IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Govt. to revisit income criterion for EWS quota
Part of: Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions
Context The Union Government has decided to revisit the criteria for determining the economically weaker sections (EWS) in terms of the provisions of the Explanation to Article 15 of the Constitution inserted by the Constitution (103rd Amendment) Act 2019.
- The committee would be set up to review the criteria and would take four weeks for the exercise.
Background
- NEET aspirants had filed a case challenging a notification announcing 27% quota to OBCs and 10% reservation to the EWS in the All India Quota (AIQ) category.
What is EWS quota?
- The EWS quota was meant for persons belonged to the Economy Based Un-Reserved Category having an annual family income less than ₹8 lakh and who do not belong to any other category such as SC/ST/OBC
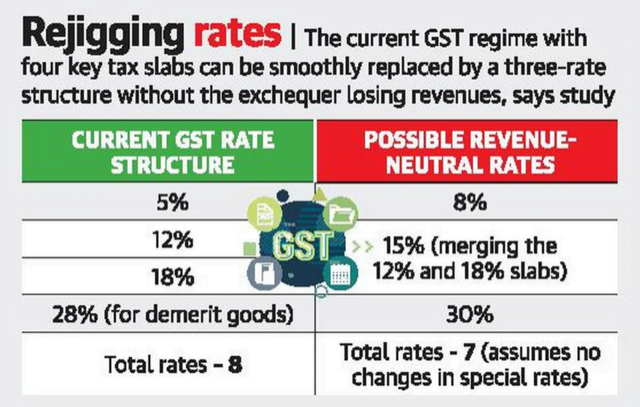
Three-rate GST structure
Part of: Prelims and GS-III – Economy
Context As per a National Institute of Public Finance and Policy (NIPFP) study, the Government can rationalise the GST rate structure without losing revenues by rearranging the four major GST rates (5%, 12%, 18% and 28%) with a three-rate framework of 8%, 15% and 30%.
- The NIPFP is an autonomous think tank backed by the Finance Ministry.
Significance of the study
- The GST Council has tasked a Group of Ministers, headed by Karnataka CM to propose a rationalisation of tax rates and a possible merger of different tax slabs by December to shore up revenues.
- The NIPFP paper also notes that raising rates on ‘high-value low volume goods’ like precious stones and jewellery ‘may encourage undisclosed transactions and revenue leakages.
Current rate structure
- GST is levied at four rates – 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%.
- The list of items that would fall under these multiple slabs are worked out by the GST council.
- Further, the tax on gold is kept at 3%. Rough precious and semi-precious stones are placed at 0.25% under GST.
What is the Goods and Services Tax (GST)?
- Value-added tax levied on most goods and services sold for domestic consumption.
- It was launched on 1st July 2017.
- It subsumed almost all domestic indirect taxes under one head.
- Paid by consumers, but it is remitted to the government by the businesses selling the goods and services.
- The GST to be levied by the Centre is called Central GST (CGST) and that to be levied by the States is called State GST (SGST).
- Integrated Goods & Services Tax (IGST): Inter-State Import of goods or services
- GST Council: Constitutional body (Article 279A) for making recommendations to the Union and State Government on issues related to GST.
Rs. 10,000 cr. more allotted for MGNREGS
Part of: Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions
Context The Finance Ministry has allocated additional funds of Rs. 10,000 crore as an interim measure for the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) after it ran out of funds allocated in the budget.
Consequences of Lack of funds
- Suppression of demand for work
- Delayed payment of wages to workers.
- Constrain economic recovery
What is Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA)?
- It was notified in 2005.
- Goal – To improve the livelihood security of people in rural areas.
- Universal scheme guaranteeing 100 days of wage employment in a year to every rural household that expresses a demand.
- It aims to guarantee the ‘Right to Work’.
- Implemented by: Gram panchayat.
- The failure of provision for employment within 15 days of the receipt of a job application will result in the payment of unemployment allowance to the job seekers.
- Employment is to be provided within 5 km of an applicant’s residence
- Employment under MGNREGA is a legal entitlement
Scorpene class submarine INS Vela
Part of: Prelims and GS-III – Defence and security
Context The fourth Scorpene class conventional submarine, INS Vela , was commissioned into the Navy
Key takeaways
- With this, the Navy currently has 16 conventional and one nuclear submarines in service.
- Vela is named after a type of Indian fish belonging to the stingray family.
Navy’s Project-75
- Six Scorpene submarines are being built under Project-75 by India under technology transfer from France under a $3.75-bn deal.
- The first submarine INS Kalvari was commissioned in December 2017.
- Second submarine INS Khanderi in September 2019.
- Third one INS Karanj in March 2021.
- The fifth submarine, Vagir , was launched in November 2020.
- Sixth one Vagsheer is in the advanced stage of outfitting.
India’s further plans
- India plans to install Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) modules on all Scorpene submarines from 2023 to enhance their endurance.
- After the Project P-75I, the Navy intends to design and build conventional submarines indigenously.
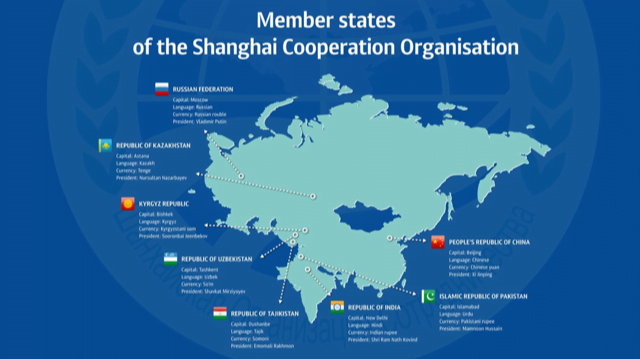
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)
Part of: Prelims and GS-II- International Relations
Context 20th meeting of the SCO Council of Heads of Government was recently held.
About Shanghai Cooperation Organization
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organization is a political, economic, and Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure of many important countries including India and its neighborhood.
- India is full member of the SCO.
- SCO Secretariat: Beijing
- 8 members: Russia, China, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, India and Pakistan.
- The internal policy of the forum is inspired by the Shanghai Spirit: based on the principles of mutual trust, mutual benefit, equality, mutual consultations, and a desire for common development.
- SCO’s Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS): Permanent organ of the SCO which serves to promote cooperation of member states against terrorism, separatism, and extremism.
- It is headquartered in Tashkent.
Classified military satellite of Russia
Part of: Prelims and GS-II- International Relations and GS-III – Defence and security
Context Russia recently successfully placed a military satellite into orbit which is believed to be part of the Kremlin’s early warning anti-missile system.
- The launch could be delivering a Tundra satellite.
- Russia has previously launched Tundra satellites in 2015, 2017 and 2019.
- The ground track of the launch “matched previous missions” delivering satellites for Russia’s missile warning system named Kupol or dome.
- Unveiled in 2019, Kupol is designed to detect launches of ballistic missiles and track them to their landing site, though its exact configuration is unknown.
(News from PIB)
Atmosphere & Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems & Services (ACROSS)
Part of: Main GS-III: Climate Change and Conservation
In News: Cabinet approves Continuation of the umbrella scheme “Atmosphere’ & Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems & Services (ACROSS)” from the 14th Finance Commission to the next Finance Commission Cycle (2021-2026).
Implemented by: Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- Objective: To conduct R & D for improving forecast of weather, climate and other hazardous events in real-time for delivery of a reliable weather and climate service.
- The entire gamut of weather/climate prediction involves assimilation of meteorological observations, understanding the processes, research and development of dynamical models and providing the forecast services.
- Each of these aspects is incorporated as sub-scheme under the umbrella scheme “ACROSS” and is being implemented through India Meteorological Department (IMD), Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune and National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting(NCMRWF).
News Source: PIB
India and USA agree on a transitional approach on Equalisation Levy 2020
Part of: Mains GS-II: International Laws and Acts
In News: India and United States have joined 134 other members of the OECD/G20 Inclusive Framework (including Austria, France, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom) in reaching agreement on the Statement on a Two-Pillar Solution to Address the Tax Challenges Arising from the Digitalization of the Economy.
India and United States have agreed that the same terms that apply under the October 21 Joint Statement shall apply between the United States and India with respect to India’s charge of 2% equalisation levy on e-commerce supply of services and the United States’ trade action regarding the said Equalisation Levy.
News Source: PIB
India, ADB sign $300 million loan
Part of: Mains GS-II: Government Policies
In News: The Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a $300 million loan to strengthen and improve access to comprehensive primary health care in urban areas of 13 states that will benefit over 256 million urban dwellers including 51 million from slum areas.
- The programme supports the Government of India’s key health initiatives – Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (AB-HWC) and Pradhan Mantri Atmanirbhar Swasth Bharat Yojana (PM-ASBY) – which has been renamed as Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) – by expanding availability and access to quality primary health care services particularly for vulnerable populations in urban areas.
- The programme complements the government’s efforts to bridge the health care gaps by strengthening institutional capacity, operation, and management of urban health and wellness centers at the central, state, and municipal levels.
- Beside the pandemic response, interventions through the program promote increased utilization of urban HWCs with provision of comprehensive primary health care packages including noncommunicable diseases and community outreach services such as awareness raising activities on health care options, particularly for women.
- Delivery and health information systems for primary health care will be upgraded through digital tools, quality assurance mechanisms, and engagement and partnership with the private sector.
- The programme is supported by a $2 million technical assistance grant from ADB’s Japan Fund for Poverty Reduction to provide support for programme implementation and coordination, capacity building, innovation, knowledge sharing and application of scalable best practices across the healthcare system.
News Source: PIB
New State of Monster black hole detected 5 Billion Light years away
Part of: Mains GS-III: Science and Technology
In News: Indian Astronomers have found an active galaxy in a very bright state with 10 times more X-ray emission than normal, equivalent to more than 10 trillion Sun, and located 5 billion light-years away that could help probe how particles behave under intense gravity and acceleration to the speed of light.
- It could help study the role of strong gravity and acceleration of matter in the formation, interaction, and evolution of galaxies in the early universe.
- Every galaxy in the Universe is believed to host a supermassive black hole (SMBH) at its center. In some galaxies, the black hole is actively devouring a large amount of material and shooting a jet of plasma almost at the speed of light towards us. These are called blazars.
- OJ 287 belongs to a class of blazars known as BL Lacerate objects which show very rapid and large amplitude flux variations but barely discernible emission line features. This class of sources emit in the whole electromagnetic spectrum, a rather uncommon phenomenon which requires extreme physical conditions.
- Hence a study of such sources tells us about the behavior of matter in an extreme gravitational field where it is difficult for light also to escape from the vicinity of the black hole.
- Significant changes in the spectral state of blazars are very rare, and so are the binary SMBH systems in the universe. Multi-wavelength studies of such sources can establish the role of strong gravity and acceleration of particles to the speed of light in the formation of the most energetic jets in the universe, and the formation, interaction, and evolution of galaxies in the early universe.
News Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
POLITY/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-2: Legislature & problems
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Pre- Legislative Consultation Policy (PLCP)
Context: The Union Government has listed 29 Bills (26 new and three pending) to be tabled in the winter session of Parliament.
About Pre-Legislative Consultation Policy (PLCP)
- Objective: The PLCP was formulated based on the broad recommendations of the National Advisory Council headed by Sonia Gandhi (2013) and the National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (2002). It aimed to create an institutionalised space for public participation in lawmaking processes.
- Mandating Placing in Domain: In 2014, the Pre-Legislative Consultation Policy was adopted which mandated that whenever the Government makes any law, it must place a draft version of it in the public domain for at least 30 days.
- Comprehensive details: The policy also says that along with the draft, a note explaining the law in simple language and justifying the proposal, its financial implication, impact on the environment and fundamental rights, a study on the social and financial costs of the bill, etc. should be uploaded.
- Transparency on Public Feedback: The respective departments should also upload the summary of all the feedback that they receive on the circulated draft.
Why is it important?
- Strengthen Democracy: This policy provides a forum for citizens and relevant stakeholders to interact with the policymakers.
- Managing Discontent: Protests in the recent past over laws such as the farm laws, the RTI Amendment Act, the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, etc. have all highlighted that there is discontent among relevant stakeholders and the public at large since they were not looped in while framing such laws.
- Changed Citizen-State relationship: Public consultations enhance transparency, increase accountability and could result in the building of an informed Government where citizens are treated as partners and not as subjects.
- For example, concerns raised by civil society members (#SaveTheInternet campaign) were addressed by the Telecom Regulatory Authority in its framing of the net neutrality rules after extensive consultation and deliberation processes adopted by them.
What is the status of its implementation?
- Poor Implementation: Since the inception of the policy, 227 of the 301 bills introduced in Parliament have been presented without any prior consultation.
- During the 16th Lok Sabha (May 2014 to May 2019) 186 bills were introduced in Parliament, of which 142 saw no consultation prior to introduction.
- During the 17th Lok Sabha (June 2019 to present), 115 bills were introduced in Parliament, of which 85 saw no consultation prior to introduction.
- Not Adhering to 30 day timeline: Of the 74 placed in public domain for comment, at least 40 did not adhere to the 30-day deadline.
- During the 16th Lok Sabha (May 2014 to May 2019) from the 44 bills placed in the public domain for receipt of comments, 24 did not adhere to the 30-day deadline.
- During the 17th Lok Sabha (June 2019 to present), from the 30 bills placed in public domain for receipt of comment, 16 of them did not adhere to the 30-day deadline.
Why is implementation difficult?
- Lacks Statutory Right: Though it is a requirement that should be heeded by all the Government departments, the absence of a statutory or constitutional right has watered down its effect.
- Requires Amendment in Parliamentary procedures: The effective implementation of the policy requires subsequent amendments in executive procedural guidelines like the Manual of Parliamentary Procedures and Handbook on Writing Cabinet Notes.
- However, during a subsequent amendment to the Manual of Parliamentary Procedures, the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs ignored the Ministry of Law and Justice when it requested them to incorporate PLCP provisions in the manual.
Way Ahead
- Incorporation of pre-legislative consultation in the procedures of the Cabinet, Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha etc. should be prioritised.
- Similarly, it must be required of ministers while introducing the bill to place an addendum note on the details of the pre-legislative consultation.
- Empowering citizens with a right to participate in pre-legislative consultations through a statutory and a constitutional commitment could be a gamechanger.
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-3: Indian Economy & its challenges
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Oil for Emergencies
Context: India has recently moved to release 5 million barrels of oil from its strategic reserves as part of a coordinated challenge led by the US against the OPEC+ producers’ cartel’s move to curb output.
- This is the first time that New Delhi would be dipping into its reserves to leverage it as a geopolitical tool.
- The oil will be released “in parallel and in consultation with” the US, China, Japan and South Korea.
- The UK has announced that it will release 1.5 million barrels of crude; the US is set to release 50 million barrels.
Why are these countries releasing oil from strategic reserves?
- It is part of a concerted effort to negate upward pressure on crude prices from OPEC+ that is keeping supply below demand leading to increase in prices.
- India has called for an increase in the supply by OPEC+ at multiple international forums and in bilateral talks with oil producing countries. India argues that high crude oil prices are impacting the post-Covid economic recovery, especially in the developing countries.
- OPEC+, which controls about half the world’s oil output, had cut production by 10 million barrels a day in April 2020 when prices fell below $20 per barrel as global demand collapsed due to lockdowns.
- The cartel has been accused of being slow to restore production levels despite a sharp increase in crude prices in 2021.
- Even after a scheduled increase in production of 400,000 barrels per day in December, the output of OPEC+ will still be lower than the reference levels of member countries by nearly 5.4 million barrels per day.
How will this affect crude oil prices?
- Talk of a coordinated release of reserves by large oil consuming countries had already played a role in bringing down prices from a high of $86.4 in late October to under $80 per barrel.
- Brent, however, recovered to $82.3 per barrel on Wednesday with some analysts noting that the US had released less oil from its reserves than was expected.
- It is expected that the coordinated release led by the US may add about 70-80 million barrels of crude supply, less than the more-than-100 million barrels the market has been pricing in.
- Saudi and Russia are the largest oil producers in the OPEC+ group, which has indicated it may revisit its plans to gradually increase production in the light of releases from strategic reserves.
How have high crude oil prices impacted India?
- High global prices have contributed to consumers paying record high prices for petrol and diesel across the country.
- In Delhi, petrol is retailing at Rs 104.0 per litre, and diesel at Rs 86.7 per litre, up 27 per cent and 21 per cent respectively from a year ago.
- Consumers are facing prices that are significantly higher than those prior to 2021, despite a recent move by the Centre to cut excise duty on petrol by Rs 5 per litre, and on diesel by Rs 10 per litre.
- The Centre had in 2020 increased central excise duties on petrol and diesel by Rs 13 and Rs 16 per litre respectively in an effort to shore up revenues as economic activity crashed due to the pandemic. Some states have also hiked VAT on fuels.
What are India’s strategic petroleum reserves, and why are they needed?
- India’s strategic reserves are the effort of a broader plan to build an emergency stockpile with millions of barrels of crude oil, on the lines of the reserves that the US and its Western allies set up after the first oil crisis of 1973-74.
- Under the first stage of the Strategic Petroleum Reserve project, underground rock caverns with total storage of 5.33 MMT, or about 38 million barrels of crude oil, have been commissioned at three locations —
- Visakhapatnam (1.33 MMT)
- Mangalore (1.5 MMT)
- Padur in Karnataka (2.5 MMT).
- These facilities can provide for about 9.5 days of India’s crude oil requirements based on 2019-20 consumption levels.
- The combined storage facilities of Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) in the country can hold enough crude oil to meet 64.5 days of requirement, bringing the total national capacity for storage of crude oil and petroleum products to 74 days, according to the Centre.
- India is in the process of expanding its strategic petroleum reserve storage by 6.5 MMT at two locations — Chandikhol in Odisha (4 MMT) and Padur (2.5 MMT).
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) recommends that all countries hold crude oil stocks worth 90 days of imports.
- India imports about 85 per cent of its crude oil requirements. Crude oil from the reserves are to be released by an empowered committee constituted by the government, in the event of any supply disruptions from abroad.
- These include any natural calamity or unforeseen global event leading to an abnormal increase in prices.
Conclusion
- This would be the first instance of India using strategic reserves to influence international prices, adding that India had also drawn down its reserves somewhat earlier this year to supply refineries as crude oil prices were rising.
- A release of 5 million barrels from strategic reserves would equate to about 13 per cent of India’s strategic petroleum reserves. A release of 50 million barrels of crude oil from the US strategic petroleum reserves would equate to about 8.3 per cent of the 604.5 million barrels of crude oil stored in US strategic petroleum reserves.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 Missile warning system named Kupol belongs to which of the following countries?
- USA
- UK
- France
- Russia
Q.2 Which of the following is not a member of Shanghai cooperation organisation?
- China
- India
- Japan
- Pakistan
Q.3 Consider the following statements regarding Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA)?
- Employment under MGNREGA is a legal entitlement
- It is is implemented by the gram panchayat
Select the correct answer from the following codes:
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 25th Nov 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | A |
Must Read
On the lessons of National Family Health Survey-5:
On Crypto Asset boom:
On link between Mental Health & Death penalty:











