IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Defence
Context: The 12th edition of the joint military exercise Ekuverin commenced at Chaubatia, Uttarakhand recently.
About Exercise Ekuverin:-
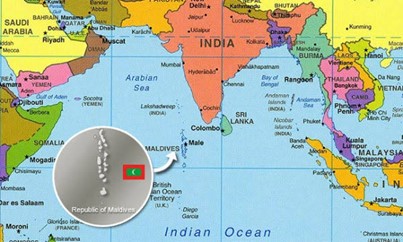
IMAGE SOURCE: Quora
- It is a joint Military Exercise between India & Maldives.
- Ekuverin means ‘Friends’ in the Maldivian language. (UPSC MAINS: India’s interests in the Maldives )
- Background: India and Maldives have been conducting Exercise Ekuverin since 2009.
- It focuses on enhancing interoperability between the two forces for carrying out counter-insurgency and counter-terrorism operations in a semi-urban environment under the United Nations mandate and carrying out joint Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief operations.
- 11th edition: was held in Maldives in December 2021.
- 12th edition: was held in Uttarakhand, India in June 2023.
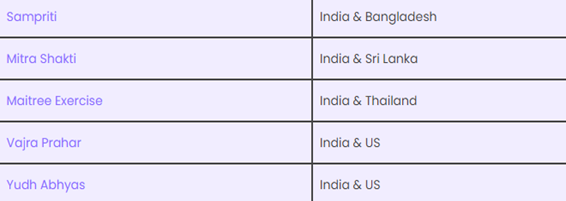
Other important joint military exercises of India:

MUST READ: India-Maldives relations
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2020)
International agreement/ set-up Subject
- Alma-Ata Declaration – Healthcare of the people
- Hague Convention – Biological and Chemical Weapons
- Talanoa Dialogue – Global Climate Change
- Under2 Coalition – Child Rights
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2,3 and 4 only
Q.2) Consider the following statements (2020)
- The value of Indo-Sri Lanka Trade has consistently increased in the last decade.
- “Textile and textile articles constitute an important item of trade between India and Bangladesh
- In the last five years, Nepal has been the largest trading partner of India in South Asia
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1,2, and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Defence
Context: The Norwegian Ambassador has paid a visit to the ISRO Chairman. The meeting concluded with a mutual agreement on the importance of maintaining a continued partnership and fostering increased engagements between India and Norway in the field of space exploration and technology.
About Svalbard mission:-
IMAGE SOURCE: gktoday.in
- This visit offers an occasion to recall the challenging Svalbard mission, which took place 26 years ago at Ny-Alesund, Svalbard.
- In 1997, under the Savalbard mission, Antrix signed an agreement with the Norwegian Space Centre for the sale of a Rohini RH-300 Mk.II Sounding Rocket. (UPSC CSE: NISAR)
- Antrix Corporation Limited (ACL): is a marketing arm of ISRO for the promotion and commercial exploitation of space products, technical consultancy services and transfer of technologies developed by ISRO. (UPSC CSE: IN-SPACe).
- The RH-300 Mk-II was given a new name by the Norwegian Space Centre as Isbjorn-1, which translates literally as ‘Polar Bear-I.’
- Challenge: the Rohini rockets had until then flown only in the tropical hot and humid conditions in India. while the Svalbard archipelago’s temperatures were on the extremely low side.
- ISRO shipped the RH-300 Mk-II to Norway after qualifying it for arctic weather conditions.
- However, the rocket, unfortunately, did not achieve the predicted height, rising only up to 71 km.
- Nevertheless, the Norwegian scientists seemed happy with the launch as the data collected during the flight led to some new findings.
- This launch marked a new era of cooperation between the two countries in space research.
RH-300
- It is a single-stage sounding rocket.
- Derived from French Belier rocket engine technology.
- Launch altitude:100 km.
- A variant, the RH-300 Mk-II, has a maximum launch altitude of 116 kilometers.
- Payload: up to 80 kilograms (20 kg of scientific payload).
- Numerous payloads can be tested in a single flight.
ISRO
- ISRO was formed on August 15, 1969 with an expanded role to harness space technology. Department of Space (DOS) was set up and ISRO was brought under DOS in 1972.
- It is the space agency under the Department of Space of the Government of India.
- HQ: Bengaluru, Karnataka.
- Vision: to harness space technology for national development, while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration.
- Objective: development and application of space technology for various national needs.
- To fulfil this objective, ISRO has established major space systems for communication, television broadcasting and meteorological services; resources monitoring and management; space-based navigation services. (UPSC CSE: ISRO’s hybrid propulsion system)
- Chairman: the activities of ISRO are guided by him.
- He would be the secretary of the Department of Space.
- He would also be Chairman of the Space Commission.
- Space Commission: the apex body that formulates the policies and oversees the implementation of the Indian Space Programme.
MUST READ: Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV)
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media? (2022)
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same surface. speed and places a probe.
Q.2) Which one of the following is a reason why astronomical distances are measured in light-years? (2021)
- Distance among stellar bodies does not change.
- Gravity of stellar bodies does not change.
- Light always travels in a straight line.
- Speed of light is always the same.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, Dubai Customs celebrated the graduation of participants from the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) programme.
About United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) –
IMAGE SOURCE: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is a global leader in the fight against illicit drugs and international crime.
- HQ: Vienna.
- Historical Background: It was established in 1997.It was named as a United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) in
- Funding: UNODC relies on voluntary contributions, mainly from Governments.
- UNODC has 20 field offices covering over 150 countries. (UPSC CSE: World Drug Report and UNODC)
- UNODC field staff develop and implement drug control and crime prevention programmes tailored to countries’ particular needs.
- It has approximately 500 staff members worldwide.
Functions:-
- It acts as the Office for Drug Control and Crime Prevention by combining the United Nations International Drug Control Program (UNDCP) and the Crime Prevention and Criminal Justice Division of the United Nations Office in Vienna.
- It is responsible for implementing the United Nations lead programme on terrorism.
- It is mandated to assist Member States in their struggle against illicit drugs, crime and terrorism.
Three pillars of the UNODC work programme are-
- Field-based technical cooperation projects: to enhance the capacity of Member States to counteract illicit drugs, crime and terrorism.
- Research and analytical work: to increase knowledge and understanding of drugs and crime issues.
- To expand the evidence base for policy and operational decisions.
- Assist States in the ratification and implementation of the relevant international treaties. (UPSC CSE: Synthetic Drugs in East and Southeast Asia: Report by the UNODC released)
MUST READ: Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act
SOURCE: THE PRINT
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) has a ‘Protocol against the
- Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air.
- The UNCAC is the ever-first legally binding global anti-corruption instrument.
- A highlight of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) is the inclusion of a specific chapter aimed at returning assets to their rightful owners from whom they had been taken illicitly.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is mandated by its members
- States to assist in the implementation of both UNCAC and UNTOC.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) In the Indian context, what is the implication of ratifying the ‘Additional Protocol’ with the ‘International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’? (2018)
- The civilian nuclear reactors come under IAEA safeguards.
- The military nuclear installations come under the inspection of IAEA
- The country will have the privilege to buy uranium from the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
- The country automatically becomes a member of the NSG.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, Honduras President formally requested the country’s admission to the BRICS-led New Development Bank (NDB).
About New Development Bank (NDB):-

IMAGE SOURCE: economywatch.com
- NDB is a multilateral development bank.
- Founded by: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa (BRICS) countries.
- It was founded at the 6th BRICS Summit in Fortaleza, Brazil in 2014.
- It was established in (UPSC CSE: NDB)
- HQ: Shanghai, China.
- Objective: mobilizing resources for infrastructure and sustainable development projects in emerging markets and developing countries (EMDCs).
- Members: – the Bank’s membership is open to all the members of the United Nations.
- Founding Members: Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa joined in
- Bangladesh & UAE joined in
- Egypt joined in
- Uruguay is a prospective member.
- Funding: The Bank had an initial authorized capital of US$ 100 billion.
- The initial subscribed capital shall be US$ 50 billion, equally shared among founding members.
- First President: V. Kamath, India.
- 2018: NDB received observer status in the United Nations General Assembly.
- Significance: NDB strives to act as a catalyst in bridging the gap between the availability of financial resources and the growing needs of our founding members and EMDCs. (UPSC MAINS: Significance of NDB, AIIB and ADB )
Objectives:-
- Fostering the development of member countries.
- Supporting economic growth.
- Promoting competitiveness and facilitating job creation.
- Building a knowledge-sharing platform among developing countries.
Focus Areas:-
- Clean energy and energy efficiency
- Transport infrastructure
- Water and sanitation
- Digital infrastructure
- Environmental protection
- Social infrastructure
Major Projects Funded by NDB in India:-
- It has committed funding to a number of major infrastructure projects in India, including:-
- Mumbai Metro rail,
- Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut Regional Rapid Transit System and
- Many Renewable Energy projects.
- 2020: India announced a 1 billion USD loan pact with NDB to boost rural employment and infrastructure.
- Recent Projects in India:-
- Bihar Rural Road (Phase II):2023
- Corridor 4 of Phase II of Chennai Metro Rail Project:2022
- Meghalaya Ecotourism Infrastructure Development Project:2022
- Assam Bridge-II (Palasbari) Project:2022
- Sustainable Low-carbon Rail Infrastructure Program:2022
MUST READ: BRICS
SOURCE: THE FINANCIAL EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In which one of the following groups are all four countries members of G20? (2020)
- Argentina Mexico, South Africa and Turkey.
- Australia Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
- Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
- Indonesia Japan Singapore and South Korea
Q.2) Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
- 1, 2, 4 and 5
- 3, 4, 5 and 6
- 1, 3, 4 and 5
- 2, 3, 4 and 6
Syllabus
- Prelims – Important Publications
Context: The Global Slavery Index 2023 was published recently.
About Global Slavery Index 2023:-
- It is an assessment of modern slavery conditions in 160 countries.
- Published by: the Walk Free Foundation
- It uses data released by the International Labour Organisation (ILO) and the International Organisation for Migration (IOM).
- ILO: it is a specialized agency of the United Nations working for social justice and is essential to universal and lasting peace.
- IOM: it is an intergovernmental organization in the field of migration.
- The Index provides rankings across 3 dimensions: Size of the problem (prevalence), Government response and Vulnerability (political instability, inequality).
Key Highlights of the Report:-
- According to the Global Slavery Index 2023, an estimated 50 million people were living in modern slavery on any given day in 2021.
- It is an increase of 10 million people since 2016.
- Modern slavery: it encompasses various forms of exploitation, including forced labour, forced marriage, debt bondage, commercial sexual exploitation, human trafficking, slavery-like practices, and the sale and exploitation of children.
- This means that one in every 160 people in the world is a victim of modern slavery.
- Countries with the highest prevalence: North Korea (104.6), Eritrea (90.3), and Mauritania (32.0).
- modern slavery in these is often state-sponsored.
- Countries with the lowest prevalence: Switzerland (0.5), Norway (0.5), and Germany (0.6).
- Asia and the Pacific: has the largest number of people in modern slavery. (29.3 million)
- India: has a prevalence of 8. (Estimated proportion of the population living in modern slavery per thousand people).
- India, China, Russia, Indonesia, Turkey, and the U.S. are among the top G20 countries with the highest number of forced labourers
- Countries hosting the maximum number of people living in modern slavery:-
- India
- China
- North Korea
MUST READ: World of Work Report
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
- Japan
- Russia
- The United Kingdom.
- The United States of America.
Q.2) International Labour Organization’s Conventions 138 and 182 are related to (2018)
- Child labour.
- Adaptation of agriculture practices to global climate change.
- Regulation of food prices and food security.
- Gender parity at the workplace.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Ancient History
Context: Recently, the Tamil Nadu Department of Archaeology declared five menhir and megalithic burial sites at Kodumanal in Erode district as protected monuments.
About Menhir and megalithic burial sites:-
- Menhirs are upright stones from the Megalithic period. (UPSC MAINS: Rock cut architecture)
- They are erected above a burial site or near a burial site as a memorial.
Megalith:-

- Megaliths are large stones that are used to construct a structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones.
- Megaliths were constructed as either burial sites or commemorative
Timeline:-
- The construction of these structures took place mainly in the Neolithic period. It continued into the Chalcolithic period and the Bronze Age.
- In India: archaeologists trace the majority of the megaliths to the Iron Age (1500 BC to 500 BC), though some sites precede the Iron Age, extending up to 2000 BC.
Distribution in India:-
- Megaliths are spread across the Indian subcontinent.
- The majority of megalithic sites are found in Peninsular India.
- It is concentrated in the states of Maharashtra (mainly in Vidarbha), Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
Types of Megalithic Structure:-
- Stone Circles: Stone circles are commonly called “cromlechs” (a word in the Welsh language).
- Dolmen: A dolmen is a megalithic structure formed by placing a large capstone on two or more support stones, forming a chamber below, sometimes closed in on three sides.
- Cist: a small stone-built coffin-like box or ossuary used to hold the bodies of the dead.
- Monolith: Any single standing stone erected in prehistoric times.
- Synonymous with “megalith” and “menhir”.
- Capstone style: Single megaliths placed horizontally, often over burial chambers, without the use of support stones.
Recent Findings in Kodumanal:-
- Potsherds containing names inscribed in Tamil-Brahmi script were found in large numbers.
- Potsherd= a broken piece of an object made of baked clay, especially one found by an archaeologist
- Roman silver coins, precious stones and quartz were found.
- Significance: these findings showed that an industrial and trade Centre had existed here about 2,300 years ago.
MUST READ: Necropolis
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following ancient towns is well known for its elaborate system of water harvesting and management by building a series of dams and channelising water into connected reservoirs? (2021)
- Dholavira
- Kalibangan
- Rakhigarhi
- Ropar
Q.2) Which one of the following is not a Harappan site? (2019)
- Chanhudaro
- Kot Diji
- Sohgaura
- Desalpur
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Recently, there have been debates regarding explosion of the red giant star, Betelgeuse.
About Betelgeuse:-
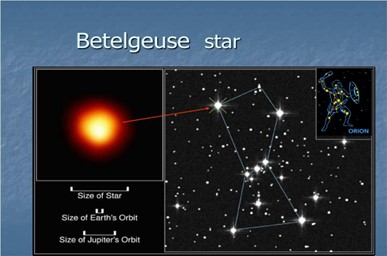
IMAGE SOURCE: SlideServe
- Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star in the constellation Orion.
- Supergiant star: over 20 times bigger than the Sun.
- It is one of the largest visible starts to the naked eye.
- It is the second-brightest in the constellation of Orion.
- The star is approximately 650 light-years from Earth.
- Betelgeuse is called ‘Thiruvathirai’ or ‘Ardra’ in Indian astronomy. (UPSC CSE: IN-SPACe)
- It is a distinctly reddish, semiregular variable star whose apparent magnitude, varies between +0.0 and +1.6.
- At near-infrared wavelengths, Betelgeuse is the brightest star in the night sky.
- It is known for its periodic dimming and brightening up.
- In massive stars like Betelgeuse, the carbon-burning stage lasts only up to a few hundred years, after which the star ‘dies’ and collapses into a supernova within a few months.
Supernova
- A supernova is the name given to the explosion of a massive star.
- They are the largest explosion that takes place in space.
- A star can go supernova in one of two ways:-
- Type I supernova: Star accumulates matter from a nearby neighbor until a runaway nuclear reaction ignites.
- Type II supernova: Star runs out of nuclear fuel and collapses under its own gravity.
Orion constellation
- Orion constellation is named after the hunter in Greek mythology.
- Orion, is one of the most prominent and recognizable constellations in the sky and can be seen throughout the world.
- In total, Orion is home to 10% of the seventy brightest stars, despite covering only 1.4% of the sky.
MUST READ: India’s Space Economy
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The experiment will employ a trio of spacecraft flying in formation in the shape of an equilateral triangle that has sides one million kilometres long, with lasers shining between the craft.” The experiment in question refers to (2020)
- Voyager-2
- New Horizons
- LISA Pathfinder
- Evolved LISA
Q.2) Recently, scientists observed the merger of giant ‘black holes’ billions of light-years away from the Earth. What is the significance of this observation? (2019)
- ‘Higgs boson particles’ were detected.
- ‘Gravitational waves’ were detected.
- Possibility of intergalactic space travel through a ‘wormhole’ was confirmed.
- It enabled the scientists to understand ‘singularity’.
Covid Vaccine Intelligence Network (CoWIN) Portal Data Breach
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity and Governance)
Context: The CoWIN portal, which is used by most Indians to register for COVID-19 vaccination, has been in the news recently after reports of a data breach by a Telegram bot.
- The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) had been asked to investigate the issue and submit a report.
- CERT-In, in its initial report, has pointed out that the back-end database for the Telegram bot was not directly accessing the APIs (application programming interfaces) of the CoWIN database.
About CoWIN Portal:
- CoWIN Portal is the digital platform to capture covid-19 vaccination program details.
- CoWIN connects to various stakeholders, including vaccine manufacturers, administrators, and verifiers, public and private vaccination facilities, and vaccine recipients etc.
- The CoWIN platform was developed at a record speed with ample consideration to its scalability, modularity and interoperability.
- CoWIN has been integrated with other government mobile applications such as Aarogya Setu and UMANG.
- CoWIN provides access to third-party applications that have been authorised by the government to use its APIs (application programming interfaces).
- APIs are a set of rules that allow two applications to communicate and share data.
Data access on the CoWIN portal:
- At present individual level, vaccinated beneficiary data access on the CoWIN portal is available at three levels.
- Beneficiary dashboard: The person who has been vaccinated can have an access to the Co-WIN data through use of registered Mobile number with OTP authentication.
- CoWIN authorized user: The vaccinator with use of authentic login credential provided can access personal level data of vaccinated beneficiaries.
- But the CoWIN system tracks and keeps record of each time an authorized user accesses the CoWIN system.
- API based access: The third party applications who have been provided authorised access of Co-WIN APIs can access personal level data of vaccinated beneficiaries only through beneficiary OTP authentication.
Implications of this data leak:
- Identity theft risks: The leaked data exposes individuals to the risk of identity theft, as sensitive information can be misused for fraudulent activities.
- Targeted frauds and phishing attacks: With access to personal details, scammers may attempt targeted frauds and phishing attacks, leading to financial loss and potential harm to individuals.
- Loss of trust in government systems: The data breach undermines public trust in the government’s ability to safeguard sensitive information, affecting confidence in the vaccination program and other government initiatives.
- Reputational damage: The incident could tarnish the reputation of the CoWIN platform and associated government agencies, affecting their credibility in managing sensitive data.
- Impact on future vaccination drive: Concerns about data security may deter individuals from participating in the vaccination program, slowing down efforts to control the spread of COVID-19.
- Calls for accountability: The data leak prompts demands for accountability from the responsible government agencies and the implementation of stricter measures to protect citizen data.
Need for Data Protection in India:
- India as a data-driven economy: As per a report by the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) in 2019, there were 665.31 million internet subscribers in India.
- This indicates that personal data is becoming available in the public domain due to high mobile internet usage.
- Younger Generation and Data: Statistics show that 30.5% of Indians are below the age of 25 and extensively use mobile apps to access social media.
- Therefore, it becomes imperative for the government to protect the personal data of its citizens.
- Risks to Individual Data: Loss of individual privacy, including the loss of individuals’ control on usage of their personal data, is one of the most significant data risks at present.
- Financial Losses: Data breaches have become a significant issue in India, resulting in financial losses to individuals.
- Hackers often target bank account details, credit card information, and other financial identifiers, leading to fraudulent activities and financial harm.
- Discrimination and Marginalization: Profiling individuals or groups based on their personal data can lead to unfair exclusion, marginalization, or discrimination.
Way Forward:
Increase awareness among the software community on producing safer software and push organisations to invest in better practices. There is need to invest in cutting-edge defence mechanisms, enact stringent legislation, and foster cross-sector collaboration to counter evolving threats.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) has approved the increase in Minimum Support Prices (MSP) for all mandated Kharif Crops for 2023-24.
About MSP:
- Minimum Support Price (MSP) is a form of market intervention by the Government of India to insure agricultural producers against any sharp fall in farm prices.
- The Cabinet Committee of Economic Affairs announces the MSP at the start of each sowing season, considering the recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP).
- The Food Corporation of India (FCI), along with state government agencies (SGAs), procures food grains under MSP.
- There are two types of systems: centralized procurement system and Decentralized procurement system
- Centralized procurement system:
- The procurement of food grains in Central Pool is undertaken by FCI either directly or by State government agencies (SGA).
- Central pool refers to stocks procured through MSP operations for welfare schemes and calamity relief.
- Quantity procured by SGAs is handed over to FCI for storage and subsequent issue against GoI (Government of India) allocations in the same State or movement of surplus stocks to other States.
- The cost of the food grains procured by State agencies is reimbursed by FCI.
- Decentralized procurement system: The State Government itself undertakes direct purchase of food grains. It also stores and distributes these food grains under NFSA and other welfare schemes.
Significance of MSP:
- Better price for their crops: With the increase in the MSP, farmers will get a better price for their crops and procurement will be done.
- Promotion to grow oilseeds: As farmers get a secured price for their crops, it will encourage more and more farmers to grow oilseeds as well as prompt them to shift away from grains.
- Crop Diversification: There are slightly higher increases in the MSP for pulses, oilseeds and coarse cereals, which helps in achieving the motive of diversifying crops.
- Differential Remuneration and protection to farmers: It helps in diversifying the crops in land use pattern. It protects farmers from the unwarranted fluctuation in prices provoked by the international level price variations. Any sharp fall in the market price of a commodity can be handled as MSP acts as a shock absorber.
- Mend demand supply imbalance: Concerted efforts were made to realign the MSPs in favor of oilseeds, pulses and coarse cereals.
- Focus on Nutri-Rich crops: The added focus on nutri-rich nutri-cereals is to incentivize its production in the areas where rice-wheat cannot be grown without long-term adverse implications for groundwater table.
- Atma-Nirbhar Bharat: To boost pulses and oilseeds production and reduce the country’s dependence on imports, the government increased the support price of tur by Rs. 300 to Rs 6,300 per quintal for the 2021-22 crop year from Rs 6,000 per quintal last year.
Issues Associated with India’s MSP Regime:
- Limited Extent: As against the official announcement of MSP for 23 crops, only two, rice and wheat, are procured as these are distributed in NFSA (National Food Security Act).
- For the rest, it is mostly ad-hoc and insignificant.
- Ineffectively Implemented: The Shanta Kumar Committee, in its report in 2015, stated that only 6 % of farmers receive MSP, which means that 94% of the farmers in the country are deprived from the benefit of the MSP.
- More of a Procurement Price: The current MSP regime is not related to prices in the domestic market.
- Makes Agriculture Wheat and Paddy Dominated: Skewed MSP dominated system of rice and wheat leads to overproduction of these crops and discourages farmers to grow other crops and horticulture products, which has higher demand and subsequently could lead to increase in farmer’s income.
- Middlemen-Dependent: The MSP-based procurement system is also dependent on intermediaries, commission agents and APMC officials, which smaller farmers find difficult to get access.
Way Forward:
The procurement policy of the government needs reforms that are easier to implement. Efforts must be made to balance market price and farmers’ support. Cash transfer gives better choices to farmers than imposing subsidies.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) With reference to the New Development Bank (NDB), consider the following statements:
- It was established by the BRICS countries.
- Digital infrastructure is one of its focus areas.
- Its Headquarters is in Beijing.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q2) With reference to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), consider the following statements:
- It is Headquartered in Montreal.
- It is a global leader in the fight against illicit drugs and international crime.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q3) With reference to Betelgeuse, consider the following statements:
- It is called ‘Thiruvathirai’ or ‘Ardra’ in Indian astronomy.
- It lies in the Orion Constellation.
- It is smaller than the sun.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 10th June 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 9th June – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – c
Q.3) -a












