IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment
Context: Researchers at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln have reported that a particular genus of plankton, namely Halteria, can ‘grow and divide given only viruses to eat’.
About Halteria:

- Halteria — microscopic ciliates (a single-celled organism with minuscule hairs) that populate freshwater worldwide — can thrive wholly on a virus-only diet or ‘virovory’.
- Plankton of the genus Halteria can each consume 10,000 to a million virus particles a day, increase their population using the metabolised energy, and provide more food for the zooplanktons that consume the Halteria.
- Virovory is sufficient to support an organism’s physiological development and even population increase.
- They’re made up of nucleic acids, a lot of nitrogen and phosphorous.
Significance of Halteria:
- Halteria plankton are found in large numbers in freshwater bodies.
- They are heterotrophs meaning they can’t produce their own food.
- Instead, they are well-known bacterivores — they consume bacteria to power themselves.
- Viruses “short-circuit” the process of nutrients moving up the food chain.
- They infect and kill both bacteria and plankton, releasing organic matter that dissolves in the water.
- By also consuming viruses for nutrition, Halteria plankton can recover the nutrients lost in the viral shunt and bring them back into the food chain.
About Planktons:
- Plankton are usually microscopic, often less than one inch in length, but they also include larger species like some crustaceans and jellyfish.
- Scientists classify plankton in several ways, including by size, type, and how long they spend drifting.
- But the most basic categories divide plankton into two groups: phytoplankton (plants) and zooplankton (animals).
- Phytoplankton are microscopic plants, but they play a huge role in the marine food web.
- Like plants on land, phytoplankton perform photosynthesis to convert the sun’s rays into energy to support them, and they take in carbon dioxide and produce oxygen.
- Zooplankton include microscopic animals (krill, sea snails, pelagic worms, etc.), the young of larger invertebrates and fish, and weak swimmers like jellyfish.
- Most zooplankton eat phytoplankton, and most are, in turn, eaten by larger animals (or by each other).
- Krill may be the most well-known type of zooplankton; they are a major component of the diet of humpback, right, and blue whales.
- During the daylight hours, zooplankton generally drift in deeper waters to avoid predators.
- But at night, these microscopic creatures venture up to the surface to feed on phytoplankton.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following kinds of organisms:
- Copepods
- Cyanobacteria
- Diatoms
- Foraminifera
Which of the above are primary producers in the food chains of oceans? (2021)
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Q.2) Which of the following are detritivores?
- Earthworms
- Jellyfish
- Seahorse
- Woodlice
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 2, 3, 4 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims – Defence
Context: The Indian Navy is set to commission the fifth of its diesel-electric Scorpene-class submarine Vagir.
About Submarine Vagir:
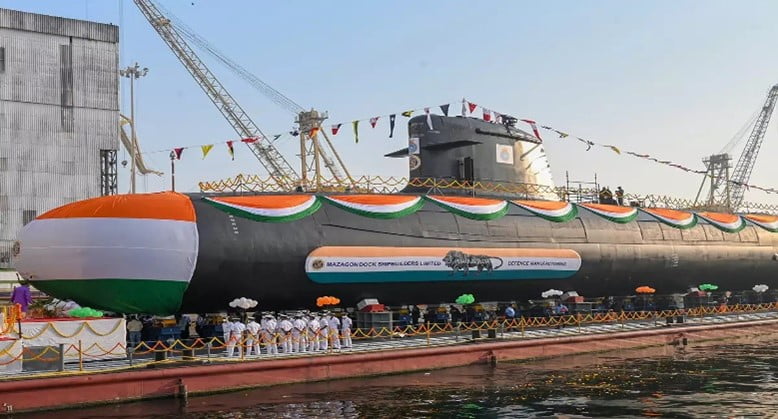

- Vagir is among the six submarines being built in India by the Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) Mumbai, in collaboration with the French M/s Naval Group under Project 75.
- INS Vagir is the fifth submarine of the first batch of six Kalvari-class submarines for the Indian Navy.
- It is a diesel-electric attack submarine based on the Scorpène class.
- It is named after the Sand Fish of the Indian Ocean.
- It is designed to operate in all theatres of operation.
- It can launch attacks with both torpedoes and tube launched anti-ship missiles, whilst underwater or on surface.
- The Kalvari class is capable of offensive operations across the entire spectrum of naval warfare including:
- anti-surface warfare,
- anti-submarine warfare,
- intelligence gathering,
- mine laying and
- area surveillance
MUST READ: Project 75I
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to `Astrosat’, the astronomical observatory launched by India, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- Other than the USA and Russia, India is the only country to have launched a similar observatory into space.
- Astrosat is a 2000 kg satellite placed in an orbit at 1650 km above the surface of the Earth.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Union Minister of State for Skill Development and Entrepreneurship and Electronics and IT, felicitated over 200 tribal women who have successfully completed training under Phase 3 of the Grameen Udyami Scheme.
About Grameen Udyami Scheme:
- Grameen Udyami Scheme was launched to expand skill training in tribal communities for their inclusive and sustainable growth.
- Under the programme, the initiative was taken to provide multiple skills to India’s youth and impart practical skills to them for enabling livelihoods.
- It is funded by National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) that aims to train tribal students in 6 states: Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, and Gujarat.
- Main Objectives of the scheme:
- Increase in Rural/Local Economy.
- Enhance employment opportunities.
- Reduce forced migration due to a lack of local opportunities.
- Conservation of natural resources.
- The overall aim is to expand the rural/local economy, enhance employment opportunities, reduce forced migration and also lead to the conservation of natural resources.
- Transportation, boarding and lodging during the learning period is provided to candidates.
- The training under the project will be conducted in the Job roles which are relevant to the local economy.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: A wildlife team has recently spotted the ‘Spot Bellied Eagle Owl’ (Bubo Nipalensis) for the first time in the Seshachalam forest, and for the third time in Andhra Pradesh.
About Spot Bellied Eagle Owl:
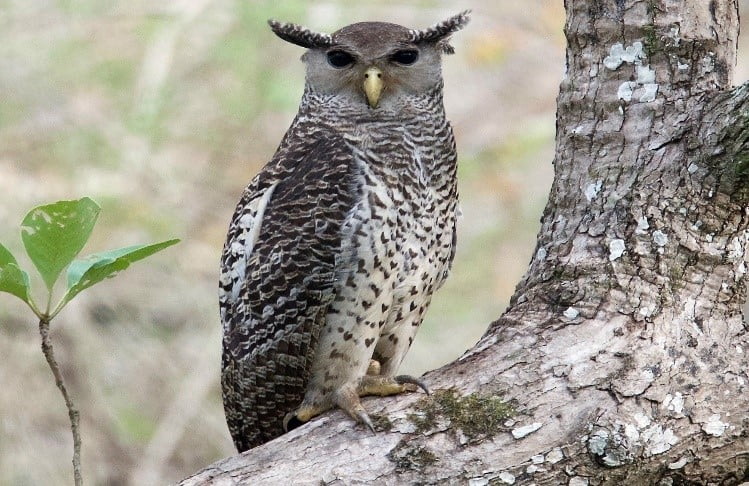

- It is overall a stark, greyish-brown bird, with dark, coarse brown coloration over the back and upper wings.
- It is a large bird of prey and is also known as the forest eagle-owl.
- It is a very powerful and bold predatory owl.
- The bird makes a strange scream similar to humans and it is hence called the ‘Ghost of the Forest’ in India and ‘Devil Bird’.
- They are mostly found in dense, evergreen forests or moist deciduous forests.
- They are found throughout the Indian subcontinent and peninsular Southeast Asia.
- IUCN Status: Least Concern
- CITES status: Appendix II
Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve:
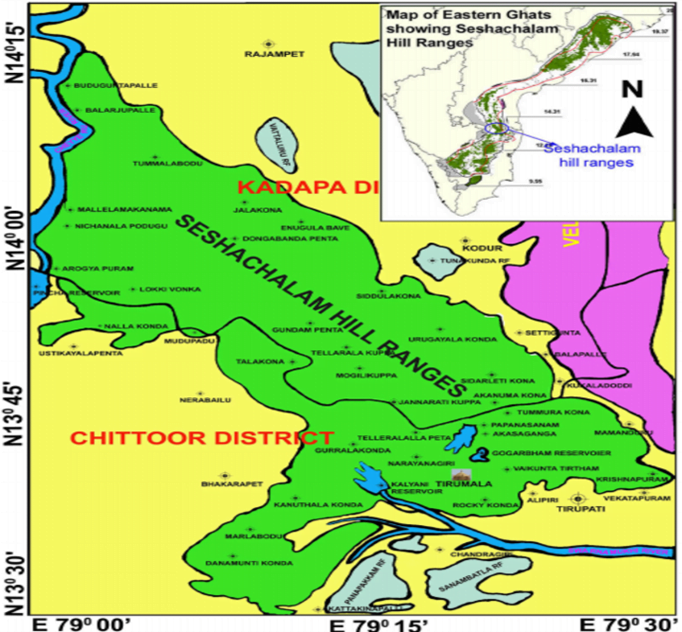
- Seshachalam Hills are the hill ranges of the Eastern Ghats, southern Andhra Pradesh state, and south-eastern India.
- They are bounded by the Rayalaseema uplands in the west and northwest and the Nandyal Valley (formed by the Kunderu River) in the northeast.
- Minerals contained in these hills include sandstone and shale interbedded with limestone.
- The hills contain seven peaks namely, Anjanadri, Garudadri, Narayanadri, Neeladri, Seshadri, Venkatadri, and Vrishabhadri.
- It was designated as a Biosphere Reserve in 2010.
- Tirupati, a major Hindu pilgrimage town and the Sri Venkateshwara National Park are located in these ranges.
- It is home to a number of endemic species including the famous Red Sanders and Slender Loris.
- Tribes of Yanadis are the native population of the reserve.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following animals
- Hedgehog
- Marmot
- Pangolin
To reduce the chance of being captured by predators, which of the above organisms rolls up/roll up and protects/protect its/their vulnerable parts? (2022)
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3
Q.2) Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”? (2019)
- Corbett
- Ranthambore
- Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam
- Sunderbans
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
In News: Families in the coastal pockets of Odisha‘s Ganjam district have been eking out a living by preparing aromatic kewda oil for years, and a recent growth in demand has put a smile on their faces.
- The price per litre of kewda oil was Rs 4.5 lakh last year
- Every year, kewda farmers, flower sellers and oil makers earn around Rs 50-60 crore.
Ganjan kewda oil
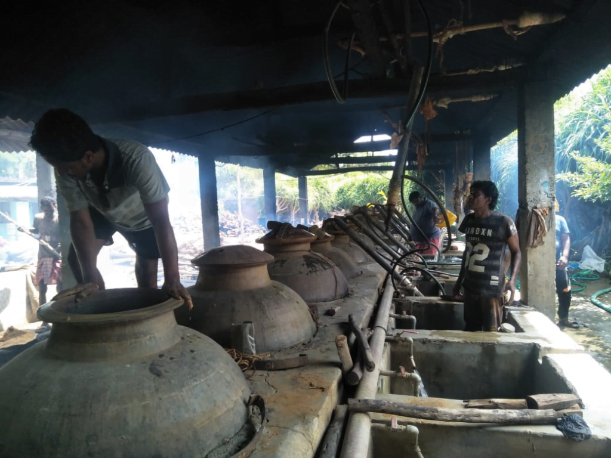


- Ganjam kewda (Pandanus fascicularis) oil is steam-distilled from the flower of the aromatic screwpine plant
- Pandanus or screwpine plant grow along seacoasts and in marshy places and forests of tropical and subtropical regions, especially in Asia, Africa, and Oceania.
- It is used as an aromatic in the food industry and other sectors.
- It is registered under the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 by the Government of India.
- The flower is harvested from around 5,000 hectares in the district.
- Its oil is produced in Ganjam, Chatrapur, Chikiti and Rangeilunda blocks of the district
- For around 200,000 people living in 220 villages of the district, it is the main source of income.
- The farmers and collectors receive an advance from Ganjam’s oil makers who buy the flowers from them during June to September — the harvesting season.
- Kewda oil makers sell to Kannauj, Agra, Kanpur, New Delhi, Mumbai and other places at around Rs 5 lakh a litre
- There is a Fragment and Flavour Development Center (FFDC) extension unit at Berhampore, Ganjam under the Union Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises.
- Flower producer groups eliminated the role of middlemen and provided proper marketing facilities.
- FFDC is also training oil makers and helping them purchase modern equipment to start distilling units through the government-managed District Industry Center
- It is used in food, zarda (flavoured tobacco) and pharmaceutical companies
Source DTE
Previous Year Question
Q.1) With reference to ’palm oil’, consider the following statements: (2021)
- The palm oil tree is native to Southeast Asia.
- The palm oil is a raw material for some industries producing lipstick and perfumes.
- The palm oil can be used to produce biodiesel.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 Only
- 2 and 3 Only
- 1 and 3 Only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – International Relations
In News: Pacific island nations are urging Japan to postpone the release of water from the stricken Fukushima nuclear power plant due to concerns that fisheries will be contaminated, according to the Pacific Island Forum (PIF)
- The PIF, a regional bloc of 17 island nations, claims that releasing the water will have a significant impact on fishing grounds that are vital to island economies and supply up to half of the world’s tuna fish.
Pacific Island Forum (PIF)

- The Pacific Islands Forum is the region’s premier political and economic policy organisation.
- Founded in 1971
- It comprises 18 members: Australia, Cook Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Fiji, French Polynesia, Kiribati, Nauru, New Caledonia, New Zealand, Niue, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Republic of Marshall Islands, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, and Vanuatu.
- The Forum’s Pacific Vision is for a region of peace, harmony, security, social inclusion and prosperity, so that all Pacific people can lead free, healthy, and productive lives.
- The Pacific Islands Forum works to achieve this by fostering cooperation between governments, collaboration with international agencies, and by representing the interests of its members.
- The Forum currently recognises 18 dialogue partners: Canada, People’s Republic of China, Cuba, European Union, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, Philippines, Spain, Thailand, Turkey, United Kingdom and the United States.
- The work of the Forum is guided by the Framework for Pacific Regionalism, which was endorsed by Forum Leaders in 2014. It sets out the strategic vision, values, objectives and approaches to achieve deeper regionalism in the Pacific.
Sources: Newsonair
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
In News: Ports, Shipping and Waterways Minister signed the Memorandum of Agreement between the Indian Ports Association and Research and Information System for Developing Countries for setting up a Centre for Maritime Economy and Connectivity in New Delhi.
Indian Ports Association
Aim:
- To make India as one of the major players in world maritime trade, creating the international standards in port operation and utilizing the great potential in our country’s 7517 km long coastline.
- To undertake and promote Techno-Economic Studies and Research into matters pertaining to the Planning Organization
- To offer complete solutions to Port Management and to create a resource of information as a tool for decision making.
- To efficiently promote the use of Work Study, Management Accounting Strategies and other top-of -the-line tools of Management with a view to increase effciency and productivity in ports
- To bring together various national as well as international organisations involved in Port and Harbour Operations, Management and allied activities and to maintain liasion between ports, Ministry of Shipping and other Government agencies.
- To promote the culture of Uniformity and Standardisation in the port functioning.
About:
- The Indian Ports Association(IPA) was constituted in 1966 under Societies Registration Act
- Primarily with the idea of fostering growth and development of all Major Ports.
- IPA is an apex body of Major Ports under the supervisory control of Ministry of Shipping, Government of India.
- Over the years, IPA has consolidated its activities and grown strength by strength and considered to be a think-tank and Centre of Excellence for Indian Maritime Sector.
Source: Newsonair
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
In News: The third meeting of the National Level Steering Committee (NLSC) of the Atal Bhujal Yojana was held at New Delhi under the Chairmanship of Secretary, Department of Water Resources, RD & GR, Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- This scheme is bringing change in Ground Water Management.
Atal Bhujal Yojana (ATAL JAL):
Aim:
- To bring in behavioural changes in the community, from the prevailing attitude of consumption to conservation & smart water management.
- Creation of awareness among the general public about the program objectives
- Creation of an enabling environment for scheme implementation at various levels through information, education and communication (IEC)
- The thrust of the campaign is at the Gram Panchayat(GP) level, where communication tools such as nukkadnataks (street plays), audio-visual clips, wall-writing, display boards, pamphlets and cable TV are being extensively used.
About:
- Central Sector Scheme
- Started in 2020 in 8220 water stressed Gram Panchayats of 229 administrative blocks/Talukas in 80 districts of seven States, viz. Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh for five year period (2020-25).
- Interventions include Water Security Plans (WSPs).
- The sustainability of the drinking water sources are to be given utmost priority while taking up interventions under this Scheme.
- Further, since incentive money is an untied fund, it can be used for undertaking pilot projects in any of the Atal Jal Gram Panchayat in order to sustain ground water.
- Since communities are at the forefront in this scheme, importance of capacity building of the communities was also emphasized.
- One of the main challenges was low convergence by the States as compared to what was expected.
Source PIB
Previous Year Question
Q1.) With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements: (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: The World Economic Forum (WEF) has chosen Hyderabad for establishing its Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution focused on healthcare and life sciences. C4IR Telangana will be the 18th centre to join WEF’s Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) network that spans four continents.
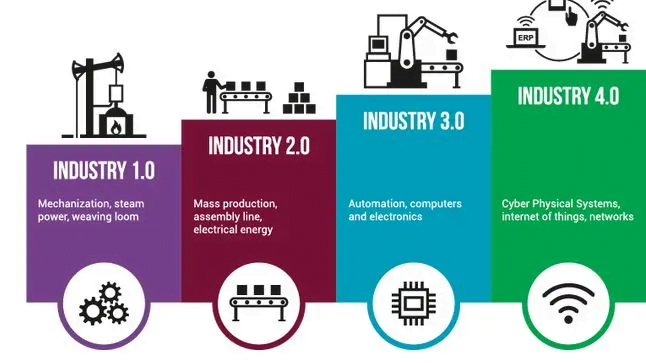
- The first industrial revolution used water and steam power to mechanise production (the 1800s).
- The second used electric power to create mass production (the early 1900s).
- The third used electronics and information technology to automate production (the late 1900s).
About Industrial Revolution 4.0:
- The term ‘Industry 4.0’ was coined by the German government in 2011.
- Industry 4.0 refers to a new phase in the Industrial Revolution that focuses heavily on interconnectivity, automation, machine learning, and real-time data.
- Industry 4.0, which encompasses IoTs and smart manufacturing, marries physical production and operations with smart digital technology, machine learning, and big data .
- Industry 4.0 comes into play when every company and organization operating today is different, they all face a common challenge—the need for connectedness and access to real-time insights across processes, partners, products, and people.
Industry 4.0 Technologies:

Significance of Industrial Revolution 4.0:
- It has the potential to raise global income levels and improve the quality of life for populations around the world.
- It will also lead to a supply-side miracle, with long-term gains in efficiency and productivity.
- Transportation and communication costs will drop, logistics and global supply chains will become more effective, and the cost of trade will diminish, all of which will open new markets and drive economic growth.
- Governments will gain new technological powers to increase their control over populations, based on pervasive surveillance systems and the ability to control digital infrastructure. .
- Advances in technology will create the potential to reduce the scale or impact of violence, through the development of new modes of protection, for example, or greater precision in targeting.
Challenges of IR 4.0:
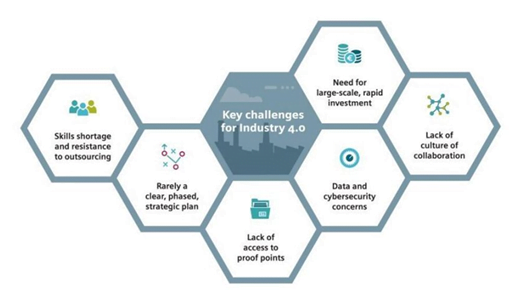
- The immediate fear is that of job loss, particularly in the informal sector.
- It could yield greater inequality, particularly in its potential to disrupt labor markets.
- Besides all these, there are several other critical concerns surrounding safety, ethics, and the short- and long-term socio-economic impact that remain unanswered.
- There is a growing concern that the existing fallacies in humans might only get more accentuated after 4IR.
- There are several studies that show how facial recognition technologies have a higher chance of misidentifying African and Asian people compared to their Western counterparts. It is also going to be skewed as developing and least developed countries lack the data framework and infrastructure.
- It will also profoundly impact the nature of national and international security, affecting both the probability and the nature of the conflict. This will lead to new fears.
- One of the greatest individual challenges posed by new information technologies is privacy.
Need for India to adopt IR 4.0:
- Advanced data analysis will help its manufacturing capacity and increase the quality of the product.
- Business Analytics will work on the prediction and prevention of production defects.
- Digitization of numerous manufacturing processes will lead to cost reduction with an improved experience for consumers.
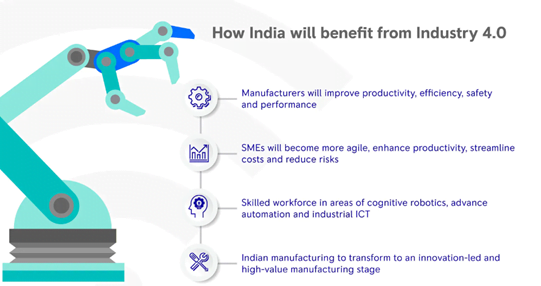
- The implementation of automation will reduce manufacturing cycles, decrease cycle time, and will reduce wasteful use of capital.
- IoT and man-machine connectivity will help supply chains to decrease lead times.
Status in India:
- India is moving towards becoming a hub of global manufacturing, 3D printing, machine learning, data analytics, and IoT are key to promoting industrial growth,
- In November 2020, the Modern Coach Factory (MCF) at Raebareli, Uttar Pradesh, rolled out smart railway coaches that are fitted with a battery of sensors to provide a comfortable experience to passengers.
- In May 2020, the Union Ministry of Heavy Industries launched the Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hub (SAMARTH) scheme, which brings together manufacturers, vendors, and customers to make them aware of 4IR technologies.
- In 2022’s budget speech, the Union finance minister announced a slew of new 4IR-driven projects, including Drone Shakti, to encourage start-ups that will facilitate the use of drone services.
- India even has a 4IR centre in Mumbai run by WEF, which is closely working with several state governments.
- The Centre has recently come up with the Fourth Industrial Revolution for Sustainable Transformation (FIRST) Cancer Care model in which 4IR technologies would be used to provide better healthcare for cancer patients
- In February 2022, Government launched the pan-India 3D maps programme by Genesys International for the 100 smart cities.
- The company plans to map an entire city in intricate detail so that many 4IR revolution technology-based projects, such as driverless cars, will become easier to implement.
Way Forward:
- Industry 4.0 has started to make an influence in manufacturing and other various sectors in India.
- Data-driven decision-making is getting implemented in numerous fields.
- Though certain steps have already been taken, a lot of work needs to be done.
- Instead of just spending more capital, the emphasis must be on increasing the current asset base.
- The implementation of smart manufacturing, data analytics, and the Internet of Things will give a positive direction to Indian industries.
- To secure India’s active involvement in the fourth industrial revolution, it will be necessary to restructure some vital domestic industries and strengthen institutional capability.
Source: DownToEarth
Syllabus
- Mains –GS 2 International Relations
Context:
- External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar has said that India is committed to increase investment flows to Sri Lanka to hasten its economic recovery
- India and Sri Lankan discussed cooperation in infrastructure, connectivity, energy, industry and health.
- Dr. Jaishankar’s visit to the island nation comes at a crucial time as Sri Lanka has been making efforts to obtain an extended fund facility from International Monetary Fund.
Bilateral Relations:
- India is Sri Lanka’s closest neighbour and the relationship between the two countries is more than 2,500 years old built upon a legacy of intellectual, cultural, religious and linguistic interaction.
- In recent years, the relationship has been marked by close contacts at the highest political level such as Bilateral exchanges at various levels
Political relations:
- Developmental assistance projects for the Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs) and disadvantaged sections of the population in Sri Lanka has helped further cement the bonds of friendship between the two countries.
- During the course of the three-decade long armed conflict between Sri Lankan forces and the LTTE(ended in 2009), India supported the right of the Government of Sri Lanka to act against terrorist forces.
- At the same time, it conveyed at the highest levels its deep concern at the plight of the mostly Tamil civilian population, emphasizing that their rights and welfare should not get enmeshed in hostilities against the LTTE.
- The need for national reconciliation through a political settlement of the ethnic issue has been reiterated by India at the highest levels. India’s consistent position is in favour of a negotiated political settlement, which is acceptable to all communities within the framework of a united Sri Lanka and which is consistent with democracy, pluralism and respect for human rights
- Prime Minister Wickremesinghe has said that India was the ‘only nation’ to help out his country through the continuing food, fuel, and pharma crisis.
Commercial relations:
- India and Sri Lanka signed the India-Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement (ISFTA) in 1998 which came into force in 2000 – provides duty-free access and duty preferences to goods.
- A Joint Study Group (JSG) was set up in 2003 to make recommendations on how to take the two countries beyond trade and achieve greater economic integration through the conclusion of a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
- Talks have resumed under a new framework called the ‘Economic and Technological Cooperation Agreement’ (ETCA) – to boost cooperation in technical areas, scientific expertise and research amongst institutions, boost standards of goods and services able to compete on the global market and improve opportunities for manpower training and human resource development.
Trade
- India is Sri Lanka’s largest trading partner with a share of 16 percent in Sri Lanka’s total trade with the world.
- Bilateral trade between India and Sri Lanka has increased by around 9 times between 2000-01 and 2018-19.
- India has always had a trade surplus with Sri Lanka
- In 2018-19, India’s top 3 exports to Sri Lanka included mineral fuels, ships and boats, and vehicles accounting for 43 percent of total exports to Sri Lanka.
- India’s top 3 imports included ships and boats, residues and waste from the food industries, and coffee, tea, mate and spices accounting for 56 percent of total imports.
- India’s exports to Sri Lanka are losing their competitiveness vis-a-vis China’s exports to Sri Lanka.
Development cooperation
- India’s grants to Sri Lanka alone amounting to around USD 570 million, the overall commitment by GOI is to the tune of more than USD 3.5 billion.
- A US$ 100 million LoC for undertaking solar projects in Sri Lanka has been signed between the Government of Sri Lanka and EXIM Bank on June 16, 2021.
- The Indian Housing Project, with an initial commitment to build 50,000 houses in war affected areas and estate workers in the plantation areas, is Government of India (GoI)’s flagship grant project in Sri Lanka.
- The country-wide 1990 Emergency Ambulance Service is another flagship project.
- Some of other notable grant projects which have been completed are the 150-bed Dickoya hospital, livelihood assistance to nearly 70,000 people from fishing and farming community in Hambantota, supply of medical equipment to Vavuniya Hospital and 150 Boats and Fishing gear for Mullaithivu fishermen.
- A modern 1500 – seat auditorium named after Rabindranath Tagore in Ruhuna University, Matara, is the largest in any University in Sri Lanka.
- Under the LOC of USD 318 million, various projects for procurement of rolling stocks for Sri Lankan Railways, upgradation of railway tracks, setting up of railway workshop etc are at different stages of implementation.
Cultural Relations
- The Cultural Cooperation Agreement signed by the Government of India and the Government of Sri Lanka in 1977 forms the basis for periodic Cultural Exchange Programmes between the two countries.
- Buddhism is one of the strongest pillars connecting the two nations and civilizations from the time when the Great Indian Emperor Ashoka sent his children Arhat Mahinda and Theri Sangamitta to spread the teachings of Lord Buddha at the request of King Devanampiya Tissa of Sri Lanka.
- the venerated relics of Lord Buddha from Kapilawasthu discovered in 1970 in India have been exhibited two times in Sri Lanka.
- Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi during the Virtual Bilateral Summit held between India and Sri Lanka on 26 September 2020, announced a USD 15 million grant assistance for protection and promotion of Buddhist ties between India and Sri Lanka
- In July 2020, the Government of India declared the Kushinagar Airport in India, the place of Lord Buddha’s Mahaparinibbana, as an international airport, to allow Buddhist pilgrims from around the world to visit the revered site associated with Lord Buddha with ease – first inaugural flight from Sri Lanka
- Swami Vivekananda Cultural Centre (SVCC) – the cultural arm of the High Commission of India, Colombo, has been playing a key role in strengthening these ties and promoting people-to-people contacts between India and Sri Lanka since its inception in 1998.
- Tourism – India launched the e-Tourist Visa (eTV) scheme for Sri Lankan tourists in 2015.
Security
- Military exercise called Mitra Shakthi and the Naval exercise called “Slinex.”
- The defence teams from the two nations recently also met at the Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) meet in Kochi, India to further their defence ties.
Issues and concerns
- Traditionally, India–Sri Lanka bilateral relations are centered on a few specific issues and concerns—security concerns (now includes security cooperation), ethnic issues, fishers dispute, and investment climate
- Investment atmosphere – Costly investment agreements had been signed with India, under the Rajapaksa regime, amidst heavy criticism from the political opposition such as in power sector.
- Chinese dominance – Sri Lanka’s balancing act with India, under the shadow of China’s BRI investments in the island to keep both India and China interested has affected Sri Lanka’s relations with India, given the latter’s antithetical relations with China.
- Fisheries front – on daily-basis Indian fishermen continued to be arrested and their boats and gears impounded on allegations of violating the IMBL and poaching in Sri Lankan waters.
- Four Maritime Boundary Agreements have been signed by the two states between 1974-76 regarding the 12 nautical miles of international waters in the Palk Strait, the terms of the agreement are hardly followed diligently.
- The Sri Lankan Navy continues to accuse India’s fishers of violating the decided lines and poaching in their territorial water.
- There is another conflict wherein, Sri Lanka criticizes India’s bottom trawler usage in the Palk Strait, which has been a recurring issue for the countries.
- India’s China concerns viz Sri Lanka continue to remain real though through the past years, there is nothing to suggest that Chinese commercial investments had led to any military/security tie-up that New Delhi should be worried about.
- China-funded Colombo Port City project any time soon looks suspect at best.
- Ethnic issues including the Tamil proposals and the Sinhala-Buddhist majority social reaction
- Till date, the 13th Amendment to Sri Lanka’s Constitution, following the Indo-Sri Lanka Accord, signed on 29 July 1987 has not been honoured.
Way forward
In light of various bilateral issues, the need for national reconciliation through a political settlement of the current issues has been reiterated by India at the highest levels which is consistent with democracy, pluralism and respect for human rights.
Source Newsonair
Baba’s Explainer – Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS)
Syllabus
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
- GS-3: Indian Economy & Development
Context: While a reasonable chunk of billers and utility providers are covered under BBPS, the RBI Governor said the platform will be extended to all payments and collections, including those that are non-recurring, such as professional service fee, tax collection and rent payment.
Read Complete Details on Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS)
Practice MCQs
Q.1) With reference to ‘kewda oil’, consider the following statements
- The kewda oil tree is native to India.
- The kewda oil is used in zarda (flavoured tobacco) and pharmaceutical companies
- The kewda oil farmers and makers earn high revenues.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 Only
- 2 and 3 Only
- 1 and 3 Only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to ‘Atal Bhujal Yojana’, consider the following statements
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme.
- It aims at behavioural change in smart water management
- It was introduced in 2020 in all the districts of the country
Which of the following statements are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding Plankton:
- Halteria plankton are found in large numbers in freshwater bodies.
- Phytoplankton are microscopic animals which play a huge role in the marine food web.
- krill, sea snails, pelagic worms and jelly fish are examples of Zooplankton.
Which of the statements given are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 20th January 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 19th January – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – b













