IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: There has been an outbreak of Nipah Virus (NiV) in the state of Kerala recently.
Background:-
- Two people have died and two others have been hospitalized, one of whom is in critical condition in the latest outbreak.
- The state government has set up a control room to monitor the evolving situation.
- NiV was first reported in the state in 2018 in Kozhikode district.
About Nipah Virus (NiV):-
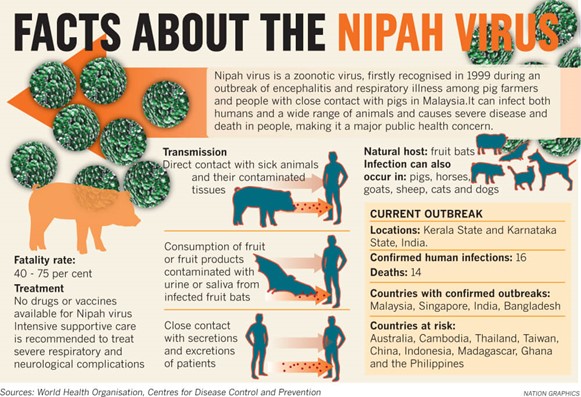
IMAGE SOURCE: gmsciencein.com
- Nipah virus (NiV) is a zoonotic virus.
- Zoonotic virus: It is transmitted from animals to humans.
- Natural host: Fruit bats (Pteropodidae family)
- Incubation period: 4 to 14 days.
- Incubation period: interval from infection to the onset of symptoms.
- Fatality rate: 40% to 75%.
- The Nipah virus was first recognized in 1999 during an outbreak among pig farmers in, (Zika Virus Disease)
- It was also recognized in Bangladesh in 2001, and nearly annual outbreaks have occurred in that country since.
- The disease has also been identified periodically in eastern India.
- The 2018 annual review of the WHO R&D Blueprint list of priority diseases indicates that there is an urgent need for accelerated research and development for the Nipah virus.
Transmission:-
- Nipah virus can be transmitted to humans from animals (such as bats or pigs), or contaminated foods.
- Human-to-human transmission of the Nipah virus has also been reported among families and caregivers of infected patients.
Signs and symptoms:-
- Human infections range from asymptomatic infection to acute respiratory infection (mild, severe), and fatal encephalitis.
- Infected people initially develop symptoms including fever, headaches, myalgia (muscle pain), vomiting and sore throat.
- This can be followed by dizziness, drowsiness, altered consciousness, and neurological signs that indicate acute encephalitis.
- Some people can also experience atypical pneumonia and severe respiratory problems, including acute respiratory distress.
- Encephalitis and seizures occur in severe cases, progressing to coma within 24 to 48 hours.
Diagnosis:-
- Nipah virus infection can be diagnosed with clinical history during the acute and convalescent phases of the disease.
- The main tests used are:-
- Real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) from bodily fluids.
- Antibody detection via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay
- Virus isolation by cell culture.
Treatment:-
- There are currently no drugs or vaccines specific for Nipah virus infection.
- WHO has identified Nipah as a priority disease for the WHO Research and Development Blueprint.
- Intensive supportive care is recommended to treat severe respiratory and neurologic complications.
Prevention:-
- Reducing the risk of bat-to-human transmission: decreasing bat access to date palm sap and other fresh food products.
- Reducing the risk of animal-to-human transmission: Gloves and other protective clothing should be worn while handling sick animals or their tissues and during slaughtering and culling procedures.
- Reducing the risk of human-to-human transmission: Close unprotected physical contact with Nipah virus-infected people should be avoided
MUST READ: Zombie Virus
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under Anaemia Mukt
Bharat Strategy :
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for preschool children, adolescents, and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with a special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies, and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following : (2022)
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Virus
Which of the above can be cultured in an artificial/ synthetic medium?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –POLITY
Context: The Government has recently, approved the e-Courts Mission Mode Project Phase -3 as part of the National e-Governance Plan.
Background:-
- It is a part of the National e-Governance Plan.
- It will span for four years with a financial outlay of seven thousand 210 crore rupees.
About e-Courts Mission Mode Project:-
- Launched:2007.
- Ministry: Ministry of Law & Justice.
- E-Courts Project is a mission-mode project undertaken by the Department of Justice, Government of India.
- Objective: to provide designated services to litigants, lawyers, and the judiciary by universal computerization of district and subordinate courts in the country and enhancement of ICT enablement of the justice system.
- Implementation: The e-Courts project is being implemented in association with the e-Committee Supreme Court of India and the Department of Justice.
- The project is aimed at providing the necessary hardware and software application to enable courts to deliver e-services, and the judiciary to be able to monitor and manage the functioning of courts.
- It is a Central Sector Scheme.
- The e Committee of the Supreme Court has been overseeing the implementation of the e Courts Project, conceptualized under the “National Policy and Action Plan for Implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the Indian Judiciary-2005”.
- The Chairperson of the e Committee is Dr Justice Dhananjaya Y Chandrachud, Judge, Supreme Court of India.
Phases:-
- Phase I: It was implemented during 2011-2015.
- Phase II: It was started in 2015 under which various District and subordinate courts have been computerized.
- Draft vision document for Phase III aims for: (Phase III of the eCourts Project)
- Digitization of court processes.
- Upgrade the electronic infrastructure of the judiciary.
- Enable access to lawyers and litigants.
- Seamless exchange of information between various branches of the State through the Interoperable Criminal Justice System (ICJS).
- These branches include the judiciary, the police, and the prison systems.
Advantages:-
- Faster justice (Digitization of Court Records)
- Clearing pendency which is around 3.27 crore cases before Indian courts.
- Reduce long delays and difficulties for ordinary litigants.
- Building people’s trust in the judiciary.
Challenges:-
- Technical Challenges: Complex process that involves upgrading existing technology and infrastructure.
- Cybersecurity Risks.
- Equity Concerns: The digitization of courts can exacerbate existing disparities in access to justice for marginalized communities, particularly those without access to technology.
- Preservation of Records: Digitizing records poses challenges for preserving historical records
MUST READ: Judiciary & AI
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Government law officers and legal firms are recognized as advocates, but corporate lawyers and patent attorneys are excluded from recognition as advocates.
- Bar Councils have the power to lay down the rules relating to legal education and recognition of law colleges.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centers within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places, and major tourist centers.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
Context: India and Russia have been exploring the use of the Northern Sea Route, and Eastern Maritime Corridor in recent times.
Background:-
- India and Russia discussed the possibility of exploring new transport corridors like the Northern Sea Route (NSR).
- Both sides also agreed that Indian seafarers will be trained on Polar and Arctic waters at the Russian Maritime Training Institute in Vladivostok, which is equipped with simulators.
- India is keen to collaborate on a partnership regarding the development of the NSR recognizing the potential it holds for enhanced connectivity and trade.
About Northern Sea Route:-
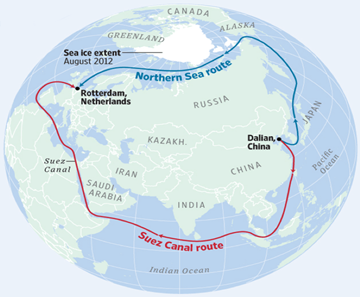
IMAGE SOURCE: eusp.org
- Eastern and western regions of the Arctic Ocean are connected via the Northern Sea Route (NSR), sometimes known as the Northeast Passage (NEP).
- It is the shortest shipping route connecting Europe and the Asia-Pacific region.
- The route between Europe and Asia is just 13,000 km long, compared to the 21,000 km covered by the Suez Canal route, which reduces the travel duration from one month to less than two weeks.
- It passes through four seas of the Arctic Ocean.
- The route starts at the boundary between the Barents and Kara seas (Kara Strait) and concludes at the Bering Strait (Provideniya Bay).
Advantages:-
- The NSR offers potential distance savings of up to 50% compared to existing shipping lanes via Suez or Panama.
- The region may hold over 40 percent of the current global reserves of oil and gas.
- There may also be significant reserves of coal, zinc, and silver.
India’s gains in NSR development:-
- Growing Cargo Traffic: NSR cargo traffic increased by about 73% during 2018-2022.
- Strategic Transit Route: India’s geographical location and reliance on sea transportation make the NSR a crucial transit route. India – Russia Relations
- Geopolitics: India would like to complement China and Russia’s potential collective influence over NSR. (India-Russia military alliance)
MUST READ: Russia-Ukraine War
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following countries: (2023)
- Bulgaria
- Czech Republic
- Hungary
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Romania
How many of the above-mentioned countries share a land border with Ukraine?
- Only two
- Only three
- Only four
- Only five
Q.2) The ‘Fortaleza Declaration’ recently in the news, is related to the affairs of: (2015)
- ASEAN
- BRICS
- OECD
- WTO
Syllabus
- Prelims –POLITY
Context: Recently, the G20 Summit witnessed a remarkable showcase of India’s rich tribal heritage and craftsmanship, curated and presented by TRIFED (Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India).
Key highlights of the event:-
- Several exquisite products, handcrafted by tribal artisans from various regions of India, captured the attention and admiration of delegates from around the world. These included:-
Longpi Pottery:-
- Location: village of Longpi in Manipur.
- Tribe: Tangkhul Naga tribes.
- Unlike most pottery, Longpi does not resort to the potter’s wheel.
Chhattisgarh Wind Flutes:-
- Location: Bastar in Chhattisgarh.
- Tribe: Gond Tribe.
- Unlike traditional flutes, it produces melodies through a simple one-handed twirl.
- Craftsmanship involves meticulous bamboo selection, hole drilling, and surface etching with fish emblems, geometric lines, and triangles.
Gond Paintings:-
- Tribe: Gond tribe.
- The artistic brilliance shines through their intricate paintings, reflecting their deep connection to nature and tradition.
Gujarat Hangings:-
- Location: Dahod, Gujarat.
- Tribe: Bhil & Patelia Tribe.
- It stems from an ancient Gujarat art form and initially dolls and cradle birds, featuring cotton cloth and recycled materials.
Sheep Wool Stoles:-
- Location: Himachal Pradesh/Jammu & Kashmir.
- Tribe: Bodh, Bhutia, and Gujjar Bakarwal tribes.
- They exhibit their ingenuity with pure sheep wool, fashioning a diverse range of apparel, from jackets to shawls and stoles.
Araku Valley Coffee:
- Location: Araku Valley in Andhra Pradesh.
- This coffee is renowned for its unique flavors and sustainable cultivation practices.
Glass Mosaic Pottery:-
- It captures the mosaic art style, meticulously crafted into lampshades and candle holders.
- When illuminated, they unleash a kaleidoscope of colors, adding vibrancy to any space.
Meenakari:-
- Location: Rajasthan.
- It is the art of decorating metal surfaces with vibrant mineral substances, a technique introduced by the Mughals.
Metal Ambabari Craft:-
- Location: Rajasthan.
- Tribe: Meena Tribe.
- It is a meticulous process that elevates metal decoration.
- Today, it extends beyond gold to metals like silver and copper.
About TRIFED:-
- Establishment: 1987.
- Ministry: Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
- Objective: to bring about the socio-economic development of tribals of the country by institutionalizing the trade of Minor Forest Produce (MFP) and surplus Agricultural Produce (SAP) collected/ cultivated by them.
- TRIFED was established in August 1987 under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 1984 by the Government of India as a National-level Cooperative body. (VanDhan Chronicle)
Functions:-
- It plays the dual role of both a market developer and a service provider, empowering the tribals with knowledge and tools to better their operations in a systematic, scientific manner and also assisting them in developing their marketing approach.
- It is involved actively in capacity building of the tribal people through sensitization and the formation of Self Help Groups (SHGs).
- It also assists them in exploring and creating opportunities to market the developed products in national and international markets on a sustainable basis.
MUST READ: Tech for Tribal
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements about G-20: (2023)
- The G-20 group was originally established as a platform for the Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors to discuss the
- International economic and financial issues.
- Digital public infrastructure is one of India’s G-20 priorities.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to India, the terms ‘Halbi, Ho, and Kui’ pertain to (2021)
- dance forms of Northwest India
- musical instruments
- pre-historic cave paintings
- tribal languages
Syllabus
- Prelims –IMPORTANT AWARDS
Context: Recently, the last date for submission of nominations for the Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar was announced.
Background:-
- The Last date of submission of nomination for the Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar is 15 September, 2023.
About Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar:-
- Organized by: Ministry of Women & Child Development.
- Objective: to celebrate the energy, determination, ability, zeal, and enthusiasm of our children.
- Eligibility: Any child who is an Indian Citizen and residing in India and is not exceeding 18 years (as of the last date of receipt of application/nomination).
- The Awards are announced on December 26 on ‘Veer Bal Diwas’.
- Veer Baal Diwas: marks a tribute to the martyrdom of Guru Gobind Singh’s sons. (Parkash Purab of Sri Guru Gobind Singh Ji)
- Conferred by: President of India.
- Ceremony: held every year in New Delhi in January every year.
- Historical Background: It was instituted in 1979 as the National Child Welfare Awards, renamed in 2018 as Bal Kalyan Puraskar. (Pravasi Bharatiya Samman Award (PBSA))
- Field: This national-level award is given in the fields of Bravery, Sports, Social Service, Science and Technology, Environment, Arts and Culture, and Innovation.
Eligibility:-
- A child who is an Indian Citizen and residing in India and is not exceeding 18 years (as of the last date of receipt of application/nomination).
- The act/incident/achievement should have been within 2 years of the last date of receipt of application/nomination.
- The applicant should not be a previous recipient of the same award earlier in any category.
Decoration:-
- Medal
- Cash prize of Rs. 1,00,000
- Certificate and citation
The Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar is given under two categories:-
Bal Shakti Puraskar
- It is given by the Government of India every year to recognize exceptional achievements of children in various fields., innovation, scholastic achievements, social service, arts & and culture, sports, and bravery. Padma awards
- Eligibility: A child who is an Indian Citizen residing in India and is between 5-18 years of age.
- Decoration: A medal, a cash prize of Rs. 1,00,000, book vouchers worth Rs.10,000, a certificate and a citation.
Bal Kalyan Puraskar
- It is given as recognition to Individuals and Institutions, who have made an outstanding contribution towards service for children in the field of child development, child protection, and child welfare.
- Eligibility: An individual who is an Indian Citizen residing in India and should have attained the age of 18 years or above (as of 31st August of the respective year).
- S/he should have worked for the cause of children for not less than 7 years.
MUST READ: Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar-2023
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of the 44th Chess Olympiad, 2022: (2023)
- It was the first time that the Chess Olympiad was held in India.
- The official mascot was named Thambi’.
- The trophy for the winning team in the open section is the Vera Menchik Cup.
- The trophy for the winning team in the women’s section is the Hamilton-Russell Cup.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following statements in respect of Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards: (2021)
- Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards are titled under Article 18(1) of the Constitution of India.
- Padma Awards, which were instituted in the year 1954, were suspended only once.
- The number of Bharat Ratna Awards is restricted to a maximum of five in a particular year.
Which of the above statements is not correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
India – Saudi Arabia Relations
Context: Recently, India and Saudi Arabia have cooperated in various sectors such as energy, trade, and culture.
About India – Saudi Arabia Relations:
Political relations:
- The establishment of diplomatic relations in 1947 was followed by high-level visits from both sides.
- The historic visit of King Abdullah to India in 2006 was a watershed moment that resulted in the signing of the ‘Delhi Declaration’, imparting a fresh momentum to the bilateral relationship.
- Saudi Arabia and India signed the Riyadh Declaration to enhance the strategic partnership covering security, economic, defense, technology and political areas and joint combat of terrorism.
Economic Cooperation, Trade and Investment:
- India is the second largest trade partner of Saudi Arabia, while Saudi Arabia is the fourth largest trade partner of India.
- Saudi Arabia is currently India’s second-largest supplier of crude oil (Iraq has been India’s top supplier).
- India imports around 18% of its crude oil requirement and around 22% of its Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG) requirement from Saudi Arabia.
- India’s imports from Saudi Arabia reached USD 34.01 billion and exports to Saudi Arabia were worth USD 8.76 billion.
Defense and security cooperation:
- AL – Mohed AL – Hindi is the maiden bilateral naval exercise between India and Saudi Arabia.
- Riyadh has largely shown an understanding of India’s terrorism-related concerns, and has agreed to work with India in countering the global menace.
Cultural Relations
- India successfully participated as ‘Guest of Honour’ in the 32nd edition of the prestigious Saudi National Festival of Heritage and Culture in 2018.
- Yoga was announced as a ‘sports activity’ in Saudi Arabia.
- Haj pilgrimage is another important component of bilateral relations.
Indian Diaspora:
- The approximately 7 million strong Indian community is the largest expatriate community in the Kingdom.
- They send remittances of over US $11 billion annually to India.
Challenges:
- The politics of the Middle East is complex and multidimensional so requires a collective and united effort.
- The Saudi Arabia-Turkey rivalry could create problems for India.
- Saudi Arabia-Iran Rivalry: India has close relations with both Saudi Arabia and Iran.
- However, India is yet to work out a way to balance its ties with Iran on the one hand and Saudi Arabia and the United States on the other.
- Hike in taxes: An astronomical hike in the ‘expatriate dependent fee’ or family tax, in Saudi Arabia is forcing thousands of Indians working in the kingdom to send their families back home.
- The Kafala system: The Kafala system requires all migrant workers to have a sponsor in the country where he or she is to work in order that a valid visa and residence permit may be issued.
- This practically places the migrant worker at the mercy of his or her employer, leading to his/her exploitation.
Way Forward:
- Economic Reform: Economic reform programs (Vision 2030) are underway in Saudi Arabia, for which it needs India’s economic as well as technological assistance.
- Saudi Arabia plays an important role in India’s energy security while India is a vital partner in Saudi Arabia’s food security.
- Investments: Saudi investment of around $100 billion is in the pipeline in areas ranging from energy, refining, petrochemicals and infrastructure to agriculture, minerals and mining.
- It is one of the largest consumers of hydrocarbons in the world and this makes India an attractive investment destination for the world.
- Countering Militias: Saudi Arabia appears to have limited experience in countering threats from groups like Houthi militias.
- This is an area where India’s expertise in fighting such threats could be imparted to the Saudi side, by enhancing joint military training programs.
Source: The Hindu
Context: Recently the CVC has reconstituted the advisory board on Banking and Financial Frauds (ABBFF) that conducts the first level examination of bank frauds before recommendations or references are made to investigative by agencies such as Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI).
About Central Vigilance Commission (CVC):
- CVC are conceived to be the apex vigilance institution, free of control from any executive authority, monitoring all vigilance activity under the Central Government and advising various authorities in Central Government organizations in planning, executing, reviewing and reforming their vigilant work.
- The Parliament enacted Central Vigilance Commission Act, 2003 conferring statutory status on the CVC.
- Organization: The CVC has its own Secretariat, the Chief Technical Examiners’ Wing (CTE), and a wing of Commissioners for Departmental Inquiries (CDI).
- Appointment: The chairperson and the members are appointed by the President on the recommendations of a Committee consisting of the Prime Minister (Chairperson), the Minister of Home Affairs, and the Leader of the Opposition in the Lok Sabha.
- Term: The term of office of the chairperson and the members is four years from the date on which they enter their office or till they attain the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- Salary and Allowances: The salary, allowances, and other service conditions of the Chief Vigilance Commissioner are similar to those of the Chairman of UPSC, and that of the Vigilance Commissioner are similar to those of the members of UPSC.
- Composition: CVC is a Multi-member Commission consisting of a Central Vigilance Commissioner (Chairperson) and not more than two Vigilance Commissioners (Members).
- Removal: The President can remove the chairperson or any other member from the office under the following circumstances:
- If the member is adjudged as insolvent.
- If the Central government holds him responsible for an offense involving moral turpitude or he is convicted for such an offense.
- engages during his term of office in any paid employment outside the duties of his office.
- If he is declared unfit by reason of infirmity of mind or body, by the President.
- The President can also remove the chairperson or any other member for proved misbehaviour or incapacity.
- In such cases, the President has to refer the matter to the Supreme Court for an enquiry.
- After the enquiry, if the Supreme Court upholds the cause of removal and advises so, then the President can remove him.
- Powers of Civil Court: It has all the powers of a Civil Court while conducting any inquiry. Its proceedings have judicial character.
- It can ask for information or report from authorities to exercise its mandate relating to vigilance and anti-corruption work.
- Advisory nature: After inquiry, it advises the Central Government or its authorities for further courses of action.
- Where the Central Government or any of its authorities does not agree with the advice of the CVC, it shall communicate the reasons to the CVC.
- Investigations: For investigation work, CVC has to depend on two external sources CBI and Chief Vigilance Officers (CVO).
- It submits its report to the President of India.
Role of CVC as a vigilant organization:
- Vigilant against corruption: One critical role is the creation of credible deterrence against corruption by promptly enforcing anti-corruption laws and regulations, including the Prevention of Corruption Act, of 1988.
- The CVC referred the 2G Spectrum Scam case to the CBI for inquiry and oversaw its advancement.
- Preventive measures: Preventive vigilance works on the “principle of Catch them before they hatch”.
- Implementing effective preventive measures to minimize the scope of corruption, thereby reducing opportunities for corrupt practices.
- Supervision of administration : The organization supervises the functioning of the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) and exercises superintendence over the vigilance administration of various central government ministries, departments, and organizations.
- This oversight helps maintain integrity and accountability within government bodies.
- Public awareness and ethical conduct: Raising public awareness is essential to inculcate ethical values and reduce society’s tolerance toward corruption.
- This aspect of the role focuses on educating and mobilizing the public against corrupt practices, fostering a culture of honesty and accountability.
Limitations of CVC:
- Very low conviction rate and delay in the investigation: This has reduced the impact of CVC and its effectiveness.
- There is huge delay in the cases that CVC handles, hence it does not act as an effective deterrent.
- Recommendatory body: CVC is often considered a powerless agency as it is treated as an advisory body only with no power to register criminal case against government officials or direct CBI to initiate inquiries against any officer of the level of Joint Secretary and above.
- The Decisions of the CVC are not binding on the organizations or ministries.
- Although CVC is “relatively independent” in its functioning, it neither has the resources nor the power to act on complaints of corruption.
- Organizational jurisdiction: In most cases, the domains and the jurisdiction of the organizations is not clear.
- CVC cannot initiate suo moto inquiries but can only act on complaints received from the public or referrals from other authorities.
Way Forward:
In the recent past, India has emerged as a progressive and vibrant economy with huge investments were made in country’s infrastructure; construction, retail and many other sectors in the government. This rapid growth in economy throws up CVCs’ challenges in the fight against the menace of corruption. Therefore, there is a need to strengthen the CVC’s powers, autonomy and resources to enable it to perform its role more efficiently and effectively.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Disease | Pathogen |
| 1.Common cold | Rhino Virus |
| 2.Measles | Rubeola virus |
| 3.Smallpox | Variola virus |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
The e-Courts Mission is undertaken by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
Statement-II:
It is being implemented in association with the e-Committee Supreme Court of India and the Department of Justice.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) With reference to the Malaria, consider the following statements:
- It is mostly found in tropical countries.
- It is not preventable and curable.
- The infection is contagious.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) Briefly explain the India-Saudi Arabia bilateral relations along with recent developments. (250 words)
Q.2) Critically analyse the role and mandate of Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) in addressing corruption in the country. (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 14th September 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 13th September – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – a












