IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
LiDAR Based Survey of Forest Areas
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Sci and Tech; Environment
In news
- Recently, the Detailed Project Reports (DPRs) of LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) based survey of forest areas in ten states was released recently.
- Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate change
- The 10 mapped states are: Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Nagaland, and Tripura.
- The project was awarded to WAPCOS in July 2020 at a cost of over Rs. 18 crore for implementation in 26 states.
Key observations
- It is a first of its kind study using LiDAR technology.
- It will help augment water and fodder in jungle areas thereby reducing human-animal conflict.
- States will be given Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA) funds to use in this project.
- One major ridge inside a forest block is identified in these states with an average area of 10,000 ha selected in each State.
Significance of the study
- It will help us in identifying areas which need groundwater recharge
- It will help in catching rainwater and prevent stream run-off
- It will help in recommending different types of Soil & Water conservation structures
About LiDAR
- It is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges & variable distances.
- These light pulses generate precise, three-dimensional information about the shape of the Earth and its surface characteristics.
- It consists of a laser, a scanner, and a specialized Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver.
- Applications:
- Surveying, archaeology, geography, geomorphology, seismology, forestry, etc.
6 Years of Transformative Urban Missions
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Polity and governance
In news
- Recently, the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) organised an online event to commemorate six years of the three transformative Urban Missions vis. Smart Cities Mission (SCM), Atal Mission for Urban Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) and Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U).
| Mission | Details | Progress |
| PMAY-U |
|
|
| AMRUT |
|
|
| SCM |
|
|
The World Drug Report 2021: UNODC
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – health and GS-III – Linkage of organised crime with Terrorism
In news
- Recently, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), in its World Drug Report 2021, has highlighted that the lockdown restrictions during Covid-19 have accelerated drug trafficking using the Internet.
Key findings of the report
- Between 2010-2019, the number of people using drugs increased by 22%, owing in part to an increase in the global population.
- Around 275 million people used drugs worldwide last year, while over 36 million people suffered from drug use disorders.
- Opioids continue to account for the largest burden of disease attributed to drug use.
- A rise in the non-medical use of pharmaceutical drugs was also observed during the coronavirus pandemic.
- In the last 24 years, cannabis potency had increased as much as four times in some parts, even as the percentage of adolescents who perceived the drug as harmful fell by as much as 40%.
- Access to drugs has also become simpler than ever with online sales, and major drug markets on the dark web are now worth some $315 million annually.
- In Asia, China and India are mainly linked to shipment of drugs sold on the 19 major darknet markets analysed over 2011-2020.
About United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
- It was established in 1997 and was named as a United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) in 2002.
- It acts as the Office for Drug Control and Crime Prevention by combining the United Nations International Drug Control Program (UNDCP) and the Crime Prevention and Criminal Justice Division of the United Nations Office at Vienna.
Link between Air Quality and Covid-19
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Health and GS III – Pollution
In news
- For the first time, a pan-India study has found a direct correlation between air pollution and Covid-19.
- The study titled ‘Establishing a link between fine particulate matter (PM2.5) zones and Covid-19 over India based on anthropogenic emission sources and air quality data’ dealt with how people living in highly polluted areas are more vulnerable to coronavirus infections.
- The study found that areas with poor air quality and higher emissions of particulate matter (PM) 2.5 are more likely to have Covid-19 infections and related deaths.
- The study was conducted by scientists from various universities such as Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, National Institute of Technology Rourkela; IIT, Bhubaneswar.
- It was partially funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, the Government of India.
The study involves three kinds of data sets
- National Emission Inventory (NEI) of PM2.5 for 2019, developed by the scientists;
- Number of Covid-19 positive cases and corresponding death as of 5th November, 2020.
- Air quality index data (in-situ observations).
Important Observations
- The regions using huge amounts of fossil fuels such as petrol, diesel and coal by combustion in transport and industrial activities also experience a far higher number of Covid-19 cases.
- The novel coronavirus sticks to fine particles like PM2.5 allowing them to move from one part to another by making the airborne transmission of Covid-19 more effective.
About Particulate Matter (PM) 2.5
- It is an atmospheric particulate matter of diameter of fewer than 2.5 micrometres, which is around 3% the diameter of a human hair.
- It is very small and can only be detected with the help of an electron microscope.
- It causes respiratory problems and also reduces visibility.
- It is an endocrine disruptor that can affect insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity, thus contributing to diabetes.
- These particles are formed as a result of burning fuel and chemical reactions that take place in the atmosphere.
- Natural processes such as forest fires also contribute to PM2.5 in the air.
- These particles are also the primary reason for the occurrence of smog.
INS Vikrant: First Indigenous Aircraft Carrier
Part of: GS Prelims and GS III – Defence and Security
In news
- Recently, the ongoing work on the Indigenous Aircraft Carrier (IAC), INS Vikrant (IAC-1) was reviewed, which is a part of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- INS Vikrant, is likely to be commissioned in 2022.
- At present, India has only one aircraft carrier, the Russian-origin INS Vikramaditya.
About INS Vikrant (IAC-1)
- The vessel, to be named Vikrant after the decommissioned maiden carrier of the Navy.
- It will have an air component of 30 aircraft, comprising MiG-29K fighter jets, Kamov-31 airborne early warning helicopters and the soon-to-be-inducted MH-60R multi-role helicopter, besides the indigenous Advanced Light Helicopters.
- The shipborne weapons include Barak LR SAM and AK-630, while it has MFSTAR and RAN-40L 3D radars as sensors.
- It has a pair of runways and a ‘short take off but arrested recovery’ system to control aircraft operations.
Significance
- The combat capability, reach and versatility of the aircraft carrier will add formidable capabilities in the defence and help secure India’s interests in the maritime domain.
- It would offer an incomparable military instrument with its ability to project air power over long distances.
Miscellaneous
Ambergris
-
Recently, the Mumbai Police has arrested five people and seized nearly 9 kg of Ambergris.
- Ambergris (French for grey amber) is generally referred to as whale vomit.
- It is a solid waxy substance originating in the intestine of the sperm whale.
- Ambergris is produced only by an estimated 1% of sperm whales.
- It is used in the perfume market, especially to create fragrances like musk.
- It is believed to be in high demand in countries like Dubai that have a large perfume market.
- It is also believed to be used in some traditional medicines and as a spice.
- The sperm whale is a protected species, hunting of the whale is not allowed.
- Sperm whales are found in temperate and tropical waters throughout the world.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: schedule I
(Mains Focus)
INTERNATIONAL/ ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
U.S. readying New Rules for the Tech Giants
Context: Recently, the U.S. House of Representatives Judiciary Committee voted to advance six Bills outlawing business practices that sit at the core of tech companies such as Google, Facebook, Amazon and Apple.
- These Bills constitute the biggest action to come out of the anti-trust scrutiny these companies have been facing in the U.S. over the last few years.
- While many nations have taken legal or legislative routes to limit the influence of the Big Four, this is the first major move on their home turf.
What is anti-trust?
- Anti-trust is an American term for laws meant to prevent unfair business practices such as monopolisation, which leads to fewer choices for consumers and higher prices.
Example of Anti-Trust – Microsoft
- Microsoft was sued in 1998 for giving away the Internet Explorer web browser for free with its Windows operating system, which led to the collapse of browser-maker Netscape.
- Microsoft was found guilty of using its market dominance in operating systems to build a monopoly in browsers and was forced to open up Windows to other developers.
Problem of Anti-Trust with new age companies
- Currently rise in consumer prices is the accepted indicator of unfair practices.
- However, the actions of companies like Google and Facebook that make money off advertising and give many products away for free, makes it difficult to gauge the anti-competitive practices of them
- The new package of six Bills that is now in Congress is an attempt to add more teeth to anti-trust proceedings against new-age tech firms.
What’s in the Bills?
- The Platform Competition and Opportunity Act would prevent big tech companies from nipping competition in the bud by buying up smaller rivals, like what Facebook had done by buying up Instagram for $1 billion.
- The Ending Platform Monopolies Act would prevent companies from becoming players on their own platforms, like how Amazon sells its own brands, competing with smaller retailers that use its e-commerce platform; Apple’s chokehold over developers on App Store is another example.
- The Augmenting Compatibility and Competition by Enabling Service Switching (ACCESS) Act promotes interoperability, forcing platforms to let users take data such as contacts lists and profile information with them while migrating to other platforms.
- The Merger Filing Fee Modernization Act increases the government fee on large corporate mergers to help fund anti-trust law enforcement.
- The American Innovation and Choice Online Act would prevent companies from giving preferences to their own products in the marketplaces they run, such as Google search results prioritising YouTube videos or Amazon highlighting its own brands.
- The State Antitrust Enforcement Venue Act would prevent companies from shifting anti-trust cases to courts that could be favourable to them.
How will the move impact India?
- Ripple Effect: Any behavioural change that these companies may be forced to adopt in the U.S, which is their largest market, would likely be adopted in all their global markets as well.
- More Teeth to similar Indian Laws: India already has versions of some of these laws such as the one that prevents Amazon from selling brands that it owns on its platform. Such rules & laws will get further legitimacy when US passes its bills.
- Level Playing Field: If implemented globally, a level playing field for brand visibility on Google and Amazon will benefit retailers in India.
Connecting the dots:
- Dominance of Big tech
- Australia’s News Media Bargaining Code
- Google’s Search Monopoly
POLITY/ GOVERNANCE/ SECURITY
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Current Challenges of Indian Economy
Context: As the Indian economy is completing the first quarter of the current financial year, policy makers need to understand the current challenges which Indian economy is facing so to take remedial measures.
Let’s have a look at the current challenges.
1: Two years worth of GDP growth has been lost
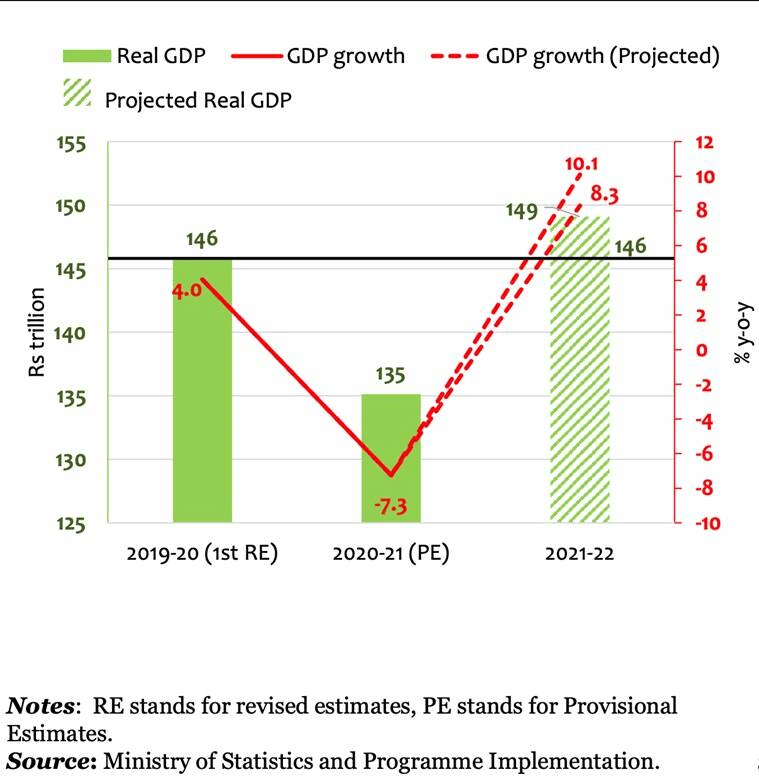
Image Source: Indian Express
- In 2019-20, India’s GDP was Rs 146 trillion. In other words, India had produced goods and services worth Rs 146 trillion that year.
- Then, in the last financial year — that is, in 2020-21 — it fell to Rs 135 trillion.
- In the current financial year — that is, in 2021-22 — the GDP is expected to grow back to Rs 146 trillion after registering a growth of 8.3%.
- This would mean that, in terms of overall economic production, India would have lost two full years of growth.
- if there was no Covid disruption and India grew by even 6% in both these years, the total GDP would have reached the level of Rs 164 trillion — that is, Rs 18 trillion more than where India is likely to end up now.
2. Both retail and wholesale inflation is trending up
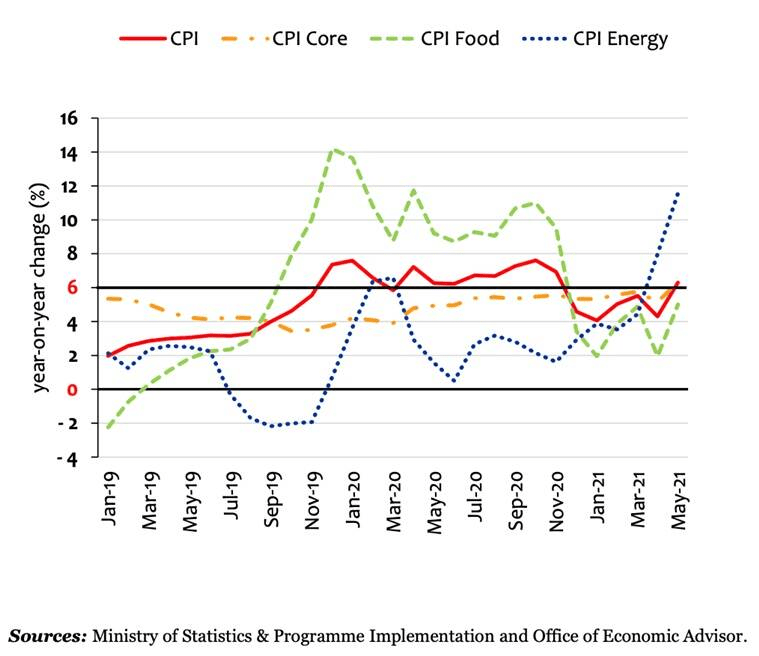
Image Source: Indian Express
- Headline retail inflation stayed above the RBI’s comfort zone (2% to 6%) between November 2019 and November 2020. But, after a brief period of relief, it has again crossed the 6%-mark in May this year.
- Even the core inflation —calculated by taking away the price rise in fuel and food items- has remained consistently close to RBI’s upper limit.
- In May, WPI inflation was nearly 13%. In other words, even the wholesale prices were rising at the rate of 13%.
3: Poor credit offtake in the commercial sector
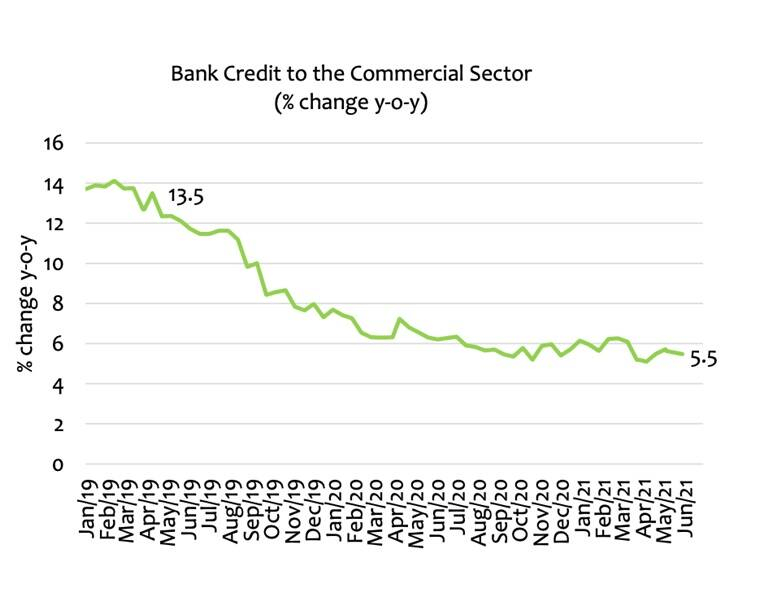
Image Source: Indian Express
- The biggest engine of GDP in the Indian economy is the expenditure that Indians undertake in their private capacity. This demand for goods and services accounts for more than 55% of all GDP in a year.
- Even before Covid, the Indian economy had reached a stage where the common man was holding back this expenditure.
- The Covid pandemic has made that trend worse with people either losing jobs or salaries being reduced in the midst of increased health expenses.
- In the absence of consumer spending, the country’s businessmen — both big and small — are holding back new investments and refusing to seek new loans.
4: Inadequate spending by the government
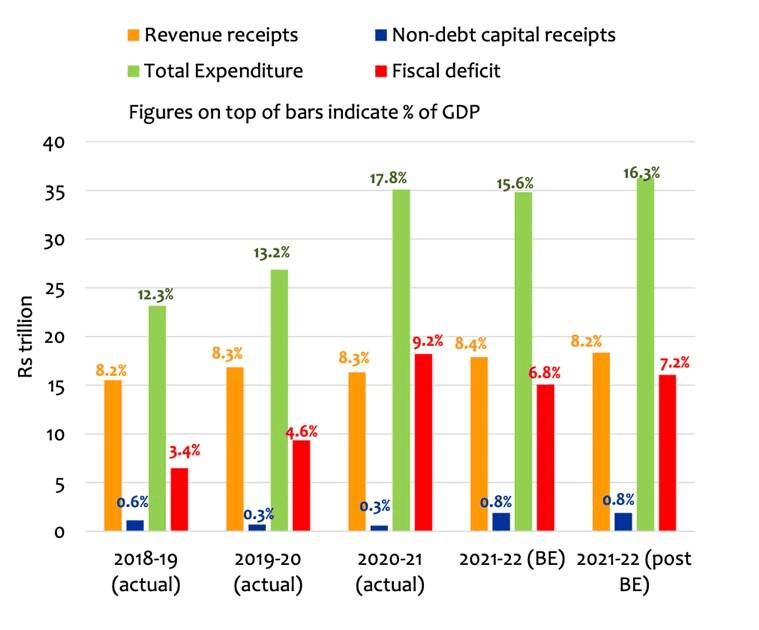
Image Source: Indian Express
- Given that domestic consumers are holding back consumption and domestic businesses are holding back investments (the second-biggest engine of GDP growth), it was incumbent on the third-biggest engine of India’s GDP growth — that is, the government — to spend more and pull the economy out of the current slowdown.
- After being forced to spend more in 2020-21, the government has actually pulled back (as a proportion of GDP) in 2021-22. It is for this reason that its deficit will fall in FY22 as against FY21.
Conclusion
The impacts of this [Covid shock] are more long term than one might imagine and the government has to take expansionary fiscal policy so as to revive the economy.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding LiDAR:
- It is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges & variable distances.
- These light pulses generate precise, three-dimensional information about the shape of the Earth and its surface characteristics.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), in its World Drug Report 2021
- Opioids continue to account for the largest burden of disease attributed to drug use.
- A rise in the non-medical use of pharmaceutical drugs was also observed during the coronavirus pandemic.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 WHich of the following is IUCN Red List status of Sperm Whale?
- Vulnerable
- Endangered
- Least concern
- Extinct
ANSWERS FOR 26th June 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
On LGBTQ+:
On Hunger & Climate Change:
On Police Reforms:














