IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and technology
Context: Recently, India’s first cloned desi Gir female calf, Ganga was produced at NDRI.
About Gir calf and breed:-
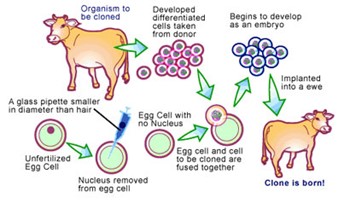
IMAGE SOURCE: THE NEW MACDONALD PHARM | SCQ (ubc.ca)
- This breed is otherwise known as Desan, Gujarati, Kathiawari, Sorthi, and Surati.
- It originated in the Gir forests of South Kathiawar in Gujarat.
- It derives its name from the Gir forest, which is the natural habitat of the breed.
- Gir cattle is a dairy cattle breed and is mainly raised for milk production in India.
- Under a project by National Dairy Research Institute, Karnal to work on cloning of indigenous cow breeds such as Gir and Sahiwal, India’s first cloned Gir female calf named ‘Ganga’.
Distribution:-
- The native tract of Gir cattle is the Gir hills and forests of Kathiawar.
- It includes the Amreli, Bhavnagar, Junagadh and Rajkot districts of Gujarat.
- The breed is also known as Bhodali, Gujarati, Sorthi, Surti, Kathiawari and Desan.
Export:-
- Gir cattle are also very popular outside India.
- United States, Mexico, Venezuela and Brazil have imported this breed.
Process:-
-
- To clone the Gir, oocytes are isolated from live animals using ultrasound-guided needles, and then, matured for 24 hours under control conditions.
- The somatic cells of elite cows are used as donor genomes, which are fused with OPU-derived enucleated oocytes.
- Following chemical activation and in-vitro culture, the developed blastocysts are transferred into recipient mothers to deliver the Gir calf.
About National Dairy Research Institute (NDRI):-
- ICAR-National Dairy Research Institute (NDRI) is located in Karnal, Haryana.
- It is one of the premier Institutes in the dairy sector.
- It has played a crucial role in India’s development in milk production with its continuous research.
- The Institute has the distinction of being a Deemed University for implementing its academic programmes since 1989.
- The Institute provides high-quality education in the field of dairying, which has no parallel in Asia
- The Institute has been ranked first among all Agricultural Universities of India including 4 Deemed Universities consecutively three times in the years 2016-17, 2017-18 and 2018-19.
- The Institute has also conferred the ‘Sardar Patel Outstanding ICAR Institute award’ in 2014.
- It was awarded Agriculture Leadership Award 2013 for setting up a benchmark in dairy research by contributing to research efforts to augment milk productivity, value addition, quality and safety of milk and economic and marketing aspects related to dairying.
- Prior to this, the Institute also received Education Leadership Award in recognition of the talent and leadership among educational institutes across India.
MUST READ: New Breeds of Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)
SOURCE: THE ECONOMIC TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2020)
- Genetic changes can be introduced in the cells that produce eggs or sperm of a prospective parent.
- A person’s genome can be edited before birth at the early embryonic stage.
- Human-induced pluripotent stem cells can be injected into the embryo of a pig.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) In the context of recent advances in human reproductive technology, ‘Pronuclear Transfer” is used for (2020)
- Fertilization of egg in vitro by the donor sperm
- Genetic modification of sperm-producing cells
- Development of stem cells into functional embryos
- Prevention of mitochondrial diseases in offspring
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy (Important Institutions)
Context: Recently, the Delhi HC restrained the Institute of Cost Accountants of India from using the ICAI acronym.
About the Institute of Cost Accountants of India:-
- It was first established in 1944 as a registered company under the Companies Act.
- Objectives: the objects of promoting, regulating and developing the profession of Cost Accountancy.
- In May 1959, the Institute was established by a special act of Parliament, namely, the Cost and Works Accountants Act, 1959 as a statutory professional body.
- The Institute of Cost Accountants of India is the only recognised statutory professional organisation and licensing body in India specialising exclusively in Cost and Management Accountancy.
- Cost Accountant: a person who offers to perform or perform services involving the costing or pricing of goods and services or the preparation, verification or certification of cost accounting and related statements.
- The head office is situated in Kolkata.
Objectives of the Institute:-
- To develop the Cost and Management Accountancy function as a powerful tool of management control in all spheres of economic activities.
- To promote and develop the adoption of scientific methods in cost and management accountancy.
- To develop the professional body of members.
- To keep abreast of the latest developments in cost and management accounting principles
- To exercise supervision for the entrants to the profession
- To ensure strict adherence to the best ethical standards by professionals.
- To organise seminars and conferences on subjects of professional interest.
- To carry out research and publication activities covering various economic spheres.
- Publishing of books and booklets for spreading information of professional interest.
MUST READ: Comptroller and Auditor-General of India (CAG) and Financial Services Institutions Bureau (FSIB)
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements is correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps Public Sector Banks develop strategies and capital-raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, Britain agreed to join the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP).
About the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP):-
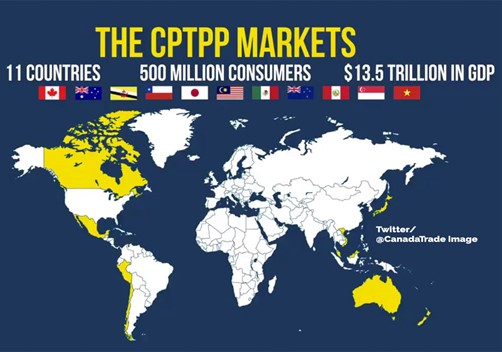
IMAGE SOURCE: The Trade File – Cosmetics Alliance Canada
- CPTPP is a free trade agreement (FTA) that was agreed upon in 2018 between 11 countries.
- These include Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore and Vietnam.
- It does not have a single market for goods or services, unlike the European Union.
- The CPTPP incorporates, by reference, the provisions of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) agreement, with the exception of a number of provisions pertaining mainly to intellectual property and investor-state dispute settlement, whose application will be suspended once the CPTPP comes into force.
- Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) agreement :
- It was originally concluded by 12 countries.
- These include Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore, the United States and Vietnam.
- It was signed in 2016, by all 12 parties.
- In January 2017, the United States notified TPP signatories of its intention to not ratify the TPP, effectively withdrawing from the TPP.
Significance:-
- CPTPP is helping to create jobs and strengthen economic relations.
- It is an ambitious and high-standard free trade agreement covering virtually all aspects of trade and investment.
- The agreement features ambitious market-access commitments in trade in goods, services, investment, labour mobility and government procurement.
- The agreement also establishes clear rules that help create a consistent, transparent and fair environment.
- It covers virtually all sectors and aspects of trade in order to eliminate or reduce barriers.
MUST READ: Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Trade-Related Investment Measures (TRIMS), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2020)
- Quantitative restrictions on imports by foreign investors are prohibited.
- They apply to investment measures related to trade in both goods and services.
- They are not concerned with the regulation of foreign investment.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known (2020)
- G20
- ASEAN
- SCO
- SAARC
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and technology
Context: Recently, IACS’s novel compound was found to be treating drug-resistant kala-azar infections.
About Kala-azar:-
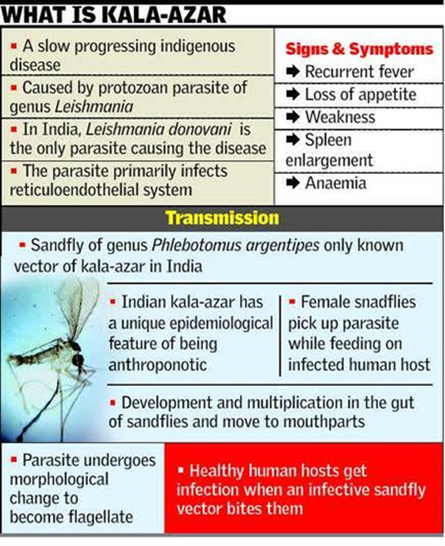
IMAGE SOURCE: Kala-Azar: Oral Nano Medicine (10pointer.com)
- It is caused by the protozoa parasite Leishmania.
- It is one of the three conditions in the disease group called leishmaniasis.
- It is a Neglected Tropical Disease.
- It is the second-largest parasitic killer in the world after Malaria.
- It is a zoonotic infection transmitted by the sand fly, a blood-sucking pest, found in moist (humid) mud and sand and close to livestock.
- The parasite is transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected female phlebotomine sandfly.
- This type of leishmaniasis affects the internal organs, usually the spleen, liver and bone marrow.
- The parasite primarily infects the reticuloendothelial system and may be found in abundance in bone marrow, spleen and liver.
Symptoms:-
- Some people have no symptoms.
- For others, symptoms may include fever, weight loss and swelling of the spleen or liver.
Treatment:-
- Medication exists to kill the parasites.
- If left untreated, severe cases are typically fatal.
- Up to 20% of the patients who are correctly treated and cured, develop a skin condition called Post-Kala-Azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL) which surfaces within months to years after treatment.
- These patients can contain large amounts of parasites in their skin lesions, making them an important source of transmission.
Initiatives of governments of India to Eliminate this Disease:-
- Development of a plan for the “unreached poorest” or underprivileged sections in endemic areas.
- Leveraging of Kala-azar elimination programme within POSHAN Abhiyaan for maximum benefit at the community level.
- Exploration of the opportunity of providing improved housing under the flagship program of the Prime Minister Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G), along with rural electrification, testing, treatment and periodic high-level review, incentivising through award distribution.
- Exploration of the opportunity of providing improved housing under State Schemes.
- Involvement of Rural Health Practitioners (RHPs).
- Coordination with the rural development department and engage with Panchayati Raj functionaries for awareness, community engagement, environment management and social empowerment.
- Supporting the states in active case detection, surveillance, and treatment as well as supply of diagnostic kits, medicines, and sprays.
MUST READ: Marburg Viral Disease Outbreak
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following are the reasons for the occurrence of multi-drug resistance in microbial pathogens in India? (2017)
- Genetic predisposition of some people.
- Taking incorrect doses of antibiotics to cure diseases.
- Using antibiotics in livestock farming.
- Multiple chronic diseases in some people.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and
- 2 and 3 only
- 1,3 and 4
- 2,3 and 4
Q.2) Which of the following statements is not correct? (2017)
- Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV
- Hepatitis B, unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine.
- Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses is several times more than those infected with HIV.
- Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, the Eravikulam National Park got a terrarium inside its premises.
About Eravikulam National Park:-
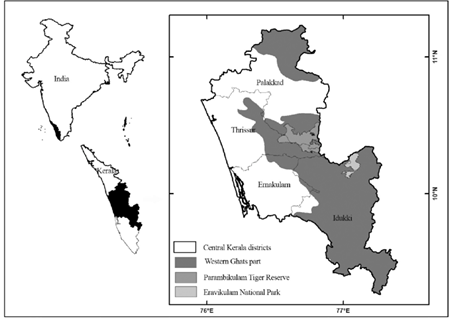
IMAGE SOURCES: Map showing the situation of Eravikulam National Park and Parambikulam… | Download Scientific Diagram (researchgate.net)
- It is located in the Eravikulam and Idukki districts of Kerala
- It is located in the High Ranges (Kannan Devan Hills).
- It hosts South India’s highest peak, Anamudi.
- It is famous for Nilgiri Tahr.
- Another speciality of Eravikulam national park is the Neelakurinji flower that blooms every 12 years.
- In 1975 the government declared the region as Eravikulam Wildlife Sanctuary.
- In 1978 the region was declared a National park.
- Vegetation: Grasslands, Shrub Land, and Shola Forests are the three major plant species present.
- It serves as a catchment area for both east-flowing rivers (tributaries of the Pambar) and west-flowing rivers (tributaries of the Periyar and Chalakkudy).
- Fauna: Lion-tailed macaques, Indian muntjac, gaur and sambar deer are the other animals found in the national park.
- Flora: The Park contains three major types of plant communities namely grasslands, shrublands, and woods.
About Ferns:-
- A fern is a member of a group of vascular plants.
- Vascular plants: plants with xylem and phloem.
- They reproduce via spores.
- They have neither seeds nor flowers.
- They have specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients and in having life cycles in which the sporophyte is the dominant phase.
- They have complex leaves called megaphylls.
Significance:-
- They are used for food, medicine, and as biofertilizers.
- They are used as ornamental plants and for remediating contaminated soil.
- They have been the subject of research for their ability to remove some chemical pollutants from the atmosphere.
- Some fern species, such as bracken (Pteridiumaquilinum) and water fern (Azollafiliculoides) are significant weeds worldwide.
- Some fern genera, such as Azolla, can fix nitrogen and make a significant input to the nitrogen nutrition of rice paddies.
- They also play certain roles in folklore.
MUST READ: Silent Valley National Park
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following are nitrogen-fixing plants? (2022)
- Alfalfa
- Amaranth
- Chickpea
- Clover
- Purslane (Kulfa)
- Spinach
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3, 5 and 6 only
- 2, 4, 5 and 6 only
- 1, 2, 4, 5 and 6
Q.2) Which of the following Protected Areas are located in the Cauvery basin? (2020)
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, the defence ministry signed a ₹3,000-crore contract with NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) for the GSAT-7B satellite.
About GSAT-7B satellite:-
- It is a communication satellite.
- It is a part of the GSAT-7 series.
- It is the first-ever in the five-tonne category that will be designed indigenously by the ISRO.
- GSAT 7 series satellites are advanced communication satellites developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to meet the communication needs of the defence services.
- The GSAT 7B will primarily fulfil the communication needs of the Indian Army.
- It is a geostationary satellite.
- It will considerably enhance the communication capability of the Indian Army.
MUST READ: OneWeb Satellites
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-stage launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors, and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct.?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
Q.2) With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements : (2018)
- IRNSS has three satellites in geostationary and four satellites in geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers the entire India and about 5500 sq. km beyond its borders.
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Recently, the Minister of State for Civil Aviation Gen.V K Singh talked about the Krishi Udan Scheme in the Rajya Sabha.
About Krishi UDAN Scheme:-
- It was launched in August 2020, on international and national routes.
- Objective: to assist farmers in transporting agricultural products so that it improves their value realisation.
- The scheme aims to ensure seamless, cost-effective, time-bound air transportation and associated logistics for all Agri-produce originating especially from Northeast, hilly and tribal regions of the country.
- It is a convergence scheme.
- It includes eight Ministries/Departments.
- These are namely the Ministry of Civil Aviation, Department of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare, Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying, Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Food Processing Industries, Department of Commerce, Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Ministry of Development of North-Eastern Region would leverage their existing schemes to strengthen the logistics for transportation of Agri-produce.
- There is no specific budget allocation under Krishi Udan Scheme.
- Implementing Agency:-
- The enhanced version of the Krishi UDAN scheme was formulated with support from AAI Cargo Logistics and Allied Services Company Limited (AAICLAS) –
- AAI Cargo Logistics and Allied Services Company Limited (AAICLAS): a 100% subsidiary of the Airports Authority of India and Invest India, India’s national Investment Promotion & Facilitation Agency
- It is under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry
MUST READ: Krishi UDAN 2.0 and Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY)
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to organic farming in India, consider the following statements: (2018)
- ‘The National ‘Programme for Organic Production’ (NPOP) is operated under the guidelines and ‘directions of the Union Ministry of Rural Development.
- ‘The Agricultural and Processed Food Product Export Development Authority ‘(APEDA) functions as the Secretariat for the implementation of NPOP.
- Sikkim has become India’s first fully organic State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements: The nationwide ‘Soil Health Card Scheme’ aims at (2017)
- expanding the cultivable area under irrigation.
- enabling the banks to assess the quantum of loans to be granted to farmers on the basis of soil quality.
- checking the overuse of fertilizers in farmlands.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently, the Women and Child Development Ministry informed the Parliament on the contribution of the MGNREGA scheme to the building of Anganwadi centres.
About Anganwadi Centres:
- Anganwadi is a centrally sponsored scheme implemented by the States / UTs which serves as a rural child and maternal care centre in India.
- It was started by the Government of India In 1975 as part of the Integrated Child Development Services program to combat child hunger and malnutrition.
- Anganwadi centres provide a package of six services: supplementary nutrition, pre-school non-formal education, immunisation, health check-up, nutrition and health education, and referral services.
- The beneficiaries under the Anganwadi Services Scheme are identified on the basis of Aadhaar.
Significance of Anganwadi scheme:
- Affordable and accessible healthcare: Today in India, about 2 million Anganwadis workers are reaching out to a population of 70 million women, children and sick people, helping them become and stay healthy.
- Anganwadi workers are the most important and soft-ignored essential link of Indian healthcare.
- Eradicating Malnourishment: One-third of the world’s stunted children live in India. Anganwadis are integral for the success of ICDS programme that caters to the nutrition, health and pre-education needs of children till six years of age as well as the health and nutrition of women and adolescent girls.
- Local Connect & Community Mobilisation: Anganwadi workers have the advantage over the physicians living in the same rural area, which gives them insight into the state of health in the locality and assists in identifying the cause of problems and in countering them.
- Ensuring Access to Government Programmes: Anganwadi workers are India’s primary tool against the menace of child malnourishment, infant mortality, and lack of child education, community health problems and in curbing preventable diseases.
- These community health workers have been point-persons for rural communities to access key health services and benefits.
- Health Crisis Management: With little training and immense risk, they went to households to spread awareness on COVID-19 as well as carry out tasks like contract tracing.
Challenges Faced by Anganwadis:
- Lack of Skill Set:-Despite being the major source of nutrition advice, Anganwadis staff may be lacking in technical skills.
- Knowledge of critical health behaviours such as complementary feeding and handwashing was poor among mothers listed as Anganwadis workers.
- Lack of Resources: Anganwadi personnel frequently lack the resources or training necessary to deliver ECCE.
- Lack of Time: Administrative obligations consume a large amount of time, and fundamental services such as pre-school education suffer as a result.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Infrastructure is frequently lacking in Anganwadis.
- According to NITI Aayog, only 59% of Anganwadis had enough seating for children and employees, and more than half were unsanitary.
- Issues in Urban Areas: According to NFHS-4 statistics, the use of early childcare services at Anganwadis in urban regions is just 28 percent, compared to 42 percent in rural areas.
Govt measures taken for Strengthening of Anganwadis:
- Convergence with MNREGA : the government has taken up Construction of 4 lakh AWC buildings across the country under Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) in convergence with Anganwadi Services (ICDS Scheme).
- Mobile Phones: Anganwadi Workers (AWWs) have been provided with Smart Phones for efficient service delivery.
- Streamlined guidelines were issued covering several aspects such as quality assurance, roles and responsibilities of duty holders, procedure for procurement, integrating AYUSH concepts and Data management
- Increased Training: the Ministry has formulated a comprehensive training strategy for the functionaries of Anganwadi Services.
- Training is imparted to the functionaries on a regular basis. Anganwadi Workers are provided job training for 26 working days.
- During this job training, the knowledge, understanding and skills of Anganwadi Workers on various Acts, Policies, Programmes related to women and children, setting up vibrant Anganwadi Centres and conducting Early Childhood Care and Education activities, .
- ICT Integration: a robust ICT enabled platform named Poshan tracker has been designed to capture real-time data on implementation and monitoring of Anganwadi Services across the country.
- The Poshan Tracker management application provides a 360 – degree view of the activities of the Anganwadi Centre (AWC), service deliveries of Anganwadi Workers (AWWs) and complete beneficiary management.
Way Forward:
AWCs play an important role in improving basic child learning and health needs for the poor people and help the government to implement its various programs especially related to child and women development. The steps like Saksham Abhiyan and technological up-gradation by states like Gujarat are positive steps but not sufficient considering issues AWCs are grappling with.
Hence, the government must resolve the issues and improve the functioning of AWCs through better schemes and adhering to recommendations of think tanks like NITI AYOG.
Source: The Hindu
Additional Information:
Integrated Child Development Services
- Launched on 2nd October, 1975, Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) is the only major national program that addresses the needs of children under the age of six years.
- It seeks to provide young children with an integrated package of services such as supplementary nutrition, health care and pre-school education.
- The scheme is under the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Integrated Child Development Services is Centrally-Sponsored and will provide the following six services to the beneficiaries:
- Supplementary Nutrition (SNP)
- Health & Nutrition Check-Up
- Immunization
- Non-Formal Education for Children in Pre-School
- Health and Nutrition Education
- Referral services
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance) and GS 3 (Economy)
Context: The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) has allowed prepaid payment instruments (PPIs) to be part of the interoperable Unified Payments Interface (UPI) ecosystem.
- The NPCI has recently introduced interchange fees of up to 1.1 per cent on merchant UPI transactions done using prepaid payment instruments (PPIs) from April 1, 2023.
Key highlights of the changes:
Applicability:
- The new NPCI guidelines on wallet interoperability establish interchange fee for wallet usage, which will be paid to issuers of wallets such as Paytm, PhonePe and Google Pay, among others.
- They also include charges for UPI-wallet-loading that will be paid by wallet issuers to remitter banks or the bank accounts from which the amount is being debited.
Benefit for wallet players:
- The inter-operability norms will enable universal acceptance of wallets across all UPI QR codes and devices, thus increasing the salience or relevance of wallets.
- It will also ensure uniformity and parity by clearly defining the interchange fees on wallet payments as against the current practice of bilateral agreements between wallet issuers and payment platforms.
Interchange fees:
- The interchange rates vary according to merchant category codes, in the range of 0.5 per cent to 1.1 per cent.
- Categories such as fuel, education, agriculture and utility payments attract a lower interchange of 0.5-0.7 per cent; convenience stores across food shops, specialty retail outlets and contractors, have the highest charge of 1.1 per cent.
Wallet transactions:
- The interchange fees are paid by merchants to wallets or card issuers and are usually absorbed by merchants.
- Smaller merchants and shopkeepers are unlikely to be impacted as it is applicable only on payments of over Rs. 2,000.
- MDR or merchant discount rate is applicable on wallets-on-UPI in certain cases and this move may lead to higher MDRs imposed on merchants, depending on payment companies’ ability and willingness to pass on the interchange.
Impact on Customers:
- The norms are expected to increase the appeal, scope, role and usability of wallets as they can now be used to make UPI payments across QR codes and devices, increasing payments alternatives for customers.
- Consumers will also be able to load their wallets from anywhere including credit or debit cards, BNPL (Buy Now Pay Later) and net banking, among others, thus creating a mechanism to use any instruments for UPI transactions, albeit directly or indirectly.
- Currently, MDR for bank-to-bank UPI transactions is zero.
About Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs):
- PPIs are instruments that facilitate purchase of goods and services, conduct of financial services, enable remittance facilities, etc., against the value stored therein.
- Prepaid payment instruments’ examples include smart cards, online accounts, online wallets, stripe cards, paper vouchers, etc.
- The primary objective of these instruments is to get access to the amount already prepaid.
- So, one can purchase the required goods without any physical exchange of cash or card.
Digital Transactions in India
- Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY), Digital Economy & Digital Payment Division has been entrusted with the responsibility of leading this initiative on “Promotion of Digital Transactions including Digital Payments”.
- MeitY is coordinating with multiple stakeholders including Banks, Payment Service Providers, Central Ministries/Departments and States/UTs, for promotion of digital payments across the country.
- Major digital payment modes: Bharat Interface for Money-Unified Payments Interface (BHIM-UPI), Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), and National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) have undergone significant growth in the last five years.
- Coordinated efforts of the Government with all stakeholders have led to a significant growth in digital payments, as given below:
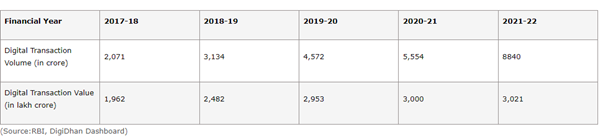
Significance of digital payments:
- Enhanced financial inclusion: Digital payments offer anytime, anywhere access to accounts, making it easy for citizens to receive and make payments using their phones.
- Recently launched UPI 123PAY enables feature phone users to make digital transactions through UPI in assisted voice mode, facilitating digital transactions and financial inclusion in rural areas.
- Instant and convenient mode of payment: Digital modes like BHIM-UPI and IMPS enable instantaneous transfer of money to the beneficiary account. BHIM-UPI has enabled access to multiple bank accounts in a single mobile app.
- Improved speed and timely delivery: Digital payments can be virtually instantaneous, regardless of the sender and receiver’s location.
- National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) system: The NETC system enables electronic payments at toll plazas using Radio Frequency Identification technology.
- Increased transparency in government system: Benefits are directly transferred to the target beneficiary account through digital modes of payments, eliminating leakage and ghost recipients.
- Bharat Bill Payment System: The BBPS provides an interoperable and easily accessible bill payment service to consumers via multiple channels like Internet banking, mobile banking, mobile apps, BHIM-UPI, etc.
Challenges of digital transactions:
- Digital illiteracy: A significant portion of the population, especially in rural areas, may not be familiar with digital payment systems and may face difficulties in using them.
- Security concerns: Digital payments can be vulnerable to cyber threats and frauds. Malicious actors can steal sensitive financial information and make unauthorized transactions.
- Connectivity issues: Digital transactions require a stable internet connection, which may not be available in all areas. This can cause delays and disruptions in the payment process.
- Technical glitches: Technical glitches can occur during digital transactions, leading to failed transactions or incorrect transfers.
- Transaction fees: Some digital payment systems may charge transaction fees, which can discourage people from using them.
- Dependence on technology: Over Reliance on digital payment systems can make people vulnerable to disruptions in case of technical failures or system outage.
- Limited acceptance: Not all merchants and service providers may accept digital payments, particularly in remote areas.
Way Forward:
The digital payment landscape in India has been transformed and India has emerged as a leader in the creation of digital assets, which can serve as an example to many other nations. The Government of India needs to make more efforts to help India attain the status of one of the most efficient payments markets in the world.
There is a need for regulatory intervention to explore alternative payment methods, such as digital wallets and UPI, which offer lower transaction fees. Overall, the benefits of digital transactions outweigh the challenges, and as technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see further innovation in the payments landscape.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding the Krishi Udan Scheme:
- The scheme aims to ensure seamless, cost-effective, time-bound air transportation and associated logistics for all Agri-produce in the country.
- It is under the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) The Eravikulam National Park is located in
- Tamil Nadu
- Kerala
- Goa
- Odisha
Q.3) Consider the following countries:
- Australia
- Canada
- USA
- Malaysia
- Russia
Which of the above are part of the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP)?
- 1 3 and 5 only
- 2 3 and 4 only
- 1 2 and 4 only
- 1 2 3 4 and 5
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 4th April 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 3rd April – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – d












