IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –ECONOMY
Context: Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs (IICA) recently, organized a workshop on Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR).
Background:-
- The Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs (IICA), organized a workshop on Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) in collaboration with UNICEF and the National Stock Exchange at the NSE premises in Mumbai on September 12, 2023.
- The workshop aimed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the BRSR framework, which is based on the nine principles of the National Guidelines for Responsible Business Conduct (NGRBC).
About Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR):-
- The BRSR framework is a mandatory disclosure mechanism for the top 1000 listed companies or businesses to report their performance on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) aspects.
- It demonstrates their commitment to responsible business practices.
- It will be applicable to the top 1000 listed entities (by market capitalization), for reporting on a voluntary basis for FY 2021 – 22 and on a mandatory basis from FY 2022 – 23.
- It includes:-
- Sustainability Reporting: disclosure and communication of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals.
- It is intended to have quantitative and standardized disclosures on ESG parameters to enable comparability across companies, sectors, and time.
- Environmental criteria: consider how a company performs as a steward of nature.
- Social criteria: examine how it manages relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities where it operates.
- Governance: deals with a company’s leadership, executive pay, audits, internal controls, and shareholder rights.
- The listed entities already preparing and disclosing sustainability reports based on internationally accepted frameworks (such as GRI, SASB, TCFD, or Integrated Reporting)
- Significance:-
- Such disclosures will be helpful for investors to make better investment decisions.
- It shall also enable companies to engage more meaningfully with their stakeholders, by encouraging them to look beyond financials and social and environmental impacts.
MUST READ: National Stock Exchange (NSE) and Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the investments in the following assets: (2023)
- Brand recognition
- Inventory
- Intellectual property
- Mailing list of clients
How many of the above are considered intangible investments?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements is correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps the Public Sector Banks in developing strategies and capital-raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –POLITY
Context: President Droupadi Murmu launched the Gujarat Assembly’s National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA) project recently.
About National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA) project:-
- National eVidhan Application (NeVA) is an online application.
- It is a Mission Mode Project (MMP) that comes under the Digital India Programme.
- Objective: to make all legislatures digital with the help of Information & Communication Technologies (ICT).
- Ministry: Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs (MoPA).
- It is the ‘Nodal Ministry’ for its implementation in all the 31 States/UTs with Legislatures.
- Funding: It is provided by the MoPA.
- The funding of NeVA is through Central Sponsored Schemee. 60:40; and 90:10 for North East & and hilly States and 100% for UTs.
- The technical support by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MietY).
- So far, 21 State Assemblies have signed Memorandums of Understanding to implement NeVA, and funding has been allocated for 17 of them.
- Nine legislatures have transitioned fully into digital Houses and actively operate on the NeVA platform.
- Himachal Pradesh was the first Digital Legislature of the country.
Significance:-
- NeVA epitomizes the concept of ‘One Nation, One Application’, with a mission to prioritize cloud-first and mobile-first approaches.
- It is to serve the Members of Legislative Assemblies more effectively.
- It enables automation of the entire law-making process, tracking of decisions and documents, and sharing of information.
- Through the cloud technology (Meghraj), data deployed can be accessed anywhere at any time.
- The live webcasting of Lok Sabha TV and Rajya Sabha TV is also available on this application.
MUST READ: Global Digital Governance
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centers within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places, and major tourist centers.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Regarding Digi Locker’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- It is a digital locker system offered by the Government under the Digital India Programme.
- It allows you to access your e-documents irrespective of your physical location.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: Recent studies have shown the positive role of probiotics in reducing Cholesterol.
Background:-
- Using probiotics to reduce cholesterol is an upcoming area of interest and the research is promising.
- Probiotics are thought to help lower cholesterol levels via a number of mechanisms.
- These include helping to incorporate cholesterol into cells and adjusting the microbiome of the gut to favor the elimination of cholesterol via the faeces.
- In a 2018 study, researchers pooled results from 32 studies and analyzed them all together in a type of study known as a meta-analysis.
- The people who took probiotics reduced their total cholesterol level by 13 percent.
- Other systematic reviews support these findings. (Indian scientists develop a next-generation probiotic)
About Probiotics:-
- Probiotics are a combination of live beneficial bacteria and/or yeasts.
- Probiotic supplements are a way to add good bacteria to our body.
- A probiotic community is made up of things called Microbes.
- We have trillions of microbes on and in our body.
- These microbes are a combination of:
- Bacteria.
- Fungi (including yeasts).
- Viruses.
- Protozoa.
- Everyone’s microbiome is unique.
- No two people have the same microbial cells.
- Even twins are different.
- The most common type of probiotic bacteria is Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium.
- Probiotics are also made up of good yeast.
- The most common type of yeast found in probiotics is Saccharomyces boulardii.
Working mechanism:-
- We constantly have both good and bad bacteria in our body. (iNCOVACC)
- When we get an infection, there are more bad bacteria, knocking your system out of balance.
- Good bacteria help eliminate extra bad bacteria, returning the balance
Characteristics of a probiotic:-
For a microbe to be called a probiotic, it must have several characteristics. These include being able to:
- Be isolated from a human.
- Survive in your intestine after ingestion (being eaten).
- Have a proven benefit.
- Be safely consumed.
- Help your body digest food.
- Keep bad bacteria from getting out of control and making you sick.
- Create vitamins.
- Help support the cells that line your gut to prevent bad bacteria that you may have consumed (through food or drinks) from entering your blood.
- Break down and absorb medications.
Probiotic-rich foods:-
- Yogurt.
- Buttermilk.
- Sourdough bread.
- Cottage cheese.
- Kombucha.
- Tempeh.
- Fermented pickles.
MUST READ: National Institute of Biologicals (NIB)
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Serum Institute of India produced a COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using an mRNA platform.
- The Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using a vector-based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen-based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements in respect of probiotics: (2022)
- Probiotics are made of both bacteria and yeast.
- The organisms in probiotics are found in foods we ingest but they do not naturally occur in our gut.
- Probiotics help in the digestion of milk sugars.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –ECONOMY
Context: The Income Tax Appellate Tribunal has recently ordered Cognizant Technology Solutions, to pay dividend distribution tax (DDT) on Rs 19,080-crore share buyback in the assessment year 2017-18
Background:-
- During the assessment year 2017-18, Cognizant bought 94,00,534 equity shares from its shareholders in the US and Mauritius at Rs 20,297 per share, totaling Rs 19,080 crore.
About Dividend distribution tax (DDT):-
- DDT was a tax imposed by the Indian government on companies distributing dividends to shareholders.
- Objective: taxing dividend income indirectly through the company.
- However, it was repealed and abolished for Indian corporations in the Finance Act 2020.
- Now, shareholders are taxed on dividends based on their individual tax brackets.
- Dividend: a return given by a company to its shareholders from its annual profits.
Salient features:-
- It was a tax levied on dividends that a company pays to its shareholders out of its profits.
- DDT was taxable at source. (Bond Yields)
- It is deducted at the time the company distributes dividends.
- All local and international businesses operating in India were to comply with the DDT.
- However, the tax rate varied based on the tax treaty between India and the foreign company’s home country.
- Significance: This tax was designed to ensure the government gets a fair part of the company’s revenues.
MUST READ: Increase in Direct Tax Collections
SOURCE: THE NEW INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the Indian economy, what are the advantages of “Inflation-Indexed Bonds (IIBs)”? (2022)
- Government can reduce the coupon rates on its borrowing by way of IIBs.
- IIGs provide protection to the investors from uncertainty regarding inflation.
- The interest received as well as capital gains on IIBs are not taxable.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) In India, which one of the following is responsible for maintaining price stability by controlling inflation? (2022)
- Department of Consumer Affairs
- Expenditure Management Commission
- Financial Stability and Development Council
- Reserve Bank of India
Syllabus
- Prelims –GOVERNANCE
Context: Recently, the centre approved the expansion of PM Ujjwala Yojana.
Background:-
- Addressing media after the Union Cabinet meeting, Information and Broadcasting Minister Anurag Singh Thakur said in New Delhi that under it, a total of 75 lakh LPG connections over three years from Financial Year 2023-24 to 2025-26 will be released.
- So far 9.60 crore LPG cylinders have been distributed under the Ujjwala scheme and another 75 lakh free LPG connections will be given to women from poor and needful families so that they can avail of the benefits from the scheme.
About PM Ujjwala Yojana:-

IMAGE SOURCE: AIR
- Launched: May 2016.
- Ministry: Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas.
- Objective: to make clean cooking fuel such as LPG available to the rural and deprived households that were otherwise using traditional cooking fuels such as firewood, coal, cow-dung cakes, etc. Pradhan MantriUjjwalaYojana (PMUY) – Diversion of LPG
- Significance: It will help achieve the Prime Minister’s vision of universal access to LPG.
Salient Features:-
- Ujjwala 1.0 had a target to provide deposit-free LPG connections to 5 crore women members of BPL households.
- The scheme was expanded in April 2018 to include women beneficiaries from seven more categories (SC/ST, PMAY, AAY, most backward classes, tea garden, forest dwellers, etc.).
- EMI facilities were given for stove and refill costs (Interest-free loan).
Ujjwala 2.0:-
- The Union budget for FY 21-22, announced the provision for an additional one crore LPG connection under the PMUY scheme.
- Additional allocation of 1.6 Crore LPG Connections under the PMUY Scheme with a special facility to migrant households.
- It will provide a deposit-free LPG connection. (UJJWALA 2.0)
- It will also give the first refill and hotplate (stove) free of cost to the beneficiaries.
- The migrants will not be required to submit ration cards or address proof.
- A self-declaration for both a ‘family declaration’ and a ‘proof of address’ will suffice.
MUST READ: Special Discussion on Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in relation to Janani Suraksha Yojana : (2023)
- It is a safe motherhood intervention of the State Health Departments.
- Its objective is to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality among poor pregnant women.
- It aims to promote institutional delivery among poor pregnant women.
- Its objective includes providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017? (2019)
- Pregnant women are entitled to three months of pre-delivery and three months of post-delivery paid leave.
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother a minimum of six creche visits daily.
- Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: Recently, Engineers’ Day 2023 was celebrated.
Background:-
- It was celebrated on September 15.
- Engineer’s Day is also celebrated in Sri Lanka and Tanzania on September 15.
About Engineers’ Day 2023:-
- The day is celebrated to recognize the contributions made by M Visvesvaraya in the field of science and technology.
- Born:1861.
- M Visvesvaraya was born in a Telugu family at Chikkaballapur near Bengaluru, Karnataka.
- He was known as the father of Modern Mysore. His full name is Mokshagundam Visvesvaraya.
- After completing his formal school education in his hometown, Visvesvaraya went to study BA at the University of Madras.
- However, he later switched and pursued a diploma in civil engineering at the College of Science in Pune.
- He was a pro in flood disaster management and irrigation techniques.
- He was recognized for his work in irrigation techniques and flood control.
- He was Diwan of Mysore from 1912 to 1918.
Contributions:
- He was the chief engineer responsible for the construction of the Krishna Raja Sagara Dam in Mysore.
- He designed and patented automatic water floodgates in 1903, which were first installed at the Khadakwasla reservoir in Pune.
- In 1917, Visvesvaraya established the Government Engineering College in Bengaluru, which was later named University Visvesvaraya College of Engineering in his honour.
- He founded the Bangalore Agricultural University.
- He was a renowned precursor of economic planning in India.
Awards:
- In 1955, the Government of India honoured him with the highest civilian honour — Bharat Ratna for his numerous industrial, economic and social projects.
- He was also conferred the British knighthood by King George V, earning the title “Sir.”
MUST READ: Satyendra Nath Bose
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? (2023)
- Australia
- Canada
- Israel
- Japan
Q.2) With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements : (2018)
- IRNSS has three satellites in geostationary and four satellites in geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers the entire India and about 5500 sq. km beyond its borders.
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
Context: Recent studies show that Lead exposure led to 30% of global cardiovascular deaths in 2019.
Background:-
- Exposure to lead accounted for 30 percent of all cardiovascular disease deaths globally in 2019, meaning about 5.5 million people, according to a study recently published in The Lancet Planetary Health journal.
- The researchers used blood lead levels as an indicator to estimate the global heavy metal exposure from 2019.
Key Highlights of reports:-
- Global lead exposure has health and economic costs on par with fine particulate matter5 (PM2.5) air pollution.
- Lead exposure affects poorer countries disproportionately.
- Despite the phase-out of leaded petrol, About 95 percent of the health impacts were observed in people living in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC).
- Deaths from cardiovascular disease were six times higher in LMICs.
- The average blood lead level in LMICs was 4.6 microgrammes per decilitre (μg/dL), compared with 1.3 μg/dL in high-income countries.
- The exposure to the heavy metal also led to the loss of 765 million intelligence quotient (IQ) points in children under the age of five.
- IQ loss in LMICs due to lead exposure was nearly 80 percent higher than a previous estimate — children in these countries lost an average of 5.9 IQ points.
- In 2019, cardiovascular disease accounted for 94 percent of mortality.
- In 2019, lead exposure led to global losses worth $6 trillion, or seven percent of the global gross domestic product (GDP).
- The number was as high as 10 percent of the GDP for LMICs in the same year.
- Other than cardiovascular disease, exposure to the metal can also lead to chronic kidney disease and idiopathic developmental intellectual disability — meaning damage to the brain and lowering brain development.
- Countries with the highest burden: Iran, Afghanistan, Yemen, Peru, Vietnam, the Philippines, and parts of Central Africa.
Other reports:-
- Around one in three children worldwide record blood lead levels of over five μg/dL (the tolerable limit set by the World Health Organization), according to a 2020 report by the United Nations Children’s Fund and Pure Earth, a US-based environmental health non-profit.
Lead:-
- Lead is a naturally occurring toxic metal.
- It is found in the Earth’s crust.
- In the body lead is distributed to the brain, liver, kidney, and bones.
- It is stored in the teeth and bones, where it accumulates over time.
- Human exposure is usually assessed through the measurement of lead in blood.
- Lead in bone is released into the blood during pregnancy and becomes a source of exposure to the developing foetus.
- There is no level of exposure to lead that is known to be without harmful effects.
- Lead exposure is Preventable.
- Lead is one of 10 chemicals of major public health concern by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- WHO has joined with the United Nations Environment Programme to form the Global Alliance to Eliminate Lead Paint.
Effect of Lead in the human body:-
- Once lead enters the bloodstream, it goes directly to the brain, particularly in children.
- Because there is no specific blood-brain barrier for lead that can restrict movement of the metal.
MUST READ: Lead Poisoning in India
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Bisphenol A (BPA), a cause of concern, is a structural/key component in the manufacture of which of the following kinds of plastics? (2021)
- Low-density polyethylene
- Polycarbonate
- Polyethylene terephthalate
- Polyvinyl Chloride
Q.2) Lead, ingested or inhaled, is a health hazard. After the addition of lead to petrol has been banned, what still are the sources of lead poisoning? (2012)
- Smelting units
- Pens and pencils
- Paints
- Hair oils and cosmetics
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Gender Responsive Budgeting
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently UNICEF India representative Cynthia McCaffrey has said the country is being looked upon as a leader in child and gender-responsive budgeting, especially in South Asia.
About Gender Responsive Budgeting (GRB):
- Gender budgeting is a fiscal strategy to achieve equality between women and men by focusing on how public resources are collected and spent.
- Gender Responsive Budgeting initiatives can help to close the gender gaps, ensuring that public money is raised and spent more effectively.
India’s Gender Responsive Budgeting:
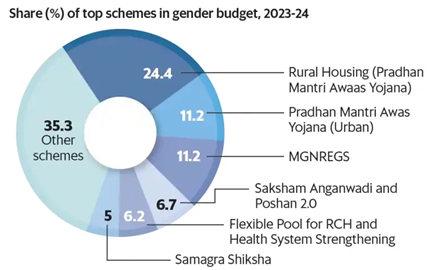
- GRB began in India in 2005-2006 as a fiscal innovation, every year since then the Ministry of Finance has been publishing “Gender Budget Statements” along with the Union Budget.
- In 2010, the Planning Commission clarified that in place of the Women Component Plan, the Ministry of Finance and MoWCD should adopt Gender Responsive Budgeting or Gender Budgeting only.
- The ‘Gender Budgeting Handbook, 2015’ released by the Ministry of Women and Child Development notes that Gender Budgeting is a tool for gender mainstreaming.
- In the 2023-24 Union budget, the Finance Minister emphasised ‘Nari-Shakti’ (woman power) and shifted the focus from women’s development to women-led development.
Significance of Gender Responsive Budgeting:
- Achievement gender equity and equality: The Constitution of India not only grants equality to women, but also empowers the State to adopt measures of positive discrimination in favour of women.
- Improving Literacy: The Government has been successfully running the Vidhya shakti program with focus on female literacy.
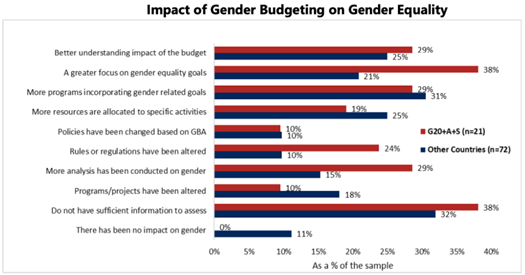
- Monitoring The Achievement Of Policy Goals: GRB is a tool to monitor the achievement of the goals of the National Policy for Empowerment of Women 2001 and other policy goals.
- Economic Growth: Ensures allocation of resources to address specific needs and challenges faced by women and girls.
- The Bharatiya Mahila Bank Ltd, first of its kind in the banking industry in India and the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana besides promoting financial inclusion are emerging as a catalyst for gender justice and equality.
Challenges need to be tackled:
- Political representation: Women comprise only 14.44 % of the 545 members of the 17th Lok Sabha.
- Education: According to the World Bank India report, while male literacy rate in the country is at 84.7 percent, for females, it is 77 percent.
- Economic Opportunities: According to the Periodic Labour Force Survey 2021-22, only 32.8 percent of women between 15-29 years were part of India’s labour force in 2021-2022, while men were at 77.2 percent.
- Low budgetary allocation: Despite having been in operation for almost two decades, budgetary expenditure on it remains a mere 4-5 percent of the total allocation in Union Budget 2023-24.
- Skewed Implementation: NITI Aayog paper on Gender Mainstreaming (June 2022) has noted that only 62 out of 119 centrally-sponsored schemes are practising GB.
- The paper noted that the record of Ministers associated with Environment and Climate Change, Urban Transformation, Skill etc. have done poorly.
- Quality gender disaggregated data: The government agencies who do not capture gender-disaggregated information from their schemes and programmes may not be able to assess the targeted expenditure towards the empowerment of women and girls.
Government Initiatives toward Gender Responsive Budgeting:
- Safe City Project: To ensure the safety of women by strengthening public resources.
- Samarthya Scheme: Launched by clubbing existing women’s empowerment programmes such as the Pradhan Mantri Vandana Yojana and Swadhar Greh etc.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS)
- Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana
- Saksham Anganwadi scheme and POSHAN 2.0
- Swachh Bharat Mission
- Beti Bachao, Beti Padao
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)
Way Forward:
Gender Responsive Budgeting (GRB) in India has made strides in promoting gender equality through government initiatives and budget allocations. However, challenges like disparities in education, economic opportunities, and political representation needs to be addressed as a top priority. By doing so, India can achieve Beijing Declaration’s principles and address deeper socio-economic issues beyond fiscal measures.
Source: Business Standard
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The new Post Office Bill (2023) recently introduced in the Rajya Sabha seeks to replace the Indian Post Office Act (1898) in the light of the changing role of post offices.
Key features of the bill:
- Exclusive privileges of the central government: The Act provides that wherever the central government establishes posts, it will have the exclusive privilege of conveying letters by post, as well as incidental services such as receiving, collecting, sending, and delivering letters.
- Services to be prescribed: The Act specifies the services provided by the Post Office to include:
- The delivery of postal articles including letters, postcards, and parcels, and money orders.
- The Bill provides that the Post Office will provide services prescribed by the central government.
- Powers to intercept shipments: The Act allows for the interception of a shipment being transmitted through the post on certain grounds.
- An interception may be carried out on the occurrence of any public emergency, or in the interest of public safety or tranquillity.
- Such interceptions may be carried out by the central government, state governments, or any officer specially authorised by them.
- Director General to make regulations regarding services: The Act, as well as the Bill, provides for the appointment of the Director General of Postal Services.
- Under the Act, the Director General has powers to decide the time and manner of delivery of postal services.
- Under the Act, the central government can notify charges for postal services through notifications.
- Examination of shipment prohibited under law or liable for duty: Under the Act, an officer in charge of the Post Office may examine a shipment if he suspects that it contains goods which are prohibited, or are liable to be paid duty upon.
- The officer must send a notice to the addressee inviting him to attend the examination in person or by agent.
- The Director General may direct the presence of two witnesses in the absence of the addressee.
- The Bill removes the powers of examination instead provides that in such cases, the central government may empower an officer of the Post Office to deliver the shipment to the customs authority or any other specified authority. The authority will then deal with the item in question.
- Removal of offences and penalties: The Act specifies various offences and penalties. For instance, theft, misappropriation or destruction of postal articles by an officer of the Post Office is punishable with imprisonment up to seven years and a fine.
- Sending certain prohibited items through post is punishable with imprisonment up to one year, a fine, or both.
- The Bill does not provide for any offences or consequences, except one.
- Exemptions from liability: The Act exempts the government from any liability related to the loss, mis delivery, delay or damage to a postal article.
- This does not apply where the liability is undertaken by the central government in express terms.
- Officers are also exempt from such liability unless they have acted fraudulently or wilfully.
- However, it provides that instead of the central government, the Post Office may prescribe the liability regarding its services.
Significance of the bill:
- Authority: While the 1898 Act had focused only on mail services, the new post office Bill authorized the Director General of Postal Services to make regulations related to activities necessary for providing various such other services as the central government may prescribe, and to fix charges of them.
- Revision of Charges: This provision is important as parliamentary approval will not be a prerequisite for revision of charges for any service offered by post offices, including traditional mail services.
Challenges associated with the new Post Office Bill (2023):
- Differing Legislation: There is no similar legislation for courier firms.
- High Control of the Government: The provision to intercept and open parcels in the course of transmission by the couriers would have given teeth to the Bill to control the movement of contraband goods in parcels.
Way Forward:
The bills brings welcome flexibility and modernization to India’s postal services. The Bill represents a positive step towards modernizing India’s postal services and adapting to contemporary communication needs challenges like differing legislation for courier firms remain. It balances the need for security with the demands of a competitive market.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Disease | Pathogen |
| 1.Anthrax | Bacillus anthracis |
| 2.Whooping cough | Clostridium tetani |
| 3.Tetanus | Bordetella pertussis |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
The National eVidhan Application (NeVA) is to serve the Members of Legislative Assemblies more effectively.
Statement-II:
Telangana was the first Digital Legislature in the country.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) With reference to the Probiotics, consider the following statements:
- Buttermilk is a Probiotic-rich food.
- Probiotics create vitamins.
- Probiotics never contain yeast.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) Discuss the key changes adopted in the New Post Office Bill 2023 to replace the Indian Post Office Act (1898). (250 words)
Q.2) What is gender budgeting? How it can help in women empowerment in India? (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 16th September 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 15th September – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – b











