IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
NIRF Rankings 2021
Part of: Prelims and GS – II – Education
Context Union Education Ministry released its India Rankings 2021 under the National Institutional Ranking Framework.
The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Madras was ranked the best higher education institution in the country for the third year in a row
Key highlights of the India Rankings 2021
- The IITs dominated the overall rankings, grabbing seven of the top 10 positions.
- Overall toppers: The Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru was ranked second, followed by the IITs in Bombay, Delhi, Kanpur, Kharagpur, Roorkee and Guwahati.
- Top Non-IITs University: Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) and Banaras Hindu University (BHU) were at rank nine and 10.
- Top universities: (1) IISc; (2) JNU; (3) the BHU; (4) the University of Calcutta; (5) the Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Coimbatore; (6) Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi
- Top engineering institutions: The IIT, Madras followed by the IITs in Delhi, Bombay, Kanpur, Kharagpur
- Top management institutions: IIM-Ahmedabad followed by IIM-Bangalore, IIM-Calcutta, IIT-Kozhikode, IIT-Delhi
- Top Pharmacy institute: Jamia Hamdard
- Top dental institute: Manipal College of Dental Sciences
What is NIRF?
-
- NIRF is an annual report card on the performance of the Higher Education Institutions (HEIs).
- It was launched in 2015, outlines a methodology to rank institutions across the country.
- The NIRF ranks institutions based on five parameters:
-
- Teaching Learning and Resources (TLR), Research and
- Professional Practice (RP),
- Graduation Outcome (GO),
- Outreach and Inclusivity (OI) and
- Perception.

News source: TH
13th BRICS summit
Part of: Prelims and GS – II – International Relations
Context The 13th BRICS summit was held virtually.
- The virtual summit was chaired by a Indian Prime Minister and was dominated by the developments in Afghanistan
Key highlights of the summit
- The summit adopted the BRICS Counter Terrorism Action Plan.
- The document, titled the New Delhi Declaration was unveiled which called for addressing the humanitarian situation in Afghanistan, and urged the need to uphold rights of women, children and minorities.
- It called for an “inclusive intra-Afghan dialogue” to ensure stability, civil peace, law and order in the country.
- The agreement on Remote Sensing Satellite Constellation was signed between BRICS countries’ space agencies.
What is BRICS?
- BRICS is an acronym for the grouping of the world’s leading emerging economies, namely Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- Headquarters: Shanghai, China
- The BRICS Leaders’ Summit is convened annually.
- The Chairmanship of the forum is rotated annually among the members, in accordance with the acronym B-R-I-C-S.
- Together, BRICS accounts for about 40% of the world’s population and about 30% of the GDP (Gross Domestic Product), making it a critical economic engine.
- Objectives:
- To deepen, broaden and intensify cooperation for more sustainable, equitable and mutually beneficial development.
- To ensure relations are built on the respective country’s economic strengths and to avoid competition where possible.
- Components of financial architecture of the BRICS:
-
- New Development Bank: NDB’s key areas of operation are clean energy, transport infrastructure, irrigation, sustainable urban development and economic cooperation among the member countries.
- Contingent Reserve Arrangement: It aims to provide short-term liquidity support to the members through currency swaps to help mitigate the BOP crisis situation and further strengthen financial stability.

News source: TH
C-295 aircraft deal
Part of: Prelims and GS – III – Defence and Security
Context The Cabinet Committee on Security approved the procurement of 56 C-295 MW transport aircraft from M/s Airbus Defence and Space S.A., Spain, giving a big boost to the Indian Air Force.
- This is the first project of its kind in which a military aircraft will be manufactured in India under technology transfer by a private company and is expected to cost close to $3billion.
Key takeaways
- The C-295MW transport aircraft is a transport carrier that has a 5-10 tonne capacity with a rear ramp door for quick reaction and para-dropping of troops and cargo.
- The transport aircraft will gradually replace the ageing Avro fleet of the IAF. The IAF has 56 Avros procured in the 1960s and they are in urgent need of replacement.
- All 56 aircraft will be installed with indigenous Electronic Warfare Suite.
- The project will give a boost to the aerospace ecosystem in India wherein several MSMEs spread over the country will be involved in manufacturing of parts of the aircraft.
- The programme is in line with the “Atmanirbhar Bharat” and will augment domestic aviation manufacturing resulting in reduced import dependence and expected increase in exports.
- The programme will also lead to employment generation in the aerospace ecosystem
News source: TH
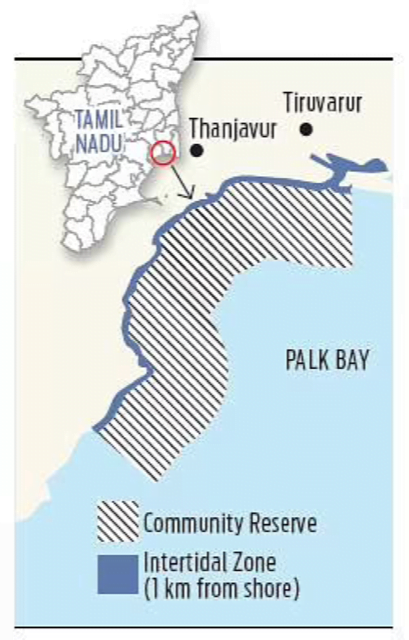
India’s first dugong conservation reserve
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- III – Environment
Context The Government of Tamil Nadu will set up India’s first Dugong Conservation Reserve in the Palk Bay Dugong.
About the Conservation Reserve
- The Conservation Reserve will cover an area of 500kms.
- The proposed conservation area has the highest concentration of dugongs in the country.
- The reserve will span the northern part of the Palk Bay from Adirampattinam to Amapattinam.
- AS part of the CAMPA-Dugong Recovery Project, various surveys were conducted in the Palk Bay and Gulf of Mannar, from November 2016 to March 2019.
- Gulf of Mannar is a shallow bay area between the south eastern end of Tamil Nadu and western Sri Lanka.
About Dugongs
- The dugong , also called the sea cow, is a herbivorous mammal.
- It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae.
- The dugong is strictly a marine mammal.
- They graze on seagrass and come to the surface to breathe.
- They are found in over 30 countries and in India are seen in the Gulf of Mannar, Gulf of Kutch, Palk Bay, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- According to Wildlife Institute of India (WII) estimates, only 200-250 Dugongs are left in the wild, of which 150 are found in the Palk Bay and Gulf of Mannar in Tamil Nadu.
- Threats:
-
- The loss of seagrass habitats
-
- water pollution
-
- degradation of the coastal ecosystem due to developmental activities
-
- accidental entanglement in fishing nets
-
- collision with boats, trawlers.
- Conservation status
-
- IUCN- Vulnerable
-
- CITES: Appendix I
-
- Wild (Life) Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
- The Government of India is also a signatory to the Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS) since 1983 where it has signed non-legally binding Memorandums of Understanding on the conservation and management of Siberian Cranes (1998), Marine Turtles (2007), Dugongs (2008) and Raptors (2016).
- Proper conservation is the only way to save dugongs from extinction.
Delegation of Financial Powers to Defence Services, 2021 Rules
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- II – Policies and interventions
Context Recently, the Ministry of Defence has released the Delegation of Financial Powers to Defence Services (DFPDS), 2021 rules.
- The primary focus is to overcome procedural delays, bring about greater decentralisation and operational efficiency.
Key Highlights of DFPDS 2021
- Financial Powers Devolved to Field Formations:
-
- Enhanced the delegation of revenue procurement powers for the Army, Navy and Air Force.
- 10% increase in Delegated Financial Powers of Vice Chiefs of Services.
- Focus on Operational Preparedness:
- Critical equipment can be hired for short periods
- Field Commanders and below can procure equipment in a speedy manner for urgent operational necessities and meeting essential sustenance requirements.
- Promoting Ease of Doing Business:
- Up to three times increase in funding related to Indigenisation/R&D to achieve ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’.
(News from PIB)
EXERCISE ZAPAD 2021
Part of: GS Prelims
In News: The Exercise ZAPAD 2021 has commenced at Nizhniy in Russia.
Aim: To train troops to undertake joint operations in conventional battlefield scenario.
- The exercise aims at strengthening long standing strategic partnership between India and Russia and also enhance better understanding, cooperation with all other participating Nations.
News Source: PIB
Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS)
Part of: GS Prelims
In News: On the basis of the data collected in PLFS, the quarterly bulletin for the quarter October- December 2020 has been released.
Considering the importance of availability of labour force data at more frequent time intervals, National Statistical Office (NSO) launched Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) in April 2017.
- To estimate the key employment and unemployment indicators (viz. Worker Population Ratio, Labour Force Participation Rate, Unemployment Rate) in the short time interval of three months for the urban areas only in the ‘Current Weekly Status’ (CWS).
- To estimate employment and unemployment indicators in both ‘Usual Status’ (ps+ss) and CWS in both rural and urban areas annually.
Conceptual Framework of Key Employment and Unemployment Indicators for the Quarterly Bulletin:
The Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) gives estimates of Key employment and unemployment Indicators like the Labour Force Participation Rates (LFPR), Worker Population Ratio (WPR), Unemployment Rate (UR), etc. These indicators, and the and ‘Current Weekly Status’ are defined as follows:
- Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR): LFPR is defined as the percentage of persons in labour force (i.e. working or seeking or available for work) in the population. (Male: 73.6, Female: 20.6; Total: 47.3)
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR): WPR is defined as the percentage of employed persons in the population. (Male: 66.7, Female: 17.9; Total: 42.4)
- Unemployment Rate (UR): UR is defined as the percentage of persons unemployed among the persons in the labour force. (Male: 9.5, Female: 13.1; Total: 10.3)
News Source: PIB
Coal Gasification Based Methanol Production Plant
Part of: GS-III: Energy
In News: BHEL R&D centre at Hydrabad began working on Indian high ash coal gasification in 2016 with support from the NITI Aayog to produce 0.25 ton per day methanol. The project was supported by the Department of Science and Technology with a Rs 10 crore grant. With four years of hard work BHEL successfully demonstrated a facility to create 0.25 TPD Methanol from high ash Indian coal using a 1.2 TPD Fluidized bed gasifier.
- India’s first demonstration plant of its kind, designed entirely in-house to work on high-ash Indian coal – BHEL R&D centre at Hydrabad
- The methanol purity of the crude methanol produced is between 98 and 99.5 percent.
- This endeavor led to the formation of in-house design expertise in BHEL for designing greater capacity coal gasification facilities, which will provide necessary impetus to the vision of ‘Atam Nirbhar Bharat.’ This in-house capability will assist India’s Coal Gasification Mission and Coal to Hydrogen Production for Hydrogen Mission
- After achieving this feat BHEL is further developing in house some critical processes such as catalytic conversion of syngas to methanol.
About Methanol
- Methanol is utilized as a motor fuel, to power ship engines, and to generate clean power all over the world.
- Methanol is also used to generate di-methyl ether (DME), a liquid fuel that is very similar to diesel — existing diesel engines simply need to be minimally changed to use DME instead of diesel.
- Methanol could be the most promising option for large-scale market penetration of a natural gas-based fuel for light-duty vehicles because of its low fuel cost and low additional cost relative to powering a vehicle with gasoline.
- Methanol, like ethanol but unlike hydrocarbon fuels, is water soluble. As a consequence, it is transported through diffusion and convection through the environment at much faster rate than hydrocarbons. In addition to fast migration, methanol bio-degrades much faster than hydrocarbons. Fast transport and degradation result in short lifetimes. Hydrocarbons, on the other hand, comprise many stable compounds, which include some, such as aromatics, that are highly toxic to bio-organisms and degrade slowly
- Promoted under the Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) initiative
The majority of worldwide methanol production is derived from natural gas, which is a relatively easy process. Since India doesn’t have much of the natural gas reserves, producing methanol from imported natural gas lead to outflow of foreign exchange and sometimes uneconomical due to excessive prices of natural gas.
The next best option is to utilise India’s abundant coal. However, due to the high ash percentage of Indian coal, most internationally accessible technology will not be adequate for our demands.
News Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
EDUCATION/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-2: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Education, Human Resources
- GS-3: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
What India must do to expand higher education enrolment
Context: According to the All India Survey of Higher Education (AISHE) 2019-20, the gross enrolment ratio (GER) in higher or tertiary education increased to 27.1% (38.5 million), from 26.3% (37.4 million) in the preceding year.
- This indicates that the remaining 72.9% of the population in the 18-23 age group is not enrolled in higher education institutions (HEIs).
NEP and HEI Enrolment Target
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 sets the target of 50% GER by 2035.
- To achieve this target, GER is required to grow at 3.53% per annum.
- The target is attainable given that the compounded growth rate of GER between 2011-12 and 2019-20 was 3.58%.
Increasing Higher education enrolment requires a multipronged, multi-tiered strategy.
- Improving the transition ratio from secondary to higher secondary, and then, to HEI is required. For Ex: In 2018-19, the net enrolment ratio at higher secondary level was only 30.8%, which limits the possibility of an increase in HEI.
- Geography is also critical to HEI. For instance, college density remains highly concentrated in urban areas. Policy intervention to expand HEIs to the hinterland along with increasing the enrolment capacity is urgent.
- Policy that Favour Larger HEIs: Earlier, the Radhakrishnan University Education Commission (1949) and Kothari Commission (1964-66) favoured small, high-quality HEIs. This is in sharp contrast with the policy of China, USA & Europe.
- In 2016, India’s 51,649 HEIs had 35.7 million students, when China’s 2,596 institutions had 41.8 million students.
- Larger HEIs with high enrolment are easier to manage and more resource-friendly.
- Expanding Open Learning: The share of distance and open learning in India has remained stagnant at around 11% for many years. Massive online open courses (MOOCs) through SWAYAM provide an avenue but only 10.7% of Indian households have access to a computer, with only 23.8% to the internet
- Improving Teacher Shortage & Quality: India needs 3.3 million more teachers in HEIs to improve the teacher-student ratio, from 1:28 to an ideal 1:15. This requires efforts to help get the best minds to choose teaching as a profession by ensuring a steady and significant career trajectory.
- India can learn from the education systems in countries such as Finland and South Korea, where teaching is a coveted profession.
- Improving Employability: Various surveys have found that graduates lack both the technical and communication skills required for skilled work. Vocational courses by HEIs in collaboration with local employers, can help improve these levels
- More Scholarships: The financial support given through scholarships is currently inadequate. The transition from “mass education” to “universal education” is through financial support to the most vulnerable.
Conclusion
- India’s GER has steadily increased over the last few years. This growth has also seen a substantial increase in the GER of Women, SCs & STs. This growth must continue. The future, therefore, lies in empowering subgroups, which will thereby accelerate GER.
- This must go hand in glove with India’s efforts to strengthen the policy of greater social inclusion proposed by NEP 2020.
Connecting the dots:
- New Education policy 2020
- Higher Education in Regional Languages
- Criticism of Board Exams
- Formative Assessment
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Big Tech & Financial Services
Context: The involvement of large tech players in the financial services segment is something that has been specifically flagged by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Recent Developments
- Amazon’s financial services unit Amazon Pay has partnered with investment platform Kuvera to offer wealth management services to the former’s customers.
- This follows Google Pay’s deal with Equitas Small Finance Bank for fixed deposits.
What is Amazon Pay’s partnership with Kuvera?
- Under the partnership, Kuvera will provide services, products and technology know-how to Amazon Pay that will facilitate investments in mutual funds, fixed deposits, etc for its customers.
- Through this partnership, there will be democratisation of investing and wealth management in India.
Have there been other partnerships like this?
- The most recent partnership involving a big tech company and a financial services firm for wealth management was Google Pay’s deal with Equitas Small Finance Bank for fixed deposits.
- Several tech companies, though, have tied up with banking partners for short-term financing instruments.
- These include Amazon Pay that has tied up with Capital Float and IDFC FIRST Bank for the Amazon Pay Later instrument, and Paytm, which has tied up with Clix Finance India Pvt. Ltd for its postpaid service.
- Credit card payment platform -CRED also has an online lending platform in partnership with IDFC FIRST Bank.
What has the RBI said about involvement of tech companies in the financial services space?
- While the RBI hasn’t commented on specific deals, in the Financial Stability Report released in July 2021, the central bank flagged concerns with big tech firms offering digital financial services.
- Big techs offer a wide range of digital financial services and have a substantial footprint in the payment systems, crowdfunding, asset management, banking and insurance of several advanced and emerging market economies.
- While this holds the promise of supporting financial inclusion and generating lasting efficiency gains, including by encouraging the competitiveness of banks, important policy issues arise.
- Big techs foraying into financial services present at least two unique challenges.
- First, they operate at many different (non-financial) lines of business with sometimes opaque overall governance structures.
- Second, they have the potential to become dominant players in financial services within short span of time by exploiting network effects. Therefore, their regulations cannot be post their establishment in the sector.
- More specifically, the concerns have intensified around
- A level-playing field with banks
- Operational risk given the huge customer base they enjoy
- Too-big-to-fail issues
- Challenges for antitrust rules
- Cyber security and data privacy
Connecting the dots:
- MFIs: Digital and Physical Micro-lending
- New Social Media Code
- Dominance of Big tech
- Australia’s News Media Bargaining Code
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 Which of the following States will set up India’s first Dugong conservation reserve
- Gujarat
- Tamil Nadu
- Odisha
- West Bengal
Q.2 Consider the following Statements regarding BRICS:
- Its headquarters is in Beijing, China
- New Development Bank and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank are the components of financial architecture of the organisation.
Select the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 India Rankings 2021 under the National Institutional Ranking Framework is released by which of the following?
- NITI Aayog
- Azim premji Foundation
- Ministry of Education
- Both (a) and (C)
ANSWERS FOR 9th Sept 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | B |
Must Read
On Marital Rape:
On Taliban, Central Asia and India:











