IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Union Minister for Housing and Urban Affairs hailed the progress of the Smart City Mission.
Background:-
- The Smart City Mission has completed eight years recently.
- Union Minister Hardeep Singh Puri appreciated the achievements of the Smart City Mission.
About Smart City Mission:-
- Launched in 2015. (UPSC CSE: SMART CITY MISSION @ 100)
- Ministry: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- Smart Cities Mission is a joint effort of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), and all state and union territories (UT) governments.
- It is an innovative and new initiative by the Government of India to drive economic growth and improve the quality of life of people.
Objectives of Smart Cities Mission:-
- To promote cities that provide core infrastructure and give a decent quality of life to its citizens, a clean and sustainable environment and application of Smart Solutions.
- To drive economic growth and improve quality of life through comprehensive work on social, economic, physical and institutional pillars of the city.
- The focus is on sustainable and inclusive development through the creation of replicable models, which act as inspirations to other aspiring cities.
The six fundamental principles on which the concept of Smart Cities is based are:-

IMAGE SOURCE: smartcities.gov.in
Financing:-
- The Smart City Mission is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS).
- The Central Government gives financial support to the Mission to the extent of Rs. 48,000 crores over five years i.e. on an average of 100 crore per city per year.
- An equal amount, on a matching basis, will have to be contributed by the State/ULB.
Implementation:-
- The implementation of the Mission at the City level will be done by a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV).
- SPV: A special purpose vehicle, also called a special purpose entity (SPE), is a subsidiary created by a parent company to isolate financial risk.
- The SPV is promoted by the state/Union Territory and the urban local body, with a 50% equity shareholding each.
- The SPV formed as a limited company is governed by the Companies Act, 2013.
- Duration:-
- The Mission was to cover 100 cities and its duration will be five years (FY2015-16 to FY2019-20).
- It was aimed to be completed by 2019-20 but has since been extended.
Smart city is envisaged to have four pillars:-
- Social Infrastructure.
- Physical Infrastructure.
- Institutional Infrastructure (including Governance).
- Economic Infrastructure.
MUST READ: Smart Cities and Academia Towards Action & Research (SAAR)
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
- Department of Science and Technology
- Ministry of Labour and Employment
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Q.2) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India ? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: Recently, tenders floated for the Kalasa Banduri project on the Mahadayi River have not shown success.
Background:-
- Tenders for implementation of the controversial Kalasa Banduri scheme were floated by the previous BJP government minutes before the Karnataka Assembly elections were announced.
- They were put out without obtaining forest and environment clearance.
- The tenders are open for bidding till 21st August 2023 but are unlikely to find takers.
About Mahadayi River:-
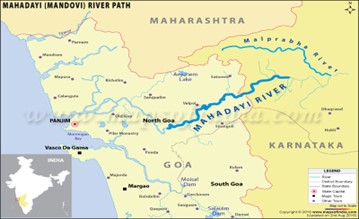
IMAGE SOURCE: MapsofIndia
- The Mahadayi River is also known as the Mandovi River.
- Origin: It originates in the Western Ghats from the Bhimgad Wildlife Sanctuary in the Belgaum district of Karnataka.
- End point: It flows for about 81 km before emptying into the Arabian Sea.
- The river is formed by the confluence of two rivers: the Daddi and the Markandeya.
- Left Bank Tributaries: Daddi River, Malaprabha River, and Markandeya River.
- Right Bank Tributaries: Tambaraparani River, Bainganga River, Wardha River.
- Dams on the Mahadayi River:-
- The Hidkal Dam: Located in the Belagavi district of Karnataka.
- The Hidkal Dam: Located in the Belagavi district of Karnataka.
- The Selaulim Dam: Located in South Goa.
- The Virdi Dam: Located in the Belagavi district of Karnataka
- The Salim Ali Bird Sanctuary is situated on the island of Chorao, which is located in the Mandovi River.
- Significance: The Mahadayi River is of great importance to the states of Goa and Karnataka, serving as a source of water for drinking, irrigation, and tourism.
Kalasa-Banduri Nala Project
- It is a project of the Government of Karnataka.
- Planned: in
- Objective: to divert water from Mahadayi to satisfy the drinking water needs of the Belagavi, Dharwad, Bagalkot and Gadag districts of Karnataka.
- It involves building dam across Kalasa and Banduri, two tributaries of the Mahadayi River to divert water to the Malaprabha River.
Kalasa-Banduri Nala Project Dispute Background
- 1989: The project was planned by the Government of Karnataka.
- 2002: two-and-a-half decades since the proposal, the Karnataka government decided to implement the project, after the Centre cleared it.
- Goa’s stand: it approached the Centre, urging it to assess the available resources in the river and allocate water to the three basin states: Goa, Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- Due to the protests in Goa, the project was put on hold by the then central government.
- 2006: The dispute gained steam in 2006 when the coalition government in Karnataka decided to start work on the project.
- Goa then approached the Supreme Court, seeking the creation of a Tribunal to settle the water-sharing dispute.
- The Mahadayi Water Disputes Tribunal was set up in
- Goa, Karnataka and Maharashtra are parties to the tribunal.
- 2018: The Tribunal 13.42 thousand million cubic feet (TMC) of water from the Mahadayi river basin to Karnataka, 1.33 TMC to Maharashtra and 24 TMC to
- 2019: After the Tribunal award, Goa filed a Special Leave Petition(SLP) in the Supreme Court challenging the quantum of allocation.
- 2020: Goa filed a contempt petition before the SC, accusing Karnataka of illegally diverting water from the Mahadayi basin. (UPSC CSE: Goa Opposition disrupts assembly proceedings over Mahadayi river dispute)
- 2023: Goa and Maharashtra governments issued a joint statement saying that they will put up a united fight against Karnataka in connection with the water diversion project.
MUST READ: Mahadayi Water Row
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- Jhelum River passes through Wular Lake.
- Krishna River directly feeds Kolleru Lake.
- Meandering of the Gandak River formed Kanwar Lake.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Gandikota canyon of South India was created by which one of the following rivers? (2022)
- Cauvery
- Manjira
- Pennar
- Tungabhadra
Syllabus
- Prelims –Art and Culture
Context: Recently, the Uttarakhand government decided to set up a high-level committee to probe allegations of a fraud in gold transactions in the Kedarnath temple.
Background: –
About Kedarnath temple:-
IMAGE SOURCE: blogspot.com
- It is a Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Shiva.
- Location: It is located on the Garhwal Himalayan range near the Mandakini River, in the Rudraprayag district of
- Mandakini River: it is a tributary of the Alaknanda River.
- It emerges from the Chorabari Glacier.
- It runs between the Rudraprayag and Sonprayag areas.
- Significance: Kedarnath forms one of the four sites of the Chota Char Dham Pilgrimage circuit.
- Chota Char Dham Pilgrimage: it refers to the journey up the mountains to four sacred temples in the North Indian state of Uttarakhand.
- The four temples are Yamunotri Dham, Gangotri Dham, Badrinath Dham and Kedarnath Dham.
- It is one of the 12 Jyotirlingas of Lord Shiva in India.
- Jyotirlinga: a shrine where Lord Shiva is worshipped in the form of a Jyotirlingam.
- Built by: It is said that the Pandavas constructed the Kedarnath Temple. (UPSC CSE: Temple Architecture in India)
- It was later reconstructed by Adi Shankaracharya in the 8th century A.D.
- It has exquisite architecture and is built of extremely large but evenly shaped grey stone slabs.
- The stone slabs are interlocked with each other with the use of iron clamps.
- No mortar has been used in the construction of the temple.
- There is a conical rock structure inside the Kedarnath temple that is worshipped as the Sadashiva form of Shiva.
- A “Garba Griha” for worship and a Mandap for pilgrims is placed inside the temple.
MUST READ: Srisailam Temple
SOURCE: THE TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- Amarkantak Hills are at the confluence of the Vindhya and Sahyadri Ranges.
- Biligirirangan Hills constitute the easternmost part of the Satpura Range.
- Seshachalam Hills constitute the southernmost part of the Western Ghats.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) The Prime Minister recently inaugurated the new Circuit House near Somnath Temple Veraval. Which of the following statements are correct regarding Somnath Temple? (2022)
- Somnath Temple is one of the Jyotirlinga shrines.
- A description of the Somnath Temple was given by Al-Biruni.
- Pran Pratishtha of Somnath Temple (installation of the present-day temple) was done by President S. Radhakrishnan.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: As per recent reports, the Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary of Odisha recorded a high prey density.
Background:-
- Following the pre-monsoon sign survey in the Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary, an herbivore or prey density of 46 animals per sq. km was recorded in the sanctuary.
- Moreover, for the first time in the last many decades, a tiger has also been sighted in Debrigarh during Census.
About Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary:-
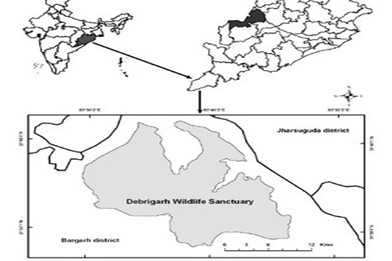
IMAGE SOURCE: ResearchGate
- Location: Bargarh district of Odisha, near Hirakud dam.
- Hirakud dam: it is on the Mahanadi River..
- Declared as a wildlife sanctuary: 1985. (UPSC CSE: Asola Bhatti sanctuary)
Biodiversity: –
- Flora: Dry deciduous forests
- Fauna:-
- Leopards, deer, sambar, elephants, gaur, wild boar and a variety of birds and other creatures can be found in the Debrigarh sanctuary’s vast and dense woodlands.
- It is also known for easy wildlife sightings, including Indian bison, sambhar, wild boars, peacocks etc.
- The four-horned antelope or Chousingha is one of the endangered animals that also inhabits this sanctuary.
- It is an Eco-sensitive Zone.
Major Protected Areas in Odisha:
National Parks:-
- Bhitarkanika National Park
- Simlipal National Park
Wildlife Sanctuaries:-
- Badrama WLS
- Chilika (Nalaban island) WLS
- Hadgarh WLS
- Baisipalli WLS
- Kotagarh WLS
- Nandankanan WLS
- Lakhari Valley WLS
- Gahirmatha (Marine) WLS
MUST READ: Tungareshwar Wildlife Sanctuary
SOURCE: NEW INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements : (2023)
Once the Central Government notifies an area as a ‘Community Reserve’
- the Chief Wildlife Warden of the State becomes the governing authority of such forest
- hunting is not allowed in such areas.
- people in such areas are allowed to collect non-timber forest produce.
- people of such areas are allowed traditional agricultural practices.
How many of the above statements are correct.?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three.
- All four
Q.2) Which of the following Protected Areas are located in the Cauvery basin? (2020)
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, The President of India conferred the Florence Nightingale Awards on 30 nurses and auxiliary midwives.
About Florence Nightingale Awards:-
- The Awards are named as a tribute to Florence Nightingale. (UPSC CSE: National Florence Nightingale Awards 2020)
- Florence Nightingale:-She was an English social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing.
- She came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during the Crimean War.
- She organized to care for wounded soldiers at Constantinople.
About the award:
- The Florence Nightingale Awards were instituted in the year
- It is the highest national distinction a nurse can achieve for selfless devotion and exceptional professionalism.
- Ministry: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Objective: It was instituted as a mark of recognition for the meritorious services rendered by the nurses and nursing professionals to society.
- The award consists of a Cash Award of 50000/-, a certificate and a medal.
- The award is given to outstanding Nursing personnel employed in Central, State/UTs, Private, Missionary and Voluntary Organizations.
MUST READ: WHO and Traditional Medicine
SOURCE: THE NEW INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017? (2018)
- Pregnant women are entitled to three months of pre-delivery and three months of post-delivery paid leave.
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother a minimum of six creche visits daily.
- Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following are the objectives of the ‘National Nutrition Mission’? (2017)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi paid homage to the brave individuals who resisted the National Emergency of 1975.
About National Emergency:-
- The emergency provisions are contained in Part XVIII of the Constitution of India, from Article 352 to 360.
- Objective: These provisions enable the Central government to meet any abnormal situation effectively.
- The Constitution stipulates three types of emergencies:- (UPSC MAINS: Compare and contrast the emergency provisions of India and Canada.)
- National Emergency
- Constitutional Emergency
- Financial Emergency
National Emergency
- Grounds of declaration:-
- Under Article 352, the president can declare a national emergency when the security of India or a part of it is threatened by war or external aggression or armed rebellion.
- The President can declare a national emergency even before the actual occurrence of war or armed rebellion or external aggression
- When a national emergency is declared on the grounds of ‘war’ or ‘external aggression’, it is known as ‘External Emergency’.
- On the other hand, when it is declared on the grounds of ‘armed rebellion’, it is known as ‘Internal Emergency’.
- This term ‘armed rebellion’ is inserted from the 44th amendment.
- Before this term, it was known as internal disturbance.
- Parliamentary approval and duration:-
- It must be approved by both houses of parliament within one month from the date of its issue.
- If the Lok Sabha is not in session or has been dissolved then the proclamation has to be approved within 30 days of the new LS being constituted
- Once approved the proclamation continues to be in force for six months.
- Such proclamations can be extended indefinitely.
- However, each extension should be approved by the Parliament through a special majority (44th amendment act, 1978)
- Revocation of proclamation:-
- The President may revoke a proclamation of Emergency at any time by a subsequent proclamation.
- Such proclamation does not require parliamentary approval.
- The emergency must be revoked if the Lok Sabha passes a resolution by a simple majority disapproving its continuation.
Declarations made so far: –
- National emergency has been proclaimed three times so far- in 1962, 1971 and 1975.
- The first proclamation of National Emergency: was issued in 1962 on account of Chinese aggression in the NEFA and was in force till 1968.
- The second proclamation of National Emergency: was made in 1971 in the wake of the attack by Pakistan.
- The third proclamation of National Emergency: was made in June 1975, even when the emergency was in operation, both were revoked in 1977.
MUST READ: 50 Years of Bangladesh Liberation War
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- A bill amending the Constitution requires a prior recommendation of the President of India.
- When a Constitution Amendment Bill is presented to the President of India, it is obligatory for the President of India to give his/her assent.
- A Constitution Amendment Bill must be passed by both the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha by a special majority and there is no provision for joint sitting.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which of the following is/are the exclusive power(s) of Lok Sabha? (2022)
- To ratify the declaration of Emergency
- To pass a motion of no-confidence against the Council of Ministers
- To impeach the President of India
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
New Assisted Reproductive Technology Regulations (ART), 2023 regulations
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The Health Ministry had notified the Assisted Reproductive Technology Regulations (ART), 2023 recently.
About the ART regulations:
Source: Shecares.com
- The ART Act 2020, defines ART to include all techniques that seek to obtain a pregnancy by handling the sperm or the oocyte (immature egg cell) outside the human body and transferring the gamete or the embryo into the reproductive system of a woman.
- Examples of ART services: gamete (sperm or oocyte) donation, in-vitro-fertilisation (fertilising an egg in the lab), and gestational surrogacy (the child is not biologically related to surrogate mother).
- ART services will be provided through:
- ART clinics, which offer ART related treatments and procedures, and
- ART banks, which store and supply gametes.
Key provisions:
- Restriction on donation: The new ART provisions impose restrictions on the number of times a donor, male or female, can donate (sperm/oocyte) in their lifetime, and specifies age limits for donors.
- Criteria for a donor: The provision states that an oocyte donor should be a person who have been married at least once in their lives and have at least one living child of her own (minimum three years of age).
- She can donate oocyte only once in her lifetime and not more than seven oocytes can be retrieved.
- Restrictions on bank: An ART bank cannot supply gamete (reproductive cell) of a single donor to more than one commissioning couple (couple seeking services).
- Insurance coverage: Parties seeking ART services will be required to provide insurance coverage in the favour of the oocyte donor (for any loss, damage, or death of the donor).
- Prohibition on sex determination: A clinic is prohibited from offering to provide a child of pre-determined sex.
- Checking for diseases: Checking for genetic diseases before the embryo implantation is needed.
Conditions for offering ART services:
- ART procedures can only be carried out with the written informed consent of both the party seeking ART services as well as the donor.
- The party seeking ART services will be required to provide insurance coverage in the favour of the oocyte donor for any loss, damage, or death of the donor.
- A clinic is prohibited from offering to provide a child of pre-determined sex.
- It also requires checking for genetic diseases before the embryo implantation.
Concerns:
- The new provisions have pushed up the already sky-high medical costs.
- It is proving to be a challenge for treating doctors and couples wanting to have children through ART because of the restricted and limited resource availability in terms of donors.
- The new ART laws are restricting the number of donation attempts.
- The act violates article 14 of India’s constitution and is also silent on the rights of children. (Article 14 states that equality before the law and equal protection of law to any person within India cannot be denied.)
Way Forward:
The ART services have the potential to increase costs and create challenges for couples relying on assisted reproductive techniques. India, much like the rest of the world, is facing a dip in fertility rates and further limiting available donors is likely to bring in more challenges.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: With the nationwide unemployment rate increasing, creating jobs will remain a key challenge for the government.
Status of job creation and recruitments in India: According to a recent report, about 2.25 lakh active jobs are open in the market as per hiring firms, about 1 lakh fewer than a year earlier.
- Specialised hiring firms claim that the white-collar workforce has taken a severe beating. This shows slower job growth as compared to growing unemployment rate.
No job security: The concept of job security has lost its relevance.
- In recent months, tech giants such as Google, Microsoft, IBM, Meta, Amazon, Cognizant, and big startups such as Byju’s and Ola have fired thousands of employees in India.
Demand for skills and IT professionals:
- In some sectors, tech talent continues to be in demand as non-tech industries undergo a digital transformation.
- Several companies in banking and non-banking, hospitality, automobiles, manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and education are seeking skilled IT talent to drive their digital progress.
- On the flip side, there is still some hope for blue- and grey-collared employees, according to hiring firms.
Need for job creation in India:
- Because of high unemployment rate
- Female labour force participation is very low
- Poverty rate is high as per the Tendulkar committee
- Impact on socio-economic indicators like HDI, Gender Gap report
Reasons for low job growth in India:
- In the last year’s survey of the labour bureau, it found that in most of the eight biggest employment generation sectors – Textiles, leather, metals, automobiles, gems and jewellery, transport, information technology and the handloom sectors – jobs were shrinking.
- A general trend of shrinking export in the last three years has led to loss of hundreds of jobs.
- Domestic manufactures face high tariffs leading to higher raw material cost at home, emanating from the unfavourable inverted duty structure.
- The automobiles sector in India faced no inverted duty structure, and thrived.
- Electronics faced an inverted duty structure and slowly electronics manufacturing has grown.
- There are a number of labour intensive manufacturing sectors in India such as food processing, leather, and footwear, wood manufacturers and furniture, textiles and apparels and garments.
- Indian economy: Since Indian economy jumps from Primary sector to tertiary sector.
- Automation: Many small industries focus om automation to gain high productivity and profit. In Packing, Finishing and other such activity were required huge labor force
- Low skills: All companies wants to book maximum profit in this competitive economy. They need upgraded skills person with multipurpose activity
- Education System: The syllabus/curriculum is taught in higher education institute is not matched the required job industry skills.
Government Initiatives:
National Career Service (NCS) Project: Project for transformation of the National Employment Service to provide a variety of career related services like job matching, career counselling, vocational guidance, information on skill development courses, apprenticeship, internships etc.
- It is under the aegis of Ministry of Labour and Employment.
Mudra loans: The facility of these loans to weaker and unserved sections of the society which aims to launch their business in form of small, micro and medium ventures.
- These will also help in serving the purpose for creating more jobs.
Skill India Mission: It deals with imparting skills to the unskilled labor force in India and as a result of this more skilled labor force at cheap cost will attract the foreign companies which will ultimately result in creation of jobs.
Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY): DDU-GKY is a part of the National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM), tasked with the dual objectives of adding diversity to the incomes of rural poor families and cater to the career aspirations of rural youth.
PM- SVANidhi Scheme: Prime Minister Street Vendor’s Aatmanirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Scheme aims to provide collateral free working capital loan to Street Vendors, vending in urban areas, to resume their businesses which were adversely affected due to COVID-1 induced lock-down.
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) implemented by National Skill Development Corporation.
Rural Self-Employment and Training Institutes (RSETIs): RSETIs are Rural Self Employment Training Institutes, an initiative of the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) to have dedicated infrastructure in each district of the country to impart training and skill upgradation of rural youth geared towards entrepreneurship development.
- RSETIs are managed by banks with active cooperation from the Government of India and State Governments.
Make in India: The Modi government has pushed several programs to catalyse employment opportunities including the ‘Make in India’.
Startup India:
- This initiative helped new entrepreneurs to give shape to their ideas and help in creating more job avenues in form of start-ups.
Way Forward:
India needs to concentrate on enabling the creation of decent work and a sustainable labor market, to which India is committed as a member of the United Nations and the International Labour Organization.
The government should re-establish its role as the principal employment generator through jobs in its ministries and CPSEs and through assured employment generation programmes like MGNREGA and private sector as well plays a significant role in this regard.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Florence Nightingale Awards are given in the field of literature.
Statement-II: The Awards are named after Florence Nightingale.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-Statement-II and I are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I.
- Both Statement-I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I.
- Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect.
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
Q2) Consider the following statements regarding National Emergency:
- It must be revoked if the Lok Sabha passes a resolution by a simple majority.
- This type of emergency has been proclaimed four times so far.
- It has no effect on the Fundamental Rights.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q3) Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary is an Eco sensitive zone.
Statement-II: Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary is located in Goa.
Which one of the following is correct in respect to the above statements?
- Both Statement-Statement-II and I are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I.
- Both Statement-I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I.
- Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect.
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 26th June 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 24th June – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – b
Q.3) -c











