IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
FinCEN and FIU-IND
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations & GS-III – Money Laundering
In news
- Recently, over 2100 Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) were filed by banks with the United States Department of the Treasury’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
- The FinCEN files shall identify at least USD 2 trillion in transactions between 1999 and 2017 flagged as possible evidence of money laundering or other criminal activity by compliance officers of banks and financial institutions.
- Individuals and companies being probed by Indian agencies in different cases are part of the SAR flagged to FinCEN.
- Like, transactions of Indian entities named in scams such as the 2G scam, the Agusta-westland scandal, etc. cases have all been listed with the FinCEN.
Important value additions
FinCEN
- It was set up in 1990.
- It serves as the leading global regulator in the battle against money laundering.
- It collects and analyzes information about financial transactions in order to combat domestic and international money laundering, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes.
Suspicious Activity Report
- SAR is a document filed by banks and financial institutions to report suspicious activity to the USA FinCEN.
- These are used to detect crime but cannot be used as direct evidence to prove legal cases
Do you know?
- Money laundering: Concealing or disguising the identity of illegally obtained proceeds so that they appear to have originated from legitimate sources. It is frequently a component of crimes such as drug trafficking, robbery or extortion.
- The Financial Intelligence Unit-India (FIU-IND) performs the same functions as FinCEN in the USA. Under the Finance Ministry, this was set up in 2004 as the nodal agency for receiving, analyzing and disseminating information relating to suspect financial transactions.
No Confidence Resolution against Rajya Sabha Deputy Chairman
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Parliament; Executive
In news
- Rajya Sabha members of 12 opposition parties moved a no-confidence resolution against Rajya Sabha Deputy Chairman over the passage of two controversial farm Bills by the voice vote.
Important value additions
Relevant Rules of Procedures and Conduct of Business
- Rule 256, Suspension of member: This is decided by the presiding officer of the house on the grounds like a member disregarding the authority of the Chair or abusing the rules of the Council.
- Rule 258 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Rajya Sabha makes a provision to enable a member to raise a point of order.
- Point of order: An objection to the pending matter or proceeding which is in violation of a written and unwritten rule of the House.
Deputy Chairman of Rajya Sabha
- The Deputy Chairman is elected by the Rajya Sabha itself from amongst its members.
- The post of the Deputy Chairman is not subordinate to the Chairman.
- He performs the duties of the Chairman’s office when: (1) It is vacant; (2) When the Vice-President acts as President; (3) When the Chairman is absent from the sitting of the House.
- While presiding over the House, he cannot vote in the first instance; he can only exercise a casting vote in the case of a tie.
- Article 90: Deals with the removal of the Deputy Chairman
Chendamangalam Saree: Kerala
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Intellectual Property Rights
In news
- The Care 4 Chendamangalam (C4C) initiative is supporting the 2018 Kerala flood-affected weavers.
Important value additions
Kerala Kasavu Sarees
- It refers to the zari (gold thread) used in the border of the Kerala saree.
- The identity of the saree comes from the geographical cluster they are associated with.
- The Indian government has identified three clusters in Kerala – Balaramapuram, Chendamangalam and Kuthampully – that have been given a Geographical Indication (GI) tag.

Chendamangalam Saree
- It is recognisable by its puliyilakara border, a thin black line that runs side by side with the sari’s selvedge.
- It has extra-weft chuttikara and stripes and checks of varying width.
MSP Raised for Rabi Crops
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Agricultural Pricing
In news
- Recently, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has marginally increased the Minimum Support Price (MSP) of six rabi crops for 2021-22.
Key takeaways
- MSP rates were hiked for wheat, barley, gram, masoor dal (lentil), safflower, and rapeseed and mustard.
- The increase in MSP is in line with the principle of fixing the MSPs at a level of at least 1.5 times of the All-India weighted average Cost of Production as announced in Union Budget 2018-19.
Important value additions
Minimum Support Price
- The MSP is the rate at which the government buys grains from farmers.
- It is to counter price volatility of agricultural commodities due to the factors like variation in their supply, lack of market integration and information asymmetry.
- The MSP is fixed for 23 crops based on the recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), Ministry of Agriculture.
- The Food Corporation of India (FCI), the nodal central agency of the Government of India, along with other State Agencies undertakes procurement of crops.
Do you know?
- Rabi crops are agricultural crops that are sown in winter and harvested in the spring in India. Eg. Wheat, barley, mustard etc.
PVTGs of Odisha infected with COVID-19
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Issues related to SCs & STs; Health
In news
- Six members of two Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (Bondas and Didiayis) in Odisha have recently contracted Covid-19.
- The National Commission for Scheduled Tribes has sought a report from the state government and has termed it a “matter of grave concern”.
Important value additions
Bondas and Didiayis Tribes
- They are found in the Malkangiri district of Odisha
- The Bondas are believed to have come to India as part of the first wave of migration out of Africa about 60,000 years ago.
- The Didayis are an Austro-Asiatic tribe.
- The population of Didayis is 7,250 according to the 2011 Census.
- They live in the Konda Kamberu hills of Malkangiri.
Read more about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group here
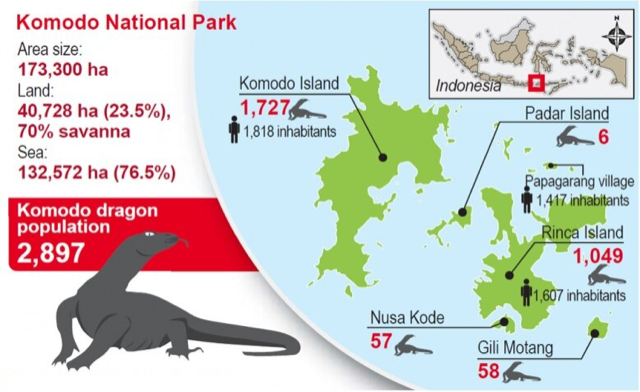
Komodo Dragon could become extinct
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Biodiversity; Conservation; Climate change
In news
- A recent study conducted by Australian universities has found out that the Komodo dragon could become extinct in the next few decades due to climate change.
Important value additions
Komodo dragon
- Scientific Name: Varanus komodoensis.
- They are the largest and heaviest lizards on Earth.
- They have long, flat heads with rounded snouts, scaly skin, bowed legs, and huge, muscular tails.
- They can eat almost anything, including invertebrates, birds, and mammals.
- They have venom glands loaded with toxins which secrete anticoagulants.
- Habitat: Komodo National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is situated in the Island of Komodo (eastern Indonesia) and is the only habitat for this lizard species.
- Threats: (1) Anthropogenic factors; (2) Less prey; (3) Climate change
- Conservation: (1) IUCN Status: Vulnerable; (2) CITES: Appendix I
Do you know?
- In February 2019, the Australian government officially declared the first known extinction of a mammal (Bramble Cay melomys) as a result of human-induced climate change.

Miscellaneous
International Day of Peace
-
Each year the International Day of Peace is observed around the world on 21st September.
- Theme for 2020: Shaping Peace Together
- The United Nations (UN) General Assembly has declared this as a day devoted to strengthening the ideals of peace, through observing 24 hours of non-violence and cease-fire.
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL / SECURITY/ HEALTH
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interest
SAARC – Uniting to combat COVID-19
Context: With the pandemic showing no signs of abating, growth prospects for the world’s fastest-growing region, South Asia, appear grim.
COVID-19 in South Asia
- India has the second largest number of COVID-19 cases in the world (over 55 lakh) after the U.S
- Bangladesh has around 3.5 lakh cases.
- Bhutan and the Maldives have managed to largely contain community transmission and avoid prolonged lockdowns due to a higher testing rate.
- Low Mortality: Unlike other regions, South Asian countries are experiencing a lower mortality rate despite having a higher infection rate.
- Reasons for Low Mortality: The region’s tropical climate, protection offered by a tuberculosis vaccine (BCG), exposure to malaria, and a weaker strain of the virus are considered as some of the reasons for low mortality
Have the governments in South Asia announced stimulus package?
- India, in late March, announced a $22.5 billion relief package to ensure food security and cash transfers to save the livelihoods of an estimated 800 million people living in poverty. RBI slashed the repo and reverse repo rate to create liquidity for businesses.
- Bangladesh, in early April, announced a stimulus package worth about $8 billion in addition to an earlier $595 million incentive package for export-oriented industries.
- Pakistan, in late March, unveiled a comprehensive fiscal stimulus package of $6.76 billion. Its central bank also slashed the interest rate.
- Maldives, in late April, mobilised a $161.8 million emergency fund and Afghan government allocated about $25 million to fight COVID-19.
Concerns:
- Inadequate Testing: Countries facing a surge in cases, such as India, could have flattened the curve by increasing the number of tests
- Data Reliability: South Asia houses one-fourth of the global population and one-third of the global poor, many COVID-19 deaths might have gone unnoticed, unreported or even under-reported.
- Implementation of Economic Package: Although countries like India and Bangladesh announced financial and material stimulus packages, distribution concerns remain unaddressed
- Inoperative SAARC COVID-19 fund: The fund was created following Indian PM Narendra Modi’s call to South Asian leaders, but governments are yet to decide on its modus operandi.
- Narrow Geopolitical Rivalry: This crisis is likely to result in prolonged economic slowdown in South Asia which will be further complicated by narrow geopolitical rivalry.
Way Ahead – A coordinated response mechanism
- South Asia region could leverage its existing institutional framework under the umbrella of SAARC to effectively respond to the crisis.
- For instance, SAARC Food Banks could be activated to tackle the imminent regional food crisis,
- The SAARC Finance Forum can be activated to formulate a regional economic policy response
Connecting the dots:
- BIMSTEC
- Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
SOCIETY / GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
Topic: General Studies 2, 3:
- Role of civil Society in a democracy. Formal/informal associations and their role in the Polity.
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
FCRA Bill and why civil society matters
Context: The Lok Sabha has passed the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Amendment (FCRA) Bill 2020 regarding non-governmental organisations (NGOs) without debate.
FCRA, 2010 was enacted to regulate the acceptance and utilisation of foreign contribution or foreign hospitality for any activities detrimental to “national interest”.
Significance of NGOs
- Interest Aggregators and Interest Articulators: Non-profit organisations play vital role in mobilizing public attention to societal problems and needs. They are the principal vehicle through which communities can give voice to their concerns.
- Complements Government Machinery: NGOs implement and monitor the government’s welfare policies, operating at the grassroots level where the official apparatus is often non-existent.
- Hold Government Accountable: NGOs broaden government’s accountability by ensuring government is responsive to citizens at large rather than to narrow sectarian interests.
- Constructive conflict resolution: In the international arena Track II diplomacy (involving non-governmental bodies) plays a crucial role in creating an environment of trust and confidence.
- Acts as Safety Valve: NGOs also provide a voice for marginal groups and social movements, offering a safety valve that prevents the country’s millions of local mutinies from becoming uprisings.
- Enriches Democratic Functioning: NGOs foster pluralism, diversity and freedom. They also perform the role of Capacity Builders – providing education, training and spreading awareness.
Key Provision of FCRA Bill, 2020 are:
- Aadhaar has been made mandatory identification document for all the office bearers of an NGO or an association seeking foreign donations.
- Foreign contribution can now be received only in an account designated by the bank as “FCRA account” in a branch of the State Bank of India, New Delhi (as notified by the central government). No funds other than the foreign contribution should be received or deposited in this account.
- Limiting administrative expenses drawn from foreign donations to 20% as against the current 50%
- The amended Bill includes “public servant” and “corporation owned or controlled by the Government” among the list of entities not eligible to receive foreign donations
Criticism of the FCRA Bill, 2020
- The legislation may be used to target political opponents and religious minorities.
- Cripples NGO Functioning: Due to the 20% cap, many NGOs will shut shop and many people will become jobless.
- Double Standards: On one hand the government invites foreign funds, but when such funds come for educational and charitable purposes, it is prevented.
- Licence-Raj on NGOs: The Bill assumes that all NGOs receiving foreign grants are guilty and thus makes Aadhar of office bearers as mandatory requirement.
- Open the doors for Bureaucratic Harassment: There is a thin line between enforcing transparency and using rules to allow official interference and harassment in the sector. Much of the present bill crosses that line and introduces a questionable degree of micro-management.
Way Ahead
- The government should send the bill to a select committee of the Rajya Sabha.
- NGOs are a necessary component of civil society and this bill needs greater public debate and scrutiny.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Bondas and Didiayis are Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups, recently seen in news. They belong to which of the following state of India?
- Odisha
- Jharkhand
- Rajasthan
- Himachal Pradesh
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Komodo Dragon:
- It is the largest Species of dragon fly known to man.
- Its IUCN status is Threatened.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 22nd September 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | D |
| 3 | C |
| 4 | A |
Must Read
About making the language of law comprehensible:
About e-learning in India:
About Happiness Index:











