IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Indigenous Games to be a part of Khelo India Youth Games 2021
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions
In news
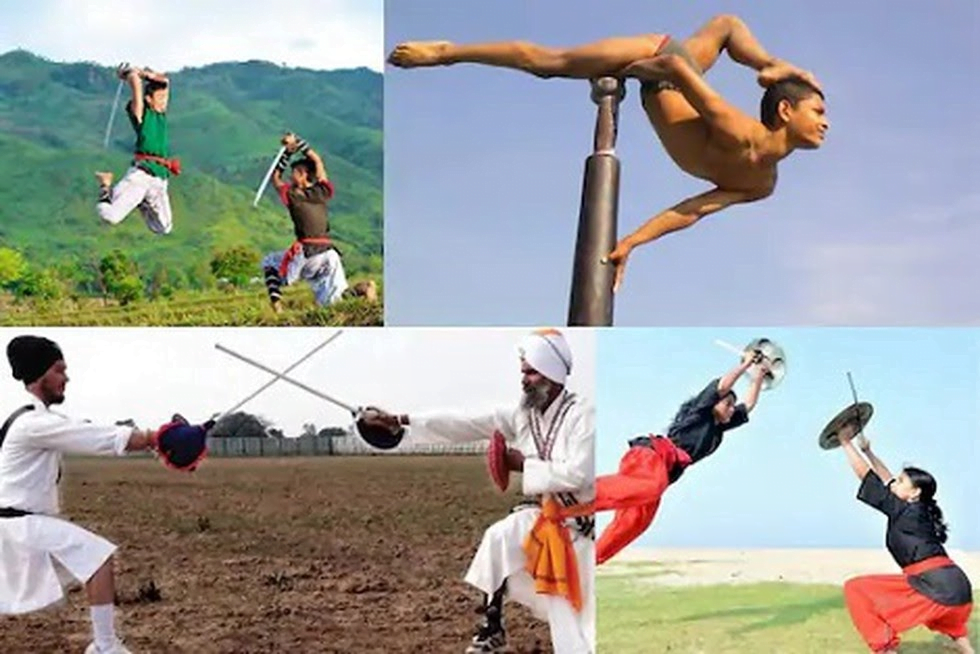
- The Sports Ministry has approved the inclusion of four Indigenous Games to be a part of Khelo India Youth Games 2021, scheduled to take place in Haryana.
- The games include: Gatka, Kalaripayattu, Thang-Ta and Mallakhamba.

Key takeaways
- Kalaripayattu has its origin from Kerala and has practitioners all over the world.
- Mallakhamba has been well-known across India. Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra have been the hotspots of this sport.
- Gatka originates from the State of Punjab. This traditional fighting style of the Nihang Sikh Warriors is used both as self-defense and a sport.
- Thang-Ta is a Manipur marital art which has passed into oblivion in the recent decades.
Gastrodia Agnicellus named as the ugliest orchid in the world
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Biodiversity
In news
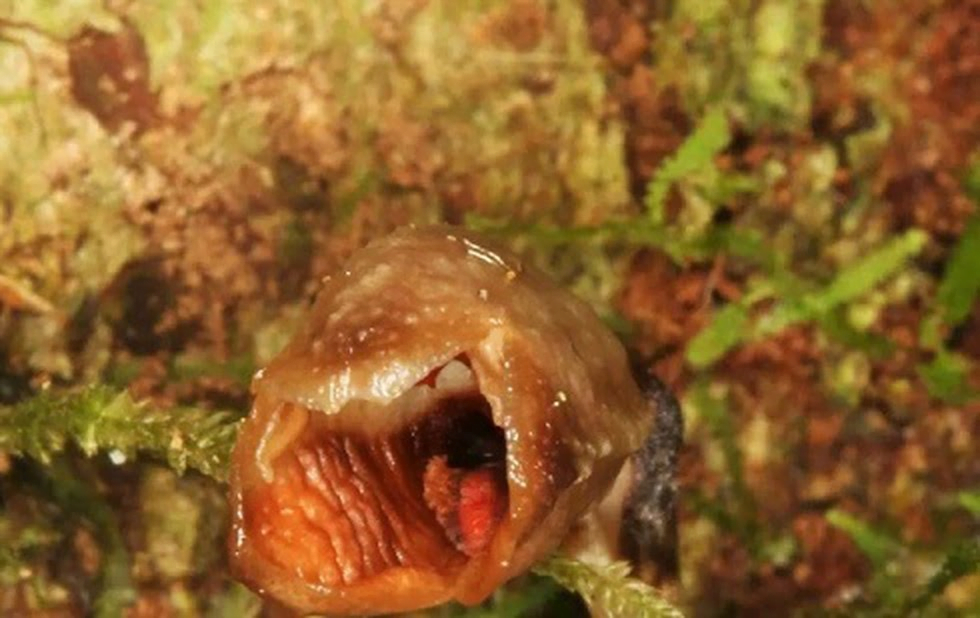
- Gastrodia agnicellus, a newly discovered orchid has been named “the ugliest orchid in the world.”

Key takeaways
- It was found in a forest in Madagascar.
- It feeds on fungi.
- It has no leaves.
- Although assessed as a threatened species, the plants have some protection because they are located in a national park.
Do you know?
- Madagascar is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately 400 kilometres off the coast of East Africa.
- Madagascar is the world’s second-largest island country.
Chang’e 5 returns with first fresh rock samples from the moon
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Sci & Tech
In news
- China’s Chang’e 5 lunar mission returned to Earth carrying around 2 kilograms of the first fresh rock samples from the moon in 44 years.
- The spacecraft recently landed in Siziwang Banner, north China’s Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region.
Key takeaways
- The probe, named after the ancient Chinese goddess of the moon, first took off from the Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site in Hainan on November 24th.
- Two of the Chang’e 5’s four modules landed on the moon on 1st December and collected about 2 kilograms (4.4 pounds) of samples by scooping them from the surface and drilling 2 meters into the moon’s crust.
- The samples were deposited in a sealed container that was carried back to the return module by an ascent vehicle.
- The retrieved re-entry capsule of Chang’e-5 will be airlifted to Beijing, where the capsule will be opened and the samples will be ready for analysis.
- With this, China became the third country after the United States and the Soviet Union, to collect lunar samples.
- These are also the first samples to be collected by any country after Russia in 1976.
Do you know?
- The samples were retrieved from a previously unvisited area of the moon.
- The latest samples come from a part of the moon known as the Oceanus Procellarum, or Ocean of Storms, near a site called the Mons Rumker that was believed to have been volcanic in ancient times.
- Mons Rumker, never sampled before, is geologically younger than the sampling areas of the U.S. and the Soviet missions.
Efforts in advanced stages to set up Coastal Radar Chain Network
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Infrastructure
In news
- Efforts are in advanced stages to set up coastal radar stations in the Indian Ocean littoral states of Maldives, Myanmar and Bangladesh.
- Objective: To further expand the coastal radar chain network meant to enable real-time monitoring of the high seas for threats.
Key takeaways
- Mauritius, Seychelles and Sri Lanka have already been integrated into the country’s coastal radar chain network.
- Similar plans are in the pipeline with Maldives and Myanmar and discussions are ongoing with Bangladesh and Thailand.
- Under Phase-I of the coastal radar chain network, 46 coastal radar stations have been set up across the country’s coastline.
- Under Phase-II of the project, which is currently underway, 38 static radar stations and four mobile radar stations are being set up by the Coast Guard and is in advanced stage of completion.
Important value additions
Other developments
- The Indian Navy’s Information Management and Analysis Centre (IMAC) located in Gurugram, which was set up after the 26/11 Mumbai terror attacks, is the nodal agency for maritime data fusion.
- As part of information exchange regarding traffic on the high seas, the Navy has been authorised by the government to conclude white shipping agreements with 36 countries and three multilateral constructs.
- So far agreements have been concluded with 22 countries and one multilateral construct.
- At the Navy’s Information Fusion Centre for the Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR) which is meant to promote Maritime Domain Awareness, three more International Liaison Officers (ILO) are expected to join soon.
- The ILOs from France, Japan and the U.S. have joined the centre.
Rehabilitation Centre For Monkeys
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment
In news
- The first rescue and rehabilitation centre for monkeys in Telangana was inaugurated at Gandi Ramanna Haritavanam near Chincholi village in Nirmal district.
Key takeaways
- Monkeys that venture into human habitations would be caught in a phased manner, brought to the centre where they would be operated on for birth control and would be released into the forests again after the rehabilitation period.
- To make the rehabilitation centre a sustainable habitat for the primates, several fruit and flowering plants, a variety of trees that provide shade, and medicinal plants would be grown.
- It is the second such facility for the primates in the country.
- The rehabilitation centre for the monkeys was also the first such facility in south India.
- The other facility in the country was in Himachal Pradesh.
JSA II: Catch The Rain Awareness Generation Campaign
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment
In news
- National Water Mission (NWM), Ministry of Jal Shakti in collaboration with Nehru Yuva Kendra Sangathan (NYKS), Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports launched the “JSA II: Catch the Rain” Awareness Generation Campaign.
Key takeaways
- Nehru Yuva Kendra Sangthan will undertake the campaign covering 623 districts across the nation from December 2020 to March 2021.
- NWM has launched a campaign Catch the rain” with tag line “catch the rain, where it falls, when it falls” in order to nudge all stake-holders to create Rain Water Harvesting Structures (RWHS) to store rain water as rains falling in the four/five months of monsoon are the only source of water for most parts of the country.
Important value additions
The objective of the National Water Mission
- Increase water use efficiency by 20% through regulations, differential entitlements and pricing.
- A considerable share of water needs of urban areas is to be met through recycling of wastewater.
- Water requirements of coastal cities are to be met through the adoption of low-temperature desalination technologies.
- Consult with states to ensure that basin-level management strategies are made to deal with variability in rainfall and river flows due to climate change.
- Enhance storage above and below ground, implement rainwater harvesting.
- Adopt large scale irrigation programmes which rely on sprinklers, drip irrigation and ridge and furrow irrigation.
Preventive measures started against Shigellosis in Kerala
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health
In news
- Health officials in Kozhikode district of Kerala began preventive measures after 6 cases of shigella infection and nearly 24 suspected cases were detected.
Important value additions
- Shigellosis, or shigella infection, is a contagious intestinal infection caused by a genus of bacteria known as shigella.
- The bacteria is one of the prime pathogens responsible for causing diarrhoea, fluctuating between moderate and severe symptoms, especially in children in African and South Asian regions.
- The bacteria, after entering the body through ingestion, attacks the epithelial lining of the colon resulting in inflammation of the cells and subsequently the destruction of the cells in severe cases.
- Symptoms: Diarrhoea (often bloody and painful), stomach pain, fever, nausea and vomiting.
- Transmission: It spreads person-to-person when the bacteria is swallowed accidentally.
- Spread through contaminated food and water is the most common form of transmission across the world.
- Prevention: Wash hands with soap especially after dealing with a child’s diaper and before preparing/eating food.
Status Of Leopards Report released
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; Biodiversity
In news
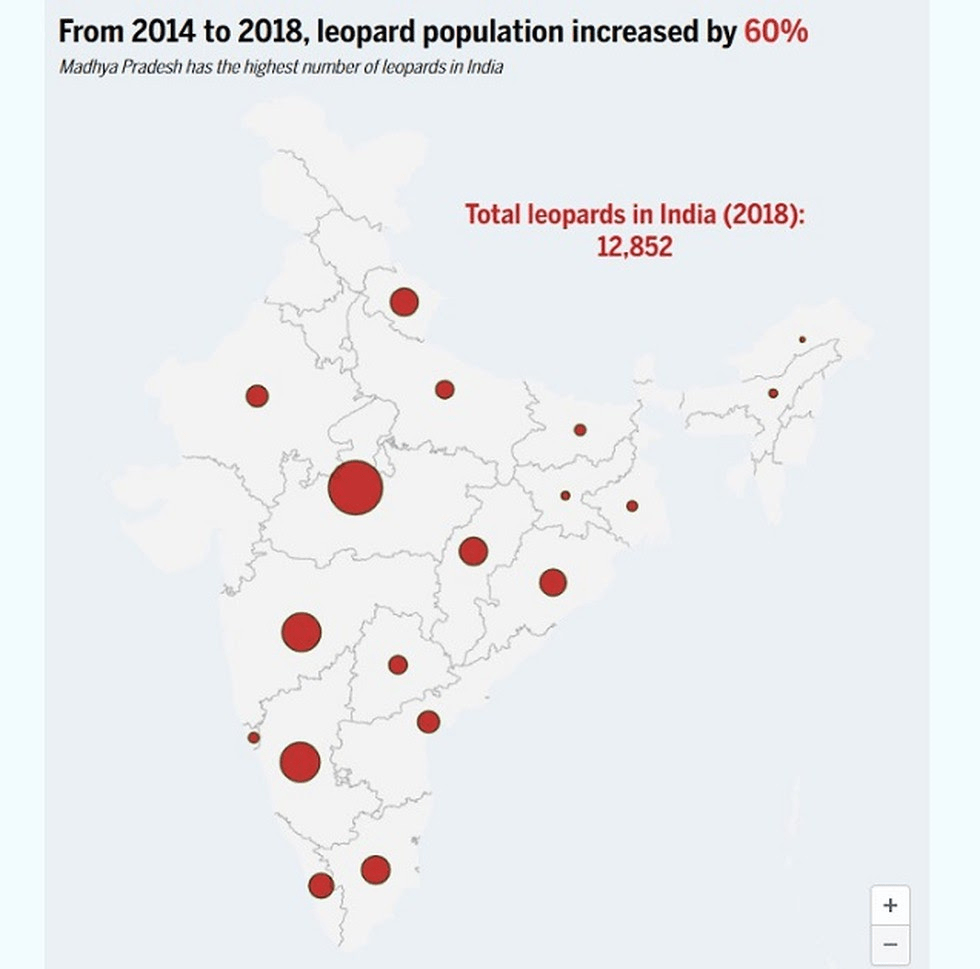
- Union Minister for Environment released the Status of Leopards report.
Key takeaways
- The leopard population has been estimated using camera trapping method.
- There are 12,852 leopards in India as of 2018 as compared to the previous estimate of 7910 conducted in 2014, an increase of 60% in 4 years.
- The highest concentration of the leopard in India is estimated to be in Madhya Pradesh (3,421) followed by Karnataka (1,783) and Maharashtra (1,690).
- Recent meta-analyses of leopard status and distribution suggest 48–67% range loss for the species in Africa and 83–87% in Asia.
- In India, leopards have experienced a possibly human-induced 75-90% population decline in the last ~120-200 years.
- In Indian subcontinent, poaching, habitat loss, depletion of natural prey and conflict are major threats to leopard populations.
- All these have resulted in changing the species status from ‘Near Threatened’ to ‘Vulnerable’ by the IUCN.
- As for region-wise distribution, the highest number of 8,071 leopards were found in central India and eastern ghats.
- In the northeast hills, there are just 141 leopards.
Do you know?
- The leopard was estimated across forested habitats in tiger range areas of the country but other leopard occupied areas such as non-forested habitats, higher elevations in the Himalayas, arid landscapes and majority of North East landscape were not sampled.
- Therefore, the population estimation should be considered as minimum number of leopards in each of the landscapes.
Cattle competing one-horned rhino’s in Assam’s Mini Kaziranga
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; Biodiversity
In news
- Too many cattle are competing against the one-horned rhinos of Assam’s Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary, referred to as ‘Mini Kaziranga’ for nutritious food.
Important value additions
Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary
- It is situated in the flood plains of River Brahmaputra in the district of Morigaon.
- In 1987, Pobitora was declared a wildlife sanctuary.
- It harbors the highest density of Rhinoceros in the world and second highest concentration of Rhinoceros in Assam after Kaziranga National Park.
- It is an Important Bird Area and home for more than 2000 migratory birds and various reptiles.
Firefly bird diverters for Great Indian Bustards
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; Biodiversity
In news
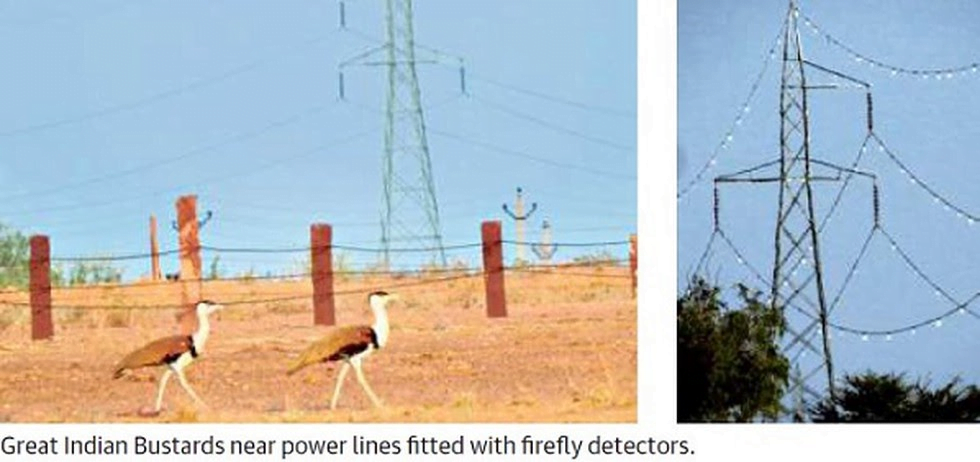
- The Ministry of Environment along with the Wildlife Conservation Society, India, has come up with a unique initiative — a “firefly bird diverter” for overhead power lines in areas where Great Indian Bustard (GIB) populations are found in the wild.

Key takeaways
- The GIB is one of the most critically threatened species in India, with fewer than 150 birds left in the wild.
- It is listed as Critically Endangered in IUCN Red List.
- A 2019 report by the Environment Ministry pointed out that power lines, especially high-voltage transmission lines with multiple overhead wires, are the most important current threat for GIBs in the Thar region, and are causing unsustainably high mortality in about 15% of their population.
Do you know?
- Firefly bird diverters are flaps installed on power lines. They work as reflectors for bird species like the GIB.
- Birds can spot them from a distance of about 50 metres and change their path of flight to avoid collision with power lines.
- The diverters are called fireflies because they look like fireflies from a distance, shining on power lines in the night.
75% districts in India hotspots of extreme climate events
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; Climate change
In news
- Over 75% districts in India, home to more than 63.8 crore people, are hotspots of extreme climate events such as cyclones, floods, droughts, heat and cold waves, according to a study released by the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW).
Key takeaways
- This is the first time that extreme weather event hotspots in the country have been mapped.
- The frequency, intensity, and unpredictability of these extreme events have risen in recent decades.
- While India witnessed 250 extreme climate events in 35 years between 1970 and 2005, it recorded 310 such weather events in only 15 years since then.
- In the last 50 years, the frequency of flood events increased almost eight times.
- Events associated with floods such as landslides, heavy rainfall, hailstorms, thunderstorms, and cloudbursts increased by over 20 times.
- Six of India’s eight most flood-prone districts in the last decade—Barpeta, Darrang, Dhemaji, Goalpara, Golaghat, Sivasagar—are in Assam.
- The yearly average of drought-affected districts increased 13 times after 2005. Nearly 68% of the districts have faced droughts and drought-like situations.
- Drought-affected district hotspots of India in the last decade were Ahmednagar, Aurangabad (both Maharashtra), Anantapur, Chittoor (both Andhra Pradesh), Bagalkot, Bijapur, Chikkaballapur, Gulbarga, and Hassan (all Karnataka).
- The study also found a shift in the pattern of extreme climate events, such as flood-prone areas becoming drought-prone and vice-versa, in over 40% of Indian districts.
Do you know?
- Microclimatic zones, or areas where the weather is different from surrounding areas, are shifting across various districts of India.
- A shift in microclimate zones may lead to severe disruptions across sectors – every 2 degrees C rise in annual mean temperature will reduce agricultural productivity by 15-20%, it has found.
- Reasons behind shift in microclimatic zones: Change in land-use patterns, disappearing wetlands and natural ecosystems by encroachment, and urban heat islands that trap heat locally.
(Mains Focus)
SOCIETY/ HEALTH/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 1,2:
- Social Empowerment
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health and Human Resources.
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Mental Healthcare
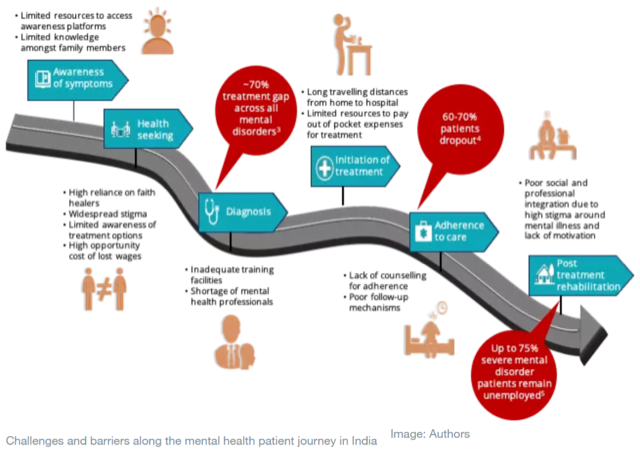
Issues
- Around 15% of India’s population suffer from poor mental health – and the number of people afflicted has been increasing steadily, from 125 million in 1990 to 197 million in 2017.
- Suicide ranks as the second-biggest cause of death among Indian adults of working age.
- India spent less than 1% of its total healthcare budget on mental health in 2017.
- Underutilization of funds, low prioritization of mental health by individual Indian states, and low coverage of health insurance for mental, neurological and substance use (MNS) disorders.
- The COVID-19 pandemic has only underscored the need for additional financing of mental health services.
Way Ahead
- Effective and innovative mental health interventions can be scaled up quickly in order to improve mental healthcare delivery in India.
- Embedding the awareness and detection of mental health problems
- Counselling and referral into well-defined care pathways through frontline workers at the community level.
- Conducting behavioural change communication campaigns to destigmatize mental health issues and to present options for care for both patients and caregivers.
- Enabling anonymous methods of seeking help, such as helplines or apps.
- Improving accessibility by leveraging digital tools and technologies.
- Strengthening mental health service delivery at the primary and secondary care levels.
- Using mobile-based (digital) decision support systems to improve patient management.
- Improving adherence to care through psycho-social education
- Setting up follow-up mechanisms or changes of treatment regimen with increased adherence.
- India needs impact financing for mental healthcare to complement public funding and for mobilizing resources from private sector and philanthropy, to bring innovative mental healthcare delivery models to scale.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding Gatka:
- Gatka originates from the state of Rajasthan.
- It is used both as Self defence and a sport.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Thang Ta is a martial art of which of the following state of India?
- Manipur
- Mizoram
- Tripura
- Assam
Q.3 Gastrodia agnicellus is a newly discovered orchid named “the ugliest orchid in the world.” Which of the following is incorrect about it?
- It was found in a forest in Madagascar
- It feeds on insects.
- It has no leaves.
- It is regarded as a threatened species
Q.4 Consider the following statements:
- Navy’s Information Fusion Centre for the Indian Ocean Region (IFC-IOR) is meant to promote Maritime Domain Awareness.
- Mauritius, Seychelles and Sri Lanka have been integrated into India’s coastal radar chain network.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 22nd December 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | A |
| 4 | A |











