IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Personalities
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi has greeted, Dalai Lama on his 88th birthday recently.
Background:-
- In a tweet, the Prime Minister informed that he has also spoken to Dalai Lama on the phone and wished him a long and healthy life.
About Dalai Lama:-

IMAGE SOURCE: pinterest.com
- The Dalai Lama is the spiritual leader who belongs to the Gelugpa tradition of Tibetan Buddhism.
- Gelugpa tradition: it is the largest and most influential tradition in Tibet.
- The Dalai Lamas are believed to be manifestations of Avalokiteshvara or Chenrezig.
- Avalokiteshvara: the Bodhisattva of Compassion and the patron saint of Tibet.
- There have been only 14 Dalai Lamas in the history of Tibetan Buddhism.
- The first and second Dalai Lamas were given the title posthumously.
- Tenzin Gyatso: the 14th and current Dalai Lama.
- In 1989, he was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for his non-violent struggle for the liberation of Tibet.
Historical Background:-
- Until China’s annexation of Tibet in the 1950s, the Dalai Lamas were the head of the Tibetan government.
- Later, plans were made to bring Tibet officially under Chinese control.
- 1959: Tibetans took to the streets demanding an end to Chinese rule.
- The current Dalai Lama fled to India during this Tibetan uprising.
- Former Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru granted him permission to form the ‘Tibetan government in exile’ in Dharamsala (Himachal Pradesh). (UPSC CSE: India-China Trade)
The Process to Choose Dalai Lama:
- Following the Buddhist belief in the principle of reincarnation, the current Dalai Lama is believed by Buddhists to be able to choose the body into which he is reincarnated.
- That person, when found, will then become the next Dalai Lama.
- According to Buddhist scholars, it is the responsibility of the High Lamas of the Gelugpa tradition and the Tibetan government to seek out and find the next Dalai Lama following the death of the incumbent.
- If more than one candidate is identified, the true successor is found by officials and monks drawing lots in a public ceremony.
- Once identified, the successful candidate and his family are taken to Lhasa (or Dharamsala) where the child studies the Buddhist scriptures in order to prepare for spiritual leadership.
Tibetan Buddhism
- Tibetan Buddhism is the combination of the teachings of Mahayana Buddhism with Tantric and Shamanic, and the teachings of Bon, an ancient Tibetan religion. (UPSC CSE: Bamiyan Buddhas)
Impact of Tibet and the Dalai Lama on India and China Relations:-
- Background: Tibet was India’s actual neighbour for centuries.
- 1914: Tibetan representatives, along with Chinese representatives, signed the Shimla convention with British India, delineating boundaries.
- However, following China’s full accession of Tibet in 1950, the convention and the McMahon line that separated the two countries were rejected.
- 1954: India and China signed an agreement in which they agreed to recognize Tibet as the “Tibet region of China.”
- Current Situation: One of the major irritants in India-China relations is the Dalai Lama and Tibet.
- China regards the Dalai Lama as a separatist with considerable clout among Tibetans.
- In the face of rising tensions between India and China, India’s Tibet policy has shifted.
- This policy shift indicates that the Indian government is actively negotiating with the Dalai Lama in public forums.
- The shift in India’s Tibet policy is increasing tensions between India and China. (UPSC CSE: India-China: Concerns)
MUST READ: India-China Relations, a Year after Galwan
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In which one of the following regions was Dhanyakataka, which flourished as a prominent Buddhist centre under
the Mahasanghikas, located? (2023)
- Andhra
- Gandhara
- Kalinga
- Magadha
Q.2) Which one of the following statements is correct? (2022)
- Ajanta Caves lie in the gorge of the Waghora River.
- Sanchi Stupa lies in the gorge of the Chambal River.
- Pandu – Lena cave shrines lie in the gorge of the Narmada River.
- Amaravati Stupa lies in the gorge of the Godavari River.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, the National Green Tribunal (NGT) imposed a fine of about 80,000 crore on states for not disposing of sewage and garbage.
Background:-
- The NGT observed that there is a huge gap in the treatment of sewage and disposal of solid waste by states and UTs.
- The highest penalty has been imposed on Tamil Nadu at Rs 15,419.71 crore followed by Maharashtra at Rs 12,000 crore, Madhya Pradesh at Rs 9,688 crore and Uttar Pradesh at Rs 5,000 crore.
About National Green Tribunal (NGT):-
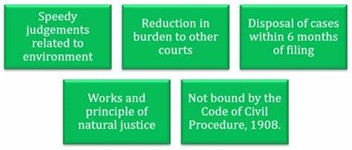
IMAGE SOURCE: universalinstitutions.com
- Establishment: 2010. (UPSC CSE: NGT)
- The National Green Tribunal is a statutory body under the National Green Tribunal Act 2010.
- Objective: for effective and expeditious disposal of cases relating to environmental protection and conservation of forests and other natural resources.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Regional Offices: Bhopal, Pune, Kolkata and Chennai.
- Language:
- It is a specialized body equipped with the necessary expertise to handle environmental disputes involving multi-disciplinary issues. (UPSC MAINS: What are tribunals)
- The Tribunal is not bound by the procedure laid down under the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908.
- It is rather guided by principles of natural justice.
- Timeline for case disposal: The Tribunal is mandated to make and endeavor for disposal of applications or appeals finally within 6 months of the filing of the same.
- Tribunal’s orders are binding and it has the power to grant relief in the form of compensation and damages to affected persons. (UPSC MAINS: Discuss the mandate of the National Green Tribunal (NGT))
- Benefits: The Tribunal’s dedicated jurisdiction in environmental matters shall provide speedy environmental justice and help reduce the burden of litigation in the higher courts.
- India became the third country in the world to set up a specialized environmental tribunal, only after Australia and New Zealand.
Composition of NGT
- Sanctioned strength: The act allows for up to 40 members (20 expert members and 20 judicial members).
- Chairman: The administrative head of the tribunal.
- He also serves as a judicial member.
- He is required to be a serving or retired Chief Justice of a High Court or a judge of the Supreme Court of India.
Selection process:-
- Members are chosen by a selection committee that reviews their applications and conducts interviews.
- The committee is headed by a sitting judge of the Supreme Court of India.
- Judicial members: chosen from applicants who are serving or retired judges of High Courts.
- Expert members: chosen from applicants who are either serving or retired bureaucrats not below the rank of an Additional Secretary to the Government of India and not below the rank of Principal Secretary if serving under a state government.
- They are required to have a minimum administrative experience of five years in dealing with environmental matters.
- Alternatively, they must have a doctorate in a related field.
MUST READ: Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA)
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) “If rainforests and tropical forests are the lungs of the Earth, then surely wetlands function as its kidneys.” Which one of the following functions of wetlands best reflects the above statement?
- The water cycle in wetlands involves surface runoff, subsoil percolation and evaporation.
- Algae form the nutrient base upon which fish, crustaceans, molluscs, birds, reptiles and mammals thrive.
- 58 15 Wetlands play a vital role in maintaining sedimentation balance and soil stabilization.
- Aquatic plants absorb heavy metals and excess nutrients.
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- The India Sanitation Coalition is a platform to promote sustainable sanitation and is funded by the Government of India and the World Health Organisation.
- The National Institute of Urban Affairs is an apex body of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs in the Government of India and provides innovative solutions to address the challenges of Urban India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Recently, an X-class solar flare led to a radio blackout in parts of the US, Pacific Ocean.
Background:-
- According to media reports, the Sun emitted an X-class solar flare on July 2, 2023, disrupting radio communications over parts of the United States and the Pacific Ocean.
- The flare, classified as an X1.0 flare, peaked at 7:14 pm ET, confirmed US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
- X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength.
About Solar flares:-
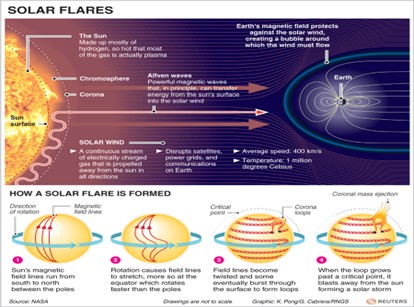
IMAGE SOURCE: blogspot.com
- Solar flares are a sudden explosion of energy caused by tangling, crossing or reorganizing of magnetic field lines near sunspots.(UPSC CSE: Solar Storms)
- Sunspots: areas that appear dark on the surface of the Sun.
- They appear dark because they are cooler than other parts of the Sun’s surface.
- The most powerful solar flares have the energy equivalent of a billion hydrogen bombs, enough energy to power the whole world for 20,000 years.
- Time period: Solar flares can last from minutes to hours.
- Sometimes the same active region on the Sun can give rise to several flares in succession, erupting over the course of days or even weeks.
Classes of solar flares:-
- Solar flares can be divided into various categories based on their brightness in X-ray wavelengths.
- There are five different classes of solar flares: A, B, C, M, and X.
- Each class is at least ten times more potent than the one before it.
- A-class flares: the smallest ones are near background levels.
- C-class flares: slight and have little effect on the Earth.
- B-class flares: smallest after the A-class flare.
- M-class flares: they are medium-sized and typically result in brief radio blackouts that affect the Earth’s Polar Regions.
- Sometimes an M-class flare is followed by small radiation storms.
- X-class flares: large, significant events that have the power to cause global radio blackouts and persistent radiation storms in the upper atmosphere.
Effects of solar flares on Earth:-
- They can affect radio communications, power grids and navigation signals and endanger astronauts and spacecraft. (UPSC MAINS: effects of solar activity)
- They can heat a substance to several millions of degrees in a matter of minutes, producing a burst of radiation that spans the electromagnetic spectrum, from radio waves to x-rays and gamma rays.
- Auroras: When charged particles reach areas near Earth, they can trigger intense lights in the sky, called auroras.
- Electricity shortages and power outages: When particularly strong, a CME can also interfere in power utility grids, causing electricity shortages and power outages.
MUST READ: International Solar Alliance
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to the Earth’s atmosphere, which of the following statements is correct? (2023)
- The total amount of insolation received at the equator is roughly about ·10 times that received at the poles.
- Infrared rays constitute roughly two-thirds of insolation.
- Infrared waves are largely absorbed by water vapour that is concentrated in the lower atmosphere.
- Infrared waves are a part of the visible spectrum of electromagnetic waves of solar radiation.
Q.2) With reference to green hydrogen, consider the following statements : (2023)
- It can be used directly as a fuel for internal combustion.
- It can be blended with natural gas and used as fuel for heat or power generation.
- It can be used in the hydrogen fud cell to run vehicles.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the Lieutenant Governor of Delhi distributed Honey Bee-Boxes and Toolkits to 130 beneficiaries under the Gramodyog Vikas Yojna.
Background:-
- The program was organized under the Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC), Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, State Office Delhi, Government of India.
- Addressing the occasion, Shri Vinai Kumar Saxena emphasized the vital role played by the Khadi and Village Industries Commission in generating employment opportunities in rural India.
About Gramodyog Vikas Yojna:-
- Launched:
- Objective: assisting and developing of agarbatti industry and its artisans thereby.
- Ministry: Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME)
- The programme aims to enhance the production of ‘Agarbatti’ in the country and create sustainable employment for the traditional Artisans, by providing them with regular employment and an increase in their wages.
Components of the Yojana:-
- Research & Development and Product Innovation: R&D support would be given to the institutions that intend to carry out product development, new innovations, design development, product diversification processes etc.
- Capacity Building: exclusive capacity building of staff, as well as the artisans, would be adequately addressed through the existing Multidisciplinary Training Centers (MDTCs) and institutions of excellence.
- Marketing & Publicity: The institutions will be provided market support.
- It will be done by way of preparation of a product catalogue, Industry directory, market research, new marketing techniques, buyer-seller meet, arranging exhibitions etc. (UPSC MAINS: Effects of globalisation on the rural population of India)
Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC)
- Establishment:
- It is a statutory body established under the Khadi and Village Industries Commission Act, of 1956.
- Objectives of KVIC:-
- To boost employment in the country. (UPSC CSE: Project Re-Hab)
- To promote the promotion and sale of Khadi articles.
- To cater to the self-reliance doctrine of the country by empowering underprivileged and rural sections of society.
- Function: The KVIC is charged with the planning, promotion, organization and implementation of programmes for the development of Khadi and other village industries in the rural areas in coordination with other agencies engaged in rural development wherever necessary.
- Ministry: Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
MUST READ: Rural Manufacturing
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements with reference to India: (2023)
- According to the ‘Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006’, ‘medium enterprises’ are those with investments in plant and machinery between (‘ 15 crores and ’25 crore.)
- All bank loans to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises qualify under the priority sector.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2020)
- Aadhaar metadata cannot be stored for more than three months.
- State cannot enter into any contract with private corporations for sharing of Aadhaar data.
- Aadhaar is mandatory for obtaining insurance products.
- Aadhaar is mandatory for getting benefits funded out of the Consolidated Fund of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the World Investment Report 2023 was released.
About the World Investment Report 2023:-
- Published by: United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD).
- Objectives: it focuses on trends in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) worldwide, at the regional and country levels and emerging measures to improve its contribution to development. (UPSC CSE: FDI Inflow)
Key Findings:-
- India and ASEAN registered foreign direct investment (FDI) increases of 10 % and 5%, respectively.(UPSC CSE: FDI Policy Change and Government Initiatives).
- FDI inflows were higher in developing countries.
- China, the second largest FDI host country in the world, saw a 5% increase.
- Gulf region: FDI declined, but the number of project announcements increased by two-thirds.
- Inflows in many smaller developing countries were stagnant, and FDI to the least developed countries (LDCs) declined.
- LDC: developing countries listed by the United Nations that exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development.
- Much of the growth in international investment in renewable energy has been concentrated in developed countries.
- The investment gap across all sectors of the Sustainable Development Goals has increased to more than $4 trillion per year from $2.5 trillion in 2015.
- The largest gaps are in energy, water and transport infrastructure.
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
- Established: 1964.
- UNCTAD is the UN’s leading institution dealing with trade and development.
- It is a permanent intergovernmental body established by the United Nations General Assembly.
- UNCTAD is part of the UN Secretariat.
- HQ: Geneva in Switzerland.
- Membership: it has a membership of 195 countries.
- It is one of the largest in the UN system.
Functions of UNCTAD: –
- It supports developing countries to access the benefits of a globalized economy more fairly and effectively.
- It provides economic, trade analysis, and facilitates consensus building.
- It offers technical assistance to help developing countries use trade, investment, finance and technology for inclusive and sustainable development.
Some of the reports published by it are-
- Trade and Development Report
- World Investment Report
- The Least Developed Countries Report
- Information and Economy Report
- Technology and Innovation Report
- Commodities and Development Report
MUST READ: Foreign Direct Investment equity flows into India
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Rapid Financing Instruments” and “Rapid Credit Facility” are related to the provisions of lending by which of the following: (2022)
- Asian Development Bank
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
- World Bank
Q.2) With reference to foreign-owned e-commerce firms operating in India, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2022)
- They can sell their own goods in addition to offering their platforms as market-places.
- The degree to which they can own big sellers on their platforms is limited.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –International Relations
Context: Recently, the seventh edition of the bilateral Japan-India Maritime Exercise 2023 (JIMEX 23) took place.
Background:-
- The event was hosted by the Indian Navy and is being conducted at/ off Visakhapatnam from 05 -10 July 2023.
- This edition marks the 11th anniversary of JIMEX, since its inception in 2012.
About Japan-India Maritime Exercise 2023 (JIMEX 23):-
- Background: JIMEX, is a series of maritime exercises conducted by the Indian Navy and the Japan Maritime Self-Defence Force (JMSDF).
- It was first commenced in 2012.
- JIMEX 23 will witness the participation of:-
- From Indian Navy:-
- INS Delhi: India’s first indigenously built Guided Missile Destroyer.
- INS Kamorta: an indigenously designed and built Anti-Submarine Warfare Corvette.
- INS Kamorta is a Kamorta-class anti-submarine warfare corvette.
- The Kamorta-class corvettes are designed to perform a range of naval operations, including anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare, and surveillance missions.
- Others: a fleet tanker INS Shakti, a submarine, maritime patrol aircraft P8I and Dornier, ship-borne helicopters and fighter aircraft.
- From JMSDF:-
- It will be represented by the guided missile destroyer JS Samidare and its integral helicopters.
- It will take place in two phases:-
- Harbour Phase: at Visakhapatnam comprising professional, sports and social interactions.
- After the Harbour Phase: the two navies will jointly hone their warfighting skills at sea and enhance their interoperability through complex multi-discipline operations in the surface, sub-surface and air domains.
Other Exercises between India and Japan:-
- Malabar: India and Japan with the United States and Australia participate in the naval war-gaming exercise named Malabar. (UPSC CSE: 26th Exercise Malabar)
- SHINYUU Maitri :Air Force
- Dharma Guardian: Military Exercise(UPSC CSE: Exercise IBSAMAR)
MUST READ: International Maritime Exercise/ Cutlass Express 2023 (IMX/CE-23) and INS Trikand
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Home Guards, consider the following statements: (2023)
- Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards Act and Rules of the Central Government.
- The role of the Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary force to the police in the maintenance of internal security.
- To prevent infiltration on the international border/ coastal areas, the Border Wing Home Guards Battalions have been raised in some states.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
- Japan
- Russia
- The United Kingdom
- The United States of America
Uniform Civil Code
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Society) and GS 2 (Polity and Governance)
Context: Recently, Prime Minister of India emphasised the crucial need for the implementation of a Uniform Civil Code (UCC) in India.
About Uniform Civil Code (UCC):
- The Uniform Civil Code (UCC) calls for the formulation of one law for India, which would be applicable to all religious communities in matters such as marriage, divorce, inheritance, adoption.
History of Uniform Civil Code:
- It dates back to colonial India when the British government submitted its report in 1835 stressing the need for uniformity in the codification of Indian law relating to crimes, evidence, and contracts, specifically recommending that personal laws of Hindus and Muslims be kept outside such codification.
- An increase in legislation dealing with personal issues at the far end of British rule forced the government to form the B N Rau Committee to codify Hindu law in 1941.
Personal Laws in India:
- Currently, not only Muslims but also Hindus, Jains, Buddhists, Sikhs, Parsis, and Jews are governed by their own personal laws.
- Personal laws are determined based on religious identity.
- The reformed Hindu Personal Law still incorporates certain traditional practices.
- Differences arise when Hindus and Muslims marry under the Special Marriage Act, where Hindus continue to be governed by Hindu Personal Law, but Muslims are not.
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 37: The “state shall endeavour by suitable legislation”, while the phrase “by suitable legislation” is absent in Article 44.
- Article 44: The “State shall endeavour to provide for its citizens a uniform civil code (UCC) throughout the territory of India.”
Arguments For Uniform Civil Code:
It will promote integration of India:
- It will promote the integration of India by establishing a shared platform for diverse communities.
- Personal laws rooted in religion are a challenge to the unity of the nation.
- The implementation will promote the integration of India by establishing a shared platform for diverse communities.
Ease for Supreme Court of India:
- The Supreme Court will find it easy to deal with cases involving marriage, divorce, property rights etc because presently it faces conflict situation due to different laws for the above subjects.
It will fulfill constitutional objective:
- The implementation of a Uniform Civil Code (UCC) is a constitutional objective aimed at ensuring equitable justice for all communities.
- It would be ideal for India to establish a codified family law that aligns with progressive interpretations of religious texts and upholds constitutional principles of justice and equality.
Reforming the Shariat law:
- The Shariat Application Act of 1937 lacks provisions pertaining to significant elements including the minimum age for marriage, consent, meher (dowry), divorce proceedings, polygamy, child custody and guardianship, as well as women’s entitlement to property.
- As a result, the practice of child marriages continues to endure.
- These practises are deemed justified based on the principles of sharia law, which stipulates that a girl becomes eligible for marriage upon reaching the age of puberty.
Arguments against the uniform civil code:
- Violation of religious freedom: Critics argue that the UCC may infringe upon the freedom to practice the religion of one’s choice, which allows religious communities to follow their own personal laws.
- For example, Article 25 of the Indian constitution gives every religious group the right to manage its own affairs, and Article 29 allows them to conserve their distinct culture.
- Threat to cultural diversity: Another argument against the UCC is the threat it could pose to India’s rich cultural diversity.
- Critics argue that individual personal laws reflect the distinct customs and traditions of different religious communities, and a uniform code could undermine this diversity.
- They contend that the UCC could lead to a homogenization of laws, which would not be in keeping with India’s multicultural ethos.
- Existing secular laws: Critics also question the need for a UCC, pointing out that there are already secular laws applicable to all citizens, irrespective of religion, in many matters, such as Section 125 of the Criminal Procedure Code, which provides for maintenance, and laws relating to domestic violence.
- Imposition of ‘Hinduised’ Code: Some critics suggest that the UCC might impose a ‘Hinduised’ code on all communities.
- For example, a UCC could include provisions for family disputes on property inheritance, which may be in line with Hindu customs and will legally force other communities to follow the same.
- Diversity in personal laws: The opposition argues that even codified civil laws and criminal laws like the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) and the Indian Penal Code (IPC) don’t follow ‘one nation, one law’.
- For example, the law of anticipatory bail differs from one state to another.
- Personal laws placed in concurrent list: Some constitutional law experts argue that perhaps the framers did not intend total uniformity, which is why personal laws were placed in Entry 5 of the Concurrent List, with the power to legislate being given to the Parliament as well as the State Assemblies.
Important Cases Related to UCC:
Shah Bano Begum v. Mohammad Ahmed Khan (1985):
- The Supreme Court upheld the right of a Muslim woman to claim maintenance from her husband under Section 125 of the Criminal Procedure Code, even after the expiry of the Iddat period.
- It also observed that a UCC would help in removing contradictions based on ideologies.
Shayara Bano v. Union of India (2017):
- The Supreme Court declared the practice of triple talaq as unconstitutional and violative of the dignity and equality of Muslim women.
- It also recommended that the Parliament should enact a law to regulate Muslim marriages and divorces.
Way Forward:
UCC is a complex issue that requires careful consideration of religious, cultural, and societal perspectives. Balancing the unity and diversity of India is crucial, as the implementation of a UCC should aim to provide equal rights and opportunities while respecting the distinct identities of different communities.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: The creative economy is one of the youngest and fastest-growing sectors in India.
About Creative Economy:
- It is an evolving concept which is building on the interplay between human creativity and ideas and intellectual property, knowledge and technology.
- It includes advertising, architecture, arts and crafts, design, fashion, film, video, photography, music, etc.
Status of India’s creative economy:
Growing recognition:
- There is now growing recognition of the economic importance of the arts sector as it helps in the creation of jobs, economic growth, tourism, exports, and overall societal development.
- Digital platforms and technology have enabled Indian artists and artisans to reach wider audiences.
- Online platforms, social media, and digital content creation enable artists, writers, film-makers, musicians, and other creatives to engage with audiences, and monetise their talents.
- Indian artists and artisans play a vital role in preserving traditional art forms and creating contemporary artworks.
UNESCO MONDIACULT 2022:
- Recognising the economic importance of culture, the UNESCO World Conference on Cultural Policies and Sustainable Development (MONDIACULT 2022) was held to address contemporary issues in multicultural societies.
- The goal was to share a vision for the future of cultural policies and to reaffirm the international community’s commitment to leveraging culture’s transformative power for sustainable development.
Challenges faced by Indian artistes:
- Economic and market challenges: Indian artists struggle with issues related to economic sustainability and gaining adequate market access to monetize their work.
- Preservation of traditional art forms: In the face of rapidly changing societal trends, preserving and promoting traditional art forms presents significant challenges.
- Inequalities in representation and support: Artists often face a lack of transparency in the selection process for financial assistance and event organization. Those based outside cities are particularly disadvantaged.
- Crime in the art world: Artists must contend with art-related crimes such as theft, forgery, and illicit trafficking. These crimes undermine cultural heritage, financial security, and public trust.
To address these challenges, the article suggests several solutions:
- Government Support and Cultural Institutions: Continued financial assistance, training programs, and opportunities provided by the government and cultural institutions can help artists sustain themselves and gain exposure.
- Transparent Selection Processes: Implementing transparent and fair selection processes for financial assistance and cultural events can ensure equal representation and opportunities for artists.
- Promotion of Artists as Brands: Private and public institutions should take initiatives to promote contemporary artists as brands, providing market support, research, business facilitation, and platforms to showcase their work.
- Enhanced Security Measures and Technology: Strengthening security measures, promoting international cooperation, raising public awareness, and utilising advanced technology for authentication and tracking can help combat crime in the art world.
- Preservation of Cultural Heritage: Regular audits, verified identification marks, and institutional records can contribute to preserving the integrity and trust of cultural collections.
Way Forward:
The economic and cultural significance of art, culture, and the creative economy in India, while addressing challenges and proposing solutions, should support the growth and development of artists and artisans as a whole.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Solar flares have the energy equivalent of a billion hydrogen bombs.
Statement-II:
X-class solar flares are the smallest and least significant events to have any impact on Earth.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-11 is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q2) Consider the following pairs:
- Malabar: Air Force exercise between India and Japan.
- SHINYUU Maitri: Naval exercise between India, Japan with the United States.
- Dharma Guardian: Military Exercise between India and Japan.
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- None
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
NGT is mandated to disposal of applications or appeals finally within 6 months of filing.
Statement-II:
NGT’s principal Place of Sitting is New Delhi but it has four zonal benches in Bhopal, Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-11 is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions:
Q.1) What do you understand by Uniform Civil Code? Examine its relevance for a secular country like India and challenges in its implementation? (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 7th July 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 6th July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – b











