IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
India joins Djibouti Code of Conduct/ Jeddah Amendment (DCOC/JA)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- India has joined the Djibouti Code of Conduct/ Jeddah Amendment, DCOC/JA, as an Observer.
Important value additions
Djibouti Code of Conduct/ Jeddah Amendment
- DCOC/JA is a grouping on maritime matters comprising 18 member states adjoining the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, the East Coast of Africa and Island countries in the Indian Ocean Region.
- The DCOC was established in January 2009.
- Aim: Repression of piracy and armed robbery against ships in the Western Indian Ocean Region, the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea.
- Japan, Norway, the UK and the US are also the Observers to the DCOC/JA.

Aircraft (Amendment) Bill 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Legislations & GS-III – Infrastructure – Airways
In news
- Recently, Indian Parliament has passed the Aircraft (Amendment) Bill, 2020 in the Rajya Sabha approving it. The Bill has already been passed by the Lok Sabha.
- It seeks to amend the Aircraft Act, 1934.
Key takeaways
- It has provisions to convert three existing bodies under the Ministry of Civil Aviation into statutory bodies.
- These three authorities are – (1) Directorate General of Civil Aviation; (2) the Bureau of Civil Aviation Security; (3) Aircraft Accidents Investigation Bureau.
- Under the bill, each of these bodies will be headed by a Director General who will be appointed by the centre.
- The Bill raises the maximum limit on fines from 10 lakh rupees to one crore rupees.
- These fines are related to carrying arms, explosives and other dangerous goods aboard aircraft and constructing building or structures within the specified radius around an aerodrome reference point.
Draft Of Electricity (Rights Of Consumers) Rules, 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Legislations & GS-III – Infrastructure
In news
- The Central Power Ministry has drafted rules recently which provide for Rights of Electricity Consumers for the first time.
- Draft Rules have been circulated by Ministry of Power on 9th of September for seeking comments and suggestions of consumers up to 30th September.
Key takeaways
- According to the draft, State Electricity Regulatory Commissions (SERCs) will fix average number and duration of outages per Electricity consumer per year for DISCOMs.
- Only two documents will be required for connection up to load of 10 KW and no estimation of demand charges will be required for loads up to 150 KW to expedite giving connection.
- There will be a time period of not more than seven days in metro cities, 15 days in other municipal areas and 30 days in rural areas, to provide new connection and modify existing connection.
- There will be option to pay bills in cash, cheque, debit cards and net banking.
- Bills of Rs. 1,000 or more have to be paid online.
Essential Commodities (Amendment) Bill, 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions
In news
- Lok Sabha passed the Essential Commodities (Amendment) Bill, 2020.
- The Bill will replace the Essential Commodities (Amendment) Ordinance which was promulgated in June, 2020.
Key takeaways
- The Bill seeks to amend the Essential Commodities Act, 1955.
- It empowers the central government in terms of production, supply, distribution, trade, and commerce of certain commodities under extraordinary circumstances.
- The Central government will be able to designate certain commodities including food items, fertilizers, and petroleum products as essential commodities.
- The Bill empowers the central government to regulate the stock of an essential commodity that a person can hold.
Do you know?
- The extraordinary circumstances include war, famine, extraordinary price rise and natural calamity of grave nature.
- The provisions of the bill regarding the regulation of food items and the imposition of stock limits will not apply to any government order relating to the Public Distribution System or the Targeted Public Distribution System.
Salary, Allowances And Pension Of Members Of Parliament (Amendment) Bill, 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions; Parliament
In news
- Lok Sabha unanimously passed the Salary, Allowances and Pension of Members of Parliament (Amendment) Bill, 2020.
- The Bill will replace the Salary, Allowances and Pension of Members of Parliament (Amendment) Ordinance which was promulgated in April, 2020.
Key takeaways
- The Bill seeks to reduce the salaries of MPs and the sumptuary allowance of Ministers by 30%.
- It also seeks to reduce the constituency allowance and office expenses allowance of MPs.
- The Bill makes these changes effective for a period of one year, effective from 1st April, 2020.
Important value additions
- The Salary, Allowances and Pension of Members of Parliament Act, 1954 provides for the salary, allowances and pension of Members of Parliament.
- Article 106: The members of either House of Parliament shall be entitled to receive such salaries and allowances as may from time to time be determined by Parliament by law.
Institute Of Teaching And Research In Ayurveda Bill 2020
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions; Health & GS-III – Medicine
In news
- The Institute of Teaching and Research in Ayurveda Bill 2020 has been passed by Rajya Sabha. The Bill has been passed in Lok Sabha.
- This paves the way to establish a state-of-the-art Ayurvedic institution called the Institute of Teaching and Research in Ayurveda (ITRA) at Jamnagar, Gujarat.
- It will also be conferred with the status of Institution of National Importance (INI) to it.
Do you know?
- ITRA will be the first institution with INI status in the AYUSH Sector.
- The ITRA is sought to be established by conglomerating the presently existing Ayurveda institutes at Gujarat Ayurved University campus Jamnagar.
India-Japan Logistics Agreement
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- Recently Logistics Agreement was signed between India and Japan.
Key takeaways
- It is aimed at greater maritime cooperation.
- It can upgrade India-Japan naval exercises.
- It establishes the enabling framework for closer cooperation between the armed forces of both countries in reciprocal provision of supplies and services.
- It will also enhance the interoperability, assistance in maintaining regional security and further increase the bilateral defence engagements.
- It will remain in force for 10 years and will be automatically extended for periods of 10 years unless one of the parties decides to end it.
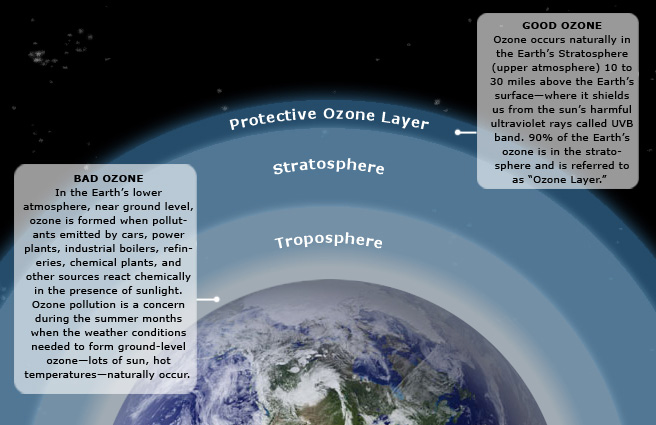
Low Ozone Over Brahmaputra River Valley observed
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Climate Change
In news
- Recently, scientists at the Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES), Nainital, have evaluated the near surface ozone in the Brahmaputra River Valley (BRV).
- They assessed seasonal characteristics of ozone to identify the emission source of ozone and its precursors, especially methane (CH4) and non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHCs).
Key takeaways
- Scientists have found relatively low concentration of ozone over BRV (Guwahati – Assam) compared to the other urban locations in India.
- The pattern of ozone concentrations in the BRV indicated that it was strongly influenced by local oxides of nitrogen (NOx) sources with an adjacent national highway being the likely major source.
- High ozone winter concentrations were observed.
- This could be due to local biomass burning providing reactive volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that contributed to ozone formation.
- In the pre-monsoon season, an impact of solar radiation (SR) on the photochemical formation of O3 was observed.

Start-Up Village Entrepreneurship Programme
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Start-ups; Entrepreneurship
In news
- Women Self Help Groups (SHGs) under the Start-Up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP) stepped up as effective frontline responders during the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic.
Important value additions
Start-Up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP)
- SVEP is a sub-scheme of the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM).
- Ministry: Ministry of Rural Development.
- Implemented: 2016.
- It has extended business support services and capital infusion to 153 blocks of 23 states as of August 2020.
- Partner: Entrepreneurship Development Institute of India (EDII), Ahmedabad.
- Aim: (1) Support the rural poor to come out of poverty; (2) Support the people to set up enterprises and provide support until the enterprises stabilise; (3) Providing self-employment opportunities with financial assistance and training
- It addresses three major pillars of rural start-ups namely finances, incubation and skill ecosystems.
Indian Brain Templates developed at NIMHANS
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Achievements of Indians in Science and Technology;
In news
- A team of neuroscientists from the National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS) has developed Indian Brain Templates (IBT) and a brain atlas.
Key takeaways
- Neuroscientists studied over 500 brain scans of Indian patients to develop five sets of Indian Brain Templates (IBT) and a brain atlas.
- IBT provides a scale that will measure an Indian Brain.
- Brain Atlas has been developed for five age groups covering late childhood to late adulthood (six to 60 years).
- These new population and age-specific Indian brain templates will allow more reliable tracking of brain development and ageing.
- They will provide more precise reference maps for areas of interest in individual patients with neurological disorders like strokes, brain tumours, and dementia.
- These will also help pool information more usefully in group studies of the human brain and psychological functions.
- These will aid in understanding of psychiatric illnesses like Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), autism, substance dependence, schizophrenia, and mood disorders.
Do you know?
- Brain Template is a gross representation from various brain images to understand brain functionality in diseased conditions.
- The Montreal Neurological Index (MNI) template that India currently uses is based on Caucasian brains, which are different from Asian brains.
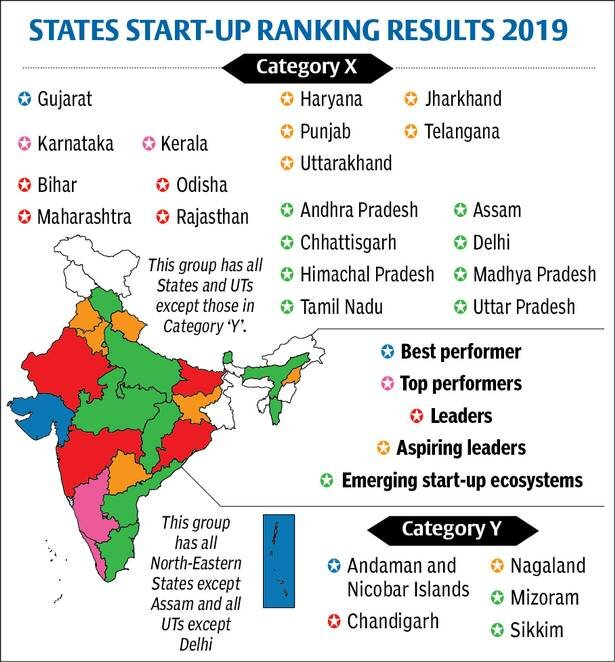
Ranking of States on Support to Startup Ecosystems: DPIIT
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Start-ups; Entrepreneurship
In news
- The Results of the 2nd edition of Ranking of States on Support to Startup Ecosystems were released recently.
- Ministry: Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- DPIIT has recently released the Ease of Doing Business Rankings of the States-2019 based on the State Business Reform Action Plan.
Key takeaways
- Objective: To foster competitiveness, mutual learning and propel States and Union Territories (UTs) to work proactively towards uplifting the startup ecosystem.
- Framework: The 2019 Ranking Framework has seven broad reform areas consisting of 30 action points – institutional support, easing compliances, relaxation in public procurement norms, incubation support, seed funding support, venture funding support, and awareness and outreach.
- Participation: 22 States and 3 Union Territories.
- 2 Categories of States and UTs: (1) Category Y: All UTs except Delhi and all States in North East India except Assam; (2) Category X: All other States and UT of Delhi.
- Best Performers: (1) Gujarat; (2) Karnataka; (3) Kerala.
- Lowest performance: (1) Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- Best performer in Category Y: Andaman & Nicobar Islands
- Worst performer in Category Y: Sikkim
Miscellaneous
Monsoon Session of Parliament Begins
-
Recently, the monsoon session of Parliament began
- However, the government has suspended Question Hour and Zero Hour for the session.
Terminologies related to Parliament session
- The President of India is empowered to summon each House of Parliament from time to time.
- The maximum gap between two sessions of Parliament cannot be more than six months.
- There are usually three sessions in a year: (1) Budget Session (February to May); (2) Monsoon Session (July to September); (3) Winter Session (November to December).
- Recess: The period between the prorogation of a House and its reassembly.
- Adjournment: It suspends the work in a sitting for a specified time, which may be hours, days or weeks.
- Adjournment sine die: It means terminating a sitting of Parliament for an indefinite period.
- The power of adjournment as well as adjournment sine die lies with the presiding officer (Speaker or Chairman) of the House.
- Prorogation: The President issues a notification for prorogation of the session after the business of a session is completed and the presiding officer declares the House adjourned sine die.
- The President can also prorogue the House while in session.
- Dissolution: Only the Lok Sabha is subject to dissolution. A dissolution ends the life of the existing House. A new House is constituted after general elections are held.
- The President is empowered to dissolve the Lok Sabha.
(MAIN FOCUS)
ENVIRONMENT/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
Welfare of Animals in India
Context:
Over the past year, there have been reports of animals being subjected to sexual abuse, acid attacks, being thrown off rooftops, and being burnt alive.
Flaws in legal framework: The Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (PCA) Act, 1960
- The law punishes the most serious forms of animal violence with a paltry fine of Rs. 50.
- Section 11 lists a series of offences, which vary from abandoning an animal to kicking it, mutilating it or killing it, and prescribes the same punishment for all these offences. Severe offences are treated on a par with less severe ones.
- At present, a majority of the offences under the Act are non-cognisable, which means the police cannot investigate the offence or arrest the accused without the permission of a Magistrate. This facilitates police inaction.
- The PCA Act creates a plethora of exceptions which significantly dilute the protections available to animals. Section 11(3) provides exceptions for animal husbandry procedures such as dehorning, castration, nose-roping, and branding.
The law does not provide any guidelines for these procedures. This allows individuals to resort to cruel methods.
- Ambiguity in definition: The law was enacted to “prevent the infliction of unnecessary pain or suffering on animals”. However, this phrase is not defined anywhere in the Act. This is crucial because what constitutes “unnecessary” is entirely a matter of subjective assessment.
Way forward:
- An amendment is required to grade the offences according to their severity, and specify punishments accordingly. Further, the more severe offences must be made cognisable and non-bailable.
- Proper regulations of animal husbandry procedures: A petition from PETA’s (People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals) suggests mandating the use of anesthetics prior to castration, replacing nose-roping with face halters and branding with radio frequency identification. Aas opposed to dehorning cattle, it recommended that farmers breed hornless cattle.
Conclusion:
The Constitution requires all citizens to “have compassion for living creatures”. We must seek to protect the most vulnerable among us. Our animal welfare laws need an overhaul.
Connecting the dots:
- For a country that claims adherence to ahimsa, India’s treatment of its animals betrays a moral failure.
NATIONAL/ENVIRONMENT
Topic: General Studies 3:
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
- Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation.
India’s track on climate change: Giving up investments on coal?
Context:
The UN Secretary General António Guterres has called on India to make no new investment in coal after 2020, and to reduce emissions by 45% by 2030.
India’s track record:
- India is one of the few countries which is currently on track to fulfilling their Paris Agreement commitments.
- Despite the accelerated economic growth of recent decades India’s annual emissions, at 0.5 tonnes per capita, are well below the global average of 1.3 tonnes.
In absolute terms it is below that of China, the United States and the European Union (EU), the three leading emitters in absolute term - In terms of cumulative emissions, India’s contribution by 2017 was only 4% for a population of 1.3 billion, whereas the European Union, with a population of only 448 million, was responsible for 20%.
Where do developed countries stand?
- The UNFCCC itself has reported that between 1990 and 2017, the developed nations (excluding Russia and east Europe) have reduced their annual emissions by only 1.3%.
- The global North continues its dependence on oil and natural gas, both equally fossil fuels, with no timeline for their phase-out.
- Large sections of First World environmentalist opinion have been unable to summon up the domestic political support required for climate action.
- They have turned to pressure the developing countries to bear the brunt of climate mitigation.
Issues:
- Any discussion on climate action should have reference to the core principles of climate convention(The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC))- global and international equity and the principle of common but differentiated responsibilities
- Unlike the developed nations, India cannot substitute coal substantially by oil and gas. A huge part of this growth needs to come from solar for which sustainable technology is not yet developed.
- Renewables, in the current scenario, at best can meet residential consumption and some part of the demand from the service sector.
- Lack of technology: Whether providing 70% to 80% of all generation capacity is possible through renewables depends critically on technology development, including improvements in:
-
- The efficiency of conversion of energy from its source into electricity.
- Management of the corresponding electricity grids.
- Improvement in storage technologies.
Technology development in climate change mitigation technologies has registered a significant fall since 2009-10 to 2017, across all subsectors and across all developed countries.
- Lacking production capacity in renewable energy technologies and their large-scale operation, deployment on this scale will expose India to increasing and severe dependence on external sources and supply chains.
- Renewables alongside coal will generate, directly and indirectly, far more employment than renewables alone.
Conclusion:
The UN’s Generals’s call seems to be a call to de-industrialise the country and abandon the population to a permanent low-development trap.
Connecting the dots:
- India must reiterate its long-standing commitment to an equitable response to the challenge of global warming. Comment.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements:
- Adjournment sine die suspends the work in a sitting for a specified time.
- Adjournment means terminating a sitting of Parliament for an indefinite period.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 The Results of the 2nd edition of Ranking of States on Support to Startup Ecosystems were released recently. Consider the following statements:
- It was released by Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade
- Karnataka is the best performer among the states.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Low Ozone was observed over which of the following River Valley?
- Godavari
- Narmada
- Brahmaputra
- Ganges
ANSWERS FOR 17th September 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | A |
| 4 | A |
Must Read
On Judiciary-
UN reforms-











