IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Personalities
Context: Recently, the Vice President of India paid homage to Shri Atal Bihari Vajpayee on his Punya Tithi on 16th August.
About Shri Atal Bihari Vajpayee:-
- He was Prime Minister thrice in 1996, 1998-1999, and 1999-2004.
- Birth: 25, December 1924.
- Born in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh.
- Death:16, August 2018.
- Sadaiv Atal: the Samadhi of Atal Bihari Vajpayee.
Political Career:-
- He was the first non-Congress PM to have finished a full term.
- He was elected 10 times to the Lok Sabha from four different States.
- He was twice a member of the Rajya Sabha.
- His birthday, December 25, is observed as Good Governance Day by the government.
Awards:-
- 2015: He was awarded India’s highest civilian honor, Bharat Ratna.
- 1992: He was also awarded Padma Vibhushan. (Padma awards)
Ideology:-
- He advocated and practiced positive nationalism.
- He proudly took Hindi to the UN first time and spoke it in the General Assembly.
Important Initiatives:-
- He conducted the nuclear test in Pokhran in 1998.
- He himself rode a bus to Lahore in 1999 for Indo-Pak peace.
- He initiated the Delhi Metro rail as a mass transit system.
- He brought in National Highway Development Project leading to East West North South Corridor or the Golden Quadrilateral.
- He envisaged and executed the first round of Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana which connected rural India greatly.
- The New Telecom Policy of 1999 brought in by him was also a crucial part of the Indian telecom revolution.
Flagship Policy Initiatives:-
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan: Launched in 2000-2001 to provide free and compulsory education to children between 6 to 14 years.
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana: it was launched on 25th December 2000 to provide all-weather access to unconnected habitations.
- Pravasi Bharatiya Divas: these conventions are being held every year since 2003.
MUST READ: Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyay
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The world’s second tallest statue in the sitting pose of Ramanuja was inaugurated by the Prime Minister of India at Hyderabad recently. Which one of the following statements correctly represents the teachings of Ramanuja? (2022)
- The best means of salvation was devotion.
- Vedas are eternal, self-existent, and wholly authoritative.
- Logical arguments were meant for the highest bliss.
- Salvation was to be obtained through meditation.
Q.2) Consider the following freedom fighters: (2022)
- Barindra Kumar Ghosh
- Jogesh Chandra Chatterjee
- Rash Behari Bose
Who of the above was/were actively associated with the Ghadar Party?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Government Schemes
Context: Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the ‘PM Vishwakarma’ scheme.
Background:-
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved a new Central Sector Scheme “PM Vishwakarma” with a financial outlay of Rs.13,000 crore for a period of five years (FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28).
About PM Vishwakarma scheme:-

IMAGE SOURCE: oneindia.com
- Launched: 2023.
- Ministry: Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME).
- It is a Central Sector Scheme.
Objectives of PM Vishwakarma scheme:-
- To strengthen and nurture the Guru-Shishya parampara or family-based practice of traditional skills by artisans and craftspeople working with their hands and tools.
- To improve the quality, as well as the reach of products and services of artisans and craftspeople.
- To ensure that the Vishwakarmas are integrated with the domestic and global value chains.
Salient Features of PM Vishwakarma scheme:-
- The artisans and craftspeople will be provided recognition through a PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card.
- Credit Support: Credit of up to Rs.1 lakh (First Tranche) and Rs.2 lakh (Second Tranche) will be given with a concessional interest rate of 5%.
- Skill learning: The Scheme will further provide Skill Upgradation, Toolkit Incentives, Incentives for Digital Transactions, and Marketing Support.
- Training: Skill development programs encompass both basic and advanced training.
- Stipend: Participants are entitled to a stipend of Rs 500 per day during their training period.
- Modern Tools and Equipment: Beneficiaries are eligible for financial support of up to ₹15,000 to procure modern tools, enhancing their efficiency and productivity.
- Sectors: Eighteen traditional trades will be covered in the first instance under PM Vishwakarma.
- These trades include (i) Carpenter (Suthar); (ii) Boat Maker; (iii) Armourer; (iv) Blacksmith (Lohar); (v) Hammer and Tool Kit Maker; (vi) Locksmith; (vii) Goldsmith (Sonar); (viii) Potter (Kumhaar); (ix) Sculptor (Moortikar, stone carver), Stone breaker; (x) Cobbler(Charmkar)/ Shoesmith/Footwear artisan; (xi) Mason (Rajmistri); (xii) Basket/Mat/Broom Maker/Coir Weaver; (xiii) Doll & Toy Maker (Traditional); (xiv) Barber (Naai); (xv) Garland maker (Malakaar); (xvi) Washerman (Dhobi); (xvii) Tailor (Darzi); and (xviii) Fishing Net Maker.
Eligibility Criteria: –
- Indian Citizenship: Applicants must be Indian.
- Artisan or Craftsman: The applicant should be a traditional artisan or craftsman.
- Age Limit: No Age Limit for applying to the scheme
Benefits of PM Vishwakarma scheme:-
- The scheme will provide support to artisans and craftspeople in rural and urban areas across India.
- It caters to both urban and rural areas, facilitating employment. (MSME Sustainable (ZED) Certification Scheme)
- Funding for training programs to enhance traditional skills.
MUST READ: PM SVANidhi scheme
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under the Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy: (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for preschool children, adolescents, and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anemia in endemic pockets with a special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies, and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements : (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Defense
Context: Recently, the Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL) supplied the entire 4000 Tonnes of Special Steel for India’s indigenous sixth frigate ship, “Vindhyagiri”.
About Vindhyagiri:-
- Lunched: 17 AUGUST 2023.
- Naming: it is named after the mountain range in Karnataka, Vindhyagiri.
- It is the sixth ship of the Project 17A programme.
- Project 17 Alpha frigates (P-17A): launched by the Indian Navy in
- The project was launched to construct a series of stealth guided-missile frigates.
- Aligning with the country’s resolute commitment to ‘AatmaNirbharta’, a substantial 75% of the orders for equipment and systems of Project 17A ships are from indigenous firms, including Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- Mazagaon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL): is responsible for constructing four of the Project 17A frigates.
- MDL: A Mumbai-based shipbuilding company. ( Dunagiri, a Project 17A Frigate)
- Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE): A shipbuilding company located in Kolkata, tasked with constructing three Project 17A frigates.
- It is a technologically advanced frigate.
- It is the sixth and final ship of this series from the Nilgiri Class Frigates.
- Nilgiri Class Frigates: A class of frigates within the Indian Navy to serve in various maritime roles, including surveillance, patrol, and anti-piracy operations.
- It is for Maritime Surveillance to ensure security, safety, and compliance with maritime laws and regulations.
MUST READ: Atmanirbhar Bharat 3.0
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Home Guards, consider the following statements: (2023)
- Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards Act and Rules of the Central Government.
- The role of the Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary force to the police in the maintenance of internal security.
- To prevent infiltration on the international border/ coastal areas, the Border Wing Home Guards Battalions have been raised in some states.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Consider the following statements (2023)
- Ballistic missiles are jet-propelled at subsonic speeds throughout their flights, while cruise missiles are rocket-powered only in the initial phase of flight.
- Agni-V is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile, while BrahMos is a solid-fuelled intercontinental ballistic missile.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has planned its next launch of the Aditya L1 satellite in August 2023
About Aditya L1:-
- Aditya L1 shall be the first space-based Indian mission to study the Sun.
- Launched by: ISRO.
- Launch Vehicle: PSLV-XL. ( PSLV-C54 launch)
- Destination: The spacecraft shall be placed in a halo orbit around the Lagrange point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, which is about 1.5 million km from the Earth.
- Lagrange points: specific locations in space where the gravitational forces of two large bodies, such as a planet and its moon or a planet and the Sun, produce enhanced regions of gravitational equilibrium.
- There are five primary Lagrangian points, labeled L1 through L5, in a Sun-Earth system.
- L1 (Lagrange Point 1):-
- Founded by: Joseph Louis Lagrange.
- Location: about 1.5 million kilometers inside Earth’s orbit, between the Sun and the Earth.
- The L1 point of the Earth-Sun system gives a clear view of the sun all the time, without any occultation/ eclipses.
- Significance of Aditya L1: It will provide a greater advantage in observing solar activities and their effect on space weather in real-time.
Objectives of Aditya L1:-
- Study of Solar upper atmospheric
- Study of chromospheric and coronal heating, physics of the partially ionized plasma, initiation of the coronal mass ejections, and flares.
- Sun’s corona: the outermost layer of its atmosphere
- Study of the Physics of the solar corona and its heating mechanism.
- Study of Diagnostics of the coronal and coronal loops plasma: Temperature, velocity, and density.
- Study of Magnetic field topology and magnetic field measurements in the solar corona.
MUST READ: Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV)
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- Ballistic missiles are jet-propelled at subsonic speeds throughout their flights, while cruise missiles are rocket-powered only in the initial phase of flight.
- Agni-V is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile, while BrahMos is a solid-fuelled intercontinental ballistic missile.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? (2023)
- Australia
- Canada
- Israel
- Japan
Syllabus
- Prelims –History
Context: Recently, President Droupadi Murmu paid tribute to Matangini Hazra and Kanaklata Barua.
About Matangini Hazra:-
- Birth: 1869.
- Birth place Tamluk, West Bengal.
- Death:1942.
- She was married at a young age and became widowed at 18.
- After her husband’s death, she dedicated herself to social causes.
- She was involved in the Nationalist movement.
- She became an active member of the Indian National Congress and took to spinning her own Khadi.
- Ideology: She supported Mahatma Gandhi’s ideals. ( Mahatma Gandhi)
- People fondly called her Gandhi Buri (Old Lady Gandhi) for her dedication towards Gandhian principles.
- Political Participation: Civil Disobedience Movement, the Salt March, and Quit India Movement. (UPSC CSE: India and Mahatma Gandhi)
- 1933: When Sir John Anderson, Governor of Bengal visited Tamluk to address a public gathering, Matangini craftily managed to avoid the security and reached the dais where she waved a black flag.
- She was awarded six months of rigorous imprisonment for her bravado.
- During the Quit India Movement in 1942, at the age of 73, she led a large procession of around 6,000 protesters, advocating for the takeover of the Tamluk police station.
- In the ensuing clash with British authorities, she was shot and killed, becoming a martyr for the cause of Indian independence.
About Kanaklata Barua:-
- Birth: 22 December 1924
- Birthplace: Assam.
- Death: 1942.
- She was a young martyr of the Quit India Movement and a symbol of courage and determination.
- Participation: At just 17 years old, she led the Mrityu Bahini, a group of freedom fighters, in an attempt to hoist the Tricolour at the Gohpur police station in Assam on September 20, 1942.
Contributions and Inspiration: –
- Despite her age, she was determined to lead the procession.
- During the confrontation with the police, she was shot and killed while holding onto the flag.
- Her sacrifice inspired many during a time when women’s involvement in the freedom struggle was gaining momentum.
- Legacy: In 2020, the Indian Coast Guard honoured her memory by naming a Fast Patrol Vessel (FPV) after her, the ICGS Kanaklata Barua.
MUST READ: Gandhi as Political thinker and a Social reformer
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) By which one of the following Acts was the Governor General of Bengal, designated as the Governor General of India? (2023)
- The Regulating Act
- The Pitt’s India Act
- The Charter Act of 1793
- The Charter Act of 1833
Q.2) Consider the following freedom fighters: (2022)
- Barindra Kumar Ghosh
- Jogesh Chandra Chatterjee
- Rash Behari Bose
Who of the above was/were actively associated with the Ghadar Party?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: The Centre has pushed for faster admission of corporate insolvency cases at the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT).
Background:-
- Faster admission of corporate insolvency cases is one of the key themes of the draft guidelines for the NCLT, which are being finalized by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
About National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT):-
- Establishment: 2016
- It was established based on the recommendation of the Balakrishna Eradi committee.
- Balakrishna Eradi committee: a committee on the law relating to the insolvency and the winding up of companies.
- Ministry: Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It is a quasi-judicial authority.
- It is incorporated for dealing with corporate disputes that are of civil nature arising under the Companies Act,2013.
- Composition: President and such number of Judicial and Technical Members as may be required.
Powers of NCLT:-
- It is not limited or bound by the rules laid down in the Code of Civil Procedure. (Criminal Procedure (Identification) Act, 2022)
- It is guided by the principles of natural justice, subject to the other provisions of this Act and of any rules that are made by the Central Government.
- It can enforce any order that it gives in the same manner as a court would enforce it.
- It has the power to scrutinize its own orders.
- It has the power to regulate its own procedure.
- It is the adjudicating authority for the insolvency resolution process of companies and limited liability partnerships under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016.
MUST READ: Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Bill, 2020
SOURCE: BUSINESS STANDARD
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following .activities of the Reserve Bank of India is considered to be part of ‘sterilization’? (2023)
- Conducting ‘Open Market Operations
- Oversight of settlement and payment systems
- Debt and cash management for the Central and State Governments
- Regulating the Functions of Nonbanking Financial Institutions
Q.2) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements: (2022)
- A share of the household’s financial savings goes towards government borrowings.
- Dated securities issued at market-related rates in auctions form a large component of internal debt.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: The Nehru Memorial Museum & Library (NMML) Society has been renamed to Pradhan Mantri Museum and Library (PMML) Society.
About Pradhan Mantri Museum and Library (PMML) S:-
- Designed by: Robert Tor Russel.
- Ministry: Ministry of Culture, Government of India.
- Location: New Delhi.
- It is located in the historic Teen Murti campus located south of Rashtrapati Bhavan in New Delhi.
- It is an autonomous institution.
- Objective: promoting advanced research on Modern and Contemporary India.
- Administration: The General Council and the President and Vice-President of the PMML Society are nominated by the Central Government.
Historical Background:-
- It was built in 1929-30 as part of Edwin Lutyens’ imperial capital.
- Teen Murti House was the official residence of the Commander-in-Chief in India.
- 1948: after the departure of the last British Commander-in-Chief, Teen Murti House became the official residence of independent India’s first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, who lived here for sixteen years until his death on May 27, 1964.
- 1964: On Jawaharlal Nehru’s 75th birth anniversary on November 14, 1964, Dr. Sarvapalli Radhakrishnan, President of India, formally dedicated the Teen Murti House to the nation as the Nehru Memorial Museum.
- 1966: On 1 April 1966, the Government set up the Prime Ministers Museum and Library (PMML) Society to manage the institution.
Major Constituents:-
It has four major constituents, namely:-
- Memorial Museum
- Library on modern India
- Centre for Contemporary Studies (Amar Jawan Jyoti, War Memorial merged)
- Nehru Planetarium
MUST READ: Sardar Patel – The Iron Man of India
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Who among the following is associated with ‘Songs from Prison’, a translation of ancient Indian religious lyrics in English? (2021)
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
- Sarojini Naidu
Q.2) In the context of Colonial India, Shah Nawaz Khan, Prem Kumar Sehgal, and Gurbaksh Singh Dhillon is remembered as (2021)
- leaders of Swadeshi and Boycott Movement
- members of the Interim Government in 1946
- members of the Drafting Committee in the Constituent Assembly
- officers of the Indian National Army
Cauvery river water dispute
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Geography) and GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently, the Tamil Nadu government urged the Supreme Court to direct Karnataka to ensure the release of water as per the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (CWDT)’s final award of February 2007 that was modified by the SC in 2018.
About Cauvery river:
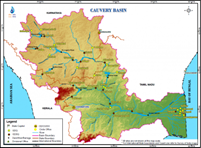
Source: Indiawris.com
- Cauvery (or Kaveri) is the largest river in the state and originates at Talakaveri at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri hills of the Western Ghats in Karnataka.
- It is often called the Dakshina Ganga (the Ganges of the South) and considered one of the sacred rivers of India.
- The origin of the River Kaveri, is a famous pilgrimage and tourist spot set amidst Bramahagiri Hills near Madikeri in Coorg.
- The tributaries of the Kaveri include:
- Harangi, Hemavathi (origin in western Ghats joins the river Kaveri near Krishnarajasagar), Lakshmanatirtha, Kabini (originates in Kerala and flows eastward and joins the Kaveri at Tirumakudal, Narasipur), Shimsha, Arkavati, Suvarnavathi or Honnuholé, Bhavani, Lokapavani, Noyyal, Amaravati.
Cauvery Water Dispute:
- The dispute involves three states and one Union Territory (Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka and Puducherry).
- The dispute is almost 150 years old and dates to the two agreements of arbitration in 1892 and 1924between the then Madras presidency and Mysore.
- It entailed the principle that the upper riparian state must obtain consent of lower riparian state for any construction activity viz. reservoir on the river Cauvery.
- From 1974, Karnataka started diverting water into its four newly made reservoirs, without the consent of Tamil Nadu resulting in a dispute.
- To resolve the matter, the CWDT (Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal) was established in 1990, which took 17 years to arrive at the final order (2007) on how Cauvery water should be shared between the 4 riparian states in normal rainfall conditions.
- CWDT was constituted by the Central Government, in exercise of the powers conferred by section 4 of the Inter-State River Water Disputes Act, 1956.( Inter State River Water Dispute Act, 1956)
Water sharing mechanism: Final order of the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal
- In 2007, the three-member Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal delivered its final award on.
- While considering that the total availability of water the Cauvery basin spread across the 4 states is 740 TMC in a “normal year” the Tribunal has allocated the water as follows:
- Tamil Nadu: 419 TMC (which had demanded 512 TMC),
- Karnataka: 270 TMC (which had demanded 465 TMC),
- Kerala: 30 TMC, and
- Pondicherry: 7 TMC
- Besides allocating 726 TMC for the four states, the award reserves 10 TMC for environmental purposes and 4 TMC for inevitable outlets into the sea.
Impacts of the Issue:
- Agricultural Distress: Farmers in the Cauvery Basin heavily depend on the river’s water for irrigating their crops, particularly during the crucial sowing and growing stages. Fluctuations in water availability due to the dispute have resulted in the following consequences:
- Crop Failures: Inconsistent water supply has led to crop failures, reducing farmers’ incomes and pushing them into debt.
- Unpredictable Planning: Farmers find it challenging to plan their agricultural activities effectively due to uncertainty about water availability, affecting crop choices and cultivation practices.
- Economic Losses: Crop losses translate to economic losses for farmers, affecting their livelihoods and contributing to the cycle of poverty.
- Water Scarcity: Water scarcity is a significant outcome of the dispute, impacting various aspects of daily life and the environment:
- Drinking Water Shortages: Reduced water allocation affects the availability of clean and safe drinking water for both urban and rural populations.
- Hygiene and Health Issues: Water scarcity can lead to inadequate sanitation and hygiene practices, increasing the risk of waterborne diseases.
- Ecological Impact: Insufficient water flow in the river affects aquatic ecosystems, biodiversity, and the overall health of the river.
- Urbanization Challenges: Rapid urbanization in both states has increased water demand for domestic and industrial purposes, exacerbating water scarcity issues.
- Political Tensions: The Cauvery water dispute has had significant political implications and has often been a source of tension between Karnataka and Tamil Nadu:
- Interstate Relations: The dispute strains relations between the two states, affecting collaboration in other areas and hindering overall development.
- Public Outcry: The public often demands strong action from political leaders, putting pressure on them to adopt aggressive stances on the issue.
- Protests and Violence: The dispute has led to protests, rallies, and even violent incidents, which disrupt normal life and can lead to law and order problems.
- Legal Battles: The protracted legal battles over water sharing consume time, resources, and energy that could be otherwise invested in pursuits that are more productive.
The current issue:
- Karnataka would have to provide 0.86 TMC a day or 12.9 TMC totally in the 15 days.
- The Authority also decided that based on future rainfall; there would be a re-evaluation of the quantity to be released.
- However, what apparently irked Tamil Nadu was the refusal of Karnataka to abide by the quantity that was agreed upon at the meeting.
- According to data of the Meteorological Department, Kodagu received 44% less rainfall during June 1-August 15 than what it was expected to experience.
- Karnataka has contended that lower rainfall in the Cauvery catchment including in Kerala has led to the poor inflow to its own reservoirs.
Way forward:
The river should not be the possession of any one state. It is a common public trust. People are the owners and the state is merely a custodian but the states have become dogmatic about their custodianship. They have started using their rights as territorial rights.
With continued efforts from all stakeholders, it is possible to find a balanced and equitable solution that ensures the sustainable use of the Cauvery River’s water resources while addressing the needs of the riparian states.
Source: The Hindu
Must Read: Indus Water Treaty
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 3 (Science and Technology)
Context: According to the Lancet Planetary Journal, Air laden with unhealthy amounts of PM2.5 can become a highway for antibiotic-resistant bacteria and genes.
About Antimicrobials and Anti-microbial resistance:
- Antimicrobials – including antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals and antiparasitics – are medicines used to prevent and treat infections in humans, animals and plants.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites change over time and no longer respond to medicines making infections harder to treat and increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness and death.
- As a result of drug resistance, antibiotics and other antimicrobial medicines become ineffective and infections become increasingly difficult or impossible to treat.
Factors that accelerates the emergence and spread of AMR:

- AMR occurs naturally over time, usually through genetic changes. Antimicrobial resistant organisms are found in people, animals, food, plants and the environment (in water, soil and air).
- They can spread from person to person or between people and animals, including from food of animal origin.
- The main drivers of antimicrobial resistance include the misuse and overuse of antimicrobials; lack of access to clean water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) for both humans and animals; poor infection and disease prevention and control in health-care facilities and farms; poor access to quality, affordable medicines, vaccines and diagnostics; lack of awareness and knowledge; and lack of enforcement of legislation.
AMR in India
- Data show that India leads the world in antibiotic use.
- The indiscriminate use of antibiotics among people and animals, poor hygiene and sanitation, and lack of awareness have fueled this rise.
- The COVID-19 pandemic only exacerbated these issues, together with a surge in the sales of antibiotics to treat bronchitis and pneumonia.
- The higher circulation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and antibiotic-resistance genes (ARGs) across humans, animals, and environments also creates new transmission pathways.
- A 2019 study found India’s rivers and lakes to be concentrated with antimicrobial-resistant bacteria. Pharmaceutical wastewater and untreated effluents from hospitals were the root causes.
Particulate Matter (PM):
- Particulate matter (PM) are inhalable and respirable particles composed of sulphate, nitrates, ammonia, sodium chloride, black carbon, mineral dust and water.
- PM 2.5 refers to tiny particles or droplets in the air that are 2 ½ microns or less in width.
- Sources: The most common human-made sources include internal combustion engines, power generation, industrial processes, agricultural processes, construction, and residential wood and coal burning.
- The most common natural sources for PM2.5 are dust storms, sandstorms, and wildfires. (UPSC CSE: Air pollution)
Relation between PM and AMR
- The authors of the journal have found that every 10% rise in air pollution was correlated with an AMR increase of 1.1% across countries and continents.
- 5 emissions from burning firewood in homes for cooking or heating could carry bacteria and antibiotic-resistant genes, be transmitted over long distances, and eventually be inhaled by individuals.
- 5 is known to penetrate the body’s defences and enter the bloodstream and lungs – a symptom associated with chronic conditions such as cancer, heart disease, and asthma.
- The analysis found that the contribution of PM2.5 to AMR was found to be greater than that of antibiotic use or due to drinking water.
Issues
- Difficulty in treating infections: Microbial resistance to antibiotics has made it harder to treat infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis (TB), blood-poisoning (septicaemia) and several food-borne diseases.
- Rising health cost: AMR also imposes a huge health cost on the patient in the form of longer hospitalisation, health complications and delayed recovery.
- AMR adds to the burden of communicable diseases and strains the health systems of a country.
- Other patients also at risk: It puts patients undergoing major surgeries and treatments, such as chemotherapy, at a greater risk.
- Many times, patients recover from advanced medical procedures but succumb to untreatable infections.
- Antimicrobials in the agri-food system: There is also an urgent need to reduce the usage of antimicrobials in the agri-food system.
- Scientific evidence suggests that the less antimicrobials are used, it is less likely that there will be an emergence of drug resistance.
Measures Taken to Rising Antimicrobial Resistance in India:
- National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (NAP-AMR): It has a focus on the One Health approach and was launched with the aim of involving various stakeholders’ ministries/departments.
- AMR Surveillance Network: ICMR established the AMR surveillance and research network (AMRSN) to generate evidence and capture trends and patterns of drug resistant infections in the country.
- AMR Research and International Collaboration: ICMR has taken initiatives to develop new drugs /medicines through international collaborations in order to strengthen medical research in AMR.
- India’s National Action Plan for containment of AMR: It focuses on an integrated One Health approach and involves coordination at the state, national and international levels.
- Key priority of National Health Policy 2017: In its National Health Policy 2017, India has identified managing AMR as a key priority and since then the health ministry has taken several initiatives to nip the epidemic that is growing fast globally.
WHO Initiatives at the global level:
- Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (GAP)
- World Antimicrobial Awareness Week (WAAW)
- The Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS)
Source: DTE
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Missions to the Sun | Space Agency |
| 1.Aditya-L1 | ISRO |
| 2.Parker Solar Probe | NASA |
| 3.DSCOVR | NASA |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
PM Vishwakarma scheme is under the Ministry of Culture.
Statement-II:
Credit support of up to Rs.1 lakh (First Tranche) and Rs.2 lakh (Second Tranche) will be given under the scheme.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Shri Atal Bihari Vajpayee was Prime Minister of India thrice.
Statement-II:
He was also awarded Padma Vibhushan in 2002.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) What are the historical roots of the Cauvery water-sharing conflict between Karnataka and Tamil Nadu? How has this dispute affected agriculture, water scarcity, and political tensions in the region? How successfully has centre handled various inter-state river water dispute? Comment (250 words)
Q.2) Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) is a classic “tragedy of the commons”. Examine. Also, analyse the correlation between pollution and antibiotic resistance. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 17th August 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 16th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – c











