IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 25th June 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
RBI to supervise cooperative banks
Part of: GS-Prelims and Mains III – Economy and related issues; Banking and RBI reforms
In news:
- Centre decides to bring all urban and multi-State cooperative banks under the supervision of the RBI.
- This means that the central bank’s powers will apply to cooperative banks as they apply to scheduled banks.
- The move is aimed to protect depositors’ money.
Do you know?
- Amendments were made to the Banking Regulation Act through ordinance to bring 1,540 cooperative banks under the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulation to strengthen cooperative banks to avoid another PMC Bank-like crisis.
- In February 1 Budget speech, Finance minister had introduced ‘The Banking Regulation (Amendment) Bill, 2020 with an aim to increasing professionalism and improving governance among the co-operative banks. However, the amendment bill is pending approval.
Important value additions:
- Co-operative banks are financial entities established on a co-operative basis and belonging to their members. This means that the customers of a co-operative bank are also its owners.
- Co-operative banks in India are registered under the States Cooperative Societies Act.
- The Co-operative banks are also regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and governed by the Banking Regulations Act 1949 and Banking Laws (Co-operative Societies) Act, 1955.
- Currently, the Registrar of Cooperative Societies (RCS) is in control of management of elections and many administrative issues as well as auditing.
Pakistan to remain on FATF ‘greylist’
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II and III – Indian and its neighbours; International Relations; Security
In news:
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF) plenary session decides to continue to keep all countries that were on the “greylist” under scrutiny for Terror Financing and Money Laundering until October 2020.
- That means Pakistan to remain on FATF ‘greylist’.
Do you know?
- Pakistan has faced criticism due to its failure to meet the finance watchdog’s 27-point action plan on countering terror financing and anti-money laundering (CFT/AML) measures.
- Pakistan has also failed to act against groups like the Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), Afghan Taliban and affiliated HQN.
According to US’s 2019 report on terrorism,
- Pakistan allowed groups targeting Afghanistan as well as groups targeting India to operate from its territory
- Pakistan continues to “serve as a safe haven” for regional terrorist groups.
From Prelims Point of View:
Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
- Inter-governmental body established in 1989 on the initiative of the G7.
- Secretariat is housed at the OECD headquarters in Paris.
- Generate the necessary political will to bring about national legislative and regulatory reforms in various areas
- to set standards and promote effective implementation of legal, regulatory and operational measures
- Combating money laundering, terrorist financing and other related threats to the integrity of the international financial system.
To know about objectives and mandate of Financial Action Task Force (FATF), CLICK HERE
India and China: “de-escalation exercise”
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Indian and its neighbours; International Relations
In news:
- India and China have agreed to “disengage from three friction points” in Ladakh and pull back from their current positions.
- The three areas are Galwan, Hot Springs and the Finger area near Pangong Tso (lake) in Ladakh.
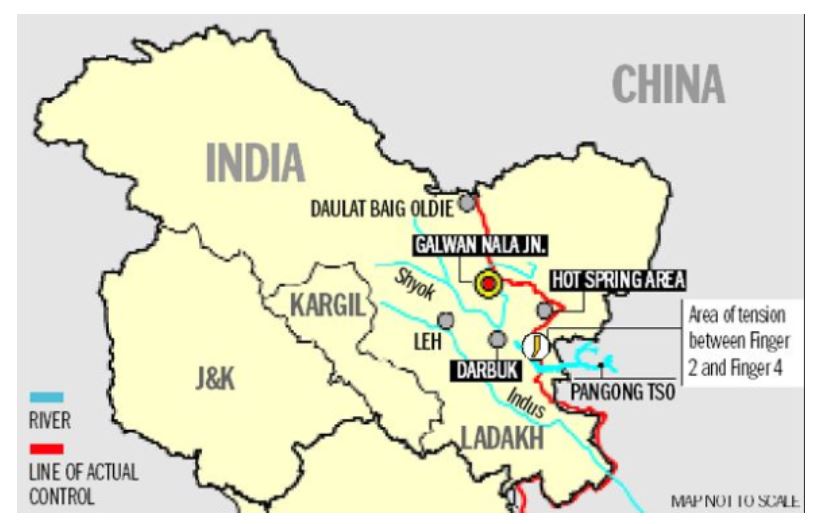
Pic: India-China dispute
Education inequalities widened due to COVID pandemic: UNESCO
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Govt schemes and programmes; Welfare/Development issue
In news:
According to 2020 Global Education Monitoring Report released by UNESCO,
- COVID-19 pandemic has increased inequalities in education systems across the world.
- About 40% of low- and lower-middle-income countries have not supported learners at risk of exclusion during this crisis.
- In April 2020, almost 91% of students around the world were out of school.
- Poor, linguistic minorities and learners with disabilities were affected more as resources for such persons may not be available outside schools.
- For poor students who depend on school for free meals or even free sanitary napkins, closures have been a major blow.
Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACe)
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains – III – Science and Technology
In news:
- Union Cabinet approves the creation of the Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACe)
- IN-SPACe will provide a level playing field for private companies to use Indian space infrastructure.
- IN-SPACe will also hand-hold, promote and guide the private industries in space activities through encouraging policies and a friendly regulatory environment.
Important value addition:
About New Space India Ltd.
- It is the Department of Space’s second commercial arm (after Antrix) that was announced in Budget 2019.
- Its objective is to use research and development carried out by ISRO over the years for commercial purposes through Indian industry partners.
- One of the mandates of NSIL aims to mass-produce and manufacture the SSLV and the more powerful PSLV in partnership with the private sector in India through technology transfers.
- NSIL will deal with capacity building of local industry for space manufacturing.
Garib Kalyan Roqwjgar Abhiyaan
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains II – Govt schemes and programmes; Welfare/Unemployment issue
In news:
- Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan was launched on 20th June 2020 to boost employment and livelihood opportunities for migrant workers returning to villages, in the wake of COVID-19 outbreak.
- This campaign will work in mission mode for 125 days with an outlay of Rs. 50,000 crore.
The major objectives of the initiative include:
- Provide livelihood opportunity to returning migrants and similarly affected rural citizens
- Saturate villages with public infrastructure and create livelihood opportunities viz. Roads, Housing, Anganwadis, Panchayat Bhavans, various livelihood assets and Community Complexes among others
- The basket of a wide variety of works will ensure that each migrant worker is able to get an opportunity of employment according to his skill, in the coming 125 days. The Program will also prepare for expansion and development of livelihoods over a longer term.
Do you know?
- The Ministry of Rural Development is the nodal Ministry for this campaign and the campaign will be implemented in close coordination with the State Governments. Central Nodal Officers of the rank of Joint Secretary and above will be appointed to oversee the effective and timely implementation of various schemes in the identified districts.
- The Railways decided to generate 8 lakh man-days of employment in various infrastructure projects till October 2020 as part of “Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan”.
Miscellaneous:
Justice G. Rohini commission to examine sub-categorisation of OBCs
In news:
- OBC panel headed by retired Delhi High Court Chief Justice G. Rohini was appointed in October 2017 to examine sub-categorisation of Other Backward Classes and look into the issues of communities that were not getting the benefits of reservation.
- The Union Cabinet has approved a six-month extension to the commission as it needs more time as its work has been affected by the pandemic.
India GDP to contract 4.5% on COVID-19: IMF
In news:
According to the updated World Economic Outlook (released by IMF) –
- Worldwide business shutdowns destroyed hundreds of millions of jobs, and the prospects for recovery are steeped in “pervasive uncertainty”.
- India’s GDP will fall 4.5% this year.
- Mexico will see a double digit decline of 10.5% while Brazil just misses that mark with a drop of 9.1%. Argentina is projected to fall 9.9%.
- Meanwhile, South Africa’s GDP is seen dropping 8%, while oil-producer Nigeria falls 5.4%.
- The U.S. economy is set to contract 8% in 2020, while China fares slightly better, posting growth of 1%
(MAINS FOCUS)
GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment
Country of Origin On Government e-Marketplace
Context: The government on 23 June 2020 made it mandatory for sellers on the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) portal to clarify the country of origin of their goods when registering new products.
What is GeM?
- GeM is a one-stop National Public Procurement Portal to facilitate online procurement of common use Goods & Services required by various Central and State Government Departments / Organizations /Public Sector Undertakings
- It was launched in 2016 to bring transparency and efficiency in the government buying process.
- It operates under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- GeM is a completely paperless, cashless and system driven e-market place that enables procurement of common use goods and services with minimal human interface
What are the new guidelines?
- Sellers on the GeM portal will now have to disclose the origins of their products.
- The portal also has a ‘Make in India’ filter, and government offices will be able to know which products have a higher content of indigenously produced raw materials.
- This would help government agencies choose products that meet the ‘minimum 50 per cent local content’ criterion when selecting bidders for their tenders
- The GeM portal now allows buyers to reserve a bid for Class I local suppliers, or suppliers of those goods with more than 50 per cent local content.
- For bids below Rs 200 crore, only Class I and Class II (those with more than 20 per cent local content) are eligible.
Significance of the move
- The move is aimed at promoting India-made goods and in line with government’s push for self-reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat Mission)
- Products sold on the GeM portal range from stationery used by government officials to medical products that are used on patients — and this might provide an opportunity to Indian manufacturers across industries to push their products in government facilities.
- It may over time filter out imported goods from use in government offices and facilities
- Weaponisation of trade ties in the wake of recent border tensions with China
- India wants to reduce its economic dependence on China so that China doesn’t use its economic might as a leverage against India during crisis times
- At $ 70.32 billion in 2018-19 and $ 62.38 billion between April 2019 and February 2020, China accounts for the highest proportion of goods imported into India (around 14 per cent in 2019-2020 so far)
Critical Analysis of the move
- The GeM move on country of origin is at best symbolic.
- This may erode Indian industry’s global competitiveness by placing a premium on ‘Indianness’ over quality or cost.
- A more direct impact may be seen if the proposal to mandate the country of origin for products on private platforms is implemented.
- Attaining genuine self-reliance is a long and capital intensive process that would require far greater investment in education, skill-building and infrastructure.
- This may further escalate tension with China transcending the boundary misunderstanding into trade war which may not be in India’s interest. For Ex: India’s drug makers depend on China for nearly 70% of requirements of bulk drugs and intermediates.
Conclusion
- Enhancing manufacturing capacities with improved efficiency and reduced cost would require an overhaul of bureaucratic processes rather than mere tweaking of government procurement rules
Connecting the dots:
- Critical analysis of Atmanirbhar Bharat Mission and its financing
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Russia-India-China Meet: Power hungry China and evasive Russia
Context: Virtual meeting of the foreign ministers of the Russia-India-China (RIC) grouping on 23rd June 2020
Did You Know?
- Together, the RIC countries occupy over 19 percent of the global landmass and contribute to over 33 percent of global GDP.
- All three countries are nuclear powers and two, Russia and China, are permanent members of the UN Security Council, while India aspires to be one.
About RIC
- RIC is a strategic grouping that first took shape in the late 1990s under the leadership of Yevgeny Primakov, a Russian politician as “a counterbalance to the Western alliance.”
- This idea of a ‘strategic triangle’ took a tangible form when former Foreign Ministers of Russia, China, and India met on the margins of the UN General Assembly in New York in September 2002.
- The group was founded on the basis of ending Russia’s subservient foreign policy guided by the USA and renewing old ties with India and fostering the newly discovered friendship with China.
- The grouping was formed in an aim to ensure that it is not left to the America-led West alone to shape the rules of global governance
Relevance of RIC for India
- Membership for India was always about containing China in Eurasia
- Forum for Cooperation: Even though India, China and Russia may disagree on a number of security issues in Eurasia, there are areas where their interests converge, like, for instance, on Afghanistan. RIC can ensure stable peace in Afghanistan and by extension, in Central Asia.
- Governance over Arctic: With the Northern Sea Route opening up due to climate change, the RIC has a common interest in ensuring that it is not left to the West and Russia alone and that India and China also have major say in rules governing the Arctic route
Key Takeaways of the Virtual RIC meet
- The special meeting of RIC on 23rd June 2020 was held to mark 75 years of the victory over the Axis powers in World War-II
- The ministerial-level engagements took place in the backdrop of ongoing border tensions between India and China, which has resulted in the first army casualties in 45 years.
- However, bilateral matters (Indo-China) were not discussed
- India stressed upon respecting international law, recognising the legitimate interests of partners, supporting multilateralism and promoting common good are the only way of building a durable world order
- There was no joint statement due to differences over few paragraphs
Critical Analysis of RIC
- India’s growing strategic partnership with the United States, Japan, and Australia conflicts with the RIC’s goals and objectives of seeking to undermine Washington’s role in the Indo-Pacific.
- There is growing Russia-China Axis which undermines the grouping relevance for India
- China is Russia’s biggest trading partner and the largest Asian investor in Russia.
- China sees Russia as a powerhouse of raw material and a growing market for its consumer goods
- The West’s approach towards Russia after the annexation of Crimea in 2014 and recent US-China trade war has brought Russia & China much closer
- There is also growing dependence of Russia on Chinese consumption.
- Also, over 70% of China’s arms imports now come from Russia
So is Russia now a permanent ally of China?
- Not necessarily, western analysts see Russia-China as a “friendship of convenience” between two countries
- Russia has been extremely calibrated in its statements on issues on which Beijing is most sensitive to: Huawei’s 5G rollout, Hong Kong and the Covid-19 pandemic
- China does not recognise Crimea as part of Russia, and Moscow, formally speaking, takes a neutral stance on Beijing’s claims in the South China Sea.
- Russia maintains steady relationship with India. Nearly 60 to 70 % of India’s defence supplies are from Russia
- India decided to reach out to RIC since it believes Russia has leverage and influence to shape and change Beijing’s stance on certain issues
Conclusion
- Far from enjoying equal status, member countries in groups like the BRI, BRICS, RIC, SCO, RCEP are seconded to Chinese special interests.
- Therefore, India’s policy makers must wriggle out of the China’s embrace and seek friends in other places like the Quad and Japan-America-India (JAI) formulation
Connecting the dots:
- Belt & Road Initiative, CPEC and String of Pearls Strategy
- India’s Act East policy
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following organizations brings out the publication known as ‘World Economic Outlook’?
- The International Monetary Fund
- The United Nations Development Programme
- The World Economic Forum
- The World Bank
Q.2 Which of the following statements is/are correct about Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan?
- The Ministry of Railways is the nodal Ministry for this campaign.
- The scheme will empower and provide livelihood opportunities to the returnee migrant workers and rural citizens who have returned to their home states due to the Covid-19 induced lockdown.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Consider the following statements about New Space India Limited (NSIL)
- It is the Department of Space’s second commercial arm.
- NSIL will deal with capacity building of local industry for space manufacturing.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4 Global Education Monitoring Report is released by –
- The International Monetary Fund
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
- The World Economic Forum
- The World Bank
Q.5 Consider the following statements about Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
- It is an inter-governmental body established by World Economic Forum.
- It is a policy-making body and promotes operational measures for combating money laundering and terrorist financing.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 24th June 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | D |
Must Read
About India-Pakistan ties:
About Kashmir conflict:
About changes to be brought in education:












