IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE) certified Trainers trained in the cluster-based Training of Trainers project under the Skill Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood Promotion (SANKALP) programme.
About SANKALP programme:-

IMAGE SOURCE: IASBABA
- It is a Centrally sponsored scheme.
- Tenure: 2018-2023.(UPSC CSE: SANKALP Scheme)
- Ministry: Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- Objectives: to improve short-term skill training through strengthening institutions, bringing in better market connectivity and inclusion of marginalised sections of society.
- Eligible age: candidate needs to be 18 years old.
- It aims to implement the mandate of the National Skill Development Mission (NSDM).
- It receives loan assistance from the World Bank. (UPSC CSE: World Bank and International Finance Corporation)
- World Bank: an international organization dedicated to providing financing, advice, and research to developing nations to aid their economic advancement.
3 Key Areas of SANKALP:-
- Institutional Strengthening at the Central, State and District level.
- Quality Assurance of skill development programmes.
- Inclusion of marginalized populations in skill development programmes.
National Skill Development Mission (NSDM)
- It aims to create convergence across various sectors and different States in terms of activities relating to skill training.
- Launched: 2015. (UPSC CSE: NSDM)
- Ministry: Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
Objectives of NSDM:-
- to consolidate efforts of skill training and development across sectors and states.
- to help expedite steps to achieve various skilling efforts at scale at a fast pace.
- to create an end-to-end framework which promotes sustainable livelihoods for citizens.
Institutional mechanisms:-
- The MSDE has set up institutional mechanisms at three tiers namely:-
- Governing Council : at the apex level for policy guidance
- Steering Committee
- Mission Directorate
- The Mission Directorate is supported by three additional institutions functioning horizontally. These include:-
- National Skill Development Agency (NSDA):-
- NSDA was established to coordinate and harmonize the skill development efforts of the government and the private sector.
- It focuses on policy research, quality assurance and implementation of quality standards across all skilling agencies etc.
- National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC):-
- NSDC is Public Private Partnership (PPP) under the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE) to create training capacity in the country, fund vocational training initiatives and create a market ecosystem for skill development.
- It overlooks training, and capacity-building aspects of trainers – both public and private, leads the engagement with industries, and drives the sector’s skills councils.
- Directorate General of Training (DGT):-
- DGT is the apex organisation for development and coordination at the National level for the programmes relating to vocational training.
- It maintains the skill training structures of training Institutes, advises on training policies, trains instructors, provides technical support, runs women-centric training institutes, etc.
MUST READ: Year End Review of Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In India under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements: (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)recently released the Gender Social Norms Index (GSNI),2023.
About Gender Social Norms Index (GSNI), 2023:-
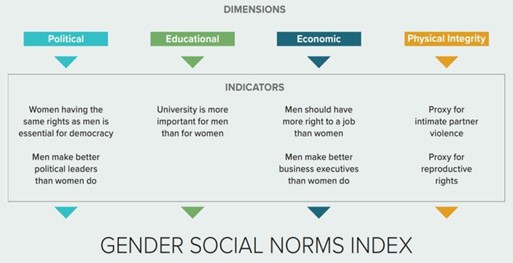
IMAGE SOURCE: UNDP
- The Gender Social Norms Index (GSNI) quantifies biases against women.
- Published by: United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- 1st edition: Gender Social Norms Index (GSNI 2020).
- Objective: to tackle gender norms which eventually are a broad contributor to gender inequalities.
- The index captures people’s attitudes on women’s roles along four key dimensions:-
- Political
- Educational (UPSC CSE: Gender gap in education)
- Economic and
- Physical integrity
- The index, covers 85 percent of the global population.
Key Findings of GSNI, 2023:-
- The past decade didn’t see any improvement in the level of prejudice shown against women.
- Nearly 90% of people still hold at least one bias against women.
- Around half the world’s population believe that men make better political leaders than women.
- Two in five believe that men make better business executives than women.
- A staggering 25 per cent of people believe it is justified for a man to beat his wife.
- Women are grossly underrepresented in leadership in conflict-affected countries at the negotiation tables.
- This can be seen in the recent conflicts: in Ukraine (0 per cent), Yemen (4 per cent) and Afghanistan (10 per cent).
- Globally, about seven of 10 peace processes did not include any women mediators or women signatories.
- However, policies aimed at achieving equal participation in education have been effective, with women catching up in education.
- Higher enrolment and completion are seen at all levels
- Even in the 59 countries where adult women are more educated than men, the average income gap is 39 per cent.
- The most significant declines were in Chile, the Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia and Kyrgyzstan.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)

IMAGE SOURCE: HuffPost
- It is a United Nations(UN) agency.
- United Nations (UN): is an international organization tasked with maintaining international peace and security.
- Objective:- assisting nations in eradicating poverty and achieving long-term economic and human development.
- HQ: New York City.
Historical Background:-
- The Expanded Programme of Technical Assistance and the United Nations Special Fund were merged in 1965.
- The two institutions were fully integrated into the UNDP in 1971.
Structure:-
- UNDP is an executive body of the United Nations General Assembly.
- After the Secretary and the Deputy Secretary-General, the UNDP Administrator is the third highest-ranking member of the UN.
- Funding: it is funded entirely by voluntary contributions from member nations.
- It operates in 177 countries.
- It works with local governments to meet development challenges and develop local capacity.
Functions of UNDP:-
- Democratic governance: UNDP aids national democratic transitions by providing policy advice and technical assistance, strengthening institutional and individual capacity within countries.
- Reduction of poverty: UNDP assists nations in developing poverty-fighting strategies.
- Prevention and recovery from crises: UNDP aims to decrease the risk of armed conflicts and natural catastrophes.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): the UNDP works internationally to help countries achieve the UN-approved SDG (2015-2030).
MUST READ: Markets
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017? (2019)
- Pregnant women are entitled to three months of pre-delivery and three months of post-delivery paid leave.
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother a minimum of six creche visits daily.
- Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) The Multi-dimensional Poverty Index developed by Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative with UNDP support covers which of the following? (2012)
- Deprivation of education, health, assets and services at the household level
- Purchasing power parity at the national level
- Extent of the budget deficit and GDP growth rate at the national level
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recent investigations led by the Indian Express have revealed, gaps in the implementation of the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana in Jharkhand.
About Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana:-
- PMKSY is an umbrella scheme. (UPSC CSE: PMKSY)
- Launched: 2015.
- Ministries: Ministries of Agriculture and Farmer’s Welfare, Water Resources and Rural Development.
Historical Background:-
- It has been formulated amalgamating ongoing schemes
- Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP):-
- It was launched in 1996 as a central assistance programme.
- Implementation: Ministry of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation.
- Objective: Accelerate the implementation of irrigation projects that exceed the resource capabilities of states.
- Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP):-
- Launch: 2009-10
- Implementation: Department of Land Resources of Ministry of Rural Development.
- Objective: to restore ecological balance by harnessing, conserving and developing degraded natural resources such as soil, vegetative cover and water.
- On Farm Water Management (OFWM):-
- Launch: 2002
- Implementation: Department of Agriculture and Cooperation of Ministry of Agriculture and Farmer’s Welfare.
- Objective: it focuses primarily on enhancing water use efficiency by promoting efficient on-farm water management technologies and equipment.
PMKSY is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme:-
- Centre- States will be 75:25 per cent.
- In the case of the northeastern region and hilly states, it will be 90:10.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: are funded entirely or partly by the central government but implemented by the states.
Implementation of PMKSY:-
- The programme architecture of PMKSY will be to adopt a ‘decentralized State level planning and projected execution’.
- It will allow States to draw up their own irrigation development plans.
The objective of PMKSY:-
- To achieve convergence of investments in irrigation at the field level.
- To expand cultivable area under assured irrigation.
- To improve on-farm water use efficiency to reduce wastage of water.
- To enhance the adoption of precision irrigation and other water-saving technologies.
Components of PMKSY:-
- Accelerated Irrigation Benefits Programme (AIBP)
- It aims for financial support to irrigation projects.
- Har Khet Ko Pani (HKKP)
- It aims for the enhancement of physical access on the farm by:-
- Creation of new water sources through Minor Irrigation (both surface and groundwater).
- Repair, restoration and renovation of water bodies.
- construction of rainwater harvesting structures (Jal Sanchay)
- Command area development: strengthening and creation of distribution network from source to the farm.
- Groundwater development in the areas where it is abundant, so that sink is created to store runoff/ flood water during peak rainy season.
- Improvement in water management and distribution system for water bodies to take advantage of the available source which is not tapped to its fullest capacity (deriving benefits from low-hanging fruits)
- Creating and rejuvenating traditional water storage systems.
- Watershed Development
- It is implemented by the Department of Land Resources.
- It focuses on the development of rainfed areas.
- It works towards soil and water conservation, regeneration of groundwater, arresting runoff and promoting extension activities related to water harvesting and management.
- Per Drop More Crop(PDMC)
- It is implemented by the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The dedicated Micro Irrigation Fund(MIF) is with NABARD under PMKSY.
MUST READ: Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana for 2021-26
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to organic farming in India, consider the following statements: (2018)
- ‘The National ‘Programme for Organic Production’ (NPOP) is operated under the guidelines and ‘directions of the Union Ministry of Rural Development.
- ‘The Agricultural and Processed Food Product Export Development Authority ‘(APEDA) functions as the Secretariat for the implementation of NPOP.
- Sikkim has become India’s first fully organic State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) What are the benefits of implementing the ‘Integrated Watershed Development Programme’? (2014)
- Prevention of soil runoff
- Linking the country’s perennial rivers with seasonal rivers
- Rainwater harvesting and recharge of groundwater table
- Regeneration of natural vegetation
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the Prime Minister, lauded the new initiative of celebrating Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana as a ‘God Bharai’ ceremony in Dausa, Rajasthan.
About Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana:-

IMAGE SOURCE: cm helpline
- Launched: 2017. (UPSC CSE: Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana(PMMVY) )
- Historical Background: It was rechristened from the erstwhile Indira Gandhi Matritva Sahyog Yojana (IGMSY).
- IGMSY was launched in 2010.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme.
- Implementation: Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Direct Benefit Transfer Scheme: Cash benefits are provided to pregnant women in their bank account directly to meet enhanced nutritional needs and partially compensate for wage loss.
Objectives of PMMVY:-
- By offering financial incentives as a partial replacement for lost wages, the mother will be able to get enough rest before and after giving birth to her first child.
- The cash incentives provided would lead to improved health-seeking behaviour amongst Pregnant Women and Lactating Mothers (PW&LM).
- Reducing maternal and infant mortality rates.
Target Beneficiaries:-
- All Pregnant Women and Lactating Mothers (PW&LM).
- All eligible Pregnant Women and Lactating Mothers who have their pregnancy on or after 1st January 2017 for the first child in the family.
- The scheme is a conditional cash transfer scheme for pregnant and lactating women.
- It provides a partial wage compensation to women for wage loss during childbirth and childcare and provides conditions for safe delivery and good nutrition and feeding practices.
Benefits:-
- Beneficiaries receive a cash benefit of Rs. 5,000 in three instalments on fulfilling the following conditions viz. early registration of pregnancy, ante-natal check-up and registration of the birth of the child and completion of the first cycle of vaccination for the first living child of the family.
- The eligible beneficiaries also receive cash incentives under Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY).
- Janani Suraksha Yojana: it was launched in 2009
- Implementation: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Objective: reducing maternal and infant mortality by promoting institutional delivery among pregnant women.
Exceptions:-
- It excludes those who are in regular employment with the Central Government or the State Governments or PSUs.
- It also excludes those who are in receipt of similar benefits under any law for the time being in force.
Funding:-
- The scheme is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme under which cost sharing ratio between the
- Centre and the States & UTs with Legislature – 60:40
- North-Eastern States & three Himalayan States–90:10.
- Union Territories without Legislature- 100% Central assistance.
Distinctive Feature:-
- Implementation of the scheme is closely monitored by the central and state governments through the Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana – Common Application Software (PMMVY-CAS).
- PMMVY-CAS: is a web-based software application that enables tracking the status of each beneficiary under the scheme, resulting in expedited, accountable and better grievance redressal.
MUST READ: PM-CARES for Children scheme
SOURCE: PMINDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Who among the following can join the National Pension System (NPS)? (2017)
- Resident Indian citizens only
- Persons of age from 21 to 55 only
- All State Government employees joining the services after the state of notification by the respective State Governments
- All Central Government employees including those of Armed Forces joining the services on or after 1st April, 2004
Q.2) Which of the following are the objectives of the ‘National Nutrition Mission’? (2017)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers. 2. To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: The second Supreme Audit Institutions of G20 countries Summit (SAI20) was organised in Goa recently.
About Supreme Audit Institutions of G20 countries Summit (SAI20) :-
- It is a forum where SAIs from G20 countries can engage with each other to share their experiences and expertise in auditing public policies and governance practices.
- Objective of the G20 SAI Summit: to promote cooperation among the SAIs in addressing
global challenges and fostering accountability in governance.
- The group meets annually to discuss important issues related to public auditing and to develop joint initiatives to promote good governance and accountability in their respective countries.
- Chairmanship: Shri Girish Chandra Murmu, the Comptroller & Auditor General of India (CAG) will chair SAI20. (UPSC CSE: CAG and ILO)
Top Priority areas for SAI20 deliberations Under India’s presidency
- Two priority areas have been selected for SAI20 deliberation:
- Blue Economy
- It is defined by the World Bank as the Sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and jobs while preserving the health of the ecosystem.
- Responsible Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial intelligence (AI): the ability of a computer or a robot controlled by a computer to do tasks that are usually done by humans.
Important functions of Supreme Audit Institutions (SAIs):-
- Independent audits: SAIs conduct independent audits of government finances and operations.
- They ensure that public funds are being used in accordance with the law and that government agencies are operating effectively and efficiently.
- Promoting transparency and accountability: SAIs promote transparency and accountability by making audit reports publicly available.
- Improving governance: By identifying weaknesses and inefficiencies in government operations, SAIs can help to improve governance.
- Supporting the legislative branch: SAIs support the legislative branch by providing information and analysis that can help lawmakers make informed decisions about government programs and policies.
- Ensuring compliance with laws and regulations: SAIs ensure compliance with laws and regulations by reviewing government operations and financial statements.
- Fostering international cooperation: SAIs collaborate and share best practices with their counterparts in other countries to promote good governance and accountability globally.
Comptroller and Auditor-General of India (CAG)
- CAG is an independent authority under the Constitution of India.
- He is the head of the Indian audit & account department.
- He is the chief Guardian of the Public purse.
- Appointment: he is appointed by the President by warrant under his hand and seal.
- Tenure: 6 years or 65 years of age, whichever is earlier.
- Removal: by the President only in accordance with the procedure mentioned in the Constitution that is the manner same as the removal of a Supreme Court Judge.
- He is ineligible to hold any office, either under the Government of India or of any state, once he retires/resigns as a CAG.
Constitutional Provisions regarding the CAG:-
- Article 148: it broadly deals with the CAG appointment, oath and conditions of service.
- Article 149: it deals with the Duties and Powers of the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India.
- Article 150: it says that the accounts of the Union and of the States shall be kept in such form as the President may, on the advice of the CAG, prescribe.
- Article 151: it says that the reports of the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India relating to the accounts of the Union shall be submitted to the president, who shall cause them to be laid before each House of Parliament.
- The reports of the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India relating to the accounts of a State shall be submitted to the Governor of the State, who shall cause them to be laid before the Legislature of the State.
- Article 279:Calculation of “net proceeds” is ascertained and certified by the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India, whose certificate is final.
- Third Schedule: Section IV of the Third Schedule of the Constitution of India prescribes the form of oath or affirmation to be made by the Judges of the Supreme Court and the Comptroller and Auditor-General of India at the time of assumption of office.
- Sixth Schedule: According to this schedule, the District Council or Regional Council should be kept in such form as the CAG prescribes with the approval of the President.
, In addition,n these bodies’ accounts are audited in such manner as CAG may think fit, and the reports relating to such accounts shall be submitted to the Governor who shall cause them to be laid before the Council.
MUST READ: Summit
SOURCE: BUISINESS LINE
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Constitution of India classifies the ministers into four ranks viz. Cabinet Minister, Minister of State with Independent Charge, Minister of State and Deputy Minister.
- The total number of ministers in the Union Government, including the Prime Minister, shall not exceed 15 per cent of the total number of members in the Lok Sabha.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- Attorney General of India and Solicitor General of India are the only officers of the Government who are allowed to participate in the meetings of the Parliament of India.
- According to the Constitution of India, the Attorney General of India submits his resignation when the Government which appointed him resigns.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Defence
Context: Two warships Anjadip, and Sanshodhak, were launched recently.
About Anjadip and Sanshodhak:-
Anjadip:
- It is an anti-submarine warfare shallow watercraft vessel built for the Indian Navy.
- Built by: Kolkata-based Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE).
- Anjadip is the third of the eight ships of the Shallow Water Craft (SWC) Project.
- Shallow Water Craft (SWC) Project: the contract that was signed between Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers, Kolkata and the Ministry of Defence in 2019.
- Historical significance of the name: –
- The ship has been named Anjadip to signify the strategic maritime importance accorded to the island of Anjadip, Karnataka.
- The island close to India’s western coast that is now part of the Indian Naval base INS Kadamba.
- INS Kadamba: is currently the third-largest Indian naval base.
- Anjadip offered strong resistance in 1961 when India took back Goa from the Portuguese.
- The island also has a memorial for the brave Indian marines who were martyred there.
- The ‘Arnala’ class of ships would replace the current ‘Abhay’ class of Anti-Submarine Warfare Corvettes of the Navy.
- These are designed to undertake anti-submarine operations in coastal waters
Features:-
- It is powered by water-jet propulsion.
- Maximum speed: 25 knots (46 km/h).
- It has an endurance of 1,800 nautical miles (3,300 km) at 14 knots (26 km/h).
- Crew: 57 members, including seven officers and 50 sailors.
- It is equipped with an Anti-submarine Combat Suite, potentially the DRDO-developed IAC MOD’C’, a Hull Mounted Sonar, and a Low-frequency Variable depth Sonar.
- It also features a fire control system (FCS), an integrated Platform Management system, an Atomic Power Management system, and a Battle Damage control system.
- The ships would have 80 per cent indigenisation.
Sanshodhak
- It is the fourth Survey Vessel Large (SVL) of the Indian Navy. (UPSC CSE: Ikshak Survey Vessel)
- The ship is named ‘Sanshodhak’, meaning ‘Researcher’.
- It signifies the primary role of the ship as a Survey Vessel.
- SVL ships will replace the existing Sandhayak Class survey ships, with new-generation hydrographic equipment.
- It will help to collect oceanographic data.
Features:-
- They have the capability to carry four Survey Motor Boats and an integral helicopter.
- The primary role of the ships would be to undertake full-scale coastal and deep-water hydrographic surveys of ports and navigational channels.
- The ships would also be deployed for collecting oceanographic and geophysical data for defence as well as civil applications.
MUST READ: MV Ganga Vilas
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) has a ‘Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air’.
- The UNCAC is the ever-first legally binding global anti-corruption instrument.
- A highlight of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) is the inclusion of a specific chapter aimed at returning assets to their rightful owners from whom they had been taken illicitly.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is mandated by its member States to assist in the implementation of both UNCAC and UNTOC.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 3 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) What is/are the consequence /consequences of a country becoming a member of the ‘Nuclear Suppliers Group’? (2018)
- It will have access to the latest and most efficient nuclear technologies.
- It automatically becomes a member of “The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT)”.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Society and Social Issues)
Context: Recently, the term Cancel culture was in the news due to the debate of its impact on society.
About Cancel culture:
- Cancel culture is a phrase contemporary to the late 2010s and early 2020s used to refer to a culture in which those who are deemed to have acted or spoken in an unacceptable manner are ostracized, boycotted or shunned.
- This shunning may extend to social or professional circles—whether on social media or in person—with most high-profile incidents involving celebrities.
- Those subject to this ostracism are said to have been “cancelled”.
Significance of Cancel culture:
- When a large number of people on social media platforms collectively object to any action by a public figure, it leads to calls to ‘cancel’ the person.
- This cancelling occurs by pressuring the individual’s workplace to fire them, pressuring brands to drop their association with the offending individual, using threats of boycott or engaging in any other action that impacts the individual’s reputation or finances.
- Demanding accountability from people holding such problematic views is central to cancel culture.
Recent examples:
- In 2020, J.K. Rowling faced a fierce backlash against her controversial tweets about the transgender community.
- In Bollywood many prominent personalities were cancelled for allegedly promoting nepotism.
- Donald Trump was ‘cancelled’ because of his racist, inappropriate conduct and words towards women, people of colour and immigrants.
- #Me too Movement, where many people took to social media to “cancel” or boycott celebrities and public personalities accused of sexual misconduct.
Arguments in favour of cancel culture:
- Cancel culture allows marginalized people to seek accountability where the justice system fails.
- Cancel culture gives a voice to disenfranchised or less powerful people.
- Cancel culture is simply a new form of boycott, a cherished tactic in the civil rights movement, to bring about social change.
Arguments against cancel culture:
- Critics argue that Cancel culture is no longer about holding people accountable, and has instead become an online form of vicious mob intimidation.
- Individuals or organisations are presumed guilty without due process, leading to loss of employment, reputational damage, psychological distress and even legal actions.
- Cancel culture affects free speech and often signifies the lack of ability to forgive and move on.
- The goalposts of cancel culture keep changing, individuals and organisations are selectively targeted and face different degrees of outrage.
- It has led to people being constantly aggravated and frustrated with each other.
- They can’t seem to move beyond that, to actually initiate change of the kind they actually want to see.
Way Forward:
Cancel culture began as a way to correct power imbalances, however it is also being used by those holding positions of power against those it intended to help. Hence for some, it is a form of harassment, mob vigilantism and an act of censorship and for some a form of justice and a way to demand accountability.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance), GS 3 (Science and Technology) and GS 4 (Ethics)
Context: During the annual Group of Seven (G-7) Summit, Leaders initiated the Hiroshima AI Process (HAP) to regulate Artificial Intelligence (AI).
About Hiroshima AI process:
- It aims at the adoption of international technical standards for trustworthy artificial intelligence (AI).
- The G7 leaders have agreed to create a ministerial forum known as the “Hiroshima AI Process” that will discuss issues regarding generative AI tools like ChatGPT, such as intellectual property rights and disinformation.
- It is scheduled to be formed by the end of this year.
Significance of Hiroshima AI process:
- It can help the countries develop a common understanding on some key regulatory issues while ensuring that any disagreement doesn’t result in complete discord.
- The process can bring greater clarity to the role and scope of the ‘fair use’ doctrine in the use of AI for various purposes.
- It can also differentiate use for machine-learning per se from other AI-related uses of copyrighted materials. This in turn could affect the global discourse and practice on the issue.
About Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. Specific applications of AI include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition and machine vision.
- Examples: Robotics and Automation, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Pattern recognition is a subset of machine learning etc.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- Healthcare Sector: Machine learning is being used for faster, cheaper and more accurate diagnosis and thus improving patient outcomes and reducing costs. For
- Example, IBM Watson and chatbots are some of such tools.
- Business Sector: To take care of highly repetitive tasks Robotic process automation is applied which perform faster and effortlessly than humans.
- Machine learning algorithms are being integrated into analytics and CRM platforms to provide better customer service.
- Education Sector: AI can make some of the educational processes automated such as grading, rewarding marks etc. therefore giving educators more time.
- Further, it can assess students and adapt to their needs, helping them work at their own pace. AI may change where and how students learn, perhaps even replacing some teachers.
- Financial Sector: It can be applied to the personal finance applications and could collect personal data and provide financial advice.
- today software trades more than humans on the Wall Street.
- Legal Sector: Automation can lead to faster resolution of already pending cases by reducing the time taken while analyzing cases thus better use of time and more efficient processes.
- Manufacturing sector: Robots are being used for manufacturing since a long time now, however, more advanced exponential technologies have emerged such as additive manufacturing (3D Printing) which with the help of AI can revolutionize the entire manufacturing supply chain ecosystem.
- Intelligent Robots: Robots can perform the tasks given by a human because of sensors to detect physical data from the real world such as light, heat, temperature, movement, sound, bump, and pressure.
- Moreover, they have efficient processors, multiple sensors and huge memory, to exhibit intelligence.
- Speech Recognition: There are intelligent systems that are capable of hearing and grasping the language in terms of sentences and their meanings while human talks to it.
- Cyber Security: In the 20th conference on e-governance in India it was discussed that AI can provide more teeth to cyber security and must be explored.
Ethical Use of AI:
- While AI tools present a range of new functionality for businesses, the use of AI also raises ethical questions because, for better or worse, an AI system will reinforce what it has already learned.
- This can be problematic because machine learning algorithms, which underpin many of the most advanced AI tools, are only as smart as the data they are given in training.
- Because a human being selects what data is used to train an AI program, the potential for machine learning bias is inherent and must be monitored closely.
- AI’s ethical challenges include the following: bias due to improperly trained algorithms and human bias; misuse due to deep fakes and phishing; legal concerns including AI libel and copyright issues; elimination of jobs; and data privacy concerns, particularly in the banking, healthcare and legal fields.
Challenges in Artificial Intelligence:
- Lack of enabling data ecosystems.
- The low intensity of AI research.
- Inadequate availability of AI expertise, manpower and skilling opportunities.
- High resource cost and low awareness for adopting AI in business processes.
- Unclear privacy, security and ethical regulations.
- Unattractive Intellectual Property regime to incentivise research and adoption of AI.
- Only 4% of AI professionals trained in Emerging technologies; low H Index (citation) and Data sets.
Government efforts regarding artificial intelligence in India:
- National Programme on Artificial Intelligence: It was announced in the Interim Budget 2019. The programme would be catalysed by the establishment of the National Centre on Artificial Intelligence as a hub along with 6 centres of excellence.
- International Centre for Transformative Artificial Intelligence: NITI Aayog and Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) initiated collaboration to set up International Centre for Transformative Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI) to conduct advanced research to incubate AI-led solutions in three important areas– healthcare, agriculture and smart mobility.
- National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems (NM-ICPS): It is a programme led by the Union Ministry of Science & Technology to enhance capabilities of cyber-physical systems. Budget 2019 allotted Rs. 5 crore for the mission.
- AIRAWAT (AI Research, Analytics and Knowledge Assimilation platform): In an attempt to achieve the goal of becoming a $5 Tn economy, the Indian government’s think-tank NITI Aayog recently released an approach paper to set up India’s first AI-specific cloud computing infrastructure called ‘AIRAWAT’ (AI Research, Analytics and Knowledge Assimilation platform).
- The platform aims to guide the research and development of new and emerging technologies.
Way Forward:
Artificial intelligence has a lot of potential for India. Nearly 200 Artificial Intelligence start-ups in India are today innovating and creating AI-based solutions for various industries. It can complement Digital India Mission by helping in the big data analysis which is not possible without using AI.
A “whole of society” approach to AI governance will enable us to develop broad-based ethical principles, cultures and codes of conduct, to ensure the needed harm-mitigating measures, reviews and audits during design, development and deployment phases, and to inculcate the transparency, accountability, inclusion and societal trust for AI to flourish and bring about the extraordinary breakthroughs it promises.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) With reference to Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana, consider the following:
- It can help reduce the maternal mortality rate.
- It is under the Ministry of Women and Child Empowerment.
Which of the statements given above is/are incorrect?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to Anjadip, consider the following:
- It is the third of the eight ships of the Shallow Water Craft (SWC) Project.
- It cannot undertake anti-submarine operations in coastal waters
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) With reference to Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana, consider the following:
- It is under the Ministry of Urban Development.
- It was launched in 2017.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 15th June 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 14th June – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – a
Q.3) -a












