IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Nai Roshni: A scheme for Leadership Development of Minority Women
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- I – Society & GS- II – Policies and Interventions
In news
- “Nai Roshni”, a scheme for Leadership Development of Minority Women is being implemented across India.
- Ministry: Ministry of Minority affairs
Key takeaways
- Aim: To empower and instill confidence in women by providing knowledge, tools, and techniques for interacting with Government systems, banks, and other institutions at all levels.
- This includes empowerment of the trainee women so that they become independent and confident members of society.
- The scheme provides for six days training programme followed by handholding for one year.
- The training covers issues relating to women viz. The leadership of Women through participation in decision making, Educational Programmes for women, Health and Hygiene, Legal rights of women, Financial Literacy, Digital Literacy, Swachh Bharat, Life Skills, and Advocacy for Social and Behavioural change.
- The Scheme is being implemented through NGOs enrolled under the Nai Roshni Scheme.
Do you know?
- In Seekho Aur Kamao (Learn & Earn) Scheme, 33% of the total beneficiaries are women.
- Similarly in the Nai Manzil scheme, 30% of the total beneficiaries are women.
- These schemes help in the economic empowerment of the Minority women
Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- III – Environment & GS- I – Geography
In news
- A glacier break is suspected to have caused the flash floods in Uttarakhand’s Chamoli.
Important value additions
- When glaciers melt, the water in glacial lakes accumulates behind loose, natural “glacial/moraine dams” made of ice, sand, pebbles, and ice residue.
- A GLOF refers to the flooding that occurs when the water dammed by a glacier or a moraine is released suddenly.
- Unlike earthen dams, the weak structure of the moraine dam leads to the abrupt failure of the dam on top of the glacial lake, which holds a large volume of water.
- A failure of the dam has the potential of releasing millions of cubic metres of water in a short period, causing catastrophic flooding downstream.
- NDMA has recommended the use of Synthetic-Aperture Radar imagery to automatically detect changes in water bodies, including new lake formations, during the monsoon months.
Reasons
- Glacial retreat due to climate change occurring in most parts of the Hindu Kush Himalaya has given rise to the formation of numerous new glacial lakes, which are the major cause of GLOFs.
- An “Inventory and Monitoring of Glacial Lakes / Water Bodies in the Himalayan Region of Indian River Basins” found that there are 352, 283, and 1,393 glacial lakes and water bodies in the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra basins respectively.
Do you know?
- Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes.
- SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide finer spatial resolution than conventional beam-scanning radars.
JATP – Center Of Excellence (JATP – CoE)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- III – Sci & Tech
In news
- DRDO signed an MoU with the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru for the creation of JATP–Center of Excellence (JATP – CoE) in the premises of IISc to expand the scope and objective of the existing Joint Advanced Technology Program.
Key takeaways
- The JATP-CoE will enable Directed Basic & Applied Research and engage with premier research institutes through multi-disciplinary & multi-institutional collaboration.
- The focused research efforts at the centre will lead to realization of indigenous technologies in the critical areas to develop state of art technologies.
- As per the MoU, DRDO will support JATP in equipping it with advanced and unique research facilities that will enable the faculty and scholars to conduct advanced research.
- DRDO will facilitate advanced research to utilize technology outcomes in futuristic applications.
Do you know?
- JATP was created by President of India Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam in 1983 where the DRDO scientists actively collaborated with the faculty of IISc to work on various missile technologies.
Measures by the Government to preserve and promote the traditional cultural heritage of India
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- I – Culture
In news
- Minister of Culture and Tourism informed Parliament about the Measures taken by the Government to preserve and promote the traditional cultural heritage of India.
Key takeaways
- The Ministry of Culture formulated a scheme titled “Scheme for Safeguarding the Intangible Heritage and Diverse Cultural Traditions of India”.
- The objective of the scheme: Promoting the rich Intangible Cultural Heritage of India.
- India has successfully inscribed 13 Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) elements in the UNESCO Representative List of Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity under the 2003 Convention.
- As the first step towards the making of a National Inventory of ICH, the Ministry of Culture (MoC) has put up a list on its website called “National list for ICH”
- The National list of ICH is an attempt to recognize the diversity of Indian Culture embedded in its Intangible Heritage.
Important value additions
- Following UNESCO’s 2003 Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage, this list has been classified into five broad domains in which Intangible Cultural Heritage is manifested:
-
- Oral traditions and expressions, including language as a vehicle of the Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Performing Arts
- Social practices, Rituals, and Festive events
- Knowledge and practices concerning nature and the Universe
- Traditional Craftsmanship
Related article:
- Culture related terms: Click here
- Hawker Culture in Singapore: Click here
USA plans to re-engage with United Nations Human Rights Council
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- II – International Relations
In news
- The USA has announced plans to re-engage with the much-maligned UN Human Rights Council that the former President withdrew from almost three years ago.
Important value additions
- The Human Rights Council is an inter-governmental body within the United Nations system.
- Location: Geneva.
- Establishment: It was founded in 2006.
- It replaced the former United Nations Commission on Human Rights (UNCHR) that had been strongly criticised for allowing countries with poor human rights records to be members.
- Functions: (1) It investigates allegations of breaches of human rights in UN member states; (2) It also addresses important thematic human rights issues such as freedom of expression, women’s rights, LGBT rights, and the rights of racial and ethnic minorities.
- The UNHRC works closely with the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR).
- Membership: 47 Member States elected by the UN General Assembly.
- The Council’s Membership is based on equitable geographical distribution.
- Members of the Council serve for three years and are not eligible for immediate re-election after serving two consecutive terms.
- India has been elected to the UNHRC for three years beginning January 1, 2019.
- India had previously been elected to the UNHRC for the 2011-2014 and 2014-2017 terms.
World Sustainable Development Summit 2021
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- III – Environment
In news
- The Indian Prime Minister will inaugurate the World Sustainable Development Summit 2021 on 10th February.

Important value additions
- Theme: Redefining our common future: Safe and secure environment for all.
- It is the 20th edition of The Energy and Resources Institute’s (TERI) flagship event
- The Summit will bring together a wide number of governments, business leaders, academicians, climate scientists, youth, and civil society in the fight against climate change.
- key partners of the Summit: India’s Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change, Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, and Ministry of Earth Sciences
Place in the news: Dhekiajuli
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- I – Modern History
In news
- Indian Prime Minister recently paid a visit to the historic martyr town of Dhekiajuli in Assam, to lay the foundation stone for two medical colleges and launch a road and highway project.
Important value additions
- Dhekiajuli is associated with the Quit India Movement of 1942.
- Dhekiajuli was home to possibly the youngest martyr of the Indian freedom struggle.
- On September 20, 1942, as part of the Quit India movement, processions of freedom fighters marched to various police stations across several towns in Assam.
- These squads, which were known as ‘Mrityu Bahini’, or death squads, had wide participation — including women and children — and set out to unfurl the tricolor atop police stations, seen as symbols of colonial power.
- The British administration came down heavily on them.
- In Dhekiajuli, at least 15 people were shot dead, three of them women, including the 12-year-old Tileswari Barua.
Do you know?
- September 20 has for long been observed as Martyrs’ Day in Dhekiajuli town.
- Recently, the Dhekiajuli police station was accorded heritage status and restored by the Assam government.
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ POLITY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Constitutional bodies and their responsibilities
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment; Government Budgeting
Fifteenth Finance Commission (15th FC)
Context: In Nov 2017, this 15th Finance Commission was set up. The recommendations of the 15th Finance Commission will cover a period of five years starting from 1st April 2020. This Commission was headed by Shri N.K.Singh, former Member of Parliament and former Secretary to the Government of India.
The commission was required to submit two reports, one for 2020-21 and the second covering the period of five years from 2021-22 to 2025-26
Basis for extension
- First, the abolition of Statehood to Jammu and Kashmir required the Commission to make an estimation excluding the Union Territory.
- Second, the deceleration in growth and low inflation has substantially slowed down the nominal GDP growth making projections for medium term risky.
- Finally, poor revenue performance of tax collection and more particularly Goods and Services Tax combined with the fact that the compensation agreement to the loss of revenue to the States was effective only two years of the period of 15FC posed uncertainties
If not for extension, making medium-term projections in the current scenario would have entailed serious risks.
For Interim Report on 2020-21: Click here
Key Points of the 15th Finance Commission report for 2021-26 tabled in Parliament are
- Vertical Devolution -Devolution of Taxes of the Union to States-
- It has recommended maintaining the vertical devolution at 41% – the same as in its interim report for 2020-21.
- It is at the same level of 42% of the divisible pool as recommended by the 14th Finance Commission.
- It has made the required adjustment of about 1% due to the changed status of the erstwhile State of Jammu and Kashmir into the new Union Territories of Ladakh and Jammu and Kashmir
- In XVFC’s assessment, gross tax revenues for 5-year period is expected to be 135.2 lakh crore. Out of that, Divisible pool (after deducting cesses and surcharges & cost of collection) is estimated to be 103 lakh crore.
- States’ share at 41 per cent of divisible pool comes to 42.2 lakh crore for 2021-26 period.
- Including total grants of Rs. 10.33 lakh crore (details later) and tax devolution of Rs. 42.2 lakh crore, aggregate transfers to States is estimated to remain at around 50.9 per cent of the divisible pool during 2021-26 period.
- Total XVFC transfers (devolution + grants) constitutes about 34 per cent of estimated Gross Revenue Receipts of the Union leaving adequate fiscal space for the Union to meet its resource requirements and spending obligations on national development priorities.
- Horizontal Devolution (Allocation Between the States):
- For horizontal devolution, it has suggested 12.5% weightage to demographic performance, 45% to income, 15% each to population and area, 10% to forest and ecology and 2.5% to tax and fiscal efforts.
- On horizontal devolution, while XVFC agreed that the Census 2011 population data better represents the present need of States, to be fair to, as well as reward, the States which have done better on the demographic front, XVFC has assigned a 12.5 per cent weight to the demographic performance criterion.
- XVFC has re-introduced tax effort criterion to reward fiscal performance
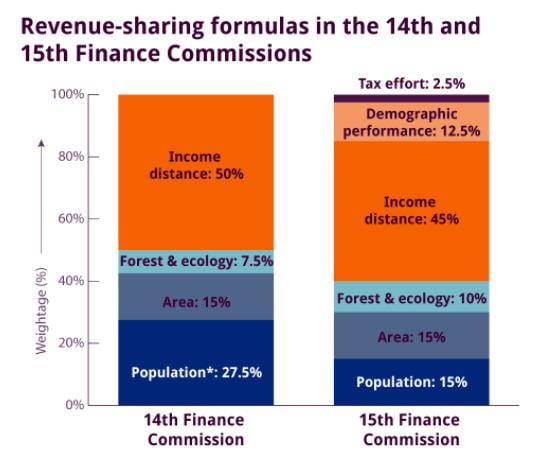
- Revenue Deficit Grants to States:
- Revenue deficit grants emanate from the requirement to meet the fiscal needs of the States on their revenue accounts that remain to be met, even after considering their own tax and non-tax resources and tax devolution to them.
- Revenue Deficit is defined as the difference between revenue or current expenditure and revenue receipts, that includes tax and non-tax.
- It has recommended post-devolution revenue deficit grants amounting to about Rs. 2.94 lakh crores over the five-year period ending FY26.
- The number of states qualifying for the revenue deficit grants decreases from 17 in FY22, the first year of the award period to 6 in FY26, the last year.
- Performance Based Incentives and Grants to States:
These grants revolve around four main themes.
- The first is the social sector, where it has focused on health and education.
- Second is the rural economy, where it has focused on agriculture and the maintenance of rural roads.
- The rural economy plays a significant role in the country as it encompasses two-thirds of the country’s population, 70% of the total workforce and 46% of national income.
- Third, governance and administrative reforms under which it has recommended grants for judiciary, statistics and aspirational districts and blocks.
- Fourth, it has developed a performance-based incentive system for the power sector, which is not linked to grants but provides an important, additional borrowing window for States.
- Fiscal Space for Centre:
- Total 15th Finance Commission transfers (devolution + grants) constitutes about 34% of estimated Gross Revenue Receipts to the Union, leaving adequate fiscal space to meet its resource requirements and spending obligations on national development priorities.
- Provided range for fiscal deficit and debt path of both the Union and States.
- Additional borrowing room to States based on performance in power sector reforms.
- XVFC has recognised that the FRBM Act needs a major restructuring and recommended that the time-table for defining and achieving debt sustainability may be examined by a High-powered Inter-governmental Group.
- This High-powered Inter-Governmental Group could also be tasked to oversee the implementation of the 15th Finance Commission’s diverse recommendations.
- State Governments may explore formation of independent public debt management cells which will chart their borrowing programme efficiently.
- Grants to Local Governments:
- The total size of the grant to local governments should be Rs. 4.3 lakh crore for the period 2021-26.
- Of these total grants, Rs. 8,000 crore is performance-based grants for incubation of new cities and Rs. 450 crore is for shared municipal services.
- A sum of Rs. 2.3 lakh crore is earmarked for rural local bodies, Rs.1.2 lakh crore for urban local bodies and Rs. 70,051 crore for health grants through local governments.
- Urban local bodies have been categorised into two groups, based on population, and different norms have been used for flow of grants to each, based on their specific needs and aspirations.
- Basic grants are proposed only for cities/towns having a population of less than a million. For Million-Plus cities, 100 per cent of the grants are performance-linked through the Million-Plus Cities Challenge Fund (MCF)
- MCF amount is linked to the performance of these cities in improving their air quality and meeting the service level benchmarks for urban drinking water supply, sanitation and solid waste management.
- Health
- XVFC has recommend that health spending by States should be increased to more than 8 per cent of their budget by 2022.
- Given the inter-State disparity in the availability of medical doctors, it is essential to constitute an All India Medical and Health Service as is envisaged under Section 2A of the All-India Services Act, 1951.
- The total grants-in-aid support to the health sector over the award period works out to Rs. 1 lakh crore, which is 10.3 per cent of the total grants-in-aid recommended by XVFC. The grants for the health sector will be unconditional.
- XVFC has recommend health grants aggregating to Rs. 70,051 crore for urban health and wellness centres (HWCs), building-less sub centre, PHCs, CHCs, block level public health units, support for diagnostic infrastructure for the primary healthcare activities and conversion of rural sub centres and PHCs to HWCs. These grants will be released to the local governments.
- Defence and Internal Security
- The Union Government may constitute in the Public Account of India, a dedicated non-lapsable fund, Modernisation Fund for Defence and Internal Security (MFDIS). The total indicative size of the proposed MFDIS over the period 2021-26 is Rs. 2.3 lakh crore.
- Disaster Risk Management
- Mitigation Funds should be set up at both the national and State levels, in line with the provisions of the Disaster Management Act.
- The Mitigation Fund should be used for those local level and community-based interventions which reduce risks and promote environment-friendly settlements and livelihood practices.
- XVFC has recommended the total corpus of Rs.1.6 lakh crore for States for disaster management for the duration of 2021-26, of which the Union’s share is Rs. 1.2 lakh crore and States’ share is Rs. 37,552 crore.
- XVFC has recommended six earmarked allocations for a total amount of Rs. 11,950 crore for certain priority areas, namely, two under the NDRF (Expansion and Modernisation of Fire Services and Resettlement of Displaced People affected by Erosion) and four under the NDMF (Catalytic Assistance to Twelve Most Drought-prone States, Managing Seismic and Landslide Risks in Ten Hill States, Reducing the Risk of Urban Flooding in Seven Most Populous Cities and Mitigation Measures to Prevent Erosion).
Connecting the dots:
- N K Singh Committee report on FRBM review
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 World Sustainable Development Summit 2021 is being organised in which of the following country?
- India
- Russia
- Japan
- Singapore
Q.2 The headquarter of United Nations Human Rights Council is situated at which of the following?
- Switzerland
- France
- Geneva
- Netherlands
Q.3 Nai Roshni is a scheme under which of the following Ministry?
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Aviation
- Ministry of Finance
- Ministry of Minority Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 9th February 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
On Government’s Disinvestment Policy:
On cutting Trans fats:
About closing the Health gap:











