IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
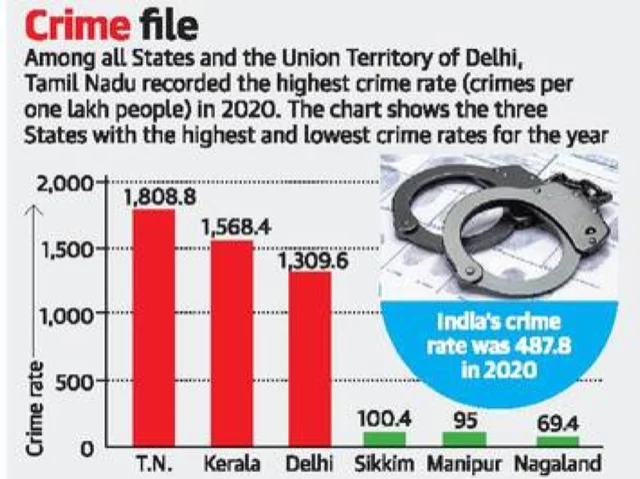
NCRB report on crime
Part of: Prelims and GS II – Laws and Policies
Context National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) report on Crime in India was recently launched.
Key findings of the report
- The Coronavirus pandemic and subsequent lockdown resulted in a drop in traditional crimes like theft, robbery, and assault on women and children in 2020.
- There was a 28% increase in the registration of cases in 2020 in the country compared to 2019, primarily owing to the violation of COVID-19 norms.
- An almost 21-fold jump was recorded in cases of disobedience to the order duly promulgated by public servants.
- Crimes against Scheduled Castes showed an increase of 9.4%.
- offences against the Scheduled Tribe communities showed an increase of 9.3% over 2019
What is The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB)?
- Headquarter: New Delhi
- Set-up: 1986
- Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs
- Objective: To function as a repository of information on crime and criminals so as to assist the investigators in linking crime to the perpetrators.
- It was set up based on the recommendations of the National Police Commission (1977-1981) and the MHA’s Task Force (1985).
News Source: TH
AUKUS: New partnership between Australia, the U.K. and the U.S.
Part of: Prelims and GS II – International Relations
Context A week before a meeting of Quad leaders in Washington DC, the Biden administration has announced a new trilateral security partnership for the Indo-Pacific between Australia, the U.K. and the U.S. (AUKUS).
- The grouping is security focused.
- It is also different from — but complementary to — arrangements such as the Quad.
Key features of the partnership
- A central feature of the partnership would involve a trilateral 18-month effort to help Australia acquire nuclear-powered submarines which are quieter, more capable and can be deployed for longer periods, needing to surface less frequently.
- The partnership would also involve a new architecture of meetings and engagements between the three countries and also cooperation across emerging technologies (applied AI, quantum technologies and undersea capabilities).
- The U.S. sharing this kind of technology on nuclear submarines had been done only once before — with the U.K. and almost 70 years ago.
- Significance: Australia has felt increasing pressure from an assertive China and has sought to strengthen its partnerships with India, the U.S. and the U.K., including through ‘plurilateral’ forums.
News source: TH
PLI scheme for auto sector
Part of: Prelims and GS -III – Economy
Context The Union Cabinet has approved a Rs. 26,058 crore production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme to enhance manufacture of advanced technology and green vehicles, auto parts and drones.
Key takeaways
- Benefits: It will attract Rs. 42,500 crore in fresh investment into the automobile and auto components industry over five years
- It will help create more than 7.5 lakh jobs.
- The scheme has been devised for both existing automotive firms and new investors.
- The ‘sales value linked’ scheme includes a ‘champion OEM’ incentive applicable on battery electric vehicles and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
- A ‘component champion’ incentive is for advanced automotive technology components.
What is the PLI scheme?
- The Product Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme aimS to boost domestic manufacturing under the government’s Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- It was introduced in March 2020 and is expected to result in a minimum production worth more than $500 billion in five years.
- The scheme provides incentives to companies for enhancing their domestic manufacturing apart from focusing on reducing import bills and improving the cost competitiveness of local goods.
- PLI scheme offers incentives on incremental sales for products manufactured in India.
- Eligibility criteria for businesses under the PLI scheme vary based on the sector approved under the scheme.
- Some of the sectors for which PLI scheme has been approved are:
- Electronic or technology products
- Pharmaceuticals drugs
- Telecom & networking products
- Food Products
- High-efficiency solar PV modules
News source: TH
Input Tax Credit (ITC)
Part of: Prelims and GS III – Economy
Context Recently, The Supreme Court said that refunds of tax credit cannot be claimed for input services under the Goods and Services Tax regime’s inverted duty structure.
- The SC has confirmed a Madras High Court judgment which upheld a fiscal formula included in the Central Goods and Service Tax Rules to execute refund of unutilised Input Tax Credit (ITC) accumulated on account of input services.
What is Input Tax Credit (ITC)?
- ITC is a mechanism to avoid cascading of taxes. Cascading of taxes, in simple language, is ‘tax on tax’.
- Input Tax Credit refers to the tax already paid by a person at time of purchase of goods or services and which is available as deduction from tax payable .
- Input tax credit in relation to GST to a registered person means, the CGST, SGST/UTGST or IGST charged on any supply of goods or services or both made to him.
- It includes IGST charged on imports & tax payable under reverse charge mechanism.
- When one buys a product/service from a registered dealer we pay taxes on the purchase.
- On selling, we collect the tax.
- We adjust the taxes paid at the time of purchase with the amount of output tax (tax on sales) and balance liability of tax (tax on sales minus tax on purchase) has to be paid to the government.
- This mechanism is called utilization of input tax credit.
- If the tax paid on inputs is higher than the tax on the output, the excess can be claimed as a refund.
- Exceptions: A business under composition scheme cannot avail of input tax credit. ITC cannot be claimed for personal use or for goods that are exempt.
(News from PIB)
National Florence Nightingale Awards 2020
Part of: GS-Prelims
In News: National Florence Nightingale Awards 2020 was conferred to 51 awardees by the President
- Florence Nightingale awards were instituted in the year 1973 by the Government as a mark of recognition for the meritorious services rendered by nurses to the society.
News Source: PIB
‘Shoonya’ Campaign
Part of: GS-Prelims and GS-III: Environment & Climate change
About the campaign: An initiative to promote zero-pollution delivery vehicles by working with consumers and industry.
- The campaign aims to accelerate adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in the urban deliveries segment and create consumer awareness about the benefits of zero-pollution delivery.
- Urban freight vehicles account for 10 percent of freight transportation-related CO2 emissions in India, and these emissions are expected to grow by 114 percent by 2030.
- EVs emit no tailpipe emissions, which can contribute immensely to an improved air quality. Even when accounting for their manufacture, they emit 15-40 percent less CO2 compared to their internal combustion engine counterparts and have lower operational cost.
News Source: PIB
Exercise ZAPAD-2021
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – International Relations
Context: A seven day long Multilateral ‘Joint Strategic Exercise’ which saw participation from seven countries; one of the theatre-level exercises of the Russian armed forces with the focus primarily on operations against terrorists.
- Nine Participating countries: Mongolia, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Serbia, Russia, India and Belarus.
- Eight Observers countries: Pakistan, China, Vietnam, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Uzbekistan and Sri Lanka.
- Military Exercise between India and Russia: The 12th Edition of Indo-Russia joint military Exercise INDRA
News Source: PIB
Development of High-quality transparent ceramics
Part of: GS Prelims
In News: Indian researchers have developed transparent ceramics, reaching theoretical transparency through a technique called colloidal processing followed by simultaneous application of temperature and pressure, for the first time in India.
- The material can be used for thermal imaging applications, especially in harsh service conditions and personal protection systems such as, helmets, face shields, and goggles.
Transparent ceramics:
- A new class of advanced materials with unique transparency and excellent mechanical properties
- Can be designed not only for transparent to visible light but also for ultraviolet (UV), Infrared (IR), and Radiofrequency (RF), giving opportunity for diverse applications.
News Source: PIB
New Species of Hybodont Shark
Part of: GS-Prelims and GS-III: Environment
In News: In a rare discovery, teeth of new species of hybodont shark of Jurassic age have been reported for the first time from Jaisalmer.
- Represent a new species named by the research team as Strophodusjaisalmerensis. The genus Strophodus has been identified for the first time from the Indian subcontinent and is only the third such record from Asia, the other two being from Japan and Thailand.
- This discovery marks an important milestone in the study of Jurassic vertebrate fossils in the Jaisalmer region of Rajasthan, and it opens a new window for further research in the domain of vertebrate fossils.
About Hybodont shark
- Hybodonts, an extinct group of sharks, was a dominant group of fishes in both marine and fluvial environments during the Triassic and early Jurassic time.
- Started to decline in marine environments from the Middle Jurassic onwards until they formed a relatively minor component of open-marine shark assemblages.
- Hybodonts finally became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous time 65 million years ago.
News Source: PIB
PLI Scheme for Drone Industry
Part of: GS-Prelims and GS-II: Governance
Context: Government has approved Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Drone Industry
- Will incentivize emergence of Advanced Automotive Technologies global supply chain in India
- Help create additional employment of over 7.6 lakh people
- Incentives worth ₹ 26,058 crore will be provided to industry over five years
- It will bring fresh investments of over₹5,000 crore in three years and incremental production of over ₹ 1,500 crore
News Source: PIB
India’s Gems & Jewellery sector
Part of: GS-Prelims
- Contribution of around 7% to GDP
- 10-12% share in country’s total merchandise export
- One of the leading sectors in terms of employment generation providing employment to approx. 5 million skilled and semi-skilled workforce.
- One of largest exporter of other segments of industry such as gold jewellery, silver jewellery, coloured gemstones and synthetic stones
Has been one of the worst-hit sectors in India during the Covid-19 pandemic and its exports saw a record decline of (-) 98% in April 2020 due to the complete lockdown situation in the country.
Policy that helped the industry bounce back
- Revamped Gold Monetisation Scheme
- Reduction in import duty of gold, hallmarking, etc.
- Various virtual trade events like virtual Buyer Seller Meets, virtual IIJS, virtual International Gems & Jewellery Show (e-IGJS), India Global Connect, Webinars etc.
News Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- GS-3: Infrastructure: Telecommunications etc.
Telecom Relief Package: 4-year moratorium on AGR dues
Context: Recently, the Union Cabinet approved relief measures for telecom sector which include the following:
- Four-year moratorium on payment of statutory dues by telecom companies, both AGR and spectrum charges
- Simplified Definition of AGR: The definition of AGR has been rationalised by excluding non-telecom revenue of telecom companies on a prospective basis (from now onwards)
- Telecom operators are required to pay licence fees and spectrum charges in the form of ‘revenue share’ to the government
- The revenue amount used to calculate this revenue share is termed as Adjusted Gross Revenue or AGR
- Relaxation in FDI: 100 per cent FDI in telecom via the automatic route has been approved (earlier 49%)
- Charges Rationalised: The regime of heavy interest, penalty and interest on penalty on payment of licence fees, spectrum charges and all kinds of charges has been rationalised.
- Reduced Interest: The Centre will do annual compounding of interest instead of the monthly compounding. The interest would be charged at a ‘reasonable’ rate of MCLR plus 2%.
- MCLR refers to the lowest lending rate banks are permitted to offer — the marginal cost of funds-based lending rate.
- Long periods of spectrum usage: Spectrum auctions will be held in the last quarter of every financial year. Spectrum auction will be done for 30 years, instead of 20 years. After completing 10-years lock-in period, the buyer will have the option to surrender by paying surrender charges.
- Ease of doing business: Spectrum sharing has been completely allowed and made free. Also, shifting between prepaid, post-paid to not require fresh KYC
What is the background of these reforms?
- In October 2019, the Supreme Court had ordered telecom operators to pay Rs 1.47 lakh crore to the Department of Telecommunications as pending AGR-dues
- However, in September 2020, the Supreme Court had granted 10 years to the telecom companies to clear their AGR dues of around Rs 1.47 lakh crore to the Centre.
- These AGR dues (along with disruption caused Jio’s entry) had impacted the cash flow of various telecos that had wider impact on the Telecom sector itself. There were fears about a duopoly emerging with just two major telecom players — Bharti Airtel and Reliance Jio.
- However, the government was keen on ensuring that there were more players in the sector and customer retaining choices. Competition in the sector will always lead to better prices and better technology.
Significance
- Relief to multiple Telecos: The package provides relief for debt-ridden Vodafone Idea which still owes roughly Rs 50,000 crore to the government as AGR dues. It also provides relief to Tata group (dues of Rs. 12,601 crores) and Aircel (Rs. 12,389 crores).
- Relief for the cash-strapped telecom sector.: Moratorium on AGR dues provides an annual cash flow relief of around ₹14,000 crore for the industry while the moratorium on spectrum dues gives another ₹32,000 crore of annual cash flow relief as a whole.
- The reform package, therefore, provides telcos the flexibility to manage their cash flows better and boosts growth in the telecoms industry
- Safeguards Banking Health: Banking sector’s exposure to the telecom players is significant at over Rs 1 lakh crore. The telecom package comes as a relief to the banks as it prevents the possibility of default by vulnerable telecos (Vodafone). This would help in stabilising and reducing the non-performing assets in the sector.
- Boost to Digital future: These fresh reforms will further boost telecos efforts to invest in future digital technologies and preparing the infrastructure for India’s digital economy.
Concerns
- Past Dues remain: The change in definition of AGR that will reduce the burden on telcos, applies only prospectively, so those past dues remain payable.
- Temporary Measure: While it provides time to put their house in order, the telcos’ overall liability does not come down and ultimately they will have to raise tariffs to generate sufficient cash flows. AGR dues will have to be paid with interest.
- Unfulfilled Demands: A long-standing demand for the government’s intervention in setting telecom floor tariffs, as it has done in the civil aviation sector to protect competition, did not find a place in the relief package
Connecting the dots:
EDUCATION/ POLITY
- GS-2: Issues relating to development and management of Education
- GS-2: Issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure
Tamil Nadu’s case against NEET
Context: Recently, Tamil Nadu Assembly has passed a bill to exempt students of the state from appearing in the NEET for admissions into medical and dental courses
What Is National Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test (NEET)?
- It is an entrance exam for medical courses like MBBS, BDS, and Post Graduation in both government and private medical colleges.
- In 2013, NEET-UG replaced the All India Pre Medical Test (AIPMT) and all individual MBBS exams conducted by states or colleges themselves.
- The NTA – National Testing Agency, the regulatory body for NEET UG Exam, conducts it every year in various parts of India in multiple languages.
- The responsibility of the NTA is limited to
- Conduct of the entrance examination
- Declaration of result and for providing an “All India Rank Merit List” to the Government of India for the conduct of counselling for 15% All India Quota Seats
- Providing the result to States/other Counselling Authorities.
- NEET is based on a core curriculum approach, whereby the syllabi of all the school boards have been taken into consideration.
- NEET has become the only means of gaining admission to medical institutions, including private colleges, after the Supreme Court’s categorical view that such a test alone could help maintain standards.
Why Tamil Nadu is opposing NEET?
- In Tamil Nadu, NEET has been a sensitive subject where several students have allegedly died by suicide over the years after failing to qualify for the exam.
- One of the primary arguments by Tamil Nadu is that NEET would push certain categories of students out of the race for MBBS degrees, and its goal of providing equitable opportunities for all would be frustrated.
- Students from government schools and rural areas would not be able to afford the coaching that would be essential for the competitive test, the State government argued.
What is the context of the recent bill?
- What sparked an uproar and led to the Bill was the death of a 19-year old boy who died by suicide, hours before he was supposed to take the NEET exam for the third time.
- This is not Tamil Nadu’s first attempt to get exemption from the exam; an effort was made in 2017 through ordinance but didn’t get President’s nod.
- President’s assent is required as the proposed State law is in conflict with the parliamentary legislation regulating medical admissions.
- Abolition of NEET was even the election promise of the current ruling party.
- The recent Tamil Nadu Admission to Undergraduate Medical Degree Courses Bill, 2021 is based on A.K. Rajan Committee observations on NEET.
- The committee viewed that NEET would adversely affect the rural and urban poor, and consequently, hurt State’s future manpower availability to run its network of primary health centres.
- 2021 law exempt students of the state from appearing in the NEET for admissions into medical and dental courses. Tamil Nadu government wants entrance to happen on the basis of marks obtained in Class 12.
- However, it will be quite difficult for the Union government to grant relief to one State alone in the face of Supreme Court judgement on NEET (mandatory to help maintain standards). It might meet the same fate as that of 2017 bill.
Way Ahead
- Need for Dispassionate Debate: The anti-NEET narrative in Tamil Nadu should not be viewed as a product of Tamil exclusivism but should be deliberated in dispassionate manner.
- Need for reviewing NEET: The time may also have come to examine whether NEET has met its purposes of improving standards and curbing commercialisation and profiteering.
- Balancing interests: Centre has to conceive a better system that will allow a fair admission process while preserving inter se merit and preventing rampant commercialisation.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 National Crime Records Bureau comes under which of the following Ministry?
- Ministry of Urban development
- Ministry of Home Affairs
- It is an independent agency
- None of the above
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding PLI scheme:
- The Product Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme aimS to boost domestic manufacturing under the government’s Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- The scheme provides incentives to companies for enhancing their domestic manufacturing apart from focusing on reducing import bills and improving the cost competitiveness of local goods.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Which of the following is not a part of the Quad group?
- India
- China
- Australia
- United Kingdom
ANSWERS FOR 15th Sept 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
On changes needed in GST:
On dealing with learning loss during Pandemic:
On India-China relations:











