IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: Recent reports suggest that Malawi is battling an outbreak of scabies.
- Hospitals register thousands of people with infectious skin disease, months after a wave of cholera swept African country.
About Scabies:-
- Scabies is a skin disease caused by a parasite named Sarcoptes scabie which is a tiny insect about 0.3 mm long called a mite.
- The female parasite burrows under the skin.
- It begins laying eggs within 2-3 hours of infection and generally lays 2-3 eggs daily.
- The eggs hatch and become adult mites (a term referring to this parasite) within 10 days.
- Scabies is a relatively contagious infection caused by a tiny mite (Sarcoptes scabie).
- Transmission is from person to person more by close skin contact.
Symptoms:–
- Severe itch
- Itchy lines and bumps on the fingers, wrists, arms, legs, and belt area
- Larger rash in infants and small children, including on the palms, soles of the feet, ankles, and scalp.
- A more severe type of scabies, called crusted scabies, makes the skin crusty and scaly and affects large areas of the body.
Treatment:-
- Several types of lotions (usually containing 5% permethrin) can be applied to the body and left on for 12-24 hours.
- One topical application is usually sufficient, although the scabicide may be reapplied after a week if mites remain.
- Itching can be lessened by the use of calamine lotion or antihistamine medications.
Prevention:-
- Good hygiene is essential in the prevention of scabies. (Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs))
MUST READ: Type 1 diabetes
SOURCE: THE GUARDIAN
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of probiotics: (2022)
- Probiotics are made of both bacteria and yeast.
- The organisms in probiotics are found in foods we ingest but they do not naturally occur in our gut.
- Probiotics help in the digestion of milk sugars.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body? (2022)
- They protect the environmental allergens. body
- They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
- They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
- They protect the body from the diseases caused by pathogens.
Syllabus
- Prelims –ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
Context: Researchers discover new freshwater fish species ‘Awaous Motla’ in Odisha’s Mahanadi River.
Background:-
- A group of scientists has discovered that an edible freshwater fish, available in the markets of western Odisha, is actually an unregistered species.
About Awaous Motla:-
- The species belongs to the family ‘Awaous’ (Oxudercidae), thus named Awaous motla and ‘motla’ by fishermen.
- The fish has a vibrant yellow-coloured body and a fleshy upper lip.
- Can be consumed both fresh and dried.
- It was discovered from the Mahanadi River.
- It is one of the major east-flowing peninsular rivers in India.
- The river originates from the Sihawa range of hills in the Dhamtari district of Chhattisgarh state.
MUST READ: Zebrafish
SOURCE: TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) ‘Microsatellite DNA’ is used in the case of which one of the following? (2023)
- Studying the evolutionary relationships among various species of fauna
- Stimulating ‘stem cells’ to transform into diverse functional tissues
- Promoting clonal propagation of horticultural plants
- Assessing the efficacy of drugs by conducting a series of drug trials in a population
Q.2) Which of the following is not a bird? (2022)
- Golden Mahseer
- Indian Nightjar
- Spoonbill
- White Ibis
Syllabus
- Prelims –DEFENSE
Context: Recently, a call was given by an Israeli lawmaker suggesting deploying a ‘ Jericho Missile System’ against Hamas and Palestine in the ongoing war.
About Jericho Missile System:-
- Jericho is Israel’s original ballistic missile programme, initiated in the 1960s.
- It was named after the biblical city located in the West Bank.
- This programme was initially a collaboration with the French aerospace company Dassault, but when France withdrew in 1969, Israel continued its development.
Jericho-1 Missile System:-
- The Jericho-1 missile system, retired in the 1990s.
- It had a weight of 6.5 tons, a length of 13.4 meters, and a diameter of 0.8 meters.
- Jericho-1 missile system had a range of 500 kilometres.
- It could carry a 1,000-kilogram payload, though it had a 50 per cent chance of hitting within a 1,000-meter radius of its target.
Jericho-2 Missile System:-
- It was developed in the late 1980s.
- It has a length of 15 metres and a diameter of 1.35 metres while maintaining the same payload capacity and range between 1,500 and 3,500 kilometres.
- It has the same payload capacity as Jericho-1.
Jericho-3 Missile System:-
- It is the first Israeli Intercontinental Missile (ICBM).
- It was first tested in 2008 and entered service in 2011.
- The payload capacity extended to about 1,300 kilograms.
- It has a range of 4,800 to 6,500 kilometres.
MUST READ: BrahMos Missiles
SOURCE: MSN
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media? (2022)
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same surface. speed and places a probe on its
Q.2) With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-stage launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors, and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
Context: Researchers have discovered a new species of frog, Alcalus fontinalis in the northeast Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh recently.
- The identification of the new species is based on molecular, morphological, and osteological characteristics.
About Alcalus fontinalis:-
- The frog was formally named Alcalus fontinalis, meaning “spring or fountain,” referencing the tiny streams or brooks where the frog was found in Arunachal Pradesh.
- It was discovered in the Namdapha Tiger Reserve, Arunachal Pradesh.
- The new species stands out from its congeners due to a unique combination of morphological features.
- These include a snout-vent length of 27–28 mm in males and 29.9–36.2 mm in females.
- It has a disc on the fingers and toes with a horizontal/transverse groove on the dorsal surface.
- It has wrinkled dorsal skin.
- It has a pair of faint dorsolateral stripes on the back.
- The new species also exhibits a DNA sequence divergence of 7.6–25.4% in the mitochondrial gene fragment 12S–tVal–16S rRNA (1533 base pairs), further distinguishing it from its congeners.
- The frog appeared to be a mix of a bush frog and a water frog.
Significance:-
- The discovery of Alcalus fontinalis contributes significantly to our understanding of biodiversity in the Indo-Burma region.
- The finding reports a species new to science and a new genus from India. (Morphological Phenotypic Plasticity in Kalinga Frog)
MUST READ: New Species of frog in Andaman found
SOURCE: GROUND REPORT
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q1. Which one of the following makes a tool with a stick to scrape insects from a hole in a tree or a log of wood? (2023)
- Fishing cat
- Orangutan
- Otter
- Sloth bear
Q2. Which of the following is not a bird? (2022)
- Golden Mahseer
- Indian Nightjar
- Spoonbill
- White Ibis
Syllabus
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
Context: Recently, an Indian Porcupine killed an adult male Tiger in Tamil Nadu.
About Indian Porcupine:-
- Scientific Name: Hystrix indica.
- Porcupines are large, thorny rodents.
- Their coats with sharp spines or quills protect them against predation.
- They are the longest-living rodent.
- Defensive behaviour displays in a porcupine depend on sight, scent and sound.
- The Indian Crested Porcupine is the largest rodent in India and is widely distributed in the Indian Subcontinent.
- It is found throughout southeast and central Asia and in parts of the Middle East, including such countries as India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Israel, Iran, and Saudi Arabia.
- It mainly occurs on rocky hillsides but is also found in tropical and temperate scrublands, grasslands, and forests.
Protection status:-
- IUCN Red List: least concern
- Wildlife Protection Act 1972: Schedule IV
MUST READ: Atelopus or harlequin frogs
SOURCE: ECONOMIC TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements : (2023)
- In India, the Biodiversity Management Committees are key to the realization of the objectives of the Nagoya Protocol.
- The Biodiversity Management Committees have important functions in determining access and benefit sharing, including the power to levy collection fees on the access of biological resources within its jurisdiction.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Recently, there was a proposal to translocate some of the lions from their natural habitat in Gujarat to which one of the following sites? (2017)
- Corbett National Park
- Kuno Palpur Wildlife Sanctuary
- Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
- Sariska National Park
Syllabus
- Prelims – SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: Recently, Scientists discovered a link between air pollution and Parkinson’s disease.
About Parkinson’s disease:-
- Parkinson’s disease is a progressive disorder that affects the nervous system and the parts of the body controlled by the nerves.
- Symptoms start slowly.
- The risk of developing it increases with age.
Symptoms:-
- Uncontrollable shaking and tremors
- Slowed movement (bradykinesia)
- Balance difficulties and eventual problems standing up
- Stiffness in limbs
- Speech changes
- Writing changes
- Loss of automatic movements
Causes:-
- Genes
- Environmental triggers
- Presence of Lewy bodies: Clumps of specific substances within brain cells are microscopic markers of Parkinson’s disease. These are called Lewy bodies.
Parkinson’s disease is often accompanied by these additional problems like:-
- Thinking difficulties
- Depression and emotional changes
- Swallowing problems
- Chewing and eating problems
- Sleep problems and sleep disorders
- People also may experience rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder, which involves acting out dreams. Medicines may improve your sleep.
- Bladder problems
- Constipation
Treatments:-
- Although there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease, medicines, surgical treatment, and other therapies can often relieve some symptoms.
- Medicines: Medicines can help treat the symptoms of Parkinson’s by:
- Increasing the level of dopamine in the brain
- Having an effect on other brain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, which transfer information between brain cells
- Helping control non-movement symptoms
- Therapy: the main therapy for Parkinson’s is levodopa.
- Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brain’s dwindling supply.
- Deep brain stimulation: For people with Parkinson’s disease who do not respond well to medications, the doctor may recommend deep brain stimulation.
MUST READ: Rare Diseases
SOURCE: TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under the Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy : (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for preschool children, adolescents, and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with a special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies, and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following : (2022)
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Virus
Which of the above can be cultured in an artificial/ synthetic medium?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS III – Environment
Context: Biomedical waste, refers to any waste generated during the diagnosis, treatment, or immunization of humans or animals, as well as research activities related to healthcare. This waste can pose serious health and environmental risks due to its potential for carrying infectious materials and hazardous substances. Proper management and disposal of biomedical waste are essential to prevent the spread of infections and protect the environment. Of the total amount of waste generated by healthcare activities, about 85% is a general, non-hazardous waste. The remaining 15% is considered hazardous material that may be infectious, toxic, or radioactive.
Environmental Impacts of Biomedical Waste
- Soil and Water Contamination: This contamination can occur when waste is dumped in landfills or improperly stored, allowing harmful substances to leach into the environment. The presence of hazardous chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and pathogens in biomedical waste can pose serious risks to the quality of soil and water resources.
- Spread of Infectious Diseases: Inadequate handling and disposal of biomedical waste can lead to the spread of infectious diseases in the environment. Pathogens from the waste can contaminate soil, water, and wildlife, potentially affecting human and ecosystem health.
- Toxin emissions: The most serious effect that biomedical waste has on our seas is the discharge of poisons into the waters that could then be consumed by ocean life creatures.
- Food chain contamination: Toxins would interject into the food chain and eventually reach humans who consume sea creatures.
- Plastic pollution: 85% of disposable plastic materials make up all medical equipment.
Bio-Medical Waste Management Rules, 2016
- The objective of the rules is to properly manage the per day bio-medical waste from Healthcare Facilities (HCFs) across the country.
- The ambit of the rules has been expanded to include vaccination camps, blood donation camps, surgical camps or any other healthcare activity.
- Pre-treatment of the laboratory waste, microbiological waste, blood samples and blood bags through disinfection or sterilization on-site in the manner prescribed by the World Health Organization (WHO) or by the National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO).
- Bio-medical waste has been classified into 4 categories instead of the earlier 10 categories to improve the segregation of waste at source.
- The rules prescribe more stringent standards for incinerators to reduce the emission of pollutants in the environment.
- The State Government provides the land for setting up common bio-medical waste treatment and disposal facilities.
Challenges to Waste Management
- Lack of awareness about the health hazards related to healthcare waste
- Inadequate training in proper waste management
- Absence of waste management and disposal systems
- Insufficient financial and human resources
- Many countries either do not have appropriate regulations or do not enforce them.
International Agreement and Conventions
The international agreements and conventions which are particularly pertinent in Biomedical Waste Management are-
Basel Convention on Hazardous Waste:
- It is the most inclusive global environmental treaty on hazardous and other wastes.
- It has 170 member countries, and its objectives are to protect human health and the environment against the adverse effects resulting from the generation, management, and disposal of hazardous wastes, specifically clinical wastes from health care in hospitals, health centers, and clinics.
Stockholm Convention on POPs:
- It is a global treaty to protect human health and the environment from POPs (POPs – dioxins and furans).
- POPs are toxic chemicals that accumulate in the fatty tissue of living organisms and cause damage.
- These chemicals are formed by medical waste incinerators and other combustion processes.
- It deals with BEP including source reduction, segregation, resource recovery and recycling, training, and proper collection and transport.
Minamata Convention on Mercury
- It is a global treaty to protect human health and the environment from the adverse effects of mercury.
- On October 10, 2014, in Japan, more than 90 nations signed the first new global convention on environment and health.
- This treaty includes the phasing out of certain medical equipment in health-care services, including mercury-containing medical items such as thermometers and blood pressure device.
Biomedical Waste Treatment in India
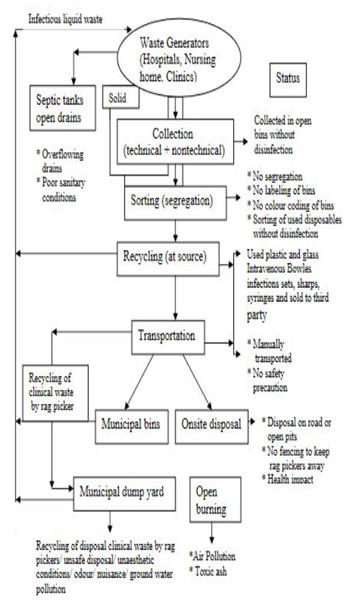
Conclusion
Proper segregation, safe storage, and effective treatment methods can minimize the risks associated with biomedical waste. Furthermore, promoting awareness and education on responsible waste management practices is crucial to ensuring the protection of the environment and public health.
Connect the Dots
How has WHO classified biomedical waste? What are different guidelines given by WHO for medical waste disposal?
Syllabus
- Mains – GS III – Science and Technology
What are Deepfakes?
- Deepfakes refer to realistic-looking, AI-generated content, typically images or videos that manipulate or replace the original content with new, often fabricated material.
- The term “Deepfake” is a combination of “deep learning” and “fake.”
- The term became popular when a Reddit contributor used publicly available AI-driven software to impose the faces of celebrities onto the bodies of people in pornographic videos.
- Deepfakes are back in news, after a video of actor Rashmika Mandanna has recently gone viral on social media.
- Researchers have observed a 230% increase in deepfake usage by cybercriminals and scammers, and have predicted the technology would replace phishing in a couple of years.
How Does Deepfake Technology Work?
- The technology involves modifying or creating images and videos using a machine learning technique called generative adversarial network (GAN).
- The AI-driven software detects and learns the subjects’ movements and facial expressions from the source material and then duplicates these in another video or image.
- To ensure that the deepfake created is as close to real as possible, creators use a large database of source images. This is why more deepfake videos are created of public figures, celebrities and politicians.
- The dataset is then used by one software to create a fake video, while a second software is used to detect signs of forgery in it.
- Through the collaborative work of the two software, the fake video is rendered until the second software package can no longer detect the forgery.
- This is known as “unsupervised learning”, when machine-language models teach themselves. The method makes it difficult for other software to identify Deepfakes.
Challenges Posed by Deepfakes
- Promotes ‘Liar’s Dividend’– Liar’s Dividend refers to the situation when an undesirable truth is dismissed as Deepfakes or fake news. Leader’s weaponries Deepfakes to replace an actual piece of media and truth. Ex- Donald Trump Deepfake videos. Deepfakes blur the line between reality and fake. People start dismissing reality as fake.
- Erosion of trust in democratic processes like elections- Doctored content, most likely in the form of a realistic fake video is presented as fact to alter public perception and create democratic deficit. For Ex- Capitol Hill violence, 2021 was incited by using deep fake media.
- Crime against women- The deepfakes are being used as a weapon to attack women dignity and chastity. According to AI company Deeptrace report, over 90% of the deepfake videos are pornographic in nature.
- Fuelling Radicalization and violence- The non-state actors like ISIS and Al-Qaeda, use fake videos to stir anti-state sentiments among people. For Ex- Fake videos showing armed forces committing ‘crimes in conflict areas’.
- Rise in cybercrimes- Cyber criminals are using deepfake technology to carry out phishing attacks, financial frauds and identity theft. Ex- CEO of a U.K. energy company was tricked using deepfake audio to transfer €2,20,000 to fraudsters.
Deepfake Regulation in India and across World
India
- India does not have specific laws or regulations that ban or regulate the use of deepfake technology.
- Sections 67 and 67A of the Information Technology Act (2000) related to defamation and publishing explicit material is applied in cases of deepfakes.
- India’s IT Rules, 2021 require that all content reported to be fake or produced using deep fake be taken down by intermediary platforms within 36 hours.
- Section 500 of the Indian Penal Code (1860) also provides punishment for defamation.
United States
- The U.S. introduced the bipartisan Deepfake Task Force Act to assist the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) to counter deepfake technology.
European Union
- European Union has updated Code of Practice on Disinformation that was introduced in 2018 to stop the spread of disinformation through deepfakes.
- The EU has issued guidelines for the creation of an independent network of fact-checkers to help analyse the sources and processes of content creation
China
- China has introduced Comprehensive Regulation on Deep Synthesis aimed at curbing disinformation.
Conclusion
Social media intermediaries have to develop technology to detect and report Deepfakes on their sites like watermarking AI-generated content. For Ex- Microsoft’s video authenticator is a new anti-deep fake technology to fight misinformation. Additionally, there should be ongoing discussions about the need for legal frameworks to address the malicious use of Deepfakes technology.
Connect the Dots
What can possible positive outcomes using Deepfakes technology?
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Disease | Caused by |
| Cholera | Vibrio cholerae |
| Plague | Yersinia pestis |
| Leprosy | Mycobacterium Leprae |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I :
Jericho-1 missile system had a range of 500 kilometres.
Statement-II :
Jericho-2 Missile System is the first Israeli Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBM).
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) With reference to theAwaous Motla, consider the following statements:
- It was discovered from the Mahanadi River.
- It costs less than several other locally available fish.
- The species belongs to the family ‘Awaous’ (Oxudercidae).
How many of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 3 only
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 10th November 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 9th November – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – a











