IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, Ecuadorians voted against the oil drilling of the protected area in Yasuni National Park in the Amazon recently.
About Yasuni National Park:-
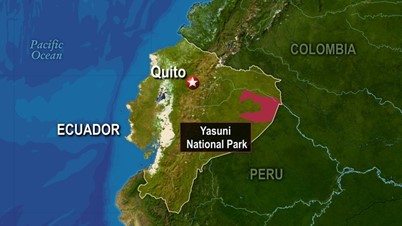
IMAGE SOURCE: pbs.org
- Location: Ecuador, South America.
- Area: 9,820 square km (3,791 square miles).
- Water bodies: It is situated between the Napo and Curaray Rivers.
- Indigenous Communities: It is home to several indigenous communities like Tagaeri and Taromenani.
- 1989: Yasuni was designated a world biosphere reserve by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). (UNESCO World Heritage Forests)
- It is part of the Amazon rainforest.
- The park is considered one of the most biologically diverse areas on Earth.
- Biodiversity:-
- 610 species of birds, 139 species of amphibians, and 121 species of reptiles.
- At least three species are
- Endemic species: any species or other taxon whose geographic range or distribution is confined to a single given area.
About Amazon Rainforests:-
- Location: South America.
- The Amazon is a vast biome that spans eight countries—Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, and Suriname—and French Guiana, an overseas territory of France.
- It is bounded by the Guiana Highlands to the north, the Andes Mountains to the west, the Brazilian Central Plateau to the south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east.
- These are the world’s largest tropical rainforests. (Deforestation in Amazon Basin)
- As of 2021, the Amazon had 74% of its area covered by tropical rainforests and 9% of other natural vegetation types.
- They are home to nearly a fifth of the world’s land species and over 45 million people.
- The rainforest of the Amazon is home to 400–500 indigenous Amerindian tribes.
- Biodiversity:-
- It is the world’s richest and most-varied biological reservoir.
- Flora: a wide variety of trees, including many species of myrtle, laurel, palm, and acacia, as well as rosewood, Brazil nut, and rubber tree.
- Fauna: jaguar, manatee, tapir, red deer, capybara, and many other types of rodents, and several types of monkeys.
MUST READ: Amazon forests are no longer acting as a carbon sink
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organization that drives climate action by building large networks and running them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) The ‘Fortaleza Declaration’ recently in the news, is related to the affairs of: (2015)
- ASEAN
- BRICS
- OECD
- WTO
Syllabus
- Prelims –History
Context: Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi paid homage to Maharaja Bir Bikram Manikya Bahadur on his 115th birth anniversary.
About Maharaja Bir Bikram Manikya Bahadur:-
- Birth: August 19, 1908.
- Death: 17 May 1947.
- Dynasty: Maniyaka
- He was the last King of Tripura.
- He was a prominent royal figure who played a pivotal role in the modernization and development of the princely state of Tripura.
- His reign marked a transformative period in Tripura’s history, characterized by progressive reforms and visionary initiatives.
Education:-
- He is popularly known as the Architect of Tripura due to his contribution to educational institutions.
- He established the Maharaja Bir Bikram College (MBB College) in Agartala, Tripura.
Infrastructure:-
- Under his leadership, significant infrastructure projects were undertaken.
- Road networks, bridges, and public buildings were constructed to enhance connectivity and elevate living standards across the state.
- He built Tripura’s first airport at Agartala.
- He also set up one of the country’s first municipalities.
Land Reforms:-
- He initiated land reforms, reserving vast tracks of land for Tripura’s tribal
Healthcare:-
- He established hospitals and medical facilities, ensuring accessible and quality medical services for the people of Tripura.
Administrative Efficiency
- He introduced administrative reforms to enhance governance and efficiency.
- His administration focused on inclusive policies that aimed at the welfare and upliftment of the people.
Cultural Preservation:-
- He supported local arts, crafts, and traditions, ensuring that the state’s identity remained intact. ( Tripura government planning to promote Risa as the signature textile)
MUST READ: Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) By which one of the following Acts was the Governor General of Bengal, designated as the Governor General of India? (2023)
- The Regulating Act
- The Pitt’s India Act
- The Charter Act of 1793
- The Charter Act of 1833
Q.2) Consider the following freedom fighters: (2022)
- Barindra Kumar Ghosh
- Jogesh Chandra Chatterjee
- Rash Behari Bose
Who of the above was/were actively associated with the Ghadar Party?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Government Initiatives
Context: Recently, a roadshow was organized in Visakhapatnam as a run-up to the Global Maritime India Summit 2023(GIMS 2023).
Background:-
- Visakhapatnam Port Authority (VPA) organized a roadshow in Visakhapatnam as part of a series of nationwide roadshows under the guidance and direction of the Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways.
- It was organized to invite and attract clients and various stakeholders to actively participate in the three-day Global Maritime India Summit 2023 (GMIS) starting on October 17 in Delhi.
About Global Maritime India Summit 2023 (GIMS 2023):-
- Ministry: Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways.
- Event duration: 17th October-19th October 2023.
- Venue: Pragati Maidan, New Delhi.
- Organizers: Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways, Indian Port Association, and Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI)
- IPA: constituted in 1966 under the Societies Registration Act, primarily with the idea of fostering the growth and development of all Major Ports.
- FICCI: is the largest and oldest apex business organization in India.
- It is an annual meeting of the Indian and international maritime community.
- Objective: to serve as a platform to showcase global best practices, foster investment partnerships, and chart a new and bright course for our collective future
- It is a flagship event aimed at propelling the Indian maritime economy by promoting global and regional partnerships and facilitating investments.
- It addresses key industry issues and exchanges ideas to bring the sector forward.
- The Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry (FICCI) is the exclusive industry partner.
- It brings together global maritime players, policymakers and regulators, key opinion leaders, and industry leaders through a series of engaging dialogues, forums, and knowledge exchange platforms.
- The event includes:-
- Investor summit and International exhibition: to facilitate interaction and collaboration among the Indian and international maritime companies, policymakers, investors, and other stakeholders.
- Global CEOs’ Forum: to encourage dialogue and cooperation among key industry leaders.
- Maritime Excellence Achievers’ ceremony: to recognize partners that have made outstanding contributions to India’s development as a leading maritime center.
MUST READ: ( GREEN MARITIME SECTOR)
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following in respect of the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS): (2017)
- Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy.
- IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime cooperation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
- Japan
- Russia
- The United Kingdom
- The United States of America
Syllabus
- Prelims –Geography
Context: The construction of the world’s new highest motorable Likaru-Mig La-Fukche road began in Ladakh recently.
Background:-
- The Border Roads Organization (BRO) is working on constructing the ‘Likaru-Mig La-Fukche’ road in Ladakh, which will be the new highest motorable road in the world.
About Likaru-Mig La-Fukche road:-
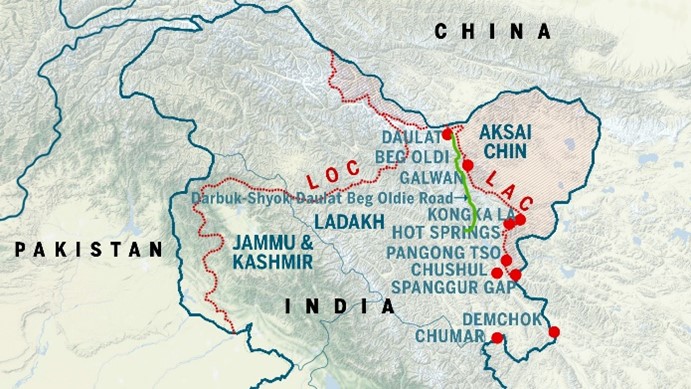
IMAGE SOURCE: The Times of India
- Location: Ladakh, India. (Operation Sadbhavana)
- It lies close to Hanle in Eastern Ladakh.
- Length:64-km.
- Altitude: about 19,400 feet.
- It is the highest motorable road in the world.
- It will surpass the Umling La Pass.
- Umling La Pass: located at an altitude of 19,300ft, is the highest motorable road in the world currently.
- It will connect Likaru to Fukche, situated 3 km from the Line of Actual Control (LAC).
- LAC: the demarcation that separates Indian-controlled territory from Chinese-controlled territory. ( India-China LAC standoff)
Significance:-
- It would also provide an alternate land connectivity route to the Fukche advanced landing pad.
- It is the first project in India to be carried out entirely by an All Woman Road Construction Company.
- It is led by a five-member All Woman Border Road Task Force.
- With this project, the BRO will break its own record of the highest motorable road.
MUST READ: India’s first-ever night sky sanctuary in Ladakh
SOURCE: HINDUSTAN TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Magnetite particles, suspected to cause neurodegenerative problems are generated as environmental pollutants from which of the following? (2022)
- Brakes of motor vehicles
- Engines of motor vehicles
- Microwave stoves within homes
- Power plants
- Telephone lines
Select the correct answer using the code given below
- 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 3, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) R2 Code of Practices” constitutes a tool available for promoting the adoption of (2022)
- Environmentally responsible practices in the electronics recycling industry
- Ecological management of ‘’Wetlands of International Importance” under the Ramsar Convention
- Sustainable practices in the cultivation of agricultural crops in degraded lands
- Environmental Impact Assessment’’ in the exploitation of natural resources
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Recently, the 26th National Conference on e-Governance was organized
About the National Conference on e-Governance:-
- Venue: Indore, Madhya Pradesh.
- Organized by: the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology in collaboration with the Government of Madhya Pradesh.
- Historical Background: The Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG), Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions, Government of India, and Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), have been jointly organizing it in partnership with one State Government since 1997.
- Theme: Developed India: Empowering Citizens. (Governance 4.0)
- Participants: Representatives from 28 states, nine union territories as well and industries will participate in the conclave.
- The conference will focus on 11 subjects including district-level initiatives, emerging technologies for providing citizen-centric facilities, and data governance.
- National e-Governance Awards 2023 in 5 categories will also be presented during the conference.
National Awards for e-Governance:-
- They are presented every year for exemplary implementation of e-governance initiatives. (Global Digital Governance)
- Purpose of Award
- Recognize achievements in the area of e-Governance.
- Disseminate knowledge on effective methods of designing and implementing sustainable e-Governance initiatives.
- Encourage incremental innovations in successful e-Governance solutions.
- Promote and exchange experiences in solving problems, mitigating risks, resolving issues, and planning.
- NAeG 2022-23
- This year, the categories under the Award Scheme of the National Awards for e-Governance 2022-23 have been revised.
- The 5 award categories are :
- Government Process Reengineering for Digital Transformation
- Application of Emerging Technologies for providing Citizen Centric Service
- District-level initiative in e-Governance
- Research on Citizen Centric Services by Academic/Research Institutions
- Application of Emerging Technologies in Governance by Startups
MUST READ: E-RUPI & Governance
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places, and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Regarding DigiLocker’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- It is a digital locker system offered by the Government under the Digital India Programme.
- It allows you to access your e-documents irrespective of your physical location.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: A Sloth bear was captured and relocated near Udhagamandalam, Tamil Nadu.
About Sloth Bear:-
- Scientific Name: Melursus ursinus.
- Distribution: India, Sri Lanka, and southern Nepal.
- Population: 90% of the global Sloth Bear population is found in India.
- Habitat: dry and moist forests and in some tall grasslands, where boulders, scattered shrubs, and trees provide shelter.
- Size: 5 to 6 feet (1.5 to 2 meters).
- Weight: 90 to 140 kilograms.
- Food: They primarily eat termites and ants.
- They have poor senses of sight and hearing.
- They have a good sense of smell.
- Sloth bears’ nostrils can close completely, protecting the animals from dust or insects when raiding termite nests or beehives.
Threats:-
- Habitat loss.
- Poaching for body parts.
- Human action: are sometimes captured for use in performances or hunted because of their aggressive behavior and destruction of crops.
Protection Status:-
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES listing: Appendix I
- Indian Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule I
MUST READ: Nandankanan Zoological Park: Odisha
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following makes a tool with a stick to scrape insects from a hole in a tree or a log of wood? (2023)
- Fishing cat
- Orangutan
- Otter
- Sloth bear
Q.2) With reference to India’s Desert National Park, which of the following statements is correct? (2020)
- It is spread over two districts.
- There is no human habitation inside the Park.
- It is one of the natural habitats of the Great Indian Bustard.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
India's Hunger Challenge
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: India has lifted 135 million people out of poverty; however, malnutrition remains an onerous challenge.
About Hunger:
- The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines hunger as the habitual (or chronic) consumption of too few calories to provide the minimum dietary energy an individual requires to live a healthy and productive life.
- It is an uncomfortable or painful physical sensation caused by insufficient consumption of dietary energy. It is one of the significant manifestations of poverty.
India’s achievements till date with regard to hunger and poverty:
- According to the Multi-dimensional Poverty Index (MDPI) prepared by the NITI Aayog, from 2015-16 to 2019-21, India lifted 135 million people out of poverty.
- When India got freedom in 1947 more than 80 percent of people were in extreme poverty, which today hovers around 15 per cent as per MDPI and about 11 per cent based on income criterion ($2.15 PPP).
- The UNDP has estimated that India lifted 415 million people out of poverty (MDPI) over the period 2005-06 to 2019-21.
- India seems to be on track to almost abolish poverty in the next five to 10 years.
- On hunger, at least in terms of food availability, India has done well.
Challenges of Hunger:
- Poverty: Poverty restricts food choices and has been the causative factor of hunger related deaths.
- The persistent high prices of food items and the regional disparities in terms of development affects the people to afford balanced nutrition.
- Associated factors: Hunger and the related malnutrition are the result of various associated factors ranging from water, sanitation, access to food items.
- A person’s ‘nutritional quotient’ is also dependent on demographic factors like gender, caste, age, etc.
- For instance, the nutritional needs of girl child and elderly are not adequately addressed in our society.
- Climate Change: Erratic rainfall and increasing frequency of extreme events have impacted agricultural activities everywhere creating unfavourable conditions for food production.
- Climate variability affecting rainfall patterns and agricultural seasons, and climate extremes such as droughts and floods, are among the key drivers behind the rise in hunger, together with conflict and economic slowdowns.
- Lack of Effective Implementation of Policies: Another important reason behind the persistent hunger is the poor implementation of the schemes and policies.
- The Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) and the National Health Mission (NHM) have not achieved adequate coverage.
- Non-communicable diseases: The rising burden of cardiovascular and other non-communicable diseases in India, particularly among the rapidly growing “middle class”, is strongly linked to diet and nutrition.
Consequences of the prevalence of hunger in India:
- Malnutrition: Hunger leads to inadequate intake of essential nutrients, which can cause malnutrition, stunting, and wasting among children and adults.
- Malnutrition can lead to impaired physical and cognitive development, weakened immune system, and higher risk of diseases.
- Health problems: Hunger can lead to several health problems such as anaemia, low birth weight, micronutrient deficiencies, and other diet-related diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
- Poverty: Hunger can lead to poverty, as people may not be able to work and earn an income due to a lack of food and energy.
- Hunger also increases health care costs and reduces productivity, which can perpetuate poverty and inequality.
- Education: Hunger also affects education, as children who suffer from hunger are more likely to miss school, have poor concentration, and drop out of school.
- Social unrest: Hunger can lead to social unrest and conflict, as people may resort to violence to obtain food or other basic needs.
Govt. Initiatives to tackle hunger in India:
- Eat Right India Movement: An outreach activity organized by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) for citizens to nudge them towards eating right.
- POSHAN Abhiyan: Launched by the Ministry of Women and Child Development in 2018, it targets to reduce stunting, undernutrition, anaemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls).
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana: A centrally sponsored scheme executed by the Ministry of Women and Child Development, is a maternity benefit programme being implemented in all districts of the country with effect from 1st January, 2017.
- Food Fortification: Food Fortification or Food Enrichment is the addition of key vitamins and minerals such as iron, iodine, zinc, and Vitamin A & D to staple foods such as rice, milk and salt to improve their nutritional content.
- National Food Security Act, 2013: It legally entitled up to 75% of the rural population and 50% of the urban population to receive subsidized food grains under the Targeted Public Distribution System.
- Mission Indradhanush: It targets children under 2 years of age and pregnant women for immunization against 12 Vaccine-Preventable Diseases (VPD).
- Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Scheme: Launched in 1975, the ICDS Scheme offers a package of six services to children in the age group of 0-6 years and pregnant and lactating mothers.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The Lok Sabha has recently passed the Indian Institutes of Management (Amendment) Bill, 2023.
About IIMs:
- Indian Institutes of Management (IIM) are the country’s premier institutions imparting the best quality education in management on globally benchmarked processes of education and training in management.
- IIMs are recognized as world-class management Institutions and Centers of Excellence and have brought laurels to the country.
- All IIMs are separate autonomous bodies registered under the Societies Act.
- Being societies, IIMs are not authorized to award degrees and, hence, they have been awarding Post Graduate Diploma and Fellow Programme in Management.
- IIM-Calcutta was the first Indian Institute of Management, established in 1961.
- Currently, there are 20 IIMs in the country.
- The Indian Institute of Management Act, 2017 provides for the creation of an academic council for each IIM.
- This academic council is the principal academic body under the Act as it decides the:
- academic content;
- criteria and processes for admissions to course; and
- guidelines for conduct of examinations.
Key provisions of IIM (Amendment) Bill, 2023:
- President of India as a Visitor: It designates the President of India as a Visitor of every Institute covered by the Act.
- Appointments: As per the IIM Act, 2017, the chairperson of the board of governors and the institute’s director are to be appointed by the board of governors.
- The board of governors includes the chairperson, director, government nominees, eminent persons, and faculty.
- The recent amendment altered the selection process to include the involvement of the Visitor (President of India) such that the Visitor nominates the chairperson, and the selection committee for director will consist of one member (out of three) nominated by the Visitor.
- Constitution of Search Committee: At present, the Search Committee comprises the Chairperson of the Board, and three members from amongst eminent administrators, industrialists and educationists.
- The Bill reduces these three members to two and adds another member to be nominated by the Visitor.
- Termination of Director: The Board will require prior approval of the Visitor before removing a Director. It also grants the Visitor the authority to terminate the services of the Director, as may be prescribed. The Bill also states the Chairperson of the Board will be nominated by the Visitor.
- Inquiries against IIMs: The Bill proposes a new procedure for inquiries against IIMs. It confers the power of inquiry upon the Visitor. The Visitor may appoint persons to review the work of any Institute and hold inquiries into its affairs.
- Based on the report of such inquiries, the Visitor may issue directions which will be binding on the Institute.
- Conditions for dissolving Board: The Bill provides that the central government may prescribe the conditions and procedure for dissolving or suspending an Institute’s Board.
- If a Board is suspended or dissolved, the central government will constitute an interim board for six months or until a new Board is constituted.
- Coordination Forum: At present, the Act provides for a Coordination Forum for all the Institutes, the Chairperson of which is selected by a Search-cum Selection Committee. Under the provisions of the Bill, the Chairperson will be nominated by the Visitor.
Need for the Amendment:
- The Indian Institutes of Management Act of 2017, hugely expanded the autonomy enjoyed by the IIMs, and contains an important clause. It requires the Board of Governors (BoG) of the IIMs to commission an independent review of the institutes at least once every three years and place the report in the public domain.
- However, very few of the 21 IIMs have done so.
- A dangerous governance vacuum has been created in the IIM system in the years since the government relinquished control over these institutes.
- The IIM Act 0f 2017 created a situation where there were no meaningful checks and balances on the director of IIMs.
Criticism:
- The Bill has raised serious concerns among the academic community and the alumni of the IIMs, who fear that it will compromise the autonomy and academic freedom of the IIMs, and make them vulnerable to political interference and bureaucratic meddling.
- They argue that the Bill goes against the spirit and intent of the 2017 Act, which was meant to empower the IIMs to manage their affairs without any external influence or pressure.
- They also contend that the Bill will adversely affect the quality and reputation of the IIMs, and hamper their ability to attract and retain talented faculty and students.
Way Forward:
The Indian Institutes of Management play a vital role in shaping the nation’s future leaders and contributing to economic growth. The 2023 IIM Amendment Bill represents a significant step by the government to address concerns of governance and accountability in the IIM system. By introducing the position of a Visitor and empowering them with oversight authority, the government seeks to strike a balance between autonomy and accountability.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| National Parks in news | Country |
| 1.Yasuni National Park | Brazil |
| 2.Yellowstone National Park | Ecuador |
| 3.Kuno National Park | Madhya Pradesh |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Sloth bear are Endangered as per the IUCN Red List.
Statement-II:
They are found in India, Sri Lanka, and southern Nepal.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Maharaja Bir Bikram Manikya Bahadur established the Maharaja Bir Bikram College (MBB College) in Agartala, Tripura.
Statement-II:
He believed in the modernization and development of the state and did not support local arts, crafts, and traditions.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) There is a growing divergence in the relationship between poverty and hunger in India. The shrinking of social expenditure by the government is forcing the poor to spend more on Non- Food essential items squeezing their food – budget. – Elucidate. (250 words)
Q.2) Analyze the role and powers of the proposed Visitor in the 2023 IIM Amendment Bill and its potential impact on the functioning of IIMs. Compare the balance between autonomy and accountability in the IIMs and other state-controlled educational bodies like IITs. (250 Words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 23rd August 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 17th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – c











