IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –
Context: Recently, the Navy carried out a twin Carrier Battle Group (CBG) operation involving both of India’s aircraft carriers INS Vikramaditya and INS Vikrant.
About INS Vikramaditya:-

IMAGE SOURCE: The Times of India
- INS Vikramaditya is the country’s most powerful aircraft carrier.
- Origin of the name: It has been renamed in honour of Vikramaditya, a legendary emperor of Ujjain, India.
- Historical Background:-
- It was converted from the Russian Navy’s decommissioned Admiral Gorshkov/Baku.
- Admiral Gorshkov/Baku
- This carrier served with the Soviet Navy and later with the Russian Navy (as Admiral Gorshkov/Baku) before being decommissioned in 1996.
- Bought by India: 2004.
- Commissioned by India: in 2013.
- It is a modified Kiev-class aircraft carrier.
- Kiev-class aircraft carrier: it was the first class of fixed-wing aircraft carriers built in the Soviet Union for the Soviet Navy.
Features:-
- Carrying Capacity: It can carry more than 1,600 personnel, including crew.
- It has the ability to carry over 30 aircraft comprising an assortment of MiG 29K/Sea Harrier, Kamov 31, Kamov 28, Sea King, ALH-Dhruv and Chetak helicopters.
- Displacement: 44,500 Tonnes.
- Maximum speed: more than 30 knots and can achieve a maximum range of 7,000nmi.
- Aircraft component: MiG 29K, Kamov 31, Kamov 28, Seaking, ALH, Chetak.
- It can endure up to 45 days at sea.
- It is powered by 8 new-generation steam boilers.
- The aircraft carrier can be armed with a wide range of weapons.
- These include anti-ship missiles, beyond visual range air-to-air missiles, guided bombs, and rockets.
- The ship is equipped with state-of-the-art launch and recovery systems along with aids to enable the smooth and efficient operation of ship-borne aircraft.
INS Vikrant
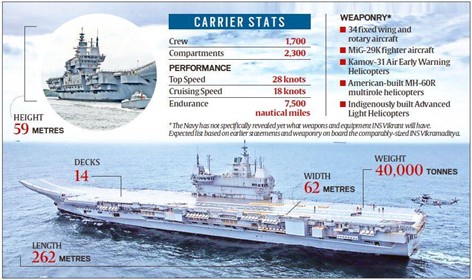
IMAGE SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
- INS Vikrant is the largest warship to be built in India. (UPSC CSE: INS VIKRANT)
- Origin of the Name:-
- Vikrant means courageous.
- It is named after India’s first aircraft carrier, bought from the UK and commissioned in 1961.
- It is India’s first indigenously designed and built aircraft carrier of the Indian Navy.
- Aircraft carrier: a large ship that carries military aircraft and has a long, flat surface from where they take off and land.
- Significance:-
- India joins the United States (US), the United Kingdom (UK), France, Russia, Italy, and China, which have similar capabilities.
- Technologies used: STOBAR (short take-off but assisted recovery).
- 76% indigenous material was used.
- Designed by: Indian Navy’s Directorate of Naval Design (DND).
- Directorate of Naval Design (DND): it is the warship design organization of the Indian Navy which came into being in 1970.
- Made: at Cochin Shipyard Limited in Kochi.
- Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL): a public sector shipyard under the Ministry of Shipping.
Carrier Battle Group (CBG)
- A Carrier Battle Group is a powerful naval fleet that consists of an aircraft carrier as its centrepiece, accompanied by various escort vessels.
- Twin Carrier Battle Group operation involved the simultaneous deployment of two aircraft carriers along with a diverse fleet of escort ships, submarines, and aircraft. (UPSC CSE: Ikshak Survey Vessel)
Significance of Indian Navy’s twin CBG operation:-
- It demonstrated the Indian Navy’s capability to effectively coordinate and deploy multiple aircraft carriers along with their accompanying assets.
- It showcased India’s commitment to maintaining a strong naval presence.
- It showed India’s ability in ensuring the security and stability of the region.
- It also marked a significant milestone in the Indian Navy’s efforts to enhance maritime security and project power in the Indian Ocean and beyond.
MUST READ: Operation Ganga
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following in respect of the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS): (2017)
- Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy.
- IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime cooperation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (2016)
- Amphibious warfare ship
- Nuclear-powered submarine
- Torpedo launch and recovery vessel
- Nuclear-powered aircraft carrier
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) directed existing Mutual Funds ‘Execution-Only Platforms’ (EOPs) to obtain registration within three months.
About Execution only platform (EOP):-
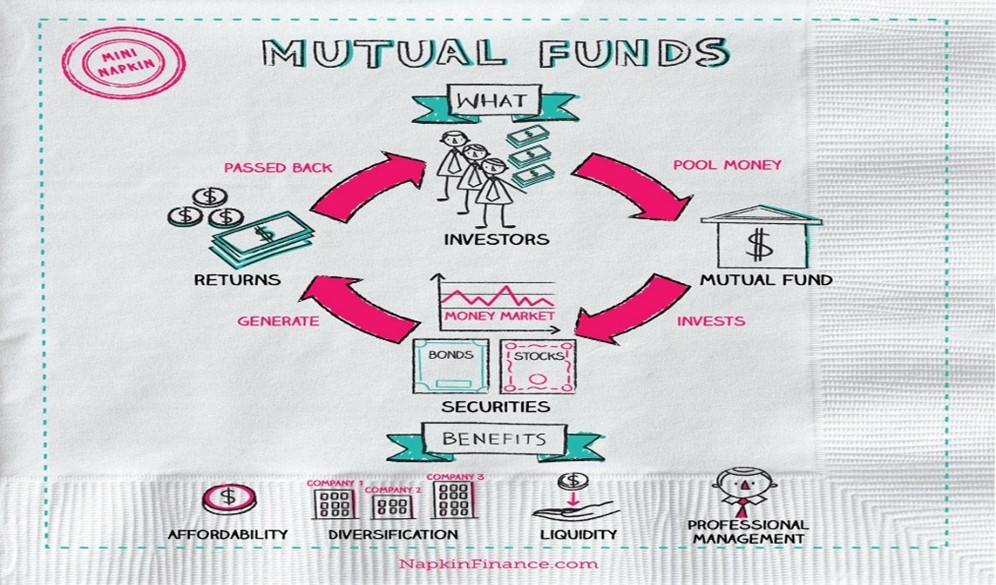
IMAGE SOURCE: Fuste
- Execution-only platform (EOP) is a digital or online platform which facilitates transactions such as subscription, redemption and switch transactions in direct plans of schemes of mutual funds.
- Mutual funds: it is a financial vehicle that pools assets from shareholders to invest in securities like stocks, bonds, money market instruments, and other assets.
- Mutual funds are operated by professional money managers, who allocate the fund’s assets and attempt to produce capital gains or income for the fund’s investors.
Historical Background:-
- Till now, there was no specific framework available for technology/digital platforms to provide execution-only services in direct plans of mutual fund schemes.
Current Status:-
- As per the new SEBI’s new guidelines, no entity would be allowed to operate as an EOP without obtaining registration from SEBI or the Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI).
- AMFI: nodal association of mutual funds across India.
Categories of EOP
- The capital markets regulator has divided EOPs into two categories:-
- Category 1 EOPs:-
- These would need to be registered with AMFI.
- Under this category, the EOPs would act as an agent of asset management companies (AMCs) and integrate their systems with AMCs and/or Registrar and Transfer Agents (RTAs) authorized by AMCs to facilitate transactions in mutual funds.
- These entities may act as an aggregator of the transactions in direct plans of schemes of mutual funds and provide services to investors or other intermediaries.
- Category 2 EOPs:-
- These would need to be registered as a stock broker with SEBI.
- It can operate as an agent of investors.
- It can operate only through the platforms provided by the stock exchanges.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
- It is a statutory body established under the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992.
- It was established in 1992. (UPSC CSE: SEBI)
- Objective: to protect the interests of investors in securities and to promote and regulate the securities market.
- HQ: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Ministry: Ministry of Finance
Historical Background:-
- Before SEBI came into existence, the Controller of Capital Issues was the regulatory authority.
- It derived authority from the Capital Issues (Control) Act, 1947.
- In 1988 the SEBI was constituted as the regulator of capital markets in India under a resolution of the Government of India.
- Initially SEBI was a non-statutory body.
- It became autonomous and given statutory powers by SEBI Act 1992.
Members:-
- Chairman: nominated by the Union Government of India.
- Two members: Officers from the Union Finance Ministry.
- One member: from the Reserve Bank of India.
- Remaining five members: nominated by the Union Government of India.
- Out of these at least three shall be whole-time members.
Functions of SEBI:-
- Quasi-legislative: it drafts regulations
- Quasi-judicial: it passes rulings and orders
- Quasi-executive: it conducts investigation and enforcement action
Powers of SEBI:-
- To approve by−laws of Securities exchanges.
- To require the Securities Exchange to amend its by−laws.
- Inspect the books of accounts and call for periodical returns from recognised Securities exchanges.
- Inspect the books of accounts of financial intermediaries.
- Registration of Brokers and sub-brokers.
MUST READ: Mutual Funds (MF) Risk-o-meter becomes effective
SOURCE: BUISINESSSLINE
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the Indian economy, what are the advantages of “Inflation-Indexed Bonds (IIBs)”? (2022)
- Government can reduce the coupon rates on its borrowing by way of IIBs.
- IIGs provide protection to investors from uncertainty regarding inflation.
- The interest received as well as capital gains on IIBs are not taxable.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), allowed wilful defaulters involved in frauds to go in for a compromise settlement with respective banks to settle their dues.
About Wilful defaulters:-
- Wilful Defaulter is an entity or a person that has not paid the loan taken back to the bank despite having the ability to repay it. Wilful defaulters are acted against comprehensively. (UPSC CSE: Time for 5th generation banking reforms)
- As per the RBI a wilful default occurs when:-
- the unit has defaulted in meeting its payment/repayment obligations to the lender when it has
the capacity to honour these commitments.
-
- The funds are not utilised for the specific purpose for which finance was availed but rather have been
diverted for other purposes.
-
- Those that have disposed of or removed movable fixed assets or immovable property given for
the purpose of securing a term loan.
Reasons for wilful defaults:-
- Businesses failure.
- Gaps in Internal audits, controls and procedures.
- Wrong investment decision.
- Bank’s failure in identifying such defaulters at an early stage of loan repayment.
Steps By Government:-
- SARFAESI Act (Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Securities Interest Act, 2002):-
- Under the provisions of this act many cases involving secured assets have been initiated.
- SARFAESI Act, 2002: allows banks and other financial institutions for auctioning commercial or residential properties to recover a loan when a borrower fails to repay the loan amount.
- RBI Instructions:–
- As per the instructions provided by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), wilful defaulters are not sanctioned any additional facilities by banks/financial institutions, their unit is debarred from floating new ventures for 5 years.
- Even criminal proceedings are initiated wherever necessary.
- SEBI Regulations:-
- Wilful defaulters and companies who have wilful defaulters as either promoters or directors have been debarred from accessing capital markets to raise funds.
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016: it has debarred wilful defaulters from participating in the insolvency resolution process.
- IBC 2016: it is India’s bankruptcy law which seeks to consolidate the existing framework by creating a single law for insolvency and bankruptcy.
- Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018: the act was enacted for effective action against wilful defaulters who flee Indian jurisdiction.
- It provides for attachment and confiscation of property of fugitive offenders and to disentitle them from defending any civil claim.
- Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018: it seeks to confiscate the properties of economic offenders who have left the country to avoid facing criminal prosecution or refuse to return to the country to face prosecution.
- Public Sector Banks (PSB): the government has also advised all PSBs to decide on publishing photographs of all concerned wilful defaulters.
- It further suggested obtaining a certified copy of the passport of promoters/directors and other authorised signatories of companies availing loans of over ₹50 crores.
- PSBs: banks owned or controlled by the government of India, which holds more than 50% of their shares.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- It was established in 1935 by the Reserve Bank of India Act, of 1934.
- It is the Central Bank of India. (UPSC CSE: RBI surplus transfer)
- HQ: Mumbai
- It plays a multi-facet role by executing multiple functions such as overseeing monetary policy, issuing currency, managing foreign exchange etc.
Structure of RBI:-
- The Reserve Bank’s affairs are governed by a central board of directors.
- The board is appointed by the Government of India in keeping with the Reserve Bank of India Act.
- Directors: are appointed/nominated for a period of four years.
Functions of the RBI:-
- It implements and monitors the monetary policy and ensures price stability while keeping in mind the objective of growth.
- Amendment to RBI Act, 1934, in 2016
- Section 45ZB of the RBI Act, 1934 was amended to provide for a six-member Monetary Policy Committee (MPC).
- It is to be constituted by the Central Government by notification in the Official Gazette.
- MPC determines the policy interest rate required to achieve the inflation target.
- It regulator and Supervisor of the Financial System.
- It manages the Foreign Exchange reserves of India.
- It issues and exchanges or destroys currency and coins not fit for circulation.
- Banker to the Government: it performs merchant banking functions for the central and state governments.
- Banker to banks: it maintains banking accounts of all scheduled banks. It also acts as the lender of last resort by providing funds to banks.
MUST READ: Non-Performing Assets (NPAs)
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In India, which one of the following is responsible for maintaining price stability by controlling inflation? (2022)
- Department of Consumer Affairs
- Expenditure Management Commission
- Financial Stability and Development Council
- Reserve Bank of India
Q.2) With reference to the Indian economy, consider the following statements: (2022)
- If the inflation is too high, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is likely to buy government securities.
- If the rupee is rapidly depreciating, RBI is likely to sell dollars in the market.
- If interest rates in the USA or European Union were to fall, that is likely to induce RBI to buy dollars.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO) announced that the United States will rejoin it after 4 years.
About United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO):-
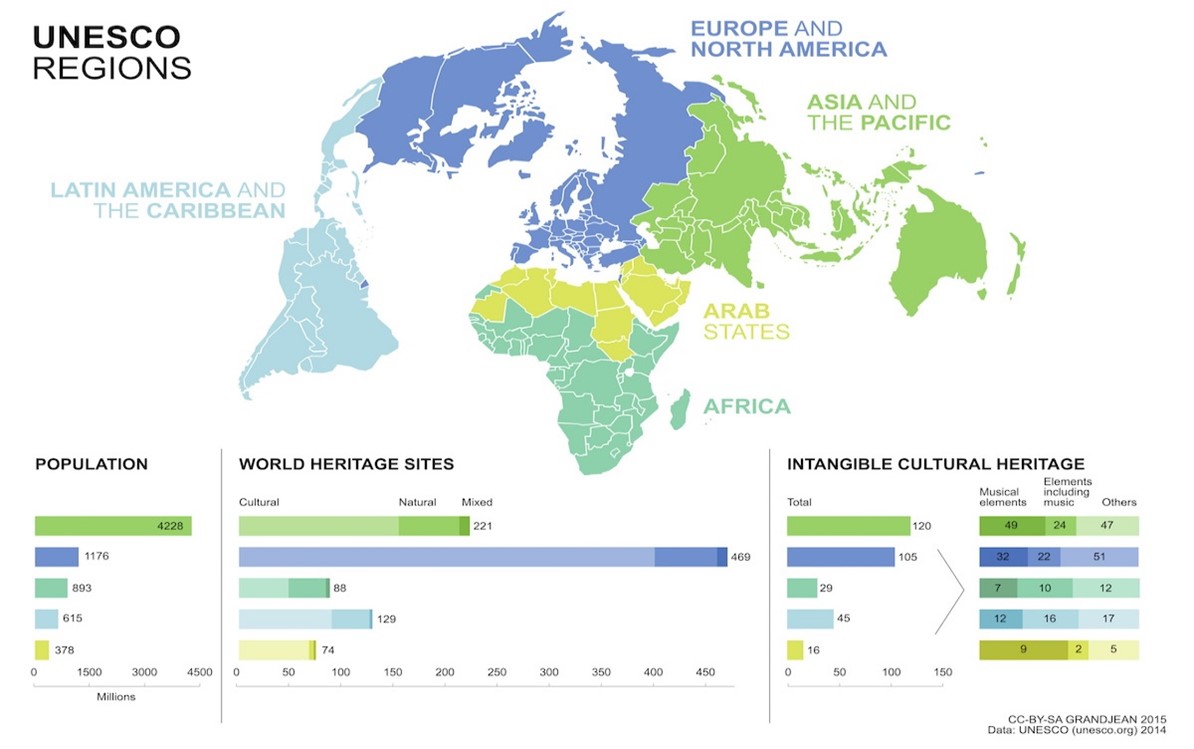
IMAGE SOURCE: vividmaps.com
- It is a specialised agency of the United Nations (UN).
- UN: is an international organization founded in 1945.
- It works for maintaining international peace and security, protect human rights, deliver humanitarian aid, promote sustainable development and uphold international law.
- Objective: promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, the sciences, and culture.
- HQ: Paris, France.
- Members:-
- It has 193 member states and 11 associate members, as well as partners in the nongovernmental, intergovernmental, and private sectors.
- UNESCO member states not UN members: Cook Islands, Niue, and Palestine.
- UN member states not UNESCO members: Israel, Liechtenstein, United States.
- It is also a member of the United Nations Sustainable Development Group (UNSDG).
- UNSDG: a coalition of UN agencies and organizations aimed at fulfilling the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Functions of UNESCO:-
- Ensuring an inclusive and equitable quality education for all.
- Safeguarding cultural heritage.
- Advancing scientific research and collaboration.
- Promoting freedom of expression.
- Fostering intercultural dialogue.
Notable Programs and Activities of UNESCO:-
- World Heritage Program: Designates and preserves sites of outstanding universal value.
- Education for All Program: Ensuring inclusive and equitable quality education for all.
- International Hydrological Program: Promoting sustainable water management and cooperation.
- Man and the Biosphere Program: Promoting sustainable development and Conservation of natural resources.
- Intangible Cultural Heritage Program: Safeguarding and promoting intangible cultural heritage. (UPSC MAINS: world heritage sites)
Issue of USA Leaving UNESCO
- In 2011, UNESCO inducted Palestine as a member.
- This led to the US halting the agency’s funding, worth millions of dollars, under then-President Barack Obama.
- Reason to stop funding UNESCO:-
- Israel and the United States termed the inclusion of Palestine and UNESCO’s naming of what Israel claims were ancient Jewish sites as Palestinian heritage sites as examples of anti–Israel bias.
- US laws, owing to the country’s historical ties with Israel, prohibit funding to any UN agency that implies recognition of the Palestinians’ demands for their own state.
- Consequently, in 2019 the US and Israel pulled out of UNESCO citing bias in the organisation in the Palestine issue.
- The US had pulled out of UNESCO once earlier in 1984 and then rejoined in 2003.
- Recent Developments: it was negotiated recently through an agreement in 2022 that the USA will begin giving UNESCO funds again.
- Issue of Palestine:-
- The Palestinians claim the West Bank, east Jerusalem and Gaza Strip territories captured by Israel in the 1967 war for an independent state.
- Israel disagrees with Palestine’s claims.
- Palestine is not recognised as a sovereign state by the United Nations.
India and UNESCO
- India has been a founding member of UNESCO.
- It had ratified UNESCO’s Constitution in 1946, while still under colonial rule.
- India has been continuously re-elected to the UNESCO Executive Board since 1946.
- Recently, India won the re-election to the executive board of the UN’s cultural and education organisation for the 2021-25 term.
Objectives of UNESCO’s Mission in India:-
- Attaining quality education for all and lifelong learning. (UPSC CSE: UNESCO fund for languages)
- Mobilizing science knowledge and policy for sustainable development.
- Addressing emerging social and ethical challenges.
- Fostering cultural diversity, intercultural dialogue and a culture of peace.
- Building inclusive knowledge societies through information and communication.
Indian National Commission for Cooperation with UNESCO (INCCU)
- It is a governmental body.
- Establishment:-
- Initially set up in 1949, it is a governmental body functioning under the Department of Secondary and Higher Education in the Ministry of Human Resource Development.
- A permanent Commission was established in 1951.
- Ministry: Department of Secondary and Higher Education in the Ministry of Education.
- Objective: to advise the Government in matters relating to UNESCO.
- President of the Commission: Minister of Human Resource Development.
MUST READ: Seabed
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2022)
The region often mentioned in the news: Country
- Anatolia Turkey
- Amhara Ethiopia
- Cabo Delgado Spain
- Catalonia Italy
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
- Only one pair
- Only two pairs
- Only three pairs
- All four pairs
Q.2) The term “Levant” often heard in the news roughly corresponds to which of the following regions? (2022)
- Region along the eastern Mediterranean shores.
- Region along North African shores stretching from Egypt to Morocco.
- Region along the Persian Gulf and the Horn of Africa.
- The entire coastal Mediterranean Sea of areas.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the Prime Minister praised the initiative of the first Janjatiya Khel Mahotsav.
About Janjatiya Khel Mahotsav:-
- The Inauguration of Janjatiya Khel Mahotsav was done in 2023.
- The Janjatiya Khel Mahotsav is a collaborative effort between the Odisha Government and the Union Ministry of Culture.
- The event successfully showcased the talent and competitive spirit of tribal communities.
- Organized at Khel Mahotsav at KIIT University, Odisha.
- Objective: to celebrate sports and promote tribal sports and unity. (UPSC CSE: Significance of Tribal Culture in Sustainable Development)
- Significance:-
- It provided a platform for athletes from diverse backgrounds to showcase their abilities.
- It fostered a sense of togetherness among the participating states.
- It celebrated indigenous athletes from across India.
- Focus areas: sports, culture, and unity.
- Participants: around 5,000 indigenous athletes from 26 states, representing a variety of tribal cultures, attended the competition.
- Karnataka: it excelled in the women’s division of Kabaddi, securing the top spot.
- It also secured first place in both the men’s and women’s categories in volleyball.
- Jharkhand earned third place.
- Odisha topped in the men’s division, in Kabaddi.
MUST READ: Integrating tribal knowledge systems
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India, the terms ‘Halbi, Ho and Kui’ pertain to (2021)
- dance forms of Northwest India
- musical instruments
- pre-historic cave paintings
- tribal languages
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India: (2019)
- PVTGs reside in 18 States and one Union Territory.
- A stagnant or declining population is one of the criteria for determining PVTG status.
- There are 95 PVTGs officially notified in the country so far.
- Irular and Konda Reddi tribes are included in the list of PVTGs.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 2 and 4
- 1, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, Hubble captured a jellyfish galaxy JO206 lying 700 million light-years away.
About jellyfish galaxy JO206:-
- It is a galaxy located approximately 700 million light-years away from Earth.
- Galaxy: a large system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and other celestial objects bound together by gravity.
- It showcases a colourful star-forming disk surrounded by a pale, luminous cloud of dust.
- It is situated in the constellation Aquarius.
- Constellations: it’s a group of stars that looks like a particular shape in the sky and has been given a name.
- Origin of the name: “Jellyfish” is given to galaxies that resemble their marine counterparts.
- This resemblance is evident in the image of JO206.
- At the bottom right in the image “tentacles” of bright star formation that trails the main disc of the galaxy are visible.
- The image was taken with the Hubble telescope.
- Hubble Space Telescope: it is a large, space-based observatory by NASA/ESA.
- It is deployed since 1990.
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration(NASA): is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
- European Space Agency(ESA): is an independent space agency.
- Its mission is to shape the development of Europe’s space capability and ensure that investment in space continues to deliver benefits to the citizens of Europe and the world.
Aquarius constellation
- Aquarius constellation is located in the southern hemisphere.
- It is one of the 12 zodiac constellations.
- It belongs to the Zodiac family of constellations, along with Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpius, Sagittarius, Capricornus, and Pisces.
- Zodiac constellations: the Sun appears to pass through these constellations over the course of a year.
- Origin of the name: it is derived from Latin, meaning “the water-bearer” or “cup-bearer.”
- Aquarius lies in the region of the sky which is sometimes referred to as the Sea, because it contains a number of other constellations with names associated with water like Pisces (the fish), Eridanus (the river), and Cetus (the whale), among others.
- Aquarius is the 10th largest constellation.
- Area: It covers an area of 980 square degrees.
- Aquarius contains the famous supergiant stars Sadalsuud (Beta Aquarii) and Sadalmelik (Alpha Aquarii).
MUST READ: India’s Space Economy
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth? (2022)
- GPS and navigation systems could fail.
- Tsunamis could occur in equatorial regions.
- Power grids could be damaged.
- Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth.
- Forest fires could take place over much of the planet.
- Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed.
- Shortwave radio communication of the aircraft flying over polar regions could be interrupted.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 4 and 5 only
- 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 only
- 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Q.2) Which one of the following is a reason why astronomical distances are measured in light-years? (2021)
- Distance among stellar bodies does not change
- The gravity of stellar bodies does not change
- Light always travels in a straight line
- Speed of light is always the same
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) Ranking 2023 was announced recently, showcasing the excellence and achievements of various educational institutions in India.
About National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) Ranking:
- The NIRF is a methodology to rank institutions across the country based on various parameters.
- NIRF was approved by the Ministry of Education (Erstwhile Ministry of Human Resource Development) and launched on 29th September 2015.
- It is the first-ever effort by the government to rank Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) in the country.
- Parameters for NIRF Ranking: The weightage for each parameter varies depending on the category of the institution.
- NIRF ranks institutes by their total score and it uses five indicators to determine this score — ‘Teaching, Learning & Resources’ (30% weightage); ‘Research and Professional Practice’ (30%); ‘Graduation Outcomes’ (20%); ‘Outreach and Inclusivity’ (10%); and ‘Perception’ (10%).
Major Highlights of NIRF Ranking 2023:
- The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Madras secured the top spot in the overall ranking for the fifth consecutive year, while the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru was ranked as the best university.
- Three Distinct Additions of 2023 Edition of India Rankings:
- Introduction of a new subject namely Agriculture & Allied Sectors
- Expansion of scope of “Architecture” to “Architecture and Planning” to include institutions imparting courses in Urban and Town Planning.
- Integration of the “Innovation” ranking previously executed by the Atal Ranking of Institutions on Innovation Achievements (ARIIA) into the India Rankings to reduce the burden on institutions of providing similar data to two different agencies.
Significance:
- India specific ranking: India specific ranking system would reduce the dependence on the international agency ranking which does not take exclusivity and gives ranking.
- Transparency: Verifiable data would help in setting up as transparent ranking system
- Status of institutions: As it included both public and private institutions it provides the actual status of higher educational institutions in the country so that students could make informed choices.
- Improve competitiveness: This will help state as well as institutional for self-check and correcting themselves.
- Thus promoting excellence.
- It is a step towards bringing the Indian institutes on a global platform.
Criticisms of the ranking framework:
Insufficient quality parameters:
- The quality of an institution is a function of several inputs and the above indicators alone may not be sufficient.
- For example., how can we include the skills that an institution/university imparts to its students as one of the important ingredients?
- Should the financial health and size of the institution not be a criterion? etc.
One-size-fits-all approach:
- The diversity in the Indian education system is large. There are fresh as well as old institutions offering degrees/diplomas/certifications.
- There is also technology vs social sciences institutions, multi-disciplinary vs single discipline, private vs public, research-based, innovation-based, language-based or even special-purpose institutions/universities.
- NIRF seems to be committing the same sin that the global rankings systems were once accused of — a one-size-fits-all approach.
Ranking Vs accreditation:
- Another glaring oversight is the disconnect that exists between the ranking and accreditation.
- Several universities have earned a National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) A grade but figure poorly in the ranking system.
Lack of international faculty:
- The world over, ranking educational institutes is a matter of debate and research. There are at least 20 global ranking agencies that measure quality on various parameters.
- Two factors that are absent and differentiate us from the global ranking systems are our lack of international faculty and students and the inadequacy of our research to connect with the industry.
Suggestive measures:
- Normalisation of performance index: Normalisation would help as there is huge resource gap between state funded and private institutions.
- Separate scheme: A separate scheme for central, state and private institutions might be better, and private industries would be voluntarily made to compete with the state funded institutions.
- Measures like extensive cross-examination of data, systematic and monitored surveys, inclusion of state representatives in the NIRF team would help obtaining a comprehensive ranking.
Way Forward:
Thus, no matter how rigorous the methods, university rankings invariably involve some level of ambiguity. The NIRF’s emphasis on rankings can lead to unhealthy competition between universities, fostering a culture that puts metrics in front of the thing they are trying to measure: excellence in education and research.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Disaster management)
Context: The recent rail accident in Balasore in Odisha, involving the collision of three trains, is a tragic reminder of the challenges that India’s Rail services are facing.
- According to the National Crime Records Bureau, an average 23,000 people died every year between 2010 and 2021 in railway accidents.
About India’s Rail services:
- The Indian Railways carries nearly 15 million passengers every day now compared to the peak of 23 million a day the year before the COVID-19 pandemic.
- India has an ambitious plan to improve its rail infrastructure, and in the year 2023-24, Rs. 2.4-lakh crore has been allocated for capital expenditure.
- In 2021, the Prime Minister announced that 75 new semi-high speed trains labelled Vande Bharat would be started over 75 weeks, and several have been started already.
- There has been attention on passenger amenities also, but nothing can be more important than safety.
- Though such deadly train accidents are usually not too frequent, they do recur occasionally.
Train Accidents: An Overview
- Derailments: Derailments have been a major cause of train accidents in India. Lapses in safety protocols, track maintenance, and failure to identify and rectify track defects have resulted in derailments.
- For example, the derailment of the Puri-Haridwar Utkal Express in 2017, which claimed 23 lives and injured many, was attributed to negligence in track maintenance.
- Collisions: Train collisions have occurred due to lapses in signalling systems, human errors, and failure to maintain safe distances between trains.
- One such incident was the collision between the Gorakhdham Express and a halted goods train in Uttar Pradesh, in 2014, resulting in a high number of casualties and injuries.
- Level crossing accidents: Lapses in ensuring the safety of level crossings have led to accidents involving trains and road vehicles. Failure to eliminate manned level crossings, inadequate warning systems, and negligence in adhering to safety procedures have contributed to such accidents.
- For instance, in 2011, 38 people have been killed and 17 others injured in a train-bus collision in the Kanshiramnagar district of Uttar Pradesh.
- Signal failures: Malfunctioning or improper signalling systems have been responsible for train accidents. Inadequate maintenance, faulty equipment, and human errors in signalling operations have resulted in collisions and other mishaps.
- The collision of two trains in Gaisal, West Bengal (1999), occurred due to a signalling error.
- Overcrowding and over speeding: Overcrowding of trains beyond their capacity and over speeding have also led to accidents. Lack of proper crowd management and failure to enforce speed limits have been significant safety concerns.
- 2018 Amritsar train accident, where a train struck a crowd watching a Dussehra event near the railway tracks, causing numerous fatalities, highlighted the risks associated with overcrowding.
Challenges and Shortcomings:
- Capacity Constraints: The high volume of passengers and freight transported daily leads to overcrowding and delays, impacting the efficiency of operations.
- Safety Concerns: Safety is a significant challenge for Indian Railways. The network has experienced a significant number of accidents and incidents, including train derailments, resulting in fatalities and injuries. Ensuring passenger and crew safety remains a top priority.
- Infrastructure Upgradation: The existing infrastructure of Indian Railways, including tracks, stations, and signalling systems, requires modernization and upgradation.
- Aging infrastructure hampers smooth operations and the ability to meet the growing demand for transportation services.
- Funding Constraints: Indian Railways faces financial challenges in funding infrastructure development and modernization projects. The cost of such projects is substantial, and securing adequate funds is essential.
- The Railways heavily rely on government funding and internal resources, which may limit the scope of investment.
- Competition from Other Modes of Transportation: Indian Railways faces competition from alternate modes of transportation, such as roadways and airways.
- Increasing competition in the freight and passenger transportation sectors poses challenges to maintaining market share and attracting customers.
- Skilled Human Resources: Indian Railways faces a shortage of skilled human resources, particularly in critical areas such as safety, maintenance, and operations.
- Filling vacancies with qualified personnel and providing appropriate training are crucial for efficient and safe railway operations.
2021 CAG Report: CAG submitted another report for the year ended March 2021.
- It observed, “Proper maintenance of the railway track is a pre-requisite for the train operation without accidents.”
- The main causes were:
- Poor planning,
- Idle track machines,
- Vacancies in the work force and
- Lack of training of Permanent Way staff.
Initiatives taken by the Government
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): The government has allowed FDI in railways-related components, attracting foreign investment to the sector.
- From April 2000 to March 2020, FDI inflow in railways-related components stood at US$ 1,107.60 million.
- National Rail Plan: The government is working on a comprehensive “National Rail Plan” that aims to integrate the rail network with other modes of transport and develop a multi-modal transportation system in the country.
- New Online Vendor Registration System: The Research Designs & Standards Organisation (RDSO), the research arm of Indian Railways, has launched a digital and transparent system called the “New Online Vendor Registration System” to streamline vendor registration processes.
- Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs): The construction of dedicated freight corridors is underway to increase the proportion of freight traffic and improve the efficiency of goods transportation.
- The Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (WDFC) from Mumbai to Uttar Pradesh and the Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC) from Dankuni in West Bengal to Ludhiana in Punjab are part of this initiative.
- Rail Kisan: The “Rail Kisan” initiative aims to boost the transportation of agricultural goods by providing dedicated trains for farmers.
- Under this program, over 49,000 tonnes of goods have been transported on eight routes, benefiting farmers across the country.
- Program for the Redevelopment of Station Infrastructure: The government has launched a program to redevelop 400 railway stations across India under a public-private partnership (PPP) model.
- The aim is to create self-sustainable stations with high standards of safety, comfort, passenger amenities, value-added services, and efficiency.
- Connecting Mining Districts and the North East: Railway connectivity in the North East region is being improved to promote inclusive development.
- Broad gauge lines are being extended to connect major cities in the region, and railway connectivity to mining districts is being mapped to enhance transportation.
- Quest for Self-reliance: As part of the “Atma Nirbhar Bharat” initiative, the railways are implementing various projects.
- These include the development of the indigenous anti-collision system called “Kavach,” the introduction of highly energy-efficient “Vande Bharat” high-speed trains, and the goal of achieving zero accidents.
Way Forward:
Accidents per million train kilometre have fallen over the last decade, but poor maintenance of tracks and the rolling stock and overstretched staff are problems that the Railways can no longer camouflage with glitzy facades. The accident in Balasore should prompt India’s railways development plans onto the right track.
Safety measures including anti-collision systems are expanding, but evidently not at an adequate pace. More important will be the corrective measures by the Railways at the operational and planning levels. It will have to find more resources to modernise and rationalise its priorities.
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following regarding, INS VIKRANT:
- It is made at Cochin Shipyard Limited in Kochi.
- It is India’s first indigenously designed and built aircraft carrier.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q2) Consider the following regarding, Wilful defaulters:
- They defaulted in meeting their payment obligations to the lender despite having the capacity to honour these commitments.
- They can participate in the insolvency resolution process under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q3) Consider the following regarding, Galaxy JO206 :
- It is situated in the constellation Aquarius.
- It is 700 million light-years away from Earth.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 16th June 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 15th June – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – a
Q.3) -d











