IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Launch of Tribal TB Initiative
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health
In news
- ‘Tribal TB Initiative’ in pursuit of TB Mukt Bharat was launched recently.
- Ministry: Ministry of Health

Key takeaways
- A Guidance Note on Joint Action Plan for Tuberculosis (TB) Elimination, a Special Edition of Tribal Ministry’s Publication ‘ALEKH’ on TB, and a document on Tribal Tuberculosis (TB) Initiative was also released.
- Over 104 million tribal population lives in India, across 705 tribes, accounting for 8.6 % of India’s population.
- 177 tribal districts were identified as high priority districts where physical remoteness, malnutrition, poor living conditions and lack of awareness contribute to the vulnerability of the tribal population to TB.
- Initially, the activities of the joint plan will focus on 161 districts across 18 identified States.
- This would involve periodic TB active case finding drives and provision of TB Preventive Therapy (IPT) to identified vulnerable population and develop long term mechanisms for vulnerability reduction.
Do you know?
- Lakshadweep and district of Badgam in Jammu and Kashmir have been declared TB Free on World TB Day 2021.
- The government has already increased the Budget allocation for TB in India a four-fold in the last 5 years.
Related articles:
MoU signed for National Clean Air Programme (NCAP)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Environment
In news
- The MoU is signed by representatives of State Pollution Control Boards, Urban Local Bodies and Institutes of Repute (IoRs) for 132 identified cities for implementation of city specific action plans under National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
Important value additions
- NCAP is a long-term, time-bound, national level strategy to tackle air pollution problem across India in a comprehensive manner.
- It targets to achieve 20% to 30% reduction in Particulate Matter concentrations by 2024 (with 2017 as base year).
- A National Knowledge Network comprising leading air quality specialists has also been constituted as a technical advisory group to support activities under NCAP and guide local IoRs in conducting air quality research.
AEG12 inhibits family of viruses
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Biodiversity; Sci & Tech
In news
- According to scientists at the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) and their collaborator, a mosquito protein, called AEG12, strongly inhibits the family of viruses that cause yellow fever, dengue, West Nile, and Zika, and also weakly inhibits coronaviruses,
Key takeaways
- The researchers found that AEG12 works by destabilising the viral envelope, breaking its protective covering.
- The protein does not affect viruses that do not have an envelope.
- At the molecular level, AEG12 rips out the lipids
- The findings could lead to therapeutics against viruses that affect millions of people around the world.
- While the researchers demonstrated that AEG12 was most effective against flaviviruses — the family of viruses to which Zika, West Nile, and others belong — they felt it is possible AEG12 could be effective against SARS-CoV-2.
- But, it will take years of bioengineering to make AEG12 a viable therapy for Covid-19.
2nd Tranche of Commercial Coal Mining
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy
In news
- India launched its 2nd Tranche of auction for commercial coal mining offering 67 mines for sale of coal.
- Union Coal Minister launched the auction process.
Key takeaways
- This is the highest number of mines on offer in a particular tranche of auction after commencement of the auction regime since 2014.
- Out of the total 67 mines offered by the Ministry of Coal, 23 mines are under CM(SP) Act and 44 under MMDR Act.
- The coal mines on offer are spread across 6 States Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh.
Do you know?
Rolling auction
- Government of India is moving towards adopting a ‘Rolling Auction’ mechanism for conducting future auctions.
- Coal is the first mineral resource where Rolling Auction mechanism is being implemented in which a pool of coal blocks will always remain available for auctions.
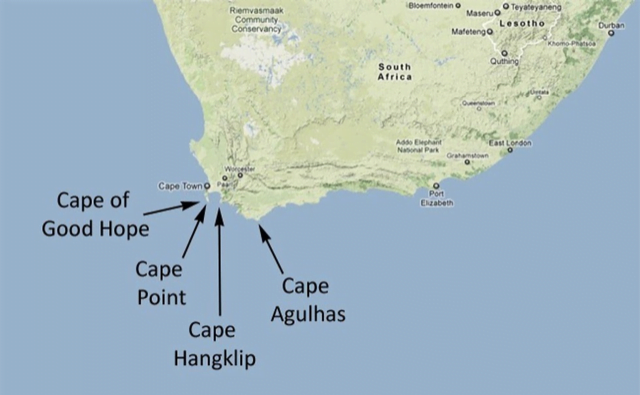
Place in news: Cape of Good Hope
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – I – Geography & GS – III – Economy
In news
- With $200 billion of India’s trade flows with Europe, North America and South America at risk due to the blockage of the Suez Canal, the Department of Commerce is planning re-routing shipments through the Cape of Good Hope.
Important value additions
- The Cape of Good Hope is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
- A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Africa.
- Contemporary geographic knowledge instead states the southernmost point of Africa is Cape Agulhas.
- When following the western side of the African coastline from the equator, however, the Cape of Good Hope marks the point where a ship begins to travel more eastward than southward.
Cape Agulhas
- Cape Agulhas is a rocky headland in Western Cape, South Africa.
- It is the geographic southern tip of the African continent and the beginning of the dividing line between the Atlantic and Indian Oceans.
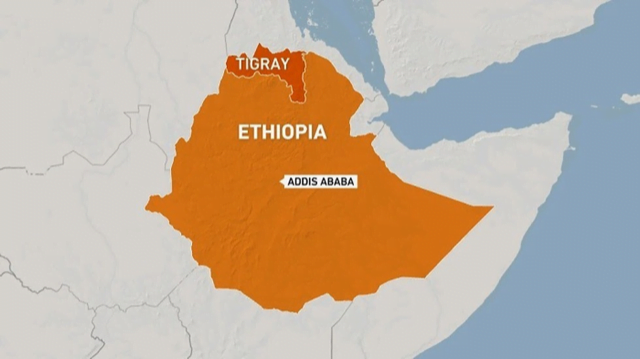
Place in news: Tigray
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – International Relations
In news
- Eritrea will pull its troops out of Ethiopia’s northern Tigray region,
- It is a potential breakthrough in a drawn-out conflict that has seen atrocities carried out against civilians.
Important value additions
- The Tigray Region is the northernmost of the nine regions (kililat) of Ethiopia.
- It is the homeland of the Tigrayan, Irob and Kunama peoples.
- It is also known as Region 1 according to the federal constitution.
- Capital and largest city: Mekelle.
- It is bordered by Eritrea to the north, Sudan to the west, the Amhara Region to the south and the Afar Region to the east and south east.
Do you know?
- The Tigray War is an ongoing armed conflict that began in November 2020 in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia.
- It is fought between the Tigray People’s Liberation Front (TPLF)-controlled Tigray Regional Government, and the Ethiopian National Defense Forces (ENDF).
- The conflict escalated in September, when Tigray held local elections in insubordination of the Ethiopian federal government.
- These elections were considered “illegal” by the federal government, further leading to conflict with Tigray authorities.
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic:
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
- GS-2: India and its neighborhood- relations
India-Bangladesh
Context: In the last decade, India-Bangladesh relations have warmed up, entering a new era of cooperation, and moving beyond historical and cultural ties to become more assimilated in the areas of trade, connectivity, energy, and defence.
| Border Settlement |
|
| Security & Insurgency |
|
| Economic & Trade relations |
|
| Act East Policy |
|
| Tourism |
|
Concerns in India-Bangladesh relations
- Unresolved Teesta water sharing issue looms large.
- Border killings are yet to stop.
- National Register of Citizens across the whole of India reflects poorly on India-Bangladesh relations.
- China, in lieu of its cheque-book diplomacy, is well-entrenched in South Asia, including Bangladesh, with which it enjoys significant economic and defence relations.
Connecting the dots:
INTERNATIONAL/ ECONOMY
Topic:
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
Blockage of Suez Canal
Context: Global trade has been impacted after a container ship got stuck in the Suez Canal.
About Suez Canal
- Located in Egypt, the artificial sea-level waterway was built between 1859 and 1869 linking the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea.
- It offers the shortest route between the Atlantic Ocean and lands around the Indian and western Pacific Oceans.
- The canal is one of the busiest waterways in the world, negating the need to navigate around the Cape of Good Hope in Africa and thus cutting distances by up to 7,000 km.
- Economic Lifeline: The canal continues to be the lifeline for all trade between the West and East as 10 per cent of the global trade passes through it every year. The average 50 ships that pass through it daily carry about $9.5 billion worth of goods, every day.
Suez Canal’s Long History
- The canal has existed in one form or the other since construction started under the reign of Senausret III, Pharao of Egypt (1887-1849 BC). Many kings who ruled later kept improving and expanding this canal.
- Construction picked up pace around 300 years back as maritime trade between Europe and Asia became crucial for many economies.
- In the mid-1800s, French diplomat and engineer Ferdinand de Lesseps convinced the Egyptian viceroy Said Pasha to support the canal’s construction.
- In 1858, the Universal Suez Ship Canal Company was tasked to construct and operate the canal for 99 years, after which rights would be handed to the Egyptian government.
- Despite facing multiple problems ranging from financial difficulties and attempts by the British and Turks to halt construction, the canal was opened for international navigation in 1869.
- The French and British held most of the shares in the canal company. The British used their position to sustain their maritime and colonial interests by maintaining a defensive force along the Suez Canal Zone as part of a 1936 treaty.
Egypt takes over Suez Canal
- In 1954, facing pressure from Egyptian nationalists, the two countries signed a seven-year treaty that led to the withdrawal of British troops.
- In 1956, Egyptian President Abdel Nasser nationalised the Suez Canal to pay for the construction of a dam on the Nile. This led to the Suez Crisis with UK, France and Israel mounting an attack on Egypt.
- The conflict ended in 1957 after the United Nations got involved and was followed by the first instance of the UN Peacekeeping Forces being deployed anywhere in the world.
- In 1967, Nasser ordered the peacekeeping forces out of Sinai leading to a new conflict between the two countries. Israelis occupied Sinai and in response, Egypt closed the canal to all shipping.
- The closure lasted until 1975, when the two countries signed a disengagement accord. The canal was the focal point of the Arab-Israeli War of 1973, with the Arab coalition led by Egypt and Syria.
Impact of longest-ever accidental closure of Suez Canal
- Blocking of all Traffic: On March 23rd, due to weather obstructions a giant container ship, MV Ever Given, en route from China to the Netherlands ended up getting stuck in one of the canal’s narrow stretches, thus blocking all traffic.
- Stress on Global Supply Chain: Over 200 ships are stuck on both sides of the canal putting stress on global supply chains.
- Increased Oil Prices: The long-term impacts of this block will depend on how long it lasts, but some countries have already seen a rise in oil prices after the blockage.
- India- the biggest importer via Suez Canal: India is the top importer of crude oil and products via the Suez Canal, higher than China, South Korea or Singapore. If the issue is not solved early then it will start to have implications on the bigger trade flow and shipping sectors and will begin to affect refining operations on a broader scale
- India-US relations: For India, though, the main hit could be seen on the import and export of ethane with the US, and the imports of crude from Latin America, the uptake of which was recently increased. The longer the closure, the more disruptive the impact is likely to be.
- Global Dependence on this narrow waterway: The incident also raises questions about finding solutions to prevent future accidents and reducing the global dependence on this narrow waterway.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following is the southernmost tip of Africa?
- Cape of Good Hope
- Cape Agulhas
- Cape Hangklip
- Cape Point
Q.2 Tigray region, often seen in news, belongs to which of the following country?
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Sudan
- Libya
Q.3 Tribal TB initiative was launched recently by which of the following?
- Ministry of Health
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs
- Ministry of Science and technology
- Ministry of Economy
ANSWERS FOR 26th March 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | A |
Must Read
On Mumbai COVID-19 hospital fire:
On net zero pledge:











