IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
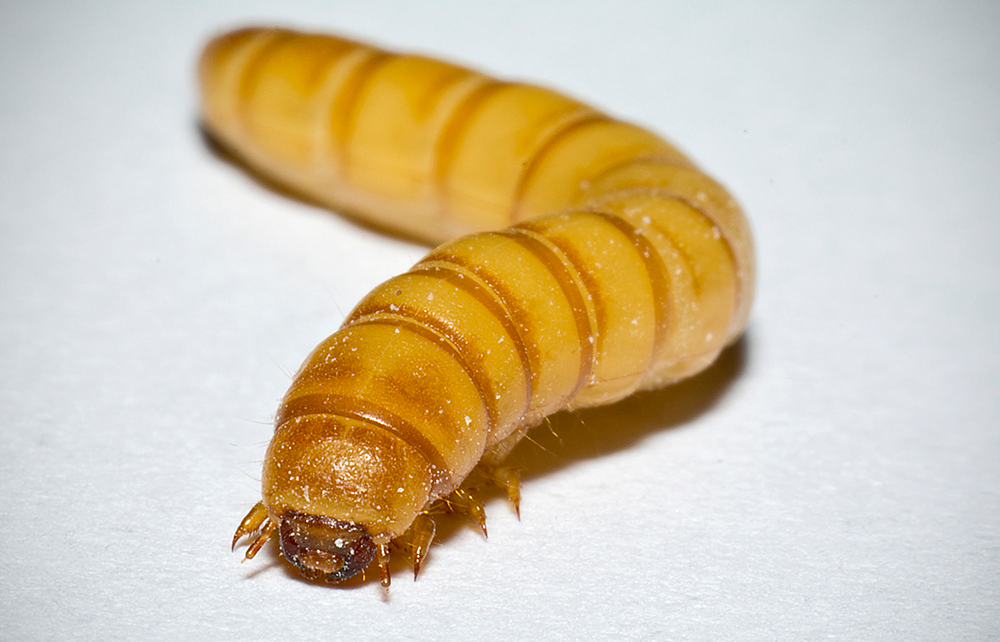
Mealworms the first insect to be approved in Europe as a human food
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Ecology; Biodiversity
In news
- Mealworm has become the first insect to be approved in Europe as a human food.
Key takeaways
- The decision by the European Food Safety Agency (EFSA) paves the way for mealworms to be used whole and dried in curries and other recipes and as a flour to make biscuits, pasta and bread.
- Rich in protein, fat and fibre, they are likely to be the first of many insects to feature on European’s plates in the coming years.
Important value additions
- Mealworms are the larval form of the mealworm beetle, Tenebrio molitor, a species of darkling beetle.
- Despite their name, mealworms are beetle larvae rather than worms.
- They also go through four life stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult like all holometabolic insects.

Mutual Funds (MF) Risk-o-meter becomes effective
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Ecology; Biodiversity
In news
- Securities and Exchange Board of India’s (SEBI’s) decision on the “risk-o-meter” came into effect on January 1.
Key takeaways
- SEBI has made it mandatory for mutual fund houses to characterise the risk level of their schemes on a six-stage scale from “Low” to “Very High”.
- All mutual funds shall, beginning January 1, assign a risk level to their schemes at the time of launch, based on the scheme’s characteristics.
- The risk-o-meter must be evaluated on a monthly basis.
- Fund houses are required to disclose the risk-o-meter risk level along with the portfolio disclosure for all their schemes on their own websites as well as the website of the Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI) within 10 days of the close of each month.
- Any change in the risk-o-meter reading with regard to a scheme shall be communicated to the unit-holders of that scheme.
- The move will help investors to make a more informed investment decision.
Important value additions
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
- It is the regulator of the securities and commodity market in India owned by the Government of India.
- It was established in 1988 and given statutory status through the SEBI Act, 1992.
- SEBI is responsible to the needs of three groups:
- Issuers of securities
- Investors
- Market intermediaries
- Functions:
- Quasi-legislative – drafts regulations
- Quasi-judicial – passes rulings and orders
- Quasi-executive – conducts investigation and enforcement action
- Powers:
- To approve by−laws of Securities exchanges.
- To require the Securities exchange to amend their by−laws.
- Inspect the books of accounts and call for periodical returns from recognised Securities exchanges.
- Inspect the books of accounts of financial intermediaries.
- Compel certain companies to list their shares in one or more Securities exchanges.
- Registration of Brokers and sub-brokers
Related articles:
- SEBI eases Fund-raising norms for firms: Click here
- Participatory notes: Click here
Virtual Buyer Seller Meet with Millet Exporters organized by APEDA
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Agriculture
In news
- The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) in association with Andhra Pradesh Drought Mitigation Project (APDMP), an externally aided project funded by IFAD, organized a Virtual Buyer Seller Meet with Millet Exporters.
- Considering the potential of increasing exports of Millets and Millet products and the focus given by Government for development of Millet sector of Nurti Cereals, APEDA is closely interacting with Indian Institute of Millet Research (IIMR) and other stakeholders.
Important value additions
- Millet is a common term to categorize small-seeded grasses that are often termed nutri-cereals.
- It includes Sorghum, Pearl Millet, Ragi, Small Millet, Foxtail Millet, Proso Millet, Barnyard Millet, Kodo Millet and other millets.
- These are known for high nutritive value.
Indian Institute of Millets Research (ICAR-IIMR)
- It is an agricultural research institute engaged in basic and strategic research on sorghum and other millets.
- It is located at Rajendranagar (Hyderabad, Telangana).
- IIMR operates under the aegis of Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- It was founded in 1958 under the Project on Intensified Research on Cotton, Oilseeds and Millets (PIRCOM).
Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority
- It is an apex body under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India, responsible for the export promotion of agricultural products.
- APEDA was established by the Government of India under the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority Act passed by the Parliament in December, 1985.
Some of the functions of APEDA are as following:
- Promotion of exports of agricultural and processed food products. Promotion of export oriented production and development of the Scheduled products.
- To make Improvement in numerous areas such as packaging, marketing for the Scheduled products outside India.
- Setting standards and specifications for the scheduled products for the purpose of exports.
- Financial assistance, reliefs and subsidy to the relating industries.
- To provide training in the related areas
Related articles:
- Export of Moringa powder: Click here
- Kiwis of Ziro Valley: Click here
India – UAE MoU For Scientific And Technical Cooperation
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations
In news
- The Union Cabinet has approved the MoU on Scientific and Technical Cooperation between National Centre of Meteorology (NCM), UAE and Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), India.
The MoU provides for:
- Exchange of experience/visits in term of scientists, research scholars and specialists, etc. for the purpose of tropical cyclones forecasting.
- Cooperation to support the Tsunami Early Warning Centre (TEWC)
- Cooperate at the field of Seismology which includes the study of Seismic activities having the potential to generate Tsunami waves in Arabian Sea and Oman Sea.
- Cooperation in Early warnings of Sand and Dust storms through the exchange of knowledge.
PM to launch Pan India Rollout of COVID-19 Vaccination drive
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health
In news
- Indian Prime Minister will launch the pan India rollout of COVID-19 vaccination drive on 16th January, 2021.
Key takeaways
- This will be the world’s largest vaccination program covering the entire length and breadth of the country.
- A total of 3006 session sites across all States and UTs will be virtually connected during the launch.
- Around 100 beneficiaries will be vaccinated at each session site on the inaugural day.
- This vaccination programme is based on the principles of priority groups to be vaccinated.
- Health Care workers, both in government and private sectors including ICDS workers, will receive the vaccine during this phase.
- The vaccination programme will use Co-WIN, which will facilitate real time information of vaccine stocks, storage temperature and individualized tracking of beneficiaries for COVID-19 vaccine.
- This digital platform will assist programme managers across all levels while conducting vaccination sessions.
- A dedicated 24×7 call centre – 1075 – has also been established for addressing the queries related to COVID-19 pandemic.
- Adequate doses of both COVISHIELD and COVAXIN have already been delivered across the country to all States/UTs with the active support of the Ministry of Civil Aviation.
Do you know?
- COWIN is an online digital platform developed by Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
PM to interact with Startups and address ‘Prarambh: Startup India International Summit’
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Start-ups; Innovation; Sci & Tech
In news
- Indian Prime Minister will interact with startups and address ‘Prarambh: Startup India International Summit’ on 16th January 2021
Key takeaways
- Organized by: Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- The two-day Summit is being organised as a follow up of the announcement made by the Prime Minister at the fourth BIMSTEC Summit held in Kathmandu in August 2018 wherein India committed to host the BIMSTEC Startup Conclave.
- The Summit marks the 5th anniversary of the Startup India initiative, launched by the Prime Minister on 16 January, 2016.
- Over 25 countries and more than 200 global speakers shall participate.
- The Summit will be the largest startup confluence organised in India since the launch of the Startup India initiative.
- Focus: Enhancing multilateral cooperation and engagement with countries from around the globe to collectively develop and strengthen the startup ecosystems.
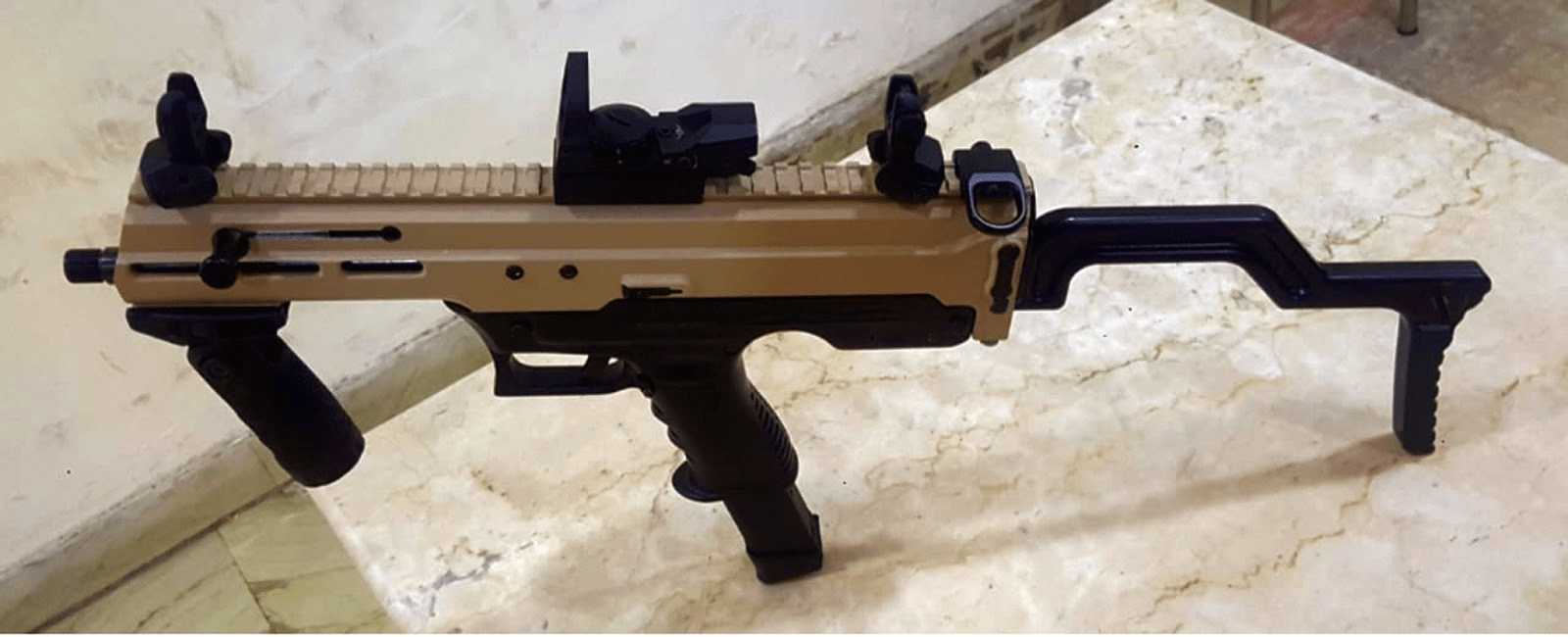
India’s First Indigenously Developed 9mm Machine Pistol
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Sci & Tech
In news
- India’s first indigenous 9mm Machine Pistol has been jointly developed by DRDO and Indian Army.
Key takeaways
- The Machine Pistol fires the in-service 9mm ammunition and sports an upper receiver made from aircraft grade Aluminium and lower receiver from carbon fibre.
- 3D Printing process has been used in designing and prototyping of various parts including trigger components made by metal 3D printing.
- The weapon has huge potential in Armed forces.
- The weapon is named “Asmi” meaning “Pride”, “Self-Respect” & “Hard Work”.
- This small step will pave way for self reliance and it is expected that the Services and Paramilitary Forces (PMFs) will induct this expeditiously.

Miscellaneous
CollabCAD
-
National Informatics Centre (NIC), MeitY along with Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE), Ministry of Education is jointly launching CollabCAD Software.
- CollabCAD software will be used for Practical assignments as part of the subject curriculum for making different types of 3D designs and 2D Drawings.
- Students from around 140 plus schools across the country and the schools in the Middle East (affiliated with CBSE, New Delhi) will have access to this software which can be used for practical projects and understanding concepts of Engineering Graphics.
(Mains Focus)
GEOGRAPHY/ ENVIRONMENT/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-1: Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone, forest fires etc.
- GS-3: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Forest fires in Himachal Pradesh
Context: Himachal Pradesh frequently witnesses forest fires during dry weather conditions. In the month of Jan 2021, a forest fire which started near Kullu raged for several days before being brought under control. Forest fires were also reported in Shimla and other parts of the state.
What is the forest cover of Himachal Pradesh?
- Legal Classification: Although two-thirds of the total geographical area of Himachal Pradesh is legally classified as forest area.
- Effective Forest Cover: Much of the declared forest area is permanently under snow, glaciers, cold desert or alpine meadows and is above the tree line. This leaves an effective forest cover of around 28% of the total area which amounts to 15,434 square kilometres, as per the Forest Survey of India.
- Common Trees: Chir Pine, Deodar, Oak, Kail, Fir and Spruce are some of the common trees found here.
Forest Fires in Himachal Pradesh a recurrent phenomenon
Except for periods of precipitation in monsoon and winter, the forests remain vulnerable to wildfires. Forest fires are a recurrent annual phenomenon in the state, and most commonly occur in Chir Pine forests.
- In the summer season, forest fires occur frequently in the low and middle hills of the state, where forests of Chir Pine are common.
- The dry summer season from March to June coincides with the shedding of highly-combustible needles by Chir Pine trees. Once the fallen dry needles catch fire, it can spread quickly over the entire forest due to the action of the wind.
- However, due to their thick bark, the Chir Pine trees are themselves relatively unharmed by these fires, and can spring back to life during the monsoon season.
- During the post-monsoon season and in winters, forest fires are also reported in higher areas, including parts of Shimla, Kullu, Chamba, Kangra and Mandi districts, where they usually occur in grasslands.
What causes the fire?
- Natural causes such as lightning or rubbing of dry bamboos with each other can sometimes result in fires
- Human Factors: When the grass is dry, even a small spark, such as someone dropping a burning matchstick, torchwood or a bidi/cigarette, can cause a massive fire. A spark can also be produced when dry pine needles or leaves fall on an electric pole.
- Forest Activities: People who frequently pass through a forest to gather minor produce, take their animals for grazing or for other purposes may set up a temporary hearth to cook food or warm themselves. If they leave behind a smouldering fire, it can develop into a forest fire.
- Agricultural Practices: Also, when people burn their fields to clear them of stubble, dry grass or undergrowth, the fire sometimes spreads to the adjoining forest.
What are the fuels of such massive fires?
- The dry leaf litter on the forest ground acts as a ready fuel. Fallen tree leaves, dry grass, weeds, low brushwood, deadwood on the forest floor, logs and stumps etc form the surface fuels.
- Below the loose litter, decaying materials such as humus, wood, shrubs, roots, much and peat can also support the combustion.
- Above the surface level, dry standing trees, mosses, lichens, dry epiphytic or parasitic plants, and fallen branches trapped in the understorey can spread the fire to the upper foliage and the tree crowns.
What damages do the forest fires cause?
- Impacts regenerative capacity of forests: Forest fires can cause a lot of damage to the regeneration in the forests and their productivity. Moisture-loving trees such as Oaks and Deodars may give way to other species and exotic weeds.
- Impact on Water system: Forests help maintain aquifers and continuous flow of streams and springs, and provide firewood, fodder and non-timber produce to the local communities – all these capacities may get adversely affected in case of a fire.
- Impact on Soil Productivity: Forest fires may destroy organic matter in the soil and expose the top layer to erosion thus negatively impacting soil fertility & productivity.
- Impact on animal and human lives: Forest fires may also impact the wildlife by burning eggs, killing young animals and driving the adult animals away from their safe haven. Sometimes, a forest fire may get out of control and extend to human settlements, thus posing danger to human life and property.
- Economic Losses: From 2016-17 to 2019-20, the annual loss to the Himachal Pradesh state due to forest fires has ranged from Rs 1.7 crore to Rs 3.5 crore. Around 1,200 to 2,500 forest fires were reported each year during this period affecting thousands of hectares.
Are the recent forest fires unusual?
- Forest fires are common every time a dry spell hits the state.
- Himachal witnessed unusually dry weather conditions last year (2020) from August to November, resulting in drought-like conditions.
- That period also saw a large number of forest fires – at least 500 fires were recorded from August till early November.
- Currently in the second week of Jan 2021, the weather has been dry resulting in some fires.
What is done to prevent and control forest fires?
- Getting rid of forest fire fuels: Clearing camping sites of dried biomass. Early burning of dry litter on the forest floor
- Changing Composition of Forest: Growing strips of fire-hardy plant species within the forest
- Defensive Mechanism: Creating fire lines in the forests (fire lines are strips in the forest kept clear of vegetation to prevent the fire from spreading).
- Better Predictions: Forecasting fire-prone days using meteorological data will help control forest fires at early stages
- Dedicated Force: Once a fire starts, early detection and quick action by fire-fighting squads is crucial. For such activities, the state forest department has a fire protection and fire control unit.
- Regulation of Forest activities: In 1999, the state government notified forest fire rules which restrict or regulate certain activities in and around forest areas such as lighting a fire, burning agricultural stubble or undergrowth (ghasnis) and stacking inflammable forest produce such as dried leaves and firewood.
Connecting the dots:
- Australian Wildfires: Click Here
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 consider the following statements regarding securities and exchange Board of India
- It was given statutory status through the SEBI Act 1992.
- It is responsible to the needs of investors only.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Agricultural and processed food products export Development Authority come under which of the following ministry?
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Ministry of Food Processing Industries
- Ministry of Consumer Affairs
Q.3 which of the following country does not share its border with UAE?
- Iran
- Qatar
- Oman
- Iraq
Q.4 Which of the following is not a factor for strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere?
- Warm sea surface temperatures
- Coriolis force so that low pressure can be developed
- High humidity in the lower to middle levels of the troposphere
- Lightning in the troposphere
ANSWERS FOR 13th January 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | A |
Must Read
About need for transparency in vaccines:
On what Indian can learn from Kenya Agri-Experiment:











