IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Launch of Revamped Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Health
In news
- Revamped Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS), Umbrella schemes of Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi (RAN) and Discretionary Grant (HMDG) on National Health Authority (NHA)’s IT platform were recently launched.
- Ministry: Ministry of Health
- Objective: For providing cashless, paperless and citizen-centric services.
Key takeaways
Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS):
- It is a comprehensive Health Scheme for Serving Employees, Pensioners, Members of Parliament, ex-MPs, etc., and their dependent family members.
- During the last 7 years it has expanded to 72 Cities.
- E-referral module developed by NIC has enabled CGHS dispensaries and wellness centres to issue online referral to empanelled hospitals.
Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi (RAN)
- Under RAN, financial assistance up to Rs 15 lakhs is provided to poor patients suffering from major life-threatening diseases for treatment at Government hospitals.
- The eligibility criteria to avail services under RAN had been based on State/UT-wise BPL threshold.
Health Minister’s Discretionary Grant (HMDG)
- Under HMDG a maximum amount of Rs.1.25 lakhs is provided to patients whose annual income is less than Rs.1.25 lakhs.
- Beneficiaries can apply for financial assistance under both schemes by providing their Ration card number
World Milk Day observed
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Economy
In news
- A virtual program organised on the occasion of World Milk Day was chaired by Union Minister for Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying.
- 1st June is observed as World Milk Day every year.
Key takeaways
- On the occasion, the launch of Gopal Ratna Awards were announced.
- E-Gopala App will be integrated with UMANG platform and users of Umang platform will get access to App.
- e-GOPALA app (Generation of wealth through Productive Livestock) is a comprehensive breed improvement marketplace and information portal for direct use of farmers.
Important value additions
Milk sector in India
- India is the world’s largest milk producer and accounts for over one-fifth of the global milk production.
- Other major producers: USA, China, Pakistan and Brazil.
- Value of output of milk is more than the value of output of wheat and paddy together
Initiatives launched to provide major fillip to the SATAT initiative
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Economy
In news
- Union Minister of Petroleum & Natural Gas launched a number of initiatives to provide major fillip to the SATAT initiative in a virtual ceremony.
Important value additions
- Aim of SATAT scheme: To set up Compressed Bio-Gas (CBG) production plants and make CBG available in the market for use as a green fuel.
- ‘SATAT’ aims to target production of 15 MMT of CBG from 5000 plants by 2023.
- It has the potential to boost availability of affordable transport fuels, better use of agricultural residue, cattle dung and municipal solid waste.
- It will also provide an investment of 1.75 lakh crore, an additional revenue source to farmers, and 75,000 direct job opportunities and lakhs of indirect jobs.
RDSO becomes first Institution to be declared SDO
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- RDSO (Research Design & Standards Organization) of Indian Railways has become the FIRST Institution to be declared Standard Development Organisation (SDO) under “One Nation One Standard” mission of BIS ( Bureau of Indian Standards)
Key takeaways
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), which is the National Standards Body, has launched a scheme which provides for “Recognition of SDO” to attain “One Nation One Standard” vision of Government of India.
- Aim of the scheme: Aggregating and integrating the existing capabilities and dedicated domain specific expertise of various organizations in India which are engaged in standards development in their specific sectors.
- It will also enable convergence of all standard development activities resulting in “One National Standard for One Subject”.
- Research Designs & Standards Organization (RDSO), Lucknow, is the only Research & Development Wing of Ministry of Railways.
Species in news: Litoria Mira
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Environment; Biodiversity
In news
- A species of frog lives in the rainforests of New Guinea that appears to be made from chocolate.
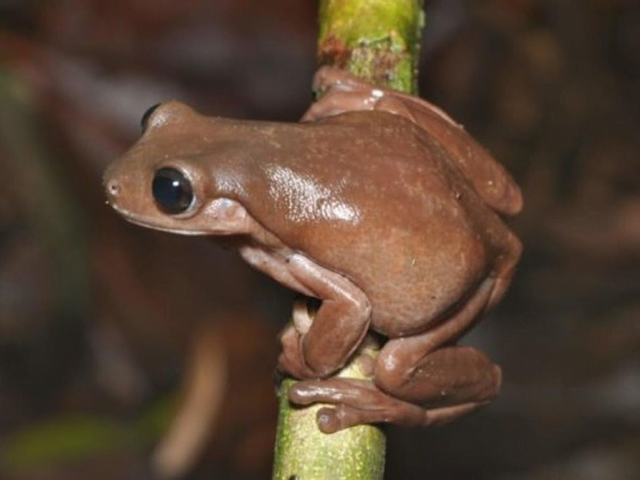

- The cocoa-coloured frogs have turned out to be a new species.
- It is called Litoria Mira.
- It is an undescribed member of the Australian Litoria genus of tree frogs.
- Litoria mira can be distinguished from all other Litoria by its unique combination of moderately large size, webbing on hand, short limbs, and small violet patch of skin on the edge of its eyes.
- The island of New Guinea is separated from the ‘horn’ of Queensland by the Torres Strait.
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ SOCIETY
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
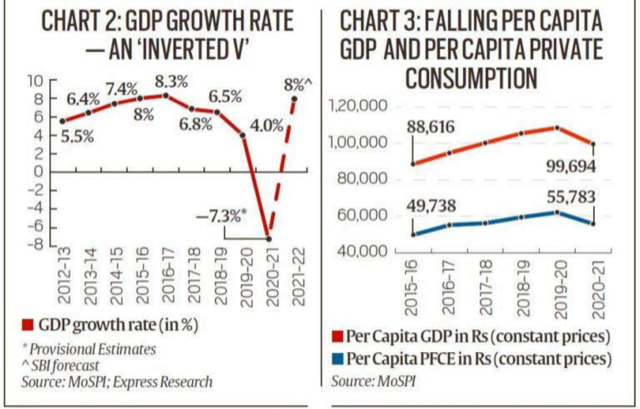
India’s GDP fall
Context: India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) contracted by 7.3% in 2020-21. Between the early 1990s until the pandemic hit the country, India grew at an average of around 7% every year.
There are two ways to view this contraction in GDP.
- One is to look at this as an outlier — after all, India, like most other countries, is facing a once-in-a-century pandemic.
- The other way would be to look at this contraction in the context of what has been happening to the Indian economy over the last decade — and more precisely over the last seven years
Perhaps the best way to arrive at such a conclusion is to look at the so-called fundamentals of the economy.
| Gross Domestic Product |
|
| GDP per capita (GDP divided by the total population) |
|
| Unemployment rate |
|
| Inflation rate |
|
| Fiscal deficit |
|
| Rupee vs dollar |
|
What’s the outlook on growth?
- The biggest engine for growth in India is the expenditure by common people in their private capacity. This “demand” for goods accounts for 55% of all GDP.
- In Chart 3, the blue curve shows the per capita level of this private consumption expenditure, which has fallen to levels last seen in 2016-17. This means if the government does not help, India’s GDP may not revert to the pre-Covid trajectory for several years to come.
- It is for this reason that the latest GDP should not be viewed as an exception
Connecting the dots:
ECONOMY/ SCIENCE & TECH
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
Cryptocurrency and RBI
Context: Days after some leading banks cautioned people against dealing in cryptocurrencies, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) said banks cannot cite its April 2018 order on virtual currencies – that had banned them – as it has been set aside by the Supreme Court of India in 2020.
How do Cryptocurrencies work?
- Cryptocurrencies work using a technology called blockchain. Blockchain is a decentralized technology spread across many computers that manages and records transactions.
- So, instead of relying on traditional financial institutions like RBI who verify and guarantee your transactions, cryptocurrency transactions are verified by the user’s computers logged into the currency’s network.
- Cryptocurrency mining is the process in which transactions between users are verified and added to the blockchain public ledger.
- The process of mining is also responsible for introducing new coins into the existing circulating supply and is one of the key elements that allow cryptocurrencies to work as a peer-to-peer decentralized network, without the need for a third party central authority.
Concerns with Cryptocurrencies
- Extreme volatility
- It isn’t backed up by a sovereign state and a public institution like a central bank
- Regulatory authorities have expressed concerns of these being used as instruments for illicit activities, including money laundering and terror funding.
- Anxiety among investors about the regulatory uncertainties plaguing India’s position on cryptocurrency. Indian investors are said to hold some Rs 10,000 crore in digital currency already.
Implication of RBI’s clarification: Relief to investors of cryptocurrencies
- As many Indians have invested in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, the RBI move will be a big respite for them and their money – estimated to be around Rs 10,000 crore — won’t be blocked.
- Also, banks can’t take action against investors in virtual currencies following the court and RBI directives.
What’s the RBI’s position?
- The RBI’s 2018 position was more restrictive. The RBI had said regulated entities which already provide such services should exit the relationship within three months from the date of the circular.
- However, the RBI which is against other virtual cryptocurrencies has warned people against such currencies several times in the past.
- RBI has indicated it’s very much in the game, and getting ready to launch its own digital currency.
- RBI Governor said recently that “Central bank digital currency is a work in progress. The RBI team is working on it, technology side and procedural side… how it will be launched and rolled out,”
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Litoria Mira is a A species of which of the following that lives in the rainforests of New Guinea?
- Frog
- Snake
- Tortoise
- Lizard
Q.2 Which of the following has launched a scheme which provides for “Recognition of SDO” to attain “One Nation One Standard” vision of Government of India.
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Health
- Bureau of Indian Standards
- Central Pollution Control Board
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) initiative:
- It is an initiative aimed at setting up of Compressed Bio-Gas production plants
- The initiative was launched by the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 1st June 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
On Child Labour:
On economic recovery:
About strengthening healthcare system:











