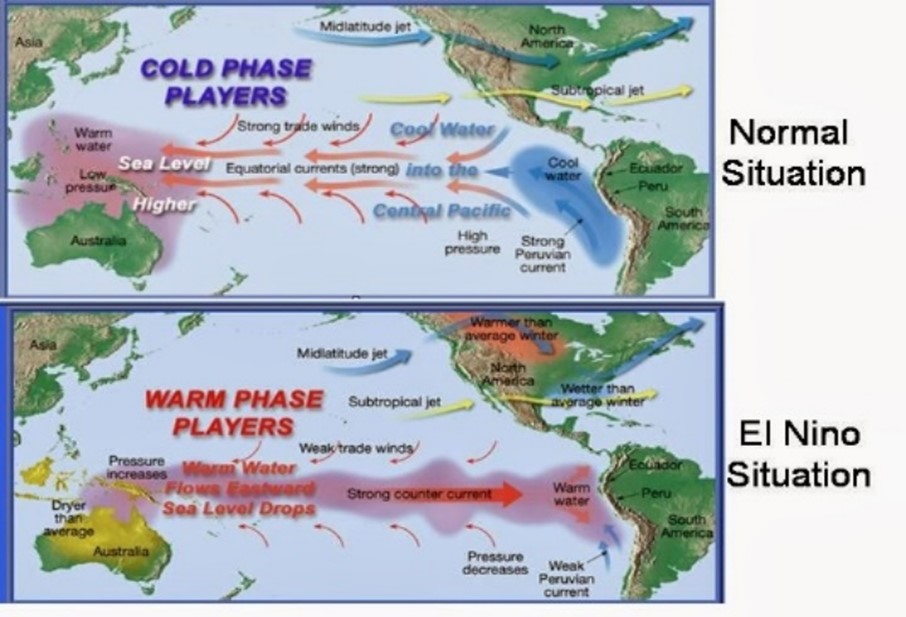
- El Niño is the warming of seawater in the central-east Equatorial Pacific that occurs every few years.
- During El Niño, surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific rise, and trade winds — east-west winds that blow near the Equator — weaken.
- Normally, easterly trade winds blow from the Americas towards Asia.
- Due to El Niño, they falter and change direction to turn into westerlies, bringing warm water from the western Pacific towards the Americas.
- It occurs every 3-6 years and lasts for about 9-12 months.
- It can cause droughts, flooding, and changes in temperature.
- It can lead to below-normal rainfall, which affects India’s agricultural sector.
Outcomes of El Nino:
- Disruptions in the food chain:
- The phenomena of upwelling, where nutrient-rich waters rise towards the surface, is reduced under El Niño.
- This in turn reduces phytoplankton.
- Thus, fish that eat phytoplankton are affected, followed by other organisms higher up the food chain.
- The phenomena of upwelling, where nutrient-rich waters rise towards the surface, is reduced under El Niño.
- Disruptions in the overall ecosystem:
- Warm waters also carry tropical species towards colder areas, disrupting multiple ecosystems.
- Alterations in wind and weather patterns:
- Since the Pacific covers almost one-third of the earth, changes in its temperature and subsequent alteration of wind patterns disrupt global weather patterns.
- El Niño causes dry, warm winters in Northern U.S. and Canada and increases the risk of flooding in the U.S. gulf coast and southeaster U.S.
- It also brings drought to Indonesia and Australia.
About La Niña:
- La Niña sees cooler than average sea surface temperature (SST) in the equatorial Pacific region.
- Trade winds are stronger than usual, pushing warmer water towards Asia.
- It is a phenomenon that is the colder counterpart of El Niño.
- It occurs when ocean temperatures in the equatorial Pacific drop to lower-than-normal levels.
Outcomes of La Nina:
- On the American west coast, upwelling increases, bringing nutrient-rich water to the surface.
- Pacific cold waters close to the Americas push jet streams — narrow bands of strong winds in the upper atmosphere — northwards.
- This leads to drier conditions in Southern U.S., and heavy rainfall in Canada.
- La Niña has also been associated with heavy floods in Australia.
- Two successive La Niña events in the last two years caused intense flooding in Australia, resulting in significant damage.
ENSO Cycle:
- El Nino–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is an irregularly periodic variation in winds and sea surface temperatures over the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean.
- Every three to seven years, the surface waters across tropical Pacific Ocean warm or cool by 1°C to 3°C, compared to normal.
- The warming phase of the sea temperature is known as El Nino and the cooling phase as La Nina.
- Thus, El Nino and La Nina are opposite phases of what is known as the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle.
- These deviations from normal surface temperatures can have large-scale impacts not only on ocean processes, but also on global weather and climate.
Impact on Cyclone Formation and Monsoons in 2023
El Niño and Monsoon Deficit:
- A transition from La Niña winter to El Niño summer tends to produce a large monsoon deficit of around 15%.
- This means weaker pre-monsoon and monsoon circulations, and weaker vertical shear, which can favour enhanced cyclone formation.
- However, intrapersonal or sub seasonal variability in sea-surface temperature and winds also plays an important role in cyclogenesis over the northern Indian Ocean.
- Overall, the net effect is for cyclogenesis to be subdued in an El Niño year.
Monsoon Deficit in 2023:
- If an El Niño state emerges by summer, India will likely have a deficit monsoon in 2023.
- Some research indicates that the Indian Ocean dipole may compensate for the negative effects of an El Niño, but it is not clear whether there is a robust relation between the dipole and the summer monsoon, nor whether the dipole will evolve in the “right” way this year.
Vagaries of Monsoon:
- The pre-monsoon cyclones are susceptible to warming in the Arctic region and could affect the onset of the summer monsoon.
- The Bay of Bengal has been receiving freshwater from heavy rains and high river runoffs, which tend to sneak into the Arabian Sea, produce surface warming, and build up subsurface heat.
- These changes together may create favourable conditions for the formation of bigger and badder cyclones, especially if the circulation and the vertical shear are weak.
Government steps to mitigate the impact of El Niño:
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): It is a crop insurance scheme launched by the government to protect farmers from crop loss due to various natural calamities, including drought, floods, and other weather-related events.
- Mission Amrit Sarovar: It is a scheme of developing 75 ponds in each district by the government to help reduce the dependence on rainfall.
- Soil Health Card scheme: This scheme aims to promote soil testing and provide farmers with the necessary information to help farmers to better manage their crops during periods of drought or other weather-related events.
- National Food Security Mission (NFSM): It aims to increase the productivity of crops in rainfed areas through the adoption of better farming practices and the use of new technologies.
- National Watershed Development Project for Rainfed Areas (NWDPRA): This project aims to promote sustainable watershed management practices in rainfed areas to improve soil moisture and water availability for crops during drought periods.
- National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (NAIS): This scheme provides financial assistance to farmers in case of crop loss due to natural calamities, including drought and other weather-related events.
- Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY): This scheme aims to promote agriculture development through various initiatives, including the development of rainfed agriculture and the use of modern technologies to improve crop productivity during drought periods.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY): It aims to promote efficient use of water resources in agriculture and increase water use efficiency to deal with drought and other weather-related events.
MUST READ: Retreating Monsoon
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- High clouds primarily reflect solar radiation and cool the surface of the Earth.
- Low clouds have a high absorption of infrared radiation emanating from the Earth’s surface and thus cause warming effect.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements:
- In the tropical zone, the western sections of the oceans are warmer than the eastern sections owing to the influence of trade winds.
- In the temperate Zone, westerlies make the eastern sections of oceans warmer than the western sections
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2021)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 and 2
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following pairs:
Major steel industry and state
- Bokaro Steel Plant –Chhattisgarh
- Bhilai Steel Plant – Jharkhand
- The Visvesvaraya Iron and Steel Plant – Karnataka
- Rourkela Steel Plant – Odisha
How many pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- One pair only
- Two pairs only
- Three pairs only
- All four pairs
Q.2) which of the following country is the largest crude steel producer in the world?
- India
- USA
- China
- Russia
Q.3) The Northern Ireland Protocol is often mentioned in the news related to
- Trade deal between the United Kingdom and The European Union
- Peace process between Ukraine and Russia
- Earthquake relief programme for Turkey and Syria
- None of the above
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 2nd March 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 1st March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – c














