IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Awards
Context: Recently, the last date of submission for the Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar was extended.
Background:-
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development has extended the last date of submission for the Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar till the 31st of August,2023.
About Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar:-

IMAGE SOURCE: noticebard.com
- The Awards are announced on December 26 on ‘Veer Bal Diwas’.
- Veer Baal Diwas: marks a tribute to the martyrdom of Guru Gobind Singh’s sons. (UPSC CSE: Parkash Purab of Sri Guru Gobind Singh Ji)
- The awards are conferred by the President of India at New Delhi at a special ceremony/function to be held in January every year.
- Historical Background: It was instituted in 1979 as the National Child Welfare Awards, renamed in 2018 as Bal Kalyan Puraskar. (UPSC CSE: Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Award (PBSA))
- Objective: It is organized to celebrate the energy, determination, ability, zeal and enthusiasm of our children.
- Field: This national-level award is given in the fields of Bravery, Sports, Social Service, Science and Technology, Environment, Arts and Culture, and Innovation.
- Awarded by: Ministry of Women and Child Development.
Eligibility:-
- A child who is an Indian Citizen and residing in India and is not exceeding 18 years (as of the last date of receipt of application/nomination).
- The act/incident/achievement should have been within 2 years of the last date of receipt of application/nomination for the year of consideration.
- The applicant should not be a previous recipient of the same award earlier in any category (including National Child Awards for Exceptional Achievement, as were awarded by the Ministry earlier)
Nomination can be done by:-
- State Governments, Union Territory Administrations, District Collectors/District Magistrates, and Panchayati Raj Institutions.
- All Central and State School Boards, Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Navodaya Vidyalaya Sangathan, National Commission for Protection of Child Rights, State Commissions for Protection of Child Rights and National Institute of Public Cooperation and Child Development.
- Ministry of Social Justice, Department of Disabilities, Department of School Education in Ministry of Education, all state Departments of School Education, Ministry of Youth Affairs, Department of Sports, Sports Authority of India, Ministry of Culture, Ministry of Science and Technology, Ministry of Environment & Forests, Ministry of Defence, Ministry of Home Affairs, and Press Information Bureau.
- National Selection Committee.
Selection Process
- The applications received are first scrutinized by the Screening Committee.
- The final selection is done by the National Selection Committee.
Decoration:-
- Medal
- Cash prize of Rs. 1,00,000
- Certificate and citation
The Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar is given under two categories:-
- Bal Shakti Puraskar
- It is given by the Government of India every year to recognize exceptional achievements of children in various fieldse., innovation, scholastic achievements, social service, arts & culture, sports and bravery.
- Eligibility: A child who is an Indian Citizen residing in India and is between 5-18 years of age.
- Decoration: A medal, a cash prize of Rs. 1,00,000, book vouchers worth Rs.10,000, a certificate and a citation.
- Bal Kalyan Puraskar
- It is given as recognition to Individuals and Institutions, who have made an outstanding contribution towards service for children in the field of child development, child protection and child welfare.
- Eligibility: An individual who is an Indian Citizen residing in India and should have attained the age of 18 years or above (as of 31st August of the respective year).
- S/he should have worked for the cause of children for not less than 7 years.
- The institution should not be entirely funded by the government and should have been in the field of child welfare for 10 years and performing consistently in the field.
MUST READ: Padma awards
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of the 44th Chess Olympiad, 2022: (2023)
- It was the first time that Chess Olympiad was held in India.
- The official mascot was named Thambi’.
- The trophy for the winning team in the open section is the Vera Menchik Cup.
- The trophy for the winning team in the women’s section is the Hamilton-Russell Cup.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Syllabus
- Prelims –Defence
Context: The Chief of Defense Staff, CDS, General Anil Chauhan inaugurated LRMR Hangar & Dispersal at Naval Air Station, INS Utkrosh in Port Blair.
- The twin hangar spread over 6000 sq. mt. can accommodate a combination of P8I aircraft with Dronier & Advanced Light Helicopters.
- It will help in strengthening the security of the Indian Oceans Region.
About INS Utkrosh:-
- It is an Indian naval air station under the joint-services Andaman and Nicobar Command of the Indian Armed Forces. (UPSC CSE: SLBM launch by INS Arihant)
- Location: Port Blair, Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
- Commissioning: It was commissioned in
- This station operates the Do-228 maritime patrol aircraft and a SAR (Search & Rescue) flight of HAL Chetak helicopters.
- Maritime patrol aircraft (MPA): a fixed-wing aircraft designed to operate for long durations over water in maritime patrol roles.
- Search and rescue (SAR) service: provided to the survivors of aircraft accidents as well as aircraft in distress (and their occupants) regardless of their nationality.
Significance:-
- The station handles courier flights from the mainland and civil flights to and from Port Blair.
- It shares airside facilities with Veer Savarkar International Airport which handles civilian traffic.
- The facilities at INS Utkrosh have been significantly upgraded.
- The runway has been lengthened to almost 11,000 feet (3,400 m).
- Except for the civilian terminal operated by the Airports Authority of India, all other air traffic operations over Port Blair are undertaken by INS Utkrosh.
MUST READ: Kalvari-Class Submarine INS Vagir
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (2016)
- Amphibious warfare ship
- Nuclear-powered submarine
- Torpedo launch and recovery vessel
- Nuclear-powered aircraft carrier
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Institutions
Context: Recently, the Directorate of Revenue Intelligence seized over 48 kg of gold paste estimated to be worth 25 crore rupees at Surat international airport.
Background:-
- DRI said that it has busted a smuggling syndicate by arresting the four persons.
- It said that based on specific intelligence, DRI officers intercepted three passengers arriving from Sharjah by an Air India Express Flight suspected to be carrying gold in paste form.
About Directorate of Revenue Intelligence:-
- It is the apex anti-smuggling agency of India. (UPSC CSE: DRI)
- Implementing Agency: Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs, Ministry of Finance.
- The Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC) was renamed as the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) in 2018 after the rollout of Goods and Services Tax (GST). (UPSC CSE: GST)
- Established: 1957.
- Objective: It is tasked with detecting and curbing the smuggling of contraband, including drug trafficking and illicit international trade in wildlife and environmentally sensitive items, as well as combating commercial frauds related to international trade and evasion of Customs duty.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- The DRI has also been designated as the lead agency for Anti-Smuggling National Coordination Centre (SCord). (UPSC CSE: Problem of cross border smuggling in India)
Functions of DRI:-
- Collection of intelligence about the smuggling of contraband goods, narcotics, under-invoicing etc.
- Analysis and dissemination of such intelligence to the field formations for action and working on such intelligence, where necessary.
- Keeping watch over important seizures and investigation cases.
- Associating or taking over the investigations which warrant specialized handling by the Directorate.
- Guiding important investigation/prosecution cases.
- Keeping liaison with foreign countries, Indian Missions and Enforcement agencies abroad on anti-smuggling matters.
- To keep liaison with C.B.I. and through them with the INTERPOL.
- To refer cases registered under the Customs Act to the Income Tax Department for action under the Income Tax Act.
- To keep statistics of seizures and prices/rates etc.
- To study and suggest remedies for loopholes in law and procedures to combat smuggling.
MUST READ: CBI and ED
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements is correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps Public Sector Banks develop strategies and capital-raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the Kharif crops took a severe hit by intense and unprecedented rainfall across India.
Background:-
- Record-breaking, heavy to extremely heavy rainfall in different regions, especially in the northwestern states of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh, has now dealt a crushing blow by inundating the fields of already sown crops.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has advised farmers to drain out excess water from their fields so that standing crops are saved from rotting.
About India Meteorological Department
- Established:1875.
- Ministry: Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- It is the principal agency responsible for meteorological observations, weather forecasting and seismology.
- IMD is also one of the six Regional Specialized Meteorological Centres of the World Meteorological Organization.
- Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre (RSMC) of Tropical Cyclones in New Delhi is responsible for naming the cyclones in the northern Indian Ocean region.
About Kharif crops:-

IMAGE SOURCE: blogspot.com
- India is a peninsular country where the climate is mostly driven by monsoon. (UPSC CSE: North East Monsoon)
- Due to this reason, India is endowed with a variety of seasons.
- These seasons, in turn, provide different weather conditions to crops, which eventually lead to different cropping patterns.
- Based on seasons, crops are classified into the following:
- Kharif crops
- Rabi crops
- Zaid crops
- Kharif crops, are cultivated and harvested in the monsoon season.
- Naming: The word “Kharif” is Arabic for autumn since the season coincides with the beginning of autumn or winter.
- Sowing and Harvesting: These are sown at the beginning of a monsoon season and farmers harvest them at the end of the season.
- Time Period: The Kharif season differs in every state of the country but is generally from June to September.
- One of the important features of Kharif crops is that they need a lot of water and hot weather for proper growth.
- Kharif crops examples: Rice, Cotton, Maize etc. (UPSC CSE: Government announces hike in MSP for Kharif season)
- India is the second-largest producer of rice in the world after China.
- India accounts for approximately 20% of the world’s rice production.
MUST READ: Agriculture Insurance Company of India (AIC)
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following trees: (2023)
- Jackfruit (Artoca7pus heterophyllus)
- Mahua (Madhuca indica)
- Teak (Tectona grandis)
How many of the above are deciduous trees?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- The Government of India provides Minimum Support Price for niger( Guizotia aoyssinica) seeds.
- Niger is cultivated as a Kharif crop.
- Some tribal people in India use niger seed oil for cooking.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: As per recent reports, evacuation of people from low-lying areas around the river Yamuna is to start soon.
Background:-
- Delhi Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal announced that evacuation of people from low-lying areas around Yamuna will start once the river touches the 206-metre mark.
About Yamuna:-
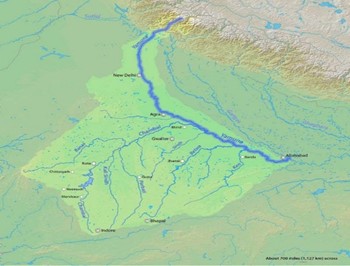
IMAGE SOURCE: SlideShare
- Origin: It originates from the Yamunotri Glacier.
- Yamunotri Glacier: it lies on the southwestern slopes or Banderpoonch Peak, in the Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand.
- Yamuna joins the Ganges (Ganga) River near Prayagraj (Allahabad).
- Drainage Basin: it flows along the states of Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, and Haryana and enters Delhi and Uttar Pradesh.
- It is the largest tributary of the Ganga in the northern plains. (UPSC CSE: Cleaning of River Ganga)
- Total length: from its origin till Allahabad is 1,376 km.
- It creates the highly fertile alluvial, Yamuna-Ganges Doab region between itself and the Ganges in the Indo-Gangetic plain.
- Important Cities: The cities of Bhagpat, Delhi, Noida, Mathura, Agra, Firozabad, Etawah, Hamirpur, and Allahabad lie on its banks. (UPSC CSE: Sutlej-Yamuna Link Canal Project)
- Tributaries of Yamuna:-
- Yamuna is joined by its biggest tributary, the Tons River near Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
- Right bank tributaries: Chambal, Hindon, Sarda and Giri rivers.
- Chambal River is Yamuna’s biggest tributary right bank tributary. (UPSC CSE: National Chambal Sanctuary)
- Left bank tributaries: Betwa and Sindh.
MUST READ: Yamuna Pollution
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- Jhelum River passes through Wular Lake.
- Krishna River directly feeds Kolleru Lake.
- Meandering of the Gandak River formed Kanwar Lake.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Gandikota canyon of South India was created by which one of the following rivers? (2022)
- Cauvery
- Manjira
- Pennar
- Tungabhadra
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) Mechanisms
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The Union government is set to launch an initiative under which women-only courts will be set up at the village-level.
Alternative Dispute Resolution:
- ADR refers to the methods of resolving a dispute, which are alternatives for litigation in Courts.
- Generally, it uses a neutral third party who helps the parties to communicate, discuss the differences and resolve the dispute.
- It offers to resolve all types of matters related to civil disputes, as explicitly provided by the law.
Important Provisions Related To ADR
- Section 89 of the Civil Procedure Code, 1908: Provides that opportunity to the people, if it appears to court there exist elements of settlement outside the court then the court formulate the terms of the possible settlement and refer the same for ADRs.
- Legal Services Authority Act, 1987 (established Lok Adalat System)
- Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996
Types of ADR
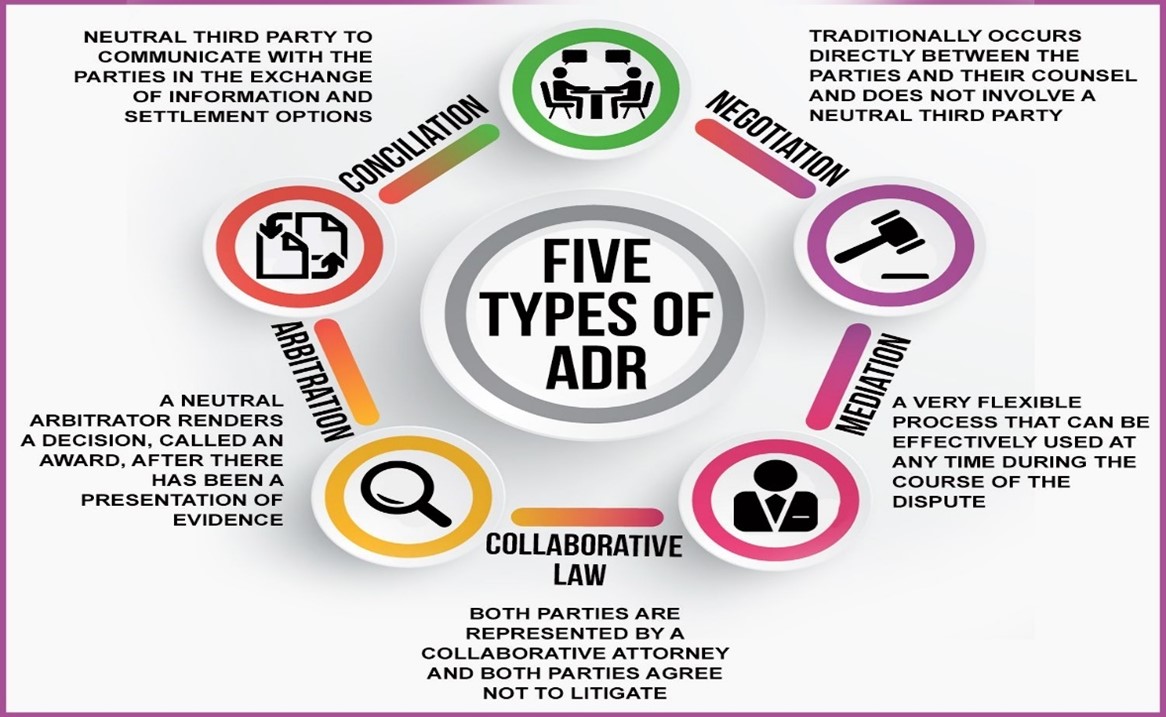
Source: https://viamediationcentre.org/readnews/NjI4/Modes-of-ADR
Status of ADR in India
- Statutory Backing: The Legal Services Authorities Act was passed in 1987 to encourage out-of-court settlements, and the new Arbitration and Conciliation Act was enacted in 1996.
- Inclusion of Plea Bargaining: Procedure for plea-bargaining was included in the Code of Criminal Procedure in 2005.
- Plea-bargaining is best described as a “pre-trial negotiation between the accused and the prosecution during which the accused agrees to plead guilty in exchange for certain concessions by the prosecution.”
- Lok Adalats: Lok Adalat or “people’s court” comprises an informal setting which facilitates negotiations in the presence of a judicial officer wherein cases are dispensed without undue emphasis on legal technicalities.
- The order of the Lok-Adalat is final and binding on the parties, and is not appealable in a court of law.
- Online Dispute Resolution (ODR): The NITI Aayog in its recently released report – The Future of Dispute Resolution discusses the concept of Online Dispute Resolution (ODR) – its evolution, significance and present status in India.
- ODR refers to the usage of ICT tools to enable parties to resolve their disputes.
- In its first phase, ODR shares its fundamentals with ADR Mechanisms of negotiation, mediation and arbitration.
Advantages of ADR:
- Amicable solution: It is a party-driven process, allowing litigants to reach an amicable settlement.
- Thus ADR mechanisms mainly focus on simplicity and convenience of the litigants.
- Speed of settlement: When compared to litigation, alternative dispute resolution devices, such as arbitration and mediation can clear a dispute within days if not months.
- Lok Adalats offer parties speed of settlement, as cases are often disposed of in a single day;
- Procedural flexibility: As there is no strict application of procedural laws such as the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, and the Indian Evidence Act, 1872 there is procedural flexibility for the parties;
- Economic affordability: Cases in courts can go on for years increasing the costs exponentially.
- ADR mechanism is much more cost effective as there are no court fees and significantly less lawyer fees.
- Finality of awards: No further appeal is allowed on the agreement reached between two parties.
- This prevents delays in settlement of disputes.
- Extra security of awards: The award issued by a Lok Adalat, after the filing of a joint compromise petition.
- It has the status of a civil court decree.
Limitations
- No Appeals: There is less or no scope of appeal in awards. Whenever there is a problem with the award, there would be no scope of appeal or correction.
- Varied Guidelines: It is difficult to choose among various guidelines and multiple institutions providing the facility of arbitration.
- Different Statutes: Due to different statutes for domestic and international arbitration, it is difficult to ascertain the applicability of the laws relating to international arbitration.
- Cross-cultural Language Barrier: Due to discrepancy in the language and culture of the two regions, it becomes difficult to bridge the gap and come to a unified solution.
- Unfamiliarity and lack of awareness: Most people still prefer the conventional method of going to courts and are also not informed about these options and the methodology.
Way Forward:
The material and social situation of the litigants forces them to approach ADR mechanism, which is cost effective. However, such mechanism might not always be fair to all parties and may favour the mighty. when dealing with equal parties and in major economic matters, ADR mechanisms can lead to significant cost reductions and reduction of burden on the judiciary.
Source:The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains –GS 3 (Environment)
Context: A parliamentary committee, set up to examine the controversial proposed amendments to the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980, has endorsed the amendment Bill in its entirety.
About Forest cover in India:
- Forest cover’, in India, refers to land greater than one hectare in size where the tree canopy density is greater than 10%.
- India’s total forest cover rose to 38,251 sq. km from 2001 to 2021.
- This increase was mainly in terms of open forest cover, where tree canopy density ranges from 10% to 40%.
- Forest cover in regions classified as ‘dense forest’ actually decreased during that period.
- The amendments which encourage plantation cultivation may increase tree cover, but will be unable to stem the loss of dense forests.
Key Features of the Forest (Conservation) Amendment Bill, 2023:
Land under the Purview of the Act : The Bill provides that two types of land will be under the purview of the Act:
- land declared/notified as a forest under the Indian Forest Act, 1927 or under any other law, or
- land not covered in the first category but notified as a forest on or after October 25, 1980 in a government record.
Exempted Categories of Land;
- The Bill exempts certain types of land from the provisions of the Act, such as forest land along a rail line or a public road maintained by the government.
Assignment/Leasing of Foreign Land
- Under the Act, a state government requires prior approval of the central government to assign forest land to any entity not owned or controlled by government.
- In the Bill, this condition is extended to all entities, including those owned and controlled by government.
- It also requires that prior approval be subject to terms and conditions prescribed by the central government.
Permitted Activities in Forest Land:
- The Act restricts the de-reservation of forests or use of forest land for non-forest purposes.
- Such restrictions may be lifted with the prior approval of the central government.
- Non-forest purposes include use of land for cultivating horticultural crops or for any purpose other than reafforestation.
- The Act specifies certain activities that will be excluded from non-forest purposes, meaning that restrictions on the use of forest land for non-forest purposes will not apply.
The Bill adds more activities to this list such as:
- zoos and safaris under the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 owned by the government or any authority, in forest areas other than protected areas,
- ecotourism facilities,
- silvicultural operations (enhancing forest growth), and
- any other purpose specified by the central government.
Power to Issue Directions:
- The Bill adds that the central government may issue directions for the implementation of the Act to any authority/organisation under or recognized by the centre, state, or union territory (UT).
Controversial parts of the Amendment
- Dilution Concerns: Some critics argue that the amendments dilute the Supreme Court’s 1996 Godavarman case judgment, which extended protection to forests not officially classified as such.
- Geographically Sensitive Areas: Projects within 100 km of international borders or the Line of Control would no longer require forest clearance, which raises concerns about the environment and security.
- Deemed Forests and Tourism: Central protection for deemed forests and restrictions on activities like tourism could be compromised, affecting biodiversity conservation and forest integrity.
- Impact on Forest Cover: Exempting land near border areas for national security projects may adversely affect forest cover and wildlife in northeastern states, which have high forest cover and are biodiversity hotspots.
- Potential Adverse Effects: Blanket exemptions for projects like zoos, eco-tourism facilities, and reconnaissance surveys may have negative consequences for forest land and wildlife.
Way Forward:
The Forest (Conservation) Amendment Bill, despite attracting objections and controversies, has received the endorsement of the parliamentary committee. The proposed amendments aim to bring clarity to the Act’s applicability and promote tree cover, national security infrastructure, and livelihood opportunities.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Directorate of Revenue Intelligence suggest remedies for loopholes in law and procedures to combat smuggling.
Statement-II:
It collects intelligence about the smuggling of narcotics.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-11 is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar can be given to a child who is an Indian Citizen not exceeding 20 years.
Statement-II:
It includes a medal, a cash prize of Rs. 1,00,000, a certificate and a citation.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following pairs:
River Origin
- Hindon Vindhya Range
- Yamuna Yamunotri Glacier
- Teesta Shivalik Hills
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- None
Mains practice questions
Q.1) Explain the various types of Alternative Dispute Resolution mechanisms available in India. What advantages do they offer over the traditional methods of settling disputes? (250 words)
Q.2) The forest conservation Bill’s focus on raising ‘tradeable vertical repositories of carbon’ can jeopardise the very purpose of the Act, which is to protect and conserve India’s forests. Critically analyse. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 11th July 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 10th July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) -d













