IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Asia-Pacific Group (Apg) On Money Laundering retains Pakistan on its ‘Enhanced Follow-Up’ list
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- Due to Pakistan’s minimal progress in combating money laundering and terror financing, the Asia-Pacific Group (APG) on Money Laundering has retained the country on its ‘Enhanced Follow-Up’ list.
Key takeaways
- According to APG, Pakistan will remain in the enhanced follow-up list.
- It will also have to continue to report back to the APG on progress to strengthen its implementation of comprehensive measures.
- Pakistan is desperate to move out of ‘grey list’ because its inclusion in the list has severely impacted its economy and image.
- Pakistan was placed in the grey list in June 2018.
Important value additions
Asia-Pacific Group (APG) on Money Laundering
- APG is a regional affiliate of the Paris-based Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
- Secretariat: Sydney, Australia.
- Founded in: 1997 in Bangkok, Thailand
- It currently consists of 41 member jurisdictions in the Asia-Pacific region.
Tech for Tribals initiative
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – SCs and STs & GS-III – Entrepreneurship; Computers
In news
- Tech for Tribals initiative shall be launched on 13th October, 2020.
- Launched by: TRIFED under Ministry of Tribal Affairs in collaboration with Chhattisgarh MFP Federation and IIT, Kanpur
Key takeaways
- Aim of the initiative: Holistic development of tribals with a focus on entrepreneurship development, soft skills, IT, and business development through SHGs operating through Van Dhan Kendras (VDVKs).
- TRIFED has tied up with national institutions such as IIT, Kanpur; Art of Living, Bangalore; TISS, Mumbai; KISS, Bhubaneswar; Vivekananda Kendra, Tamil Nadu and SRIJAN, Rajasthan.
- Vandhan-ESDP Training Programs shall be conducted under these institutes.
Important value additions
Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India (TRIFED)
- It came into existence in 1987.
- It is a national-level apex organization.
- The basic objective of the TRIFED is to provide good price of the ‘Minor Forest Produce (MFP) collected by the tribes of the country.
- It functions under Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Govt. of India.
- TRIFED has its Head Office at New Delhi.
- It has a network of 13 Regional Offices located at various places in the country.
Nation- wide campaign to celebrate Kamdhenu Deepawali Abhiyan started
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies
In news
- Rashtriya Kamdhenu Aayog (RKA) recently started a nation- wide campaign to celebrate Kamdhenu Deepawali Abhiyan on the occasion of Deepawali festival.
- Through this campaign, the RKA is promoting extensive use of cow-dung/ Panchgavya products during this Diwali Festival.
Important value additions
Rashtriya Kamdhenu Aayog (RKA)
- It was constituted by Indian Prime Minister for the conservation, protection and development of cows and their progeny and for giving direction to the cattle development programmes.
- It is a high powered permanent body to formulate policy and to provide direction to the implementation of schemes related to cattle so as to give more emphasis on livelihood generation.
Sets of measures announced to generate consumption demand
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- Union Finance Minister recently announced two sets of measures to generate consumption demand and boost capital spending in the economy.
Key takeaways
- Leave Travel Concession (LTC) Cash Voucher Scheme: The Government has decided to give cash payment to employees in lieu of one LTC during 2018-21. Full payment on Leave encashment and tax-free payment of LTC fare depending on class of entitlement will be given.
- Special Festival Advance Scheme: It was meant for non-gazetted government employees. It is being revived as a one-time measure for gazetted employees too. All central govt. employees can now get interest-free advance of Rs. 10,000, in the form of a prepaid RuPay Card, to be spent by March 31, 2021.
- Capital Expenditure Boost for States: A special interest-free 50-year loan to states is being issued. For ₹ 12,000 crore capital expenditure which is to be spent by March 31, 2021: (1) ₹ 200 crore each for 8 North East states; (2) ₹ 450 crore each for Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh; (3) ₹ 7,500 crore for remaining states, as per share of Finance Commission’s devolution
Higher cytotoxicity in human lung cells suggested due to presence of Particulate Matter (PM) 2.5
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment; Pollution
In news
- A recent study – ‘Insights on the biological role of ultrafine particles of size PM<0.25: a prospective study from New Delhi’ was conducted recently.
Key takeaways
Proportion of Ultrafine Particles:
- Particulate matter of below 0.25 micrometres constituted the highest share in the composition of PM2.5 around the year as compared to particles of other sizes.
- Exposure to ultrafine particles of below 0.25 micrometres was also associated with over two-fold higher cytotoxicity as compared to exposure to other sizes.
Reasons:
- Celebration of Diwali.
- Stubble burning in neighbouring states of Punjab and Haryana.
- Secondary formation of particles due to favourable meteorological conditions.
- The low temperature and high humidity during winter nights enhance the fog-smog-fog cycle and result in 2-3-fold increase in PM concentration compared to pre-monsoon and South-West monsoon season.
Health Impacts:
- Stroke
- Lung cancer
- Other heart and lung related problems
Blocking Factor D Protein may reduce inflammatory reactions associated with Covid-19
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Biotechnology
In news
- A new study by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers suggests that blocking a human protein factor D may reduce the deadly inflammatory reactions that many patients have due to COVID-19.
Key takeaways
- Team focused on two proteins, factor H and factor D.
- These are known as “complement” proteins.
- They help the immune system clear pathogens from the body.
- The researchers discovered that Covid-19’s spike protein causes factor D to overstimulate the immune response, which in turn prevents factor H from mediating that response.
- When SARS-CoV-2 attacks the ACE2 receptors to proliferate and infect more cells in the human body, it also prevents Factor H from using the sugar molecule to bind with cells.
- The team found that by blocking factor D, they were able to stop the destructive chain of events triggered by SARS-CoV-2.
Status of Bharatmala Pariyojana
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions
In news
- A total of 322 projects in a length of 12,413 km have been awarded and 2921 km has been constructed under Bharatmala Pariyojana till August 2020.
- Phase-I of Bharatmala Pariyojana: Implementation of 34,800 km of national highways in 5 years (from 2017 to 2022) has been approved (Rs. 5,35,000 crore).
- Phase-II: Around 48,000 km of road network across India by 2024.
Important value additions
Bharatmala Pariyojana
- It is an umbrella program for the highways sector.
- Initiated by: Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
- Objectives: (1) To optimise the efficiency of freight and passenger movement across India by bridging critical infrastructure gaps through effective interventions; (2) To generate a large number of direct and indirect employment opportunities in the construction and infrastructure sector; (3) To connect 550 districts in the country through national highway linkages.
- Effective measures: Development of economic corridors, inter corridors and feeder routes, national corridor efficiency improvement, border and international connectivity roads, coastal and port connectivity roads and Greenfield expressways.
- Features: (1) Improvement in the efficiency of existing corridors through the development of Multimodal Logistics Parks and elimination of chokepoint; (2) Improving connectivity in North East and increasing harmony with Inland Waterways; (3) Emphasis on the use of scientific and technological planning; (4) Satellite mapping of corridor; (5) Delegation of powers for successful completion of Phase I by 2022.
Do you know?
- Economic Corridors: These are integrated networks of infrastructure within a geographical area designed to stimulate economic development.
- Greenfield Projects: They lack constraints imposed by prior work on the site. Typically, it entails development on a completely vacant site and architects start completely from scratch.
- Brownfield Projects: They carry constraints related to the current state of the site and might be contaminated or have existing structures that architects have to tear down or modify in some way before the project can move forward.
- Multimodal Logistics Parks: These are a key policy initiative of the Government of India to improve the country’s logistics sector by lowering overall freight costs, reducing vehicular pollution and congestion, and cutting warehousing costs.
- Chokepoint: It is a single point through which all incoming and outgoing network traffic is funnelled and hence, leads to congestion and traffic.

Miscellaneous
Nechiphu Tunnel
-
Nechiphu Tunnel shall be constructed on the Balipara-Charduar-Tawang (BCT) road in West Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh.
- Constructed by: Border Roads Organisation (BRO).
(MAINS FOCUS)
AGRICULTURE/ GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2, 3:
- Public Distribution System- objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping; issues of buffer stocks and food security
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
MSP in the age of Surplus
Context: New Agricultural Laws being introduced by Union Government with an objective of making agriculture sector market oriented that would in turn help increase farmers’ income.
What is Minimum Support Price (MSP)?
- MSP is the price set by the government to purchase crops from the farmers, whatever may be the market price for the crops.
- MSP assures farmers agricultural income besides providing a clear price signal to the market
- The major objectives are to support the farmers from distress sales and to procure food grains for public distribution.
- The MSP is an assurance (not legal binding) by the government to the farmers that it will buy at this assured price if the market prices go below it.
MSP and the Changed Situation of Agriculture Sector
- The MSP regime was the creation of the era of scarcity in the mid-1960s
- Indian agriculture has, since then, turned the corner from scarcity to surplus.
- The policy instruments of dealing with shortages are different from those dealing with surpluses
- In a surplus economy, unless we allow a greater role for markets and make agriculture demand-driven, the MSP route can spell financial disaster.
- The new laws are trying to increase the relative role of markets without dismantling the MSP system.

Source: Indian Express
Criticism of MSP System
- Distorted Procurement: MSPs pertain primarily to paddy and wheat in selected states — in recent years, the government has also been buying some amounts of pulses, oilseeds and cotton occasionally.
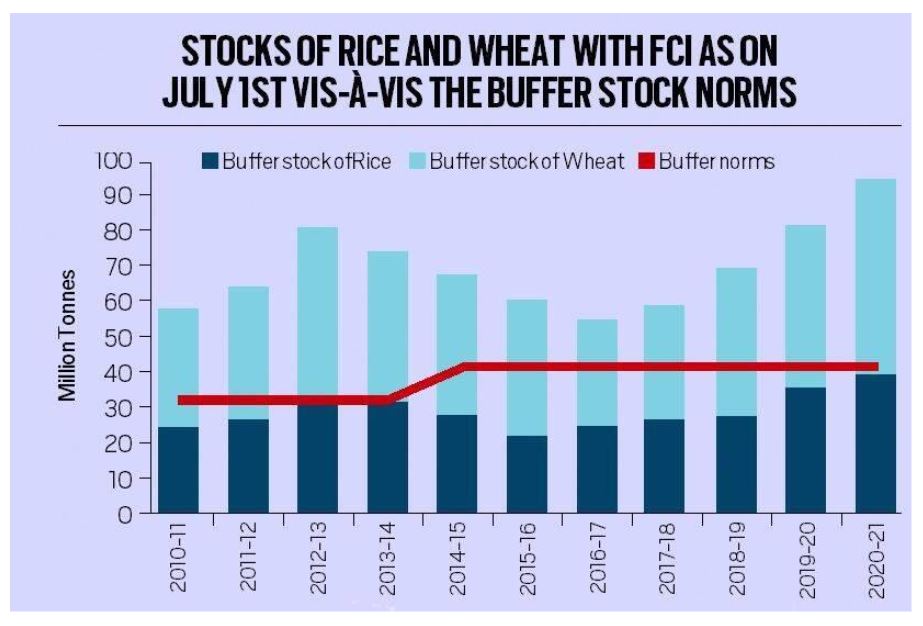
- Buffer exceeding Limits: Due to MSP dominated system of rice and wheat, the stocks with the government are way above the buffer stock norms (see figure).
- High Cost of Procurement: The economic cost of procured rice comes to about Rs 37/kg and that of wheat is around Rs 27/kg.
- High Wages in FCI: The CTC (cost to company) of departmental labour of the Food Corporation of India is six to eight times higher than contract labour in the market.
- As a result, market prices of rice and wheat are much lower than the economic cost incurred by the FCI. In Bihar’s rural areas, for example, one can easily get rice in the retail market at Rs 23-25/kg.
- Export Inefficiency: The bottom line is that grain stocks with the FCI cannot be exported without a subsidy, which invites WTO’s objections.
- Food Subsidy Bill: The real bill of food subsidy is going through the roof but that is not reflected in the Central budget as the FCI is asked to borrow more and more. The FCI’s burden is touching Rs 3 lakh crore.
Is it right to compare sugarcane pricing and milk pricing by co-operatives in the same vein as the MSP?
- Sugarcane Pricing
- In the case of sugarcane, the government announces a “fair and remunerative price” (FRP) to be paid by sugar factories
- This has created mess in the Sugar Sector
- The sheer populism of SAP has resulted in cane arrears amounting to more than Rs 8,000 crore, with large surpluses of sugar that can’t be exported.
- This sector has, consequently, become globally non-competitive.
- Unless sugarcane pricing follows the C Rangarajan Committee’s recommendations — somewhat akin to milk pricing — the problems of the sugar sector will not go away.
- Milk Pricing
- The most important commodity of Indian agriculture, milk, whose value is more than that of rice, wheat, and sugarcane combined.
- In the case of milk co-operatives, pricing is done by the company in consultation with milk federations, not by the government. It is more in the nature of a contract price.
- Milk does not have a MSP and competes with private companies, be it Nestle, Hatsun or Schreiber Dynamix dairies
- Result: The milk sector has been growing at a rate two to three times higher than rice, wheat and sugarcane.
- Today, India is the largest producer of milk — 187 million tonnes annually — way ahead of the second-ranked US which produces around 100 million tonnes every year.
What are the good prospects with new agricultural laws?
- In the next three to five years, hundreds and thousands of companies will be encouraged to build efficient supply lines somewhat on the lines of milk, as a result of these changes in farm laws.
- These supply lines — be it with farmers producer organisations (FPOs) or through aggregators — will, of course, be created in states where these companies find the right investment climate.
- These companies will help raise productivity, similar to what has happened in the poultry sector.
- Milk and poultry don’t have MSP and farmers do not have to go through the mandi system paying high commissions, market fees and cess.
Conclusion
- The MSP system is much more costly and inefficient, while the market-led system will be more sustainable provided we can “get the markets right”.
- The pricing system has its limits in raising farmers’ incomes.
- More sustainable solutions lie in augmenting productivity, diversifying to high-value crops, and shifting people out of agriculture to high productivity jobs
Connecting the dots:
- History of Agriculture Produce Market Committees (APMCs)
- How has agri-marketing policy changed over years
EDUCATION / GOVERNANCE
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Education, Human Resources
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
DU’s Cut-off reflects a broken system
Context: Delhi University (DU)’s first cut-off list for admission to its undergraduate programmes was announced on October 10, and it touched the 100% ceiling for the first time since 2011.
Cut-offs are decided by calculating the best of four subjects’ marks in Class 12 board exams
For Example: The Lady Sri Ram (LSR) College of DU has pegged the cut off at 100 % for three undergraduate programmes—Psychology (Hons), Economics (Hons), and Political Science (Hons)
Do You Know?
- As many as 5,500 students out of 3.54 lakh students, who have applied for admission in Delhi University, have scored perfect 100% in their four best subjects.
- This is not the first time when the cut off for admission in Delhi University has gone up to reach 100%. In 2015, the College of Vocational Studies and Indraprastha College had also kept the cut off at 100 % for admission to Computer Science.
What explains the high cut-offs?
- One, there is a higher number of applications vis-a-vis the number of seats.
- Two, the Class 12 evaluation process is distorted, leading to such high marks
- Three, colleges set high cut-offs to prevent “over admissions”.
- Four, there is a paucity of good-quality public universities.
- And finally, students are attracted to Delhi due to its academic and physical infrastructure, extra-curricular activities, and scholarships; the opportunity to interact with a diverse student population; and eventually access better job opportunities
What does the Phenomenon of High Cut-offs indicate?
- The phenomenon of high cut-offs is not just an academic-administrative problem.
- It is a subset of more critical issues that ail the education system, and the lack of democratisation of resources.
Way Ahead
- To improve, the Centre and states must invest more in public education;
- Need to boost academic infrastructure across the country;
- Governments have to make the Class 12 evaluation process more holistic;
- Administration has to ensure that all students, irrespective of where they are studying, get a level-playing field when it comes to availing good teachers and infrastructure.
Connecting the dots:
- New Education policy 2020
- Right to Education Act
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India (TRIFED):
- It is an autonomous cooperative.
- It is a state-specific organization functioning only in tribal-majority regions.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Recently, a new study by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers suggests that blocking a human protein factor D may reduce the deadly inflammatory reactions that many patients have due to COVID-19. What is the basic function of Factor D Protein?
- Blood clotting
- Clear pathogens from the body
- Builds muscles in the body
- Burns extra fat in the body
Q.3 Bharatmala Pariyojana comes under which of following Ministry?
- Ministry of Road Transport and Highways
- Ministry of Commerce
- Ministry of Home Affairs
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs
Q.4 Nechiphu Tunnel shall be constructed in which of the following state/Union Territory of India?
- Ladakh
- Himachal Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
ANSWERS FOR 12th October 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | D |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | D |
Must Read
About gene editing and 2020 Nobel prize in Chemistry:
About the Purpose of Protests:
About Finance Minister’s recent economic package to boost demand:











