IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Great Barrier Reef recommended to be added to a list of “in danger” World Heritage Sites
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Climate change
In news
- Recently, the UNESCO World Heritage Committee has recommended that the Australia’s Great Barrier Reef should be added to a list of “in danger” World Heritage Sites.
- It was recommended to add to the list because of the impact of climate change.
- Despite Reef 2050, the coral reef ecosystem has suffered three major bleaching events since 2015 due to severe marine heatwaves.
- The Reef 2050 Long-Term Sustainability Plan is the Australian and Queensland Government’s framework for protecting and managing the Great Barrier Reef by 2050.
- Australia, which is one of the world’s largest carbon emitters per capita, has remained reluctant to commit to stronger climate action and has pointed out jobs as a major reason to continue fossil fuel industries.
- It has not updated its climate goals since 2015.
About Great Barrier Reef
- It is the world’s most extensive and spectacular coral reef ecosystem composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands.
- The reef is located in the Coral Sea (North-East Coast), off the coast of Queensland, Australia.
- It can be seen from outer space and is the world’s biggest single structure made by living organisms.
- This reef structure is composed of and built by billions of tiny organisms, known as coral polyps.
- Polyps are tiny, soft-bodied organisms.
- At their base is a hard, protective limestone skeleton called a calicle, which forms the structure of coral reefs.
- These polyps have microscopic algae called zooxanthellae living within their tissues. The corals and algae have a mutualistic (symbiotic) relationship.
- It was selected as a World Heritage Site in 1981.
Initiatives to Protect Corals
- International Coral Reef Initiative
- Global Coral Reef Monitoring Network (GCRMN)
- Global Coral Reef Alliance (GCRA)
- The Global Coral Reef R&D Accelerator Platform
- The Ministry of Environment and Forests and Climate Change (MoEF&CC), India has included the studies on coral reefs under the Coastal Zone Studies (CZS).
- The Zoological Survey of India (ZSI), with help from Gujarat’s forest department, is attempting a process to restore coral reefs using “biorock” or mineral accretion technology.
- National Coastal Mission Programme, to protect and sustain coral reefs in India.
WHO declares Ebola outbreak in Guinea over
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Health
In news
- Recently, the World Health Organisation (WHO) has declared that the Ebola outbreak that started in February 2021 in Guinea, is over now.
About Ebola Virus Disease (EVD)
- Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) or Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever of humans and other primates caused by ebolaviruses.
- It is transmitted to people from wild animals and spreads in the human population through human to human transmission.
- Ebola virus was first discovered in 1976 near the Ebola River (the present Democratic Republic of Congo)
- Transmission: Fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family are natural Ebola virus hosts.
- Animal to Human Transmission: Ebola is introduced into the human population through close contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected animals such as fruit bats, chimpanzees, gorillas, found ill or dead or in the rainforest.
- Human-to-Human Transmission: Ebola spreads via direct contact (through broken skin or mucous membranes) with:
- Blood or body fluids of a person who is sick with or has died from Ebola.
- Objects that have been contaminated with such body fluids (like blood, feces, vomit).
- Symptoms:
- Fever, Fatigue, Muscle pain, Headache, Sore throat, Vomiting, Diarrhoea, and in some cases, both internal and external bleeding.
- Diagnosis:
- ELISA (antibody-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)
- Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay, etc.
- Vaccines:
- The Ervebo vaccine.
- In May 2020, the European Medicines Agency recommended granting marketing authorization for a 2-component vaccine called Zabdeno-and-Mvabea for individuals 1 year and older.
- Treatment:
- Two monoclonal antibodies (Inmazeb and Ebanga) have been approved for the treatment of Zaire ebolavirus infection in adults and children by the US.
Increase in Direct Tax Collections
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- India’s direct tax collections in the first two and a half months (April – June) of 2021-22 stand at nearly Rs. 1.86 lakh crore, which is double the collections over the same period of last year that was affected by the national lockdown.
- It includes Corporation Tax collections and Personal Income Tax inflows.
- The increase in the direct tax collections is mainly attributed to healthy exports and a continuation of various industrial and construction activities.
- It is expected that GDP will record a double-digit expansion in Quarter 1 of 2021-22.
About Direct Tax
- A direct tax is a tax that a person or organization pays directly to the entity that imposed it.
- An individual taxpayer, for example, pays direct taxes to the government for various purposes, including income tax, real property tax, personal property tax, or taxes on assets.
Government Initiatives to Improve Direct Taxes
- The Finance Act, 2020 has provided an option to individuals and co-operatives for paying income-tax at concessional rates if they do not avail specified exemption and incentive for Personal Income Tax
- Vivad se Vishwas: Under Vivad se Vishwas, declarations for settling pending tax disputes are currently being filed.
- This will benefit the Government by generating timely revenue and also to the taxpayers by bringing down mounting litigation costs.
- For widening the tax base, several new transactions were brought into the ambit of Tax Deduction at Source (TDS) and Tax Collection at Source (TCS).
- These transactions include huge cash withdrawal, foreign remittance, purchase of luxury cars, e-commerce participants, sale of goods, acquisition of immovable property, etc.
- ‘Transparent Taxation – Honoring The Honest’ platform: It is aimed at bringing transparency in income tax systems and empowering taxpayers.
New Doppler Radars in Maharashtra: IMD
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Indigenization of Technology
In news
- Recently, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) announced that it will install seven new doppler radars in Maharashtra, including Mumbai in 2021.
-
- In January 2021, Ministry of Earth Sciences commissioned two of the ten indigenously built X-Band Doppler Weather Radars (DWR) to closely monitor the weather changes over the Himalayas.
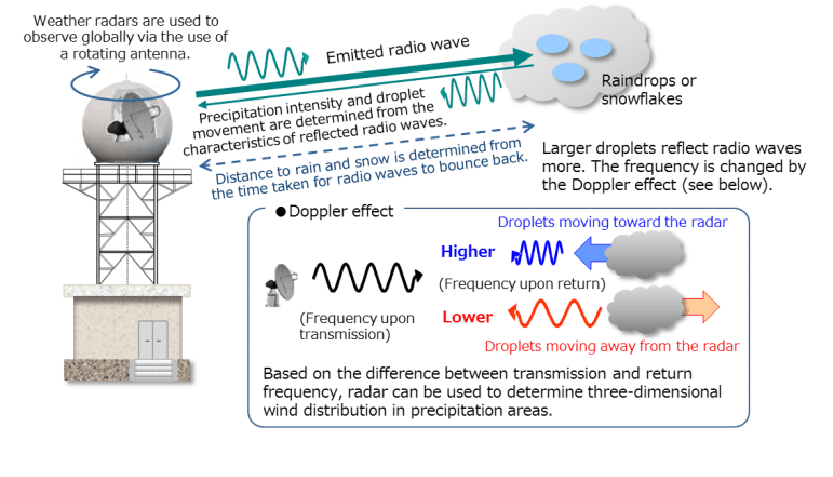
About Doppler Radar
- It is a specialized radar that uses the Doppler effect to produce velocity data about objects at a distance.
- Doppler effect: When the source and the signal are in relative motion to each other there is a change in the frequency observed by the observer.
- If they are moving closer, frequency increases and vice versa.
- Based on Doppler principle the radar is designed to improve precision in long-range weather forecasting and surveillance using a parabolic dish antenna and a foam sandwich spherical radome.
- DWR has the equipment to measure rainfall intensity, wind shear and velocity and locate a storm centre and the direction of a tornado or gust front.
About India Meteorological Department
- It is an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences, established in 1875.
- It is the principal agency responsible for meteorological observations, weather forecasting and seismology.
Pic courtesy: Researchgate
Drone Survey Mandatory for All National Highways Projects
Part of: GS Prelims and GS III – Infrastructure
In news
- The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has made use of drones mandatory for video recording of the national highway projects during different stages of development, construction, operation and maintenance.
- These videos will be saved on NHAI’s portal “Data Lake” to assess the progress made on the projects.
Significance
- Enhance transparency and uniformity.
- The videos can be used during the physical inspection of the projects.
- They can also be used as evidence during the dispute resolution process before Arbitral Tribunals and Courts.
- The mandatory deployment of Network Survey Vehicle (NSV) to carry out road condition surveys on the National Highways will enhance the overall quality of the highways.
About National Highways Authority of India (NHAI)
- NHAI was set up under NHAI Act, 1988.
- It has been entrusted with the National Highways Development Project (NHDP), along with other minor projects for development, maintenance and management.
- NHAI maintains the National Highways network to global standards and in a cost effective manner
NHAI’s Portal “Data Lake”
- NHAI has gone ‘Fully Digital’ with the launch of Data Lake and Project Management Software.
- It is cloud based and Artificial Intelligence powered Big Data Analytics platform
- All project documentation, contractual decisions and approvals are now done through the portal only.
Miscellaneous
4th Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan
- Recently, the Ramgarh Vishdhari wildlife sanctuary received a nod from the National Tiger Conservation Authority’s (NTCA) technical committee to become the 4th Tiger reserve of Rajasthan.
- Other Three Tiger Reserves of Rajasthan:
- Ranthambore Tiger Reserve (RTR) in Sawai Madhopur
- Sariska Tiger Reserve (STR) in Alwar
- Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve (MHTR) in Kota.
- Protection Status of Tiger
- Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- IUCN Red List: Endangered.
- CITES: Appendix I.
- The NTCA was launched in 2005, following the recommendations of the Tiger Task Force.
- It is a statutory body of the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change., with an overarching supervisory/coordination role, performing functions as provided in the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ SCIENCE & TECH
Topic:
- GS-3: Economy, development and challenges
- GS-3: Awareness in the fields of IT, computers, robotics
Robo Sapiens- Future of the Work
Context: A recent study by McKinsey flags that ultimately it is activities rather than jobs that are being automated. $2tn in wages or 45% of work activities in the US could already be automated with existing technologies
Evolution of robots in present times
- Pandemic accelerated adoption of robots: Covid has hastened the adoption of technologies such as AI, chatbots, robot process automation (RPA) in white collar roles and industrial robots in blue collar jobs—all of which could displace 2 billion jobs by 2030
- Rapid pace of AI development: A recent survey of AI researchers places a 50% probability on all human tasks being automated in 45 years where there is a 50:50 likelihood of full AI (human level AI, full breadth of human capabilities) by 2040-50E and a 90% possibility by 2075E.
- Increased Productivity of economy: Robots can function for 24 hours per day and this represents a significant saving of up to 10:1 vs. human labour.
Concerns with emergence of robots/automation:
- Premium on Creative Skills: There will be increased demand for jobs within occupational groups that require social intelligence, creativity and complex problem solving as opposed to repetitive, low dexterity skills.
- Job Losses: Up to 47% of US jobs could be at risk over the next 20 years from computerisation. And in Emerging Markets, this figure could reach 85%.
- Impact on India IT Sector jobs: India-based IT outsourcers, who spearheaded the growth post 1991 reforms, appear to be planning for a 3 million/30% reduction in ‘low-skilled’ roles globally by 2022 because of Robot Process Automation (RPA) upskilling. This represents $100 bn in reduced salary costs.
- Workers disputes: The nature of the work for human are undergoing changes for instance recent decade saw rise of gig jobs rather than 9 t 5 employment. Emergence of robots is also bound to change nature of human jobs which might give rise to regulatory disputes around sick/overtime pay, insurance, worker’s rights, etc
- Global disconnect between labour & Technology: This disconnect is due to the 20th century education practices dating back to the Victorian age which have not kept up with the rapidly changing 21st century workplace
- Reskilling Burden on Governments: Around 100 million Europeans may need to acquire new skills this decade to transition to new jobs. One area of retraining could be from fossil to renewables where in the US, it could cost just $180mn to retrain 90,000 coal workers to work in solar.
Conclusion
Lifelong learning, corporate training and development, vocational education, and massive open online courses (MOOCs) will also be critical tools to future-proofing employment prospects.
Connecting the dots:
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development
- GS-3: Infrastructure: Energy
Power Sector: Issues with DISCOMS
Context: There was a sharp decline in the dues owed by power distribution companies, discoms, to power generating companies as they made use of liquidity facility arranged by the Centre.
Issues
- Sustenance Issues: Improvement in DISCOM’s financial and operational indicators not being sustained calling for another rescue package from centre.
- High AT&C (Aggregate Technical and Commercial) losses, at 21.7%, due to poor or inadequate infrastructure or on account of theft or bills not being generated or honoured.
- Profitability: The gap between discoms’ costs (average cost of supply) and revenues (average revenue realised), supposed to have been eliminated by now, stands at Rs 0.49 per unit due to lack of regular and commensurate tariff hikes.
- Pandemic Impact: With demand from industrial and commercial users falling, revenue from this stream, which is used to cross-subsidise other consumers, has declined, leading to build up of stress on DISCOMS.
- Lack of Data: Even six years after UDAY was launched, various levels in the distribution chain — the feeder, the distribution transformer (DT) and the consumer — have not been fully metered. This lack of data makes it difficult to ascertain the level in the chain where losses are occurring.
Some of the suggestions put forward to alter the status quo are:
- National power distribution company.
- Privatisation of distribution chain.
- Deduct discom dues, owed to both public and private power generating companies, from state balances with the RBI forcing states to take the necessary steps to fix discom finances.
- Linking additional state borrowings to the completion of distribution reforms can incentivise states to act.
Connecting the dots:
- India’s DISCOM Stress – Financial issue and hurdles in timely payment
- Draft of Electricity (Rights Of Consumers) Rules, 2020
- Ujwal DISCOM Assurance Yojana (UDAY)
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 How are coral reefs made?
- From hardened lava from volcanoes
- From rocks that are forced up from the ocean floor
- From hardened sea salt
- From small living organisms call polyps
Q.2 Which of the following recently became the 4th Tiger reserve of Rajasthan?
- Bhadra Wildlife sanctuary
- Chinnar Wildlife sanctuary
- Kutch Desert Wildlife sanctuary
- Ramgarh Vishdhari wildlife sanctuary
ANSWERS FOR 23rd June 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
On Gender Gap in Tech:
On Aviation Sector:
On blended learning:











