IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: The Global Biodiversity Framework Fund (GBFF) was ratified and launched at the Seventh Assembly of the Global Environment Facility (GEF) held recently.
Global Biodiversity Framework Fund’s (GBFF) implications:-
- Governments, non-profits, and the private sector can now contribute their funds to GBFF.
- This will ensure that the world meets the goals and targets of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) formulated by the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) by 2030.
- As much as 20 percent of the funds would support Indigenous-led initiatives to protect and conserve biodiversity.
- It will also prioritize support for Small Island Developing States and Least Developed Countries, which will receive more than a third of the fund’s resources.
- This is the first time there would be funds channeled to non-state actors like the indigenous communities.
- Under Target 19 of GBF, at least $200 billion per year will need to be raised by 2030.
- Canada and the United Kingdom have already donated 200 million Canadian dollars and 10 million pounds respectively to the GBFF.
- After donations from Canada and the UK, $40 million is still needed to operationalize the fund by the end of 2023.
- The first GBFF Council meeting will be held in January 2024, with a view to approving the first work programme at the June 2024 Council meeting.
- The first tranche of the fund is likely to be disbursed after the council meeting to ensure that the first projects under the new Fund can be launched ahead of CBD’s CoP16.
About Global Environment Facility (GEF):-
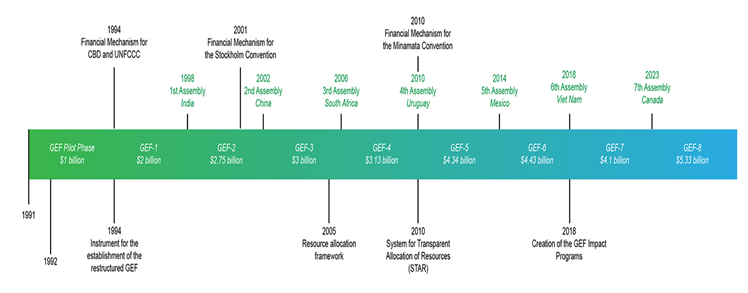
IMAGE SOURCE: GEF
- Established:1991.
- It was established on the eve of the 1992 Rio Earth Summit of UNFCC.
- HQ: Washington, D.C. United States.
Historical Background:-
- It was set up as a fund under the World Bank.
- Restructured: in 1994.
- 1992: At the Rio Earth Summit, the GEF was restructured and moved out of the World Bank system to become a permanent, separate institution.
- Since 1994, however, the World Bank has served as the Trustee of the GEF Trust Fund.
- Rio Earth Summit: It was a major United Nations conference held in Rio de Janeiro (Brazil) in 1992.
- It highlighted the impact of human socio-economic activities on the environment. ( Climate Ambition Summit 2020 held virtually)
- Members of GEF: It has 184 member
- India is a member.
- Venue of the seventh Assembly of GEF: Vancouver, Canada.
- It is a family of funds dedicated to confronting biodiversity loss, climate change, pollution, and strains on land and ocean health.
- Its grants, blended financing, and policy support to help developing countries address their biggest environmental priorities and adhere to international environmental conventions.
- It provides financial assistance for five major international environmental conventions:-
The Minamata Convention on Mercury.
- Signed: 2013.
- Effective from 2014.
- It is an international treaty designed to protect human health and the environment from anthropogenic emissions and releases of mercury and mercury compounds.
The Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs).
- Signed:2001.
- Effective from 2004.
- It is an international environmental treaty that aims to eliminate or restrict the production and use of persistent organic pollutants (POPs).
The United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (UNCBD) (UN Biodiversity Summit)
- Signed: 5 June 1992 – 4 June 1993.
- Effective from 1993.
- It is the international legal instrument for “the conservation of biological diversity, the sustainable use of its components, and the fair and equitable sharing of the benefits.
The United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD).
- Signed: 14 October 1994 – 13 October 1995.
- Effective from 1996.
- It was established in 1994 to protect and restore our land and ensure a safer, just, and more sustainable future.
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- Signed:1992-1993.
- Effective from 1994.
- It was adopted in 1992 with the ultimate aim of preventing dangerous human interference with the climate system.
Organization of GEF:-
- The GEF’s governing structure is organized around an Assembly, Council, Secretariat, 18 implementing agencies, a Scientific and Technical Advisory Panel, and the Independent Evaluation Office.
- GEF Council: it is the GEF’s main governing body, and comprises 32 members appointed by constituencies of member countries.
Functions of GEF:-
- It supports developing countries’ work to address the world’s most pressing environmental issues.
- It organizes work around five focal areas – biodiversity loss, chemicals and waste, climate change, international waters, and land degradation.
- It takes an integrated approach to support more sustainable food systems, forest management, and cities.
GEF and India:
- India is a founder member of GEF.
- It is both a donor and recipient of GEF funds.
- India represents the GEF South Asia Constituency (including, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, and Sri Lanka) in the GEF Council.
- GEF Political Focal Point: Department of Economic Affairs (DEA).
- It is responsible for issues related to GEF governance, including policies and decisions, as well as relations between member countries and the GEF Council and Assembly.
- GEF Operational Focal Point (OFP): The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
MUST READ: Climate Adaptation Summit 2021
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following : (2023)
- Aerosols
- Foam agents
- Fire retardants
- Lubricants
In the making of how many of the above are hydrofluorocarbons used?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) With reference to ‘Global Environment Facility’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2014)
- It serves as a financial mechanism for ‘Convention on Biological Diversity and ‘United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
- It undertakes scientific research on environmental issues at the global level
- It is an agency under the OECD to facilitate the transfer of technology and funds to underdeveloped countries with the specific aim of protecting their environment
- Both (a) and (b)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Gold prices declined 50 rupees at Multi Commodity Exchange for October 2023.
Background:-
- Gold was trading at 58,769 rupees per 10 grams.
- Silver was also down by 404 rupees to trade at 73,600 rupees per kilogram for September 2023 Contracts.
About Multi Commodity Exchange:-
- A commodities exchange is a legal entity that facilitates the trading of standardized commodity contracts and related investment products.
- Commodity Exchange was first regulated by the Forward Market Commission (FMC).
- After the merger of FMC with SEBI in 2015 it is now regulated by
Major Commodity Exchange in India:-
- Multi Commodity Exchange (MCX)
- National Commodities and Derivative Exchange (NCDEX)
- National Multi-commodity Exchange (NMCE)
- Of these commodity exchanges, the NCDEX and NCME focus primarily on agricultural commodities trading.
Multi Commodity Exchange (MCX):-
- Established: 2003.
- Ministry: Ministry of Finance.
- HQ: Mumbai.
- It is India’s first listed exchange.
- It facilitates online trading of commodities like gold, silver, copper, zinc, lead, crude oil, natural gas (NG) nickel, aluminum, etc. (Gold Reserve)
- It holds 86% of the market share of commodity exchanges in India.
- It is the world’s largest exchange for silver and gold.( Bureau of Indian Standards(BIS) and Hallmark)
- It involves trading in more than 40 commodities.
- Promoters: National Spot Exchange Limited, India Energy Exchange, Singapore Mercantile Exchange Global Board of Trade, IBS Forex, etc.
- Traded commodities: metal, fibre, bullion, energy, spices, etc.
MUST READ: Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme 2022-23
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2017)
- The Standard Mark of the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) is mandatory for automotive tyres and tubes.
- AGMARK is a quality Certification Mark issued by the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO).
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) What is/are the purpose/purposes of the Government’s ‘Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme’ and ‘Gold Monetization Scheme’? (2016)
- To bring the idle gold lying with Indian households into the economy
- To promote FDI in the gold and jewelry sector
- To reduce India’s dependence on gold imports
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Union Law and Justice Minister Arjun Ram Meghwal launched Tele-Law- 2.0 recently.
About Tele-Law- 2.0:-
- Ministry: Ministry of Law & Justice.
- It Integrates Tele-Law and Nyaya Bandhu App.
- Objective: to further enhance citizen accessibility to legal aid.
- It will enable the common citizen to access legal advice, legal assistance, and legal representation through a single registration and single gateway of Tele-Law. (Lakhs of people benefit through Tele-Law)
About the Tele-Law programme:-
- Ministry/ministries: Ministry of Law and Justice and Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Objective: the programme connects the disadvantaged section with a panel of lawyers through an e-interface platform.
Working:-
- It uses video conferencing facilities and telephone services to connect lawyers to litigants who need legal advice.
- It is to facilitate the delivery of legal advice through a panel of lawyers stationed at the State Legal Services Authorities (SALSA) and CSC (Common service centres).
Fee:-
- The service is free for those who are eligible for free legal Aid under Section 12 of the Legal Services Authority Act, 1987.
- For all others, a nominal fee is charged.
MUST READ: Citizens’ Tele-Law Mobile App
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places, and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Regarding Digi Locker’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- It is a digital locker system offered by the Government under the Digital India Programme.
- It allows you to access your e-documents irrespective of your physical location.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Important Awards
Context: Recently, Prime Minister Modi became the first Foreign Head of a Govt. to be awarded ‘The Grand Cross of the Order of Honour’ by the Greek govt.
Background:-
- This recognition was given during Prime Minister Modi’s official visit to Greece.
About The Grand Cross of the Order of Honour:-
IMAGE SOURCE: IASBABA
- Established:1975.
- Conferred by: President of Greece. (Aegean sea & islands)
- Description: The head of the goddess Athena is depicted on the front side of the Star with the inscription “ONLY THE RIGHTEOUS SHOULD BE HONOURED”.
- Conferred to: Prime Ministers and eminent personalities who by reason of their distinguished position, have contributed to enhancing the stature of Greece. (Greece- Turkey Clash)
MUST READ: NATO
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The term “two-state solution” is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (2018)
- China
- Israel
- Iraq
- Yemen
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Recently, the Winners of the India Smart Cities Awards Contest 2022 were announced.
Key Highlights:-
- President Droupadi Murmu will felicitate the winners of the ISAC 2022 awards on the 27th of September in Indore, Madhya Pradesh.
About India Smart Cities Awards Contest 2022:-
- The India Smart Cities Awards Contest (ISAC) recognizes the exemplary work championed by cities, projects, innovations, and partners in promoting ‘smart’ development in cities. (Smart City Mission)
- Participants: All 100 smart cities have participated in the ISAC.
- There have been three editions of the ISAC, viz., ISAC 2018, ISAC 2019 and ISAC 2020.
- It was the Fourth edition of the awards.
- Ministry: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
Selection Process:-
- The award has a two-stage submission process:-
- First stage or ‘Qualifying Stage’: It involves an overall assessment of the city’s performance.
- Second stage or ‘Proposal Stage’: requires smart cities to submit their nominations for six award categories viz.
- These include Project Award, Innovation Award, City Award, State/UT Award, Leadership Award and Partners Award. (Fifth anniversary of the Smart Cities Mission)
- The Partners Award is a new addition to the Award categories.
- It is to honour the various collaborators of the smart city ecosystem, e.g., industry partners, knowledge partners, and community-based organizations for their contribution to championing the cause of the Smart Cities Mission.
- Results of the ISAC 2022 announced: 15th August 2022.
MUST READ: Smart Cities and Academia Towards Action & Research (SAAR)
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
- Department of Science and Technology
- Ministry of Labour and Employment
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Q.2) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places, and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Government initiatives
Context: Recently, the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), launched Project ‘AMBER’.
Background:-
- MSDE started the project in collaboration with Generation India Foundation (GIF) and Amazon Web Services India Private Limited (AWS India).
About Project ‘AMBER’:-
- Launched: 2023.
- Ministry: Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- It is a joint initiative of the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC), Generation India Foundation (GIF), and Amazon Web Services India Private Limited (AWS India).
- The initiative has been undertaken under the SANKALP programme.
- Objective: to train 30,000 youth, focusing on women and underprivileged groups.
- Among the 30,000 youth, 50% will be women.
- Learners engage in the AWS (re/Start) program, gaining fundamental AWS cloud skills and practical career guidance.
Features of the project:-
- The learners take part in AWS (re/Start), a workforce development program for unemployed and underemployed individuals.
- It covers fundamental AWS cloud skills as well as practical career tips, including resume writing and interview preparation.
- Through real-world scenario-based exercises, labs, and coursework, learners are trained in multiple technologies, including Linux, Python, networking, security, and relational databases.
- The program covers the cost for learners to take the AWS Cloud Practitioner Certification exam.
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Certification exam: an industry-recognized credential that validates their cloud skills and knowledge and connects the participants with job interview opportunities in cloud or IT with local employers.
Significance:-
- It will bring entry-level talent into the workforce.
- It helps individuals to launch successful cloud careers. (Cloud Computing)
- It helps organizations to increase their competitive edge with in-demand talent, and communities.
- It focuses on women to improve gender diversification in the tech industry and underprivileged groups.
MUST READ: National Super Computing Mission (NSM)
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to foreign-owned e-commerce firms operating in India, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2022)
- They can sell their own goods in addition to offering their platforms as marketplaces.
- The degree to which they can own big sellers on their platforms is limited.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Private and public hospitals must adopt it.
- As it aims to achieve universal health coverage, every citizen of India should be part of it ultimately.
- It has seamless portability across the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
India and One Health Approach
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently the G20 health ministers prioritise, commit to tackling antimicrobial resistance (AMR) with One Health approach during their meet in Gandhinagar, Gujrat.
About the One Health Approach:
- ‘One Health’ is an interdisciplinary approach that recognises the interconnections between the health of humans, animals, plants, and their shared environment.
- An early articulation can be found in the writings of Hippocrates, who contemplated the relationships between public health and clean environments.
- The 19th-century German physician and pathologist Rudolf Virchow later wrote that between animal and human medicines there are no dividing lines – nor should there be.”
- Recently, the eminent veterinarians James Steele and Calvin Schwabe have championed the value of ecology for both animal and human health.
Significance of One Health approach:
- Requirement of less resources: It minimises resource requirements across sectors.
- An important way it does this is by encouraging coordination across governmental units.
- Exchange of information: Taking a One Health approach allows researchers to share their laboratories and findings, and ultimately make decisions that lead to resilient, sustainable, and predictable policies.
- Potential economic benefits: The economic benefits of One Health are understood in contrast to the cost of managing a pandemic with a non-One-Health approach.
- An assessment of the G20 Joint Finance and Health Taskforce estimated the latter to be around $30 billion a year.
- On the other hand, estimates by the World Bank have indicated that the former would cost $3 billion to $11.5 billion annually.
- Integrated approach: The COVID-19 pandemic has renewed interest among scientists and policy makers for building an integrated approach for prevention, early detection and instituting appropriate response to control such public health emergencies.
Associated challenges:
- Spread of disease: About 60 per cent of the known infectious diseases in humans and 75 percent of all emerging infectious diseases are caused by pathogens that originate in animals.
- Antibiotic-resistant microbes also can effectively be transmitted from animals to humans and cause diseases in humans which may not respond to affordable antibiotics.
- Extensive and irrational use of antibiotics especially in the livestock sector for increasing yield and preventing diseases causes emergence and selection of resistant pathogens. These spread through animal-human interaction or food chain.
Govt Initiatives on One health approach:
- Consortium on One Health: The Department of Biotechnology launched India’s first consortium on One Health in 2021.
- It brings together 27 organisations from several ministries and plans to assess the burden of five transboundary animal diseases and 10 select zoonotic diseases.
- Standing Committee on Zoonoses: The Government of India established its ‘Standing Committee on Zoonoses’ in 2006 under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
- It is to provide the Union and the State governments guidance and recommendations on challenges related to zoonoses.
- Pilot projects: Pilot projects in some states: In 2022 a One Health pilot project was launched in Karnataka and Uttarakhand.
- It intends to strengthen intersectoral collaborations through capacity-building, with the goal of improving livestock health, human health, wildlife health, and environmental health.
- National One Health Mission: India is also currently preparing for a wider ‘National One Health Mission’ to be spearheaded by the Office of the Principal Scientific Advisor.
- The idea is to coordinate, support and integrate all existing One Health initiatives in the country.
Way Forward:
India should move beyond short-term collaborations and create an integrated, science-based environment. This is a prerequisite for platforms to not just share office space but to also provide access to laboratories and biological samples to the relevant researchers. Therefore nexus of science, social science, indigenous knowledge and policy at national, state and local levels can put forward strategies and institutions for implementation of One Health.
Source: DTE
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Polity and Governance)
Context: The bill was recently introduced in Rajya Sabha will consist of the Prime Minister as the chairperson, the Leader of the Opposition as a member, and a Union Cabinet Minister nominated by the Prime Minister as another member.
- This bill proposes to exclude the Chief Justice of India (CJI) from the three-member committee that recommends the names of the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and the Election Commissioners (ECs) to the President.
Background:
- The Supreme Court (SC) in recently ruled that CEC and ECs will be appointed by the President of India on the advice of a Committee consisting of the Prime Minister, and Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha, and the Chief Justice of India until a law is enacted by Parliament on their appointments.
- This ruling emerged from a 2015 Public Interest Litigation (PIL) challenging the appointment process.
Key provisions of the bill:
- Composition of the commission: The bill maintains the existing structure of the Election Commission, consisting of the CEC and other ECs.
- The CEC and ECs are appointed by the President of India.
- However, the bill introduces the requirement that their appointments will be made on the recommendation of a Selection Committee.
- Selection committee: The Selection Committee will comprise the Prime Minister as the Chairperson, the Leader of the Opposition in the Lok Sabha, and a Union Cabinet Minister nominated by the Prime Minister.
- If there is no recognized Leader of the Opposition, the leader of the largest opposition party in the Lok Sabha will take on this role.
- Search committee: A Search Committee will be responsible for preparing a panel of five potential candidates for the Selection Committee’s consideration.
- The Search Committee will be headed by the Cabinet Secretary and will have two other members who are senior government officials with expertise in election-related matters.
- The Selection Committee can also consider candidates who were not included in the panel prepared by the Search Committee.
- Qualification: Individuals who hold or have held positions equivalent to the rank of Secretary in the central government will be eligible for appointment as CEC and ECs.
- Additionally, these individuals should possess expertise in managing and conducting elections.
- Salaries and allowances: The bill stipulates that the salary, allowances, and service conditions of the CEC and other ECs will be the same as those of the Cabinet Secretary.
- Term of office: Both the CEC and other ECs will serve for a term of six years or until they reach the age of 65, whichever comes first.
- If an EC is elevated to the position of CEC, its total term cannot exceed six years.
- The bill also specifies that the CEC and ECs will not be eligible for reappointment.
- Conduct of business: The Election Commission’s business will continue to be conducted through unanimous decisions.
- If a difference of opinion arises between the CEC and other ECs on any matter, it will be resolved through a majority vote.
- Removal and resignation: The bill maintains the existing procedure for removing the CEC and ECs from office.
- The CEC can only be removed through a process similar to the removal of a Supreme Court judge, requiring a motion passed by both Houses of Parliament with majority support of the total membership and at least two-thirds support from members present and voting.
- The recommendation of the CEC is required for the removal of an EC. Resignation provisions remain the same as well.
Criticisms associated with the bill:
- Balance of Power: The Prime Minister and a Cabinet Minister (nominated by the Prime Minister) forming part of the three-member committee, the Leader of Opposition is left with a minority vote even before the process begins.
- This raises questions about the balance of power within the committee and whether the selection process truly ensures independence or remains skewed in favour of the Executive.
- Impact on electoral governance: The proposed changes may have implications for the autonomy and functioning of the ECI.
- The independence of the Election Commission is crucial for ensuring impartiality and integrity in the conduct of elections. Any perceived influence of the Executive in the selection process might raise concerns about the EC’s ability to carry out its responsibilities without bias.
- Alignment with Framers Intentions: The SC, in its previous ruling, emphasized that the framers of the Constitution intended for an independent body to oversee elections.
- Critics of the proposed Bill raise questions about whether the new composition of the Selection Committee aligns with the framers’ objective of creating an impartial and independent body responsible for elections.
Way Forward:
Therefore, preserving the autonomy of the Election Commission is not only crucial for maintaining the integrity of elections but also for upholding the very foundation of democracy. The government should look after the review the composition of the selection committee and consider making it more balanced. This might involve giving the opposition a stronger representation to ensure a fair decision-making process.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Conventions | Signed in |
| 1.United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification | 1998 |
| 2.Minamata Convention on Mercury | 2003 |
| 3. Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs). | 2011 |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Project AMBER Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
Statement-II:
The initiative is under the SANKALP programme.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
India Smart Cities Awards Contest 2022 winners will be felicitated by President Droupadi Murmu in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
Statement-II:
Surat held the top position India Smart Cities Awards Contest 2022.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) What is ‘One Health Approach’ (OHA)? Discuss the significance of OHA in context of rising zoonotic infections in the country. (250 words)
Q.2) Highlighting the significance of independence of Election Commissioner. Discuss the challenges associated with the recently introduced Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners (Appointment, Conditions of Service and Term of Office) Bill, 2023. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 26th August 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 25th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – c












