IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 2nd April 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation (Adaptation of State Laws) Order, 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Polity and Governance
In News:
- The Central government passed Jammu And Kashmir Reorganisation (Adaptation of State Laws) Order, 2020 recently.
Key takeaways:
- The order defined new domicile rule for Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) according to which a person residing in J&K for at least 15 years will now be eligible to be a domicile of the Union Territory.
- If a person has studied for a period of 7 years and appeared in class 10th or 12th examination in an educational institution located in the UT of J&K will also be considered as the domicile of the UT.
- Tehsildar shall be the competent authority for issuing the domicile certificate, as opposed to Deputy Commissioner.
- Section 5-A states that no person shall be eligible for appointment to a post carrying a pay scale for not more than level 4 unless he is a domicile of UT of J&K.
- Through the same order, the Centre has repealed the J&K Civil Services (Special Provisions) Act.
Important value additions:
The Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019
- It is an act of the Parliament of India.
- It contains provisions to reconstitute the Indian-administered state of Jammu and Kashmir, into two Indian-administered union territories, one to be called Jammu and Kashmir, and the other Ladakh.
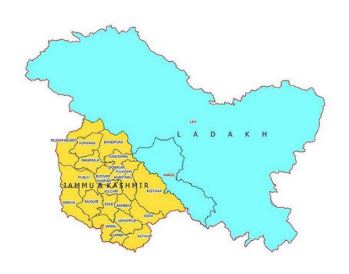
Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation
Image source: Click herel
Ways and Means Advances (WMA) reviewed: RBI reviewed its limits
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In News:
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has reviewed the Limits of Way and Means Advances for Center and States/UTs.
Key takeaways:
- For central Government: Recently, The Government of India increased the ceiling on WMA with RBI by 60% to Rs 1.20 lakh crore (from Rs 75,000 crore last year) to tide over the cash flow mismatch in FY21 expected from higher spending to combat the spread of COVID-19.
- For States/UTs: RBI had constituted an Advisory Committee (Chairman: Shri Sudhir Shrivastava) to review the WMA limits for States/UTs. Meanwhile, it has been decided to increase their WMA limit by 30%.
Important value additions:
- Under Section 17(5) of RBI Act, 1934, the RBI provides Ways and Means Advances (WMA) to the central and State/UT governments.
- It is a temporary liquidity arrangement with the central bank.
- It enables the centre and the states to borrow money up to 90 days from the RBI to tide over their liquidity mismatch between its inflow of revenues and outflow of expenditure.
- A higher limit would provide the government flexibility to raise funds from RBI without borrowing them from the market.
- WMA is not a security as it is not tradable.
- Interest rate for WMA is currently charged at the repo rate.
- The limits for WMA are mutually decided by the RBI and the Government of India.
Taxation and Other Laws (Relaxation of Certain Provisions) Ordinance, 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In News:
- The Government of India promulgated the Taxation and Other Laws (Relaxation of Certain Provisions) Ordinance, 2020.
- It was done to bring into effect various tax compliance related measures announced in the wake of COVID-19 pandemic.
Key takeaways:
- Time limits related to direct and indirect tax filings, passing of order or issuance of notice by tax authorities have been extended to June 30.
- Taxpayers can also avail the Sabka Vishwas Legal Dispute Resolution Scheme 2019 till June 30, giving more time to settle their indirect tax disputes.
- Donations made to PM Cares fund will be 100% exempted of the income tax.
- The limit on deduction of 10% of gross income shall also not be applicable for such donations.
Important value additions:
Sabka Vishwas Legal Dispute Resolution Scheme
- The aim of Sabka Vishwas (Legacy Dispute Resolution) Scheme, 2019 is to help taxpayers, including small taxpayers, in clearing the baggage of disputes under legacy taxes (Service Tax and Central Excise), which are subsumed in Goods and Service Tax.
Medical Devices Notified as Drugs
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health
In News:
- With effect from 1st April, 2020, all Medical Devices shall be regulated by the Government as Drugs for quality control and price monitoring.
Key takeaways:
- The Maximum Retail Prices (MPRs) of all the Medical Devices would be monitored by the Government under the provisions of Para 20(1) of the Drugs (Prices Control) Order, 2013.
- This will ensure that no manufacturer/importer increases the MRP of a drug more than 10% of MRP during preceding 12 months, failing which penalty shall be imposed.
Important value additions:
- National Pharmaceutical Pricing Policy (NPPP) – governs price control.
- Drug Price Control Orders (DPCO) – enforces price control.
- National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) – monitors and controls drug prices.
- National Pharmaceutical Pricing Policy-2012 – places a regulatory framework for pricing of drugs.
Miscellaneous
Azithromycin -Hydroxychloroquine Combination
- The Union Health Ministry has allowed the use of Hydroxychloroquine in combination with Azithromycin under severe conditions.
- The earlier guidelines which included use of Anti-HIV drugs Ritonavir-Lopinavir in high risk patients, now stand repealed.
- Azithromycin is commonly used as an antibiotic.
- Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is used in treatment of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. It is also used in treating malaria.
- The azithromycin-hydroxychloroquine combination is part of an upcoming multi-country trial anchored by the World Health Organization to against COVID-19.
Natuna Islands
- Natuna Islands are within Indonesia’s exclusive economic zone but are also claimed by China.
- Recently, China has sparked a major maritime confrontation with Indonesia near the South China Sea by entering waters along with dozens of Chinese fishing vessels.
Medical Devices Notified as Drugs
Image source: Click here
(MAINS FOCUS)
ECONOMY/ SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
- Security challenges
Indian defence Trade: Still no bullseye, in volume and value
India’s defence sector has been largely dependent on foreign imports that is not in the long term Security interest of the Nation. However, the trend has been changing in recent times.
During 2009-18, Indian defence imports reduced even as exports increased as per study by Stockholm International Peace Research Institute
Do You Know?
- India has four companies among the top 100 biggest arms producers of the world –Indian Ordnance Factories, HAL, BEL and Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL).
- In 2017-18 and 2018-19, exports have increased from ₹7,500 crores to ₹11,000 crores, representing a 40% rise.
- SMEs until 2016 accounted for a 17.5% share of the Indian defence market.
Reasons for India’s reduced imports:
- Make in India initiative
- Defence Procurement Procedure (DPP) of 2016 lays out measures necessary for building India’s defence Industry
- A new category called ‘Buy Indian Indigenously Designed, Developed and Manufactured’ (IDDM) was created under DPP-2016 which was given highest preference in defence procurement.
- For imported defence goods, its Components & service parts from Indian enterprises (private & public sector) have been prioritised by the government
- Simplifying “Make” procedures especially for MSMEs to encourage indigenous defence production
- Technology Transfer: Relaxed norms that makes private partners eligible for technology transfers so as to boost their capabilities.
- Outcome: In 2018-19, the three armed services sourced 54% of their defence equipment from Indian industry for their combined capital and revenue expenditures
- Reducing the size (or cancellation) of defence contracts by government has led to significant reduction of import bill
- Acquisition of Rafale jets reduced from 126 aircrafts to 36 aircrafts
- Cancellation of Indo-Russian joint venture for development of Su-57 stealth Fighter Aircraft
- Delays in supplying equipment by vendors also led to falling imports. Example: T-90 battle tanks & Su-30 combat aircraft from Russia; Submarines from France
Reasons for rise of defence exports
- Removal of export barrier: Government has removed several products that were earlier restricted from exports
- Easing regulations: Government dispensed with the No Objection Certificate (NOC) under the DPP that restricted exports of aerospace products & several dual-use items
Areas that need action by government:
- India’s defence production is largely driven by Public Sector (no Indian private player in top 100 arms producer of world)
- India’s defence model tends to create disincentives for the private sector – Despite “Make in India”, Defence-PSUs are privileged over private industry
- Inadequate R&D in defence sector (both Public & Private sector)
- Export of ammunition and arms still remain low (bulk of India’s major defence exports are Small naval crafts)
- Small contribution to overall trade: Defence-related exports for 2017-18 and 2018-19 were 0.8% and 0.73% of the total trade, respectively, which needs to be substantially increased
Connecting the dots:
- Foundational defence agreements signed between India and USA – its impact on India’s indigenisation efforts
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Planning institution: Need to Think national and act local
In the event of crisis created by the pandemic, an all-round plan for recovery is much needed.
However, there is a general criticism that Planning bodies (Erstwhile Planning Commission and present NITI Aayog) has failed to produce all-round development of India’s economy.
Some of the drawbacks/criticisms of National Planning Body
- Short-termism in policymaking: In electoral democracies like India, governments change in shorter spans whereas national plans need consistent action over decades.
- The disruption caused due to absence of long-term planning is not faced in the case of China, that has been one of the reason for its rapid rise.
- Compromised Independence: Lack of constitutional status makes the planning body bend to the will of elected governments thus derailing long term plans
- Failure to address the constitutional relationship between the States and Centre – States who are self-sufficient have often questioned the value of guidance (one-size-fits-all approach) from National planning bodies
- Failure to synergise with Finance Commission that determines the fund allocation of central resources amongst States.
- Lack of Holistic plans/policies: Planning bodies must assist in achieving not just faster GDP growth, but also more socially inclusive, and more environmentally sustainable growth.
- Lack of insights into systems structures – In the era of Globalisation, the production factors keeps moving (out of India) to lower cost sources. Neglecting this systemic factors leads to ineffective policies.
- Planning is weak when planners do not have the powers to allocate money for national priorities (which NITI Aayog does not have)
Way Ahead
- Devising a good developmental model in which inequality, societal and environmental forces are integrated into growth process
- Decentralised Solutions– Planning bodies need to promote local solutions to national problems, taking into account the unique conditions of the region.
- If fund allocation powers are granted to NITI Aayog then it must be backed by a constitutional charter, and accountable to Parliament.
Connecting the dots:
- National planning bodies must be a force for persuasion, not control centre. Elaborate.
- Three-year action plan of NITI Aayog and the progress made.
- Why did the government adopt Five Year Planning strategy during the early days of Independence? Why was it discontinued after 12th FYP?
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q 1. Consider the following statements regarding Jammu And Kashmir Reorganisation (Adaptation of State Laws) Order, 2020:
- Under new domicile rule, a person residing in J&K for at least 15 years will now be eligible to be a domicile of the UT.
- Tehsildar shall be the competent authority for issuing the domicile certificate.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 2. Consider the following statements regarding Ways and Means Advances:
- It is a temporary liquidity arrangement with the Reserve Bank of India.
- The government can borrow money only up to 50 days.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 3. Consider the following statements:
- Taxpayers avail the Sabka Vishwas Legal Dispute Resolution Scheme to settle their indirect tax disputes.
- Donations made to PM Cares fund will be 100% exempted of the income tax.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q 4. Consider the following statements:
- National Pharmaceutical Pricing Policy (NPPP) is the policy governing price control.
- Drug Price Control Orders (DPCO) is the order by which price control is enforced.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 1st April 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | A |
| 4 | B |
| 5 | C |
Must Read
About the present Oil Price war:
About measures to tackle COVID-19:
About COVID-19 and comparison with Spanish Flu of 1918-20:













