IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
In News: Nineteen opposition members were suspended from Rajya Sabha for a week
What is the reason for suspending an MP?
- The general principle is that it is the role and duty of the Presiding Officer — Speaker of Lok Sabha and Chairman of Rajya Sabha — to maintain order so that the House can function smoothly.
- In order to ensure that proceedings are conducted in the proper manner, the Speaker/ Chairman is empowered to force a Member to withdraw from the House.
- Opposition MPs who had been protesting since the beginning of the session, entered the Well, and ignored Deputy Chairman requests to them to return to their seats.
What are the Rules under which the Presiding Officer acts?
Rule Number 373 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business says:
- The Speaker, if he is of the opinion that the conduct of any Member is grossly disorderly, may direct such Member to withdraw immediately from the House, and any Member so ordered to withdraw shall do so forthwith and shall remain absent during the remainder of the day’s sitting.
- To deal with more recalcitrant Members, the Speaker takes recourse to Rules 374 and 374A.
Rule 374 says:
- The Speaker may, if deems it necessary, name a Member who disregards the authority of the Chair or abuses the rules of the House by persistently and wilfully obstructing the business thereof.
- If a Member is so named by the Speaker, the Speaker shall, on a motion being made forthwith put the question that the Member be suspended from the service of the House for a period not exceeding the remainder of the session: Provided that the House may, at any time, on a motion being made, resolve that such suspension be terminated.
- A member suspended under this rule shall forthwith withdraw from the precincts of the House.
Rule 374A
- It was incorporated in the Rule Book on December 5, 2001.
- The intention was to skirt around the necessity of moving and adopting a motion for suspension.
- Notwithstanding anything contained in rules 373 and 374, in the event of grave disorder occasioned by a Member coming into the well of the House or abusing the Rules of the House persistently and wilfully obstructing its business by shouting slogans or otherwise, such Member shall, on being named by the Speaker, stand automatically suspended from the service of the House for five consecutive sittings or the remainder of the session, whichever is less: Provided that the House may, at any time, on a motion being made, resolve that such suspension be terminated.
- On the Speaker announcing the suspension under this rule, the Member shall forthwith withdraw from the precincts of the House.
What happens in Rajya Sabha?
- Like the Speaker in Lok Sabha, the Chairman of Rajya Sabha is empowered under Rule Number 255 of its Rule Book to direct any Member whose conduct is in his opinion grossly disorderly to withdraw immediately from the House.
- Under Rule 256, the Chairman may name a Member who disregards the authority of the Chair or abuses the rules of the Council by persistently and wilfully obstructing business.
- In such a situation, the House may adopt a motion suspending the Member from the service of the House for a period not exceeding the remainder of the session.
- The House may, by another motion, terminate the suspension.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity (Constitutional And Non Constitutional Bodies)
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity & Governance)
In News: The Supreme Court asked the Centre to find out from the Finance Commission whether there is a way to curb political parties from promising and distributing “irrational freebies” during election campaigns.
- A Bench led by Chief Justice of India N. V. Ramana flagged the issue as “serious” and asked for means to control the promise of “freebies” to entice votes.
- The Election Commission of India (ECI), on the other hand aid it has no power to regulate the same or take action against parties making such poll promises.
- In an affidavit, the poll body said “offering/distribution of any freebies either before or after election is a policy decision of the party concerned, and whether such policies are financially viable or its adverse effect on the economic health over the state is a question that has to be considered and decided by the voters.
- Finally the court has asked Additional Solicitor General to explore this avenue and get instructions from the government
- The hearing came on a writ petition filed by Ashwini Kumar Upadhyay, who had argued that the offer and distribution of “irrational freebies” amounted to bribery and unduly influencing voters. It vitiated free and fair elections in the country.
- Upadhyay claimed that States in total had debts of over ₹70 lakh crore.
- He suggested that the Law Commission of India should be asked to examine the statutes to control the giving away of unreasonable freebies.
Finance Commission (FC)
- The FC is a constitutional body that determines the method and formula for distributing the tax proceeds between the Centre and states, and among the states as per the constitutional arrangement and present requirements.
- Under Article 280 of the Constitution, the President of India is required to constitute a Finance Commission at an interval of five years or earlier.
- The 15th Finance Commission was constituted by the President of India in November 2017, under the chairmanship of NK Singh.
Finance Commission – Members Qualifications
- Parliament may by law determine the qualifications which shall be requisite for appointment as members of the Commission and the manner in which they shall be selected.
- The Chairman of the Commission is selected from among persons who have experience in public affairs, and the four other members are selected from among persons who:
- are, or have been, or are qualified to be appointed as Judges of the High Court;
- have special knowledge in the finances and accounts of the Government;
- have had wide experience in financial matters and in administration;
- have special knowledge of economics.
Tenure of Finance Commission
- The President of India specifies the term of office for Members of the Finance Commission, they are normally appointed for five years, and in some situations, the members are re-appointed.
Functions of the Finance Commission
It is the duty of the Commission to make recommendations to the President as to:
- The distribution between the Union and the States of the net proceeds of taxes which are to be, or maybe, divided between them and the allocation between the States of the respective shares of such proceeds.
- The principles which should govern the grants-in-aid of the revenues of the States out of the consolidated fund of India.
- The measures needed to augment the Consolidated Fund of a state to supplement the resources of the Panchayat in the State on the basis of the recommendation made by the Finance commission of these states.
- The measures needed to augment the Consolidated Fund of a state to supplement the resources of the Municipalities in the State on the basis of the recommendation made by the Finance commission of these states.
- Any other matters referred to the Commission by the President in the interests of sound finance.
- The Commission determines its procedure and has such powers in the performance of their functions as Parliament may by law confer on them.
Source: The Hindu
Must Read: freebie culture + Growing Freebies + Election Commission of India
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha, consider the following statements: (2022)
- As per the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha, the election of Deputy Speaker shall be held on such date as the Speaker may fix.
- There is a mandatory provision that the election of a candidate as Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha shall be from either the principal opposition party or the ruling party.
- The Deputy Speaker has the same power as of the Speaker when presiding over the sitting of the House and no appeal lies against his rulings.
- The well established parliamentary practice regarding the appointment of Deputy Speaker is that the motion is moved by the Speaker and duly seconded by the Prime Minister.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
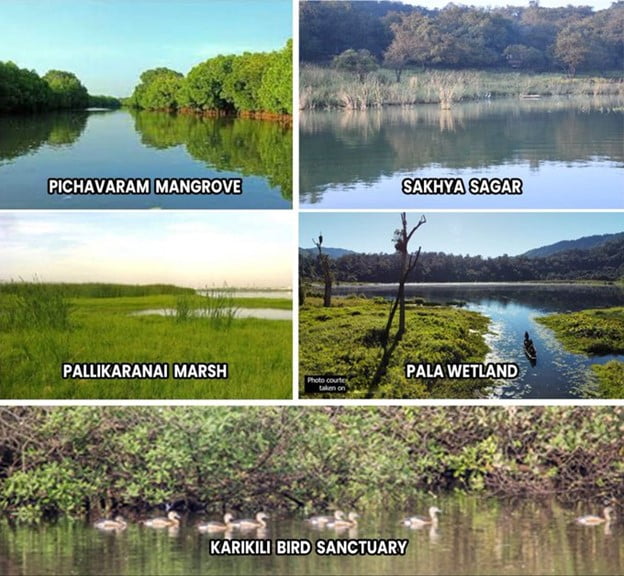
In News: India has added five more Ramsar sites, or wetlands that are of international importance, bringing the number of such sites to 54.
- These are the Karikili Bird Sanctuary, Pallikaranai Marsh Reserve Forest and Pichavaram Mangrove in Tamil Nadu, the Sakhya Sagar in Madhya Pradesh and Pala Wetland in Mizoram.

Wetlands
- Wetlands are an area of marsh, fen, peatland or water; whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with water that is static or flowing, fresh, brackish or salt, including areas of marine water the depth of which at low tide does not exceed six metres, but does not include river channels, paddy fields, human-made water bodies/ tanks specifically constructed for drinking water purposes and structures specifically constructed for aquaculture, salt production, recreation and irrigation purposes.
- To be Ramsar site, however, it must meet at least one of nine criteria as defined by the Ramsar Convention of 1961.
Wetlands in India
- India’s Ramsar wetlands are spread over 11,000 sq km — around 10% of the total wetland area in the country — across 18 States.
- No other South Asian country has as many sites though this has much to do with India’s geographical breadth and tropical diversity.
- The United Kingdom (175) and Mexico (142) have the maximum Ramsar sites whereas Bolivia spans the largest area with 148,000 sq km under the Convention protection.
- Wetlands are also known to have among the highest soil-carbon densities and therefore play a major role in buffering carbon dioxide emissions.
- The National Wetland Inventory and Assessment compiled by the Indian Space Research Organisation, estimates India’s wetlands to span around 1,52,600 square kilometres which is 4.63% of the total geographical area of the country.
- India has 19 types of wetlands whereas Gujarat has the maximum area followed by Andhra Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal.
- Wetlands in Uttar Pradesh and Gujarat serve as important spaces for migratory birds.
Significance
- Being designated a Ramsar site ensure States and the Centre take steps to keep these tracts of land are conserved and spared from man-made encroachment.
- Acquiring this label also helps with a locale’s tourism potential and its international visibility.
Source: Pib.Gov
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
Wetland/Lake: Location
- Hokera Wetland Punjab
- Renuka Wetland Himachal Pradesh
- Rudrasagar Lake Tripura
- Sasthamkotta Lake Tamil Nadu
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Q.2) “If rainforests and tropical forests are the lungs of the Earth, then surely wetlands function as its kidneys.” Which one of the following functions of wetlands best reflects the above statement? (2022)
- The water cycle in wetlands involves surface runoff, subsoil percolation and evaporation.
- Algae form the nutrient base upon which fish, crustaceans, molluscs, birds, reptiles and mammals thrive.
- Wetlands play a vital role in maintaining sedimentation balance and soil stabilization.
- Aquatic plants absorb heavy metals and excess nutrients.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
- Mains – GS 3 (Environment – Pollution)
In News: The Brihan Mumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC) has tied up with Indian Institute of Technology (IIT-B) for in-situ treatment of sewage in nullahs in the city.
- This pilot project will prevent coastal pollution due to sewage from 25 nullahs from flowing untreated into the sea or creeks.
What is N-Treat technology?
- N-Treat is a seven-stage process for waste treatment that uses screens, gates, silt traps, curtains of coconut fibres for filtration, and disinfection using sodium hypochlorite.
- According to the detailed project report for N-Treat, it is a natural and environment friendly way for sewage treatment.
- It’s set up takes place within the nullah channels that is through the in-situ or on-site method of treatment, and does not require additional space.
What does the process involve?
- The first stage involves screening to prevent the entry of floating objects such as plastic cups, paper dishes, polythene bags, sanitary napkins, or wood.
- The second stage has proposed construction of a silt trap, which creates an inclination and ‘parking spot’ on the bed of the nullah for sedimentation.
- The next three stages are installation of ‘bio zones’ in the form of coconut fibre curtains that will act as filters and promote growth of biofilm to help in decomposition of organic matter.
- Next Stage (as proposed by IIT-B) is use of florafts. It involves suspending floating rafts vertically, called florafts.
- According to its proposal, Their hanging roots would provide a large surface area for passive filtration as well as development of microbial consortium.
- The final stage for sewage treatment will include disinfection using sodium hypochlorite, to kill the bacteria in the water.
Significance
- The N-Treat method suggested to the civic body is cost effective, as it does not require manual pumping, and saves electricity, and does not require extensive man-power for maintenance.
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) “Biorock technology” is talked about in which one of the following situations? (2022)
- Restoration of damaged coral reefs
- Development of building materials using plant residues
- Identification of areas for exploration/extraction of shale gas
- Providing salt licks for wild animals in forests/protected areas
Syllabus
- Prelims – History
- Mains – GS 1 (History)
In News: The Union Home Minister announced that the Ahmedabad Railway Station at Kalupur in Ahmedabad City will be developed on the theme of Modhera Sun Temple in the next five years
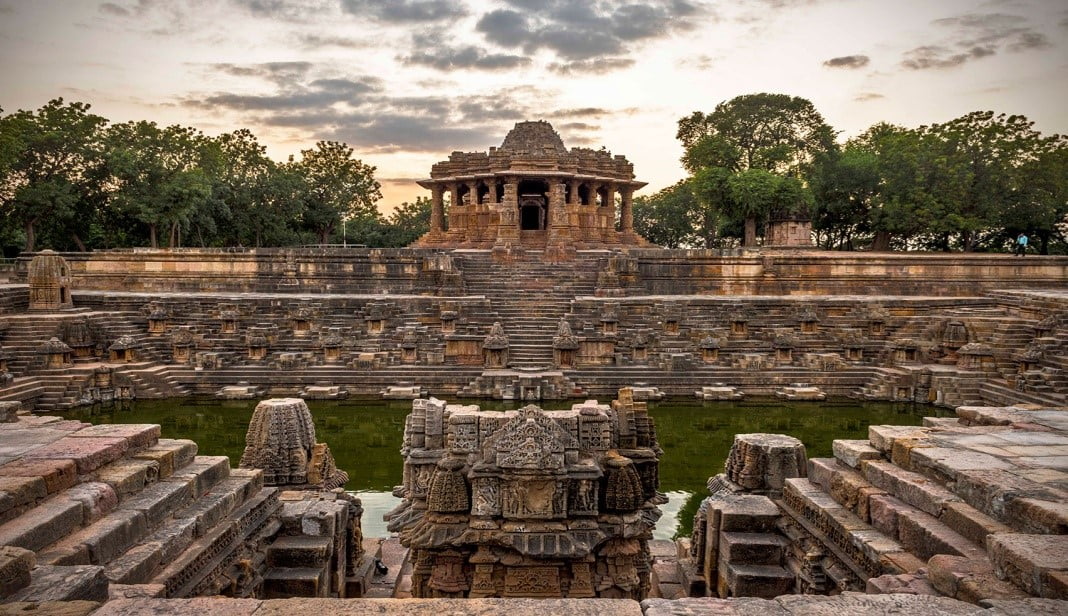
Sun Temple, Modhera
- The Sun Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to the solar deity Surya located at Modhera village of Mehsana district, Gujarat, India.
- It is situated on the bank of the river Pushpavati.
- It was built after 1026-27 CE during the reign of Bhima I of the Solanki dynasty.
- No worship is offered now and is protected monument maintained by Archaeological Survey of India.
- The temple complex has three components: Gudhamandapa, the shrine hall; Sabhamandapa, the assembly hall and Kunda, the reservoir.

Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) Which of the following is/are famous for Sun temples? (2017)
- Arasavalli
- Amarakantak
- Omkareshwar
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to Chausath Yogini Temple situated near Morena, consider the following statements: (2021)
- It is a circular temple built during the reign of Kachchhapaghata Dynasty.
- It is the only circular temple built in India.
- It was meant to promote the Vaishnava cult in the region.
- Its design has given rise to a popular belief that it was the inspiration behind the Indian Parliament building.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3 Only
- 1 and 4
- 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
In News: China and Pakistan had held a meeting to bring other countries into the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
- India said that efforts to broaden CPEC’s scope are “inherently illegal” as it directly infringe on India’s sovereignty and territorial integrity.
CPEC
- A bilateral project between Pakistan and China.
- Intended to promote connectivity across Pakistan with a network of highways, railways, and pipelines accompanied by energy, industrial, and other infrastructure development projects.
- Aims to link the Western part of China (Xinjiang province) to the Gwadar Port in Balochistan, Pakistan via Khunjerab Pass in the Northern Parts of Pakistan.
- It will pave the way for China to access the Middle East and Africa from Gwadar Port, enabling China to access the Indian Ocean.
- India has been severely critical of the CPEC, as it passes through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, which is a disputed territory between India and Pakistan.
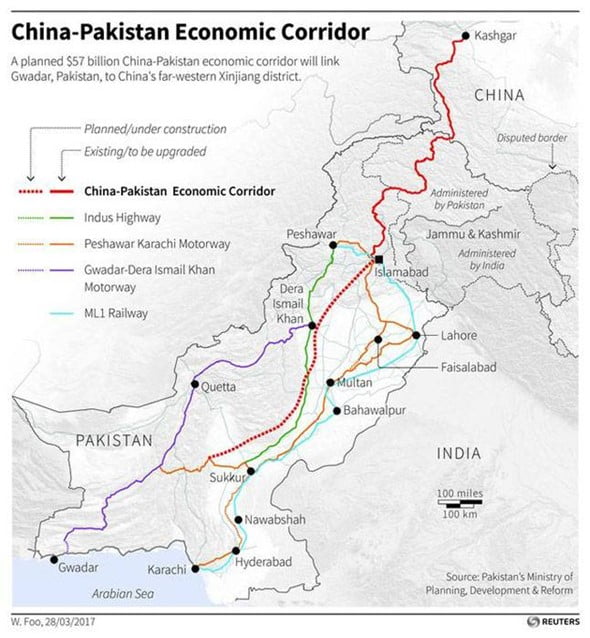
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Economy – Infrastructure – Energy )
Context: the Tamil Nadu Generation and Distribution Corporation (Tangedco) filed a general retail power tariff revision petition with the Tamil Nadu Electricity Regulatory Commission proposing to hike power tariffs by 10% to 35%.
- Mounting losses, outstanding loans and the consequent increase in interest burden, have compelled the Tangedco to file the petition.
- In this context let us a look at status of DISCOMS and request for tariff revision
Reasons behind the tariff revision demand
- Mounting losses
- Outstanding loans
- The consequent increase in interest burden
- Case in point: Even after joining the Ujwal DISCOM Assurance Yojana (UDAY) — a scheme meant for improving the health of state-owned electricity distribution companies (DISCOM)—in January 2017, Tamil Nadu could not bring down the gap between the Average Cost of Supply (ACS) and the Average Revenue Realised (ARR) to nil.
What is happening with the DISCOMs across the country?
- According to Niti Aayog’s report of August 2021, most power DISCOMs incur losses every year — the total loss was estimated to be ₹90,000 crore in the financial year 2021.
- Due to these accumulated losses, DISCOMs were unable to pay for generators on time — as of March 2021, an amount of ₹67,917 crore was overdue.
- To help these DISCOMs, the Centre in May 2020, announced a Liquidity Infusion Scheme (Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan), under which loans of ₹1,35,497 crore have been sanctioned. As of December 31, 2021, a total of ₹1.03 lakh crore has been disbursed.
Where do States stand on power tariffs?
- Despite the Centre’s prescription for annual or periodical revision of retail power tariff, States have found the exercise painful, as the parties in power in the States link the process to their prospects at the time of Assembly or Lok Sabha elections.
- The general approach of many parties is to use electricity as a tool for their political agenda and make promises to allure people despite knowing that such assurances, if implemented, are not sustainable in the long run.
- A common feature of the power distribution policies of the States is to provide free or heavily subsidised supply to agriculture. The connections for the farm sector are unmetered
- DisComs cash flow is disrupted due to dues that are payable to them.
These dues are of three types.
- Improper Tariff fixation by regulators: Regulators themselves have failed to fix cost-reflective tariffs thus creating Regulatory Assets, which are to be recovered through future tariff hikes.
- Pending Subsidies: Second, about a seventh of DisCom cost structures is meant to be covered through explicit subsidies by State governments. Cumulative unpaid subsidies, with modest carrying costs, make DisComs poorer by over ₹70,000 crore just over the last 10 years.
- Consumer Bills pending: Third, consumers owed DisComs over ₹1.8 lakh crore in FY 2018-19, booked as trade receivables.
Way Ahead
- More Stimulus: There is a need a much larger liquidity infusion so that the entire electricity chain will not collapse
- Working on AT&C losses is important, but will not be sufficient. We need a complete overhaul of the regulation of electricity companies and their deliverables.
- Rationalisation of subsidies whereby doling out of free electricity can be eliminated to those who do not deserve such support.
- Segregation of feeders has been suggested as an option to arrive at the accurate consumption of the farm sector so that the disproportionate quantum of consumption is not attributed to agriculturists in the absence of meters.
- Gujarat is cited as a success story in this regard.
- The Madhya Pradesh Electricity Regulatory Commission, in its tariff order of March 2022, came out with an incentive package in the area of demand side management.
- It stipulated that an incentive equal to 5% of energy charges should be given on installation and pushed for the use of energy saving devices such as ISI energy efficient motors for pump sets and programmable on-off/ dimmer switch with automation for street lights.
- Proper Regulation: Regulators must allow cost-covering tariffs.
Note: Launched in July 2021, the Revamped Distribution Sector Reform Scheme (RDSS) is the latest of many central government grant-based programmes towards electricity distribution network investments.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
In News: Government is slowly chipping away at the rights of civil society groups using laws such as FCRA, PMLA
- It is being reported that the Indian state is deeply suspicious of non-governmental organisations (NGOs) and civil society leaders.
- The Constitution and law sought to protect minority communities and mandated equal rights and protection from the state to persons of all faiths and identities.
- According to that idea of India, these rights were deemed essential for the consolidation of the Indian state where citizens needed to feel a sense of belonging.
- Even though civil society organisations have contributed to the constitutional frame, they undoubtedly need to be regulated for defending those values.
Ways in which Civil Society is Targeted
- The Foreign Contributions (Regulation) Act (FCRA), and the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), used in conjunction with a range of other measures such as the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA), are deployed by the government
- Indian NGOs need an FCRA clearance for using foreign funds for developmental work.
- NGOs now needed to renew their licences every five years.
- Cancellation of License: Of the 16,692 NGOs that lost their licences between 2015 and 2022, 16,679 were denied the right between 2015 and 2019 before the Act was amended in 2020.
- A cursory look at these withdrawals suggests that increased compliance requirements enabled the state to flush out a large number of NGOs.
- FCRA amendment of 2020
- NGOs could spend less on administrative costs.
- All NGOs were required to operate their foreign accounts through the State Bank of India’s branch located at Parliament Street in New Delhi. This would enable the state to track foreign funding organisations even more closely.
- The tax-free status of domestic donations would be reviewed every five years.
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) has been reimagined as a tool against civil society leaders and politicians.
- The Enforcement Directorate (ED) of the Department of Revenue has wide-ranging powers to search and arrest citizens under the PMLA.
- The ED was used to attack NGOs such as Amnesty International and the Centre for Equity Studies that have worked incessantly for minority rights.
Conclusion
FCRA and PMLA are potent weapons for subduing the pluralistic nature of Indian society that is at the heart of India’s democracy. Social values can be saved if democratic politics protects those values.
Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA)
- It was enacted in January 2003 and the Act along with the Rules framed there under has come into force with effect from 1st July 2005.
Provisions:
Definition of money laundering
- 3 of PMLA defines offence of money laundering as whosoever directly or indirectly attempts to indulge or knowingly assists or knowingly is a party or is actually involved in any process or activity connected with the proceeds of crime and projecting it as untainted property shall be guilty of offence of money-laundering.
Prescribes obligation:
- PMLA prescribes the obligation of banking companies, financial institutions and intermediaries for verification and maintenance of records of the identity of all its clients and also of all transactions and for furnishing information of such transactions in a prescribed form to the Financial Intelligence Unit-India (FIU-IND).
Empowerment of officers:
- PMLA empowers certain officers of the Directorate of Enforcement to carry out investigations in cases involving offence of money laundering and also to attach the property involved in money laundering.
Setting up of Authority:
- PMLA envisages setting up of an Adjudicating Authority to exercise jurisdiction, power and authority conferred by it essentially to confirm attachment or order confiscation of attached properties.
- It also envisages setting up of an Appellate Tribunal to hear appeals against the order of the Adjudicating Authority and the authorities like Director FIU-IND.
Special Courts:
- It envisages designation of one or more courts of sessions as Special Court or Special Courts to try the offences punishable under PMLA and offences with which the accused may, under the Code of Criminal Procedure 1973, be charged at the same trial.
Source: The Hindu
Must Read: Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA)
Previous Year Question
Q.1) At the national level, which ministry is the nodal agency to ensure effective implementation of the Scheduled Tribes and other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006? (2021)
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
- Ministry of Panchayati Raj
- Ministry of Rural Development
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Security)
In News: Lok Sabha was told there have been 674,021 cyber attacks in the country this year until June (2022) — almost 3,700 cyber attacks a day, making India the third most impacted by network attacks in the world.
- From Covid vaccine research centres to banking and financial entities to PSU major Oil India Limited — a range of institutions came under cyber attack during the two years of the pandemic.
- The April 2022 attack on Oil India in Assam was one of the “most serious” incidents of ransomware attacks. “There were over 200 computers of Oil India that got encrypted during the attack and operations of Oil India came to a halt for almost a week.
- Health and banking were among the sectors hit hardest.
- While these attacks were successfully thwarted, these have underlined the need for constant vigil and global cooperation.
Present Government Initiatives for Cyber Security
Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative
- It was launched in 2018 with an aim to spread awareness about cybercrime and building capacity for safety measures for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT staff across all government departments.
Cyber Swachhta Kendra
- The Cyber Swachhta Kendra (Botnet Cleaning and Malware Analysis Centre) is a part of the Government of India’s Digital India initiative under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- It intends to create a secure cyberspace by detecting botnet infections in India and to notify, enable cleaning and securing systems of end users so as to prevent further infections.
Online cybercrime reporting portal
- Launched in 2019, it is a citizen-centric initiative enabling citizens to report cybercrimes online.
- The portal specifically focuses on crimes against women, children, particularly child pornography, child sex abuse material, online content pertaining to rapes/gang rapes, etc.
- It also focuses on crimes like financial crime and social media related crimes like stalking, cyberbullying, etc.
Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C).
- The scheme to set up I4C was approved in October 2018, to deal with all types of cybercrimes in a comprehensive and coordinated manner.
National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC).
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) is an organisation of the Government of India created under the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- The Information Technology Act, 2000 defines Critical Information Infrastructure (CII) as those computer resource, the incapacitation or destruction of which, shall have debilitating impact on national security, economy, public health or safety.
Source: Indian Express
Baba’s Explainer – Political Crisis in Myanmar
Syllabus
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
- GS-2: India and its neighborhood- relations.
Context: On July 25, Myanmar’s junta(military) executed four pro-democracy activists. The junta spokesperson called the executions “lawful” and said it was “justice for the people.”
- They were sentenced to death in a closed-door trial that rights groups criticised as being unjust.
- News of the killing was met with intense criticism from opposition groups and human rights organisations.
- In 2021, the country’s military seized power, an event which triggered widespread demonstrations, prompting a military crackdown on pro-democracy protesters, activists and journalists.
Read Complete Details on Political Crisis in Myanmar
Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements about Modhera Sun temple
- It is situated on the bank of the river Tapi
- It was built during the reign of Bhima I of the Solanki dynasty
- The temple complex has three components: Gudhamandapa, Sabhamandapa, and Kunda
Choose the correct statements:
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements
- Under the Constitution the Presiding officer of Lok Sabha has been empowered to suspend a MP from the House for disorderly conduct
- The termination of the suspension order of the respective MP can only be done by the Speaker of Lok Sabha.
Choose the incorrect statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Which of the below given pairs is/are correctly matched?
| Wetland | State |
| Renuka Wetland | Himachal Pradesh |
| Pala Wetland | Madhya Pradesh |
| Rudrasagar Lake | Tripura |
Choose the correct code:
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1 only
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’27th JULY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.
ANSWERS FOR 26th JULY 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – d











