IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Temple in news: Gavi Gangadhareshwara Temple
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I – Art & Architecture
In news
- Gavi Gangadhareshwara Temple in Gavipuram was in news recently.
- For the first time in 50 years, sun’s rays didn’t fall on idol on Sankranti day.
Important value additions
- Gavi Gangadhareshwara Temple is also known as Gavipuram Cave Temple.
- It is an example of Indian rock-cut architecture.
- This cave temple is dedicated to Shiva and cut into a monolithic stone.
- It is located in Bangalore, Karnataka.
- It was built in the 16th century by Kempe Gowda I, the founder of the city.
- The temple is famous for its mysterious stone discs in the forecourt and the exact planning allowing the sun to shine on shrine in certain time of the year.
- Lakhs of devotees come in mid January every year on Makar sankranti Day to this temple.
- This is a special day when the sun’s rays fall on the Shivalinga for one hour as it passes between the horns of the Nandi.
Indian Army signs $20-million contract with ideaForge
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Defence and Security
In news
- The Indian Army has signed a $20-million contract with ideaForge to procure undisclosed quantities of a high-altitude variant of SWITCH UAV.
- ideaForge is a player in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) technology.
Important value additions
- SWITCH UAV is an indigenous system built to cater to the most demanding surveillance operations of the Indian forces.
- This fixed-wing vertical take-off and landing UAV can be deployed at high altitudes and under harsh environments for day and night surveillance.
Section 230 Of The US’ Communications Decency Act
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – International Relations & GS-III – Sci & Tech
In news
- Soon after a mob of President Donald Trump’s supporters stormed the US Capitol last week, his social media accounts were suspended by Big Tech companies like Twitter and Facebook for his alleged role in inciting violence and spreading misinformation.
Key takeaways
- The incident spurred a renewed debate about Section 230 of the US’ Communications Decency Act.
- The Act is a controversial piece of internet legislation.
- It permits these tech companies to use their powers and ban the president in the first place.
- The Act was passed in 1996.
- It provides legal immunity to internet companies for content that is shared on their websites.
- The act was first introduced to regulate pornography online.
- Section 230 is an amendment to the act, which holds users responsible for their comments and posts online.
- Also, according to the Act, online companies, including social media platforms, are not liable for the content shared on their website by its users.
- So if a user posts something illegal on the website, the company is protected from lawsuits.
Do you know?
Why Section 230 is widely criticised?
- It was passed before social media existed in its present form.
- Political leaders and internet activists have long called for the law to be updated.
Related articles:
- US Capitol Violence: Click here
India home to both species of red panda: ZSI
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Ecology and Biodiversity
In news
- Scientists from the Zoological Survey of India have concluded that India is home to both the (sub) species — Himalayan red panda (Ailurus fulgens) and the Chinese red panda (Ailurus styani).
Key takeaways
- The Siang river in Arunachal Pradesh splits the red panda into these two phylogenetic species.
- The red panda was considered a monotypic species till 2020 until the scientists studied its genetic make-up with respect to the geographical distribution and described the occurrence of the two species.
- The reason for the reduction in the population size of the Himalayan red panda is due to the geological and climatic oscillations as the landscape was exposed to heavier topographic and geological changes through repeated cycles of the wet and dry periods during the last glacial maxima and Pleistocene Era.
- It is considered an indicator species for ecological change, the red panda is shy, solitary and arboreal animal. It primarily feeds on bamboo and avoids human presence.
- Director of the ZSI, said the overall conservation of this ecologically sensitive species required an effort from both the national and international stakeholders and adequate awareness among the local communities.
Important value additions
- The red panda (Ailurus fulgens) is a mammal species native to the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China.
- It is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List
- Threats: Habitat loss and fragmentation, poaching, and inbreeding depression.
- Despite its name, it is not closely related to the giant panda

Related articles:
- Zoological Survey of India lists 62 species of Skinks: Click here
- Malayan Giant Squirrel could decline by 90% in India by 2050: Zoological Survey of India (ZSI): Click here
- Red Panda: Click here
Saksham: a month long campaign for consumers of fossil fuels launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Environment
In news
- With a view to create awareness among the consumers of fossil fuels, ‘SAKSHAM’, a month long campaign, was recently launched.
- Launched by: Petroleum Conservation Research Association (PCRA), Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas
Key takeaways
- The campaign shall highlight the adverse health and environmental impacts of increasing carbon footprints.
- ‘SAKSHAM’s idea is to convince consumers to switch to cleaner fuels and bring in behavioural change to use fossil fuel intelligently.
- The campaign will also spread awareness about 7 key drivers that Prime Minister recently mentioned, that would help India move towards cleaner energy.
- The key drivers include: (1) Moving towards a gas-based economy; (2) Cleaner use of fossil fuels; (3) Greater reliance on domestic sources to drive bio-fuels; (4) Achieving renewable targets with the set deadlines; (5) Increased use of electric vehicles to decarbonize mobility; (6) Increased use of cleaner fuels like Hydrogen; (7) Digital innovation across all energy systems.
Model Tender for public procurement drafted by the Finance Ministry
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The Finance Ministry (Expenditure Department) has drafted a model tender document for public procurement by all central government departments, in order to standardise the language and clauses included, and avoid contractual disputes.
Key takeaways
- Public procurement refers to the purchase of goods and services by the public sector or the government, accounting for an average 15% of GDP globally.
- In India, government procurement is estimated to constitute about 30% of GDP with the central government accounting for a major chunk.
- There is no standardised nomenclature in public procurement in India and a mix of American, European and Indian nomenclature has become common. E.g. participants in the Tender are called tenderers and bidders.
- The standard bidding document developed now, seeks to ease out this duality by mooting that the ‘Tender’ should refer to the tender document and process, while the term ‘Bid’ shall refer to the bidders’ pitches;
- ‘Bidder’ is to be used instead of ‘Tenderer’ to refer to potential suppliers and the usage ‘Bid document’ be done away with, as per the proposed model.
Startup India Seed Fund announced
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Start-ups; innovation
In news
- Indian Prime Minister announced launching of Startup India seed fund with 1,000 crore rupees so that there is no shortage of seed money for startups.
- This was announced during the ‘Prarambh: Startup India International Summit’.
- This will help in starting and growing new startups.
- Fund of funds scheme is already helping startups raising equity capital.
- The Government will also help the startups in raising capital through guarantees.
Related articles:
- Prarambh: Startup India International Summit’: Click here
Iron-Ore Policy 2021
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Infrastructure; Economy
In news
- The Ministry of Railways has approved a new iron-ore policy governing the allocation of rakes and transportation of iron-ore.
Key takeaways
- This new policy has been named as Iron-ore Policy 2021 and shall come into effect from February 10, 2021.
- The provisions of the new policy will be updated in the rake allotment system module by the Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS).
- Scrutiny of documentation by Railways has been removed.
- Executive Director Rake Movement of Railway Board (EDRM) office, Kolkata which has been sanctioning programmes for movement of iron-ore traffic will have no regulatory role in the new policy.
- Customers now desirous of moving their traffic under any priority will have to give (an) undertaking that they have procured, transported and utilized materials as per rules and regulations of Central and State Governments.
- Higher priority will be given to the movement of iron-ore traffic for domestic manufacturing activity.
- Old and new plants will be treated similarly as far as allotment and loading of rakes is concerned.
Do you know?
- Iron ore is the second most important stream of traffic of Railways and along with steel accounts for nearly 17% of total 1210 million tonne freight loading of Indian Railways in 2019-2020.
(Mains Focus)
ECONOMY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Financial Stability Report: RBI’s Warning
Context: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released the 22nd issue of its biannual Financial Stability Report outlining the risks to financial stability as well as the resilience of the financial system in the contemporary context.
Key takeaways from the latest GDP estimates released: Click Here
Significance of Financial Stability report
- The FSR is a hugely useful publication as it receives contributions from all the financial sector regulators in the country.
- As such, it provides a rather comprehensive picture of the so-called macro-financial risks facing the economy.
- The FSR released by the RBI is the biannual alert of such risks in the Indian economy.
An Example of Macro-Economic Risk – High NPAs
- If lots of banks in an economy find that the loans they extended to different businesses are unlikely to be repaid, it is a macro-financial risk.
- Because if banks do not get their money back, they won’t be able to fund the next set of investments. Lack of access to credit thus impairs the economic growth as expansion of firms is curtailed.
- Even if the government decides to use the taxpayer’s money to bail banks out, it will have to curtail some other expenditure — perhaps on education or healthcare or infrastructure, thus impacting the welfare of citizens
- So, one thing can lead to another and the economic growth of a country can take a massive hit just because too many banks had too many non-performing assets (NPAs or bad loans) all at the same time.
What are the major concerns highlighted by FSR Report of RBI?
- High Bank NPAs
- According to the RBI’s analysis, the level of Gross NPA ratio in India’s banking system could almost double between September 2020 (7.5% of all loans extended) and September 2021 (13.5% to 14.8% depending on economic deterioration)
- To see these percentages in perspective, one must note that when the economy was growing fast — before the 2008 financial crisis — NPAs hovered around the 2.5% level.
- The banking system is the financier of the whole economy. If its wheels get jammed or malfunction, it can derail the fledgling economic recovery.
- Disconnect between certain segments of financial markets and the real economy
- The RBI noted that measures taken to support the economy and safeguard the financial system during the COVID-19 pandemic “may have unintended consequences as reflected, for instance, in the soaring equity valuations disconnected from economic performance”.
- While the country’s experienced historic recession(economic output shrank by 7.5% in Q2 and 23.9% in Q1 of FY21) the stock markets have been seemingly disconnected and soaring to record highs.As of the close of trading on January 11 (the day the RBI released its report), the benchmark S&P BSE Sensex had appreciated almost 90% from its closing level on March 23, 2020.
- It is a fact that stock market indices, both in India and elsewhere, have surged even when the real economy — that is the number of cars/TVs/ACs/ phones/ houses/ travel trips etc. — has struggled in contrast.
- RBI warned, “Stretched valuations of financial assets pose risks to financial stability,” adding, “banks and financial intermediaries need to be cognisant of these risks and spillovers in an interconnected financial system.”
How did the above situation arise (stock market rise while economy shrank)?
- Stimulus Packages across world: The onset of the pandemic saw monetary and fiscal authorities worldwide, including in India, introducing a slew of support measures to ensure that the restrictions imposed on economic activity did not completely devastate national economies and household incomes.
- Easy money in Financial System: The stimulus measures, which included interest rate cuts and infusion of liquidity, have driven a substantial surge in funds in the financial system, including in India’s case from overseas investors. Availability of lower-cost borrowings also spur people to borrow money to invest in stocks.
- Resurgence of Foreign Portfolio Investment(FPI) to India: Latest data from the NSDL. show that net FPI into equities in the current fiscal year had surged more than 38-fold to ₹2,36,781 crore (as on January 16), from the meagre ₹6,153-crore inflow in the preceding year.
- Lack of alternatives for higher returns: Worldwide, easy money conditions have in the past invariably spurred stock market rallies as investors seek higher returns at a time when interest rates on fixed income assets such as deposits and bonds decline.
Why is the RBI worried?
- Creation of Asset bubble: Easy money often creates asset bubbles. An asset bubble is when assets such as housing, stocks, or gold dramatically rise in price over a short period that is not supported by the value of the product. The hallmark of a bubble is irrational exuberance—a phenomenon when everyone is buying up a particular asset.
- Possibility of Economic Crisis caused by bursting of such bubble: RBI is wary of the risk that a sudden sharp reversal in the trend (of easy money flowing into stock markets) could cause the asset bubble to pop, triggering wider contagion effects.
- Example: Imagine a man investing his savings in a travel company because the stock is rising fast in the hope that with a vaccine being available, travel business will take off. But if there is a second, more infectious strain of the virus and the travel company goes bust, its share price will plummet and the pain will be shared with all the shareholders
- Spill over effect: What makes these asset bubble burst worse is the level of interconnectedness it has among financial institutions. A sell-offs can potentially transmit asset market shocks across the financial system (ex Mutual Funds, Asset Management Companies, Banks and NBFCs, HFCs, NABARD, EXIM, NHB, SIDBI etc)
- Worldwide Experience: The 2001 recession in the U.S., for instance, was sparked by the bursting of the dotcom bubble (overvaluation of Tech companies), which, coupled with the September 11 terrorist attacks and a series of accounting scandals at major companies.
Conclusion
Active intervention by central banks and fiscal authorities has to be taken to be able to ward off any risks to macro-financial stability of the system.
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic:
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries
Russia’s exit from the Open Skies Treaty
Context: Russia has announced that it was leaving the Open Skies Treaty (OST). In November 2020, USA left the OST after accusing Russia of violating the pact– allegations that Russia denied. Moscow has now blamed Washington for its own decision of leaving the treaty.
What is the Open Skies Treaty?
- It is an accord that allows participants to fly unarmed reconnaissance flights over any part of their fellow member states
- First proposed in 1955 by former US President Dwight Eisenhower as a means to deescalate tensions during the Cold War. Claiming the initiative would be used for extensive spying, Moscow rejected Eisenhower’s proposal.
- However, the landmark treaty was eventually signed in 1992 between NATO members and former Warsaw Pact countries following the demise of USSR.
- It went into effect in 2002 and had 35 signatories, including key players US and Russia, along with one non-ratifying member (Kyrgyzstan).
- The OST aims at building confidence among members through mutual openness, thus reducing the chances of accidental war.
- Under the treaty, a member state can “spy” on any part of the host nation, with the latter’s consent. A country can undertake aerial imaging over the host state after giving notice 72 hours before, and sharing its exact flight path 24 hours before.
- The information gathered, such as on troop movements, military exercises and missile deployments, has to be shared with all member states.
- Only approved imaging equipment is permitted on the surveillance flights, and officials from the host state can also stay on board throughout the planned journey.
Signatories
35 states – Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Canada, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Kyrgyzstan, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, the Slovak Republic, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Turkey, Ukraine, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
Significance of the Open Skies Treaty
- Importance for Intelligence Gathering: The OST was signed in 1992, much before the advent of advanced satellite imaging technology which is currently the preferred mode for intelligence gathering. Yet, surveillance aircraft provide key information that still cannot be gathered by satellite sensors, such as thermal imaging data.
- Helps Smaller Countries party to Treaty: Though satellites can provide the same, and even more detailed, information, not all of the treaty states-parties have such capabilities.
- Confidence Building Tool: The treaty is also aimed at building confidence and familiarity among states-parties through their participation in the overflights.
- USA has utilized the treaty more than Russia: Between 2002 and 2016, the U.S. flew 196 flights over Russia compared to the 71 flights flown by Russia. A former Trump official had also hailed OST data gathered during the 2014 Russia-Ukraine conflict.
So, why did the US leave the Open Skies Treaty?
- While it was envisaged as a key arms control agreement, many in US had for over a decade accused Russia of non-compliance with OST protocols, blaming Moscow of obstructing surveillance flights on its territory, while misusing its own missions for gathering key tactical data.
- US President Donald Trump was also unhappy that a Russian reconnaissance flew over his golf course in New Jersey state in 2017.
- In May 2020, the Trump administration announced its intention of withdrawing from the OST, accusing Russia of “flagrantly and continuously violating the Treaty in various ways for years”, and left it in November 2020.
Why did Russia leave after the US?
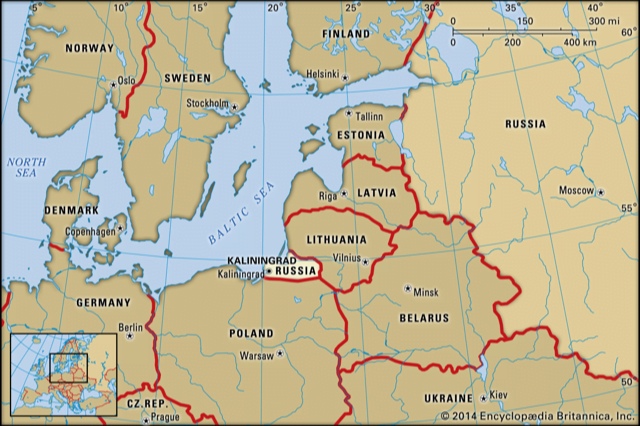
- A contentious issue regarding Russia’s compliance with the OST was its alleged reluctance to allow flights over Kaliningrad, its exclave in Eastern Europe that sits between NATO allies Lithuania and Poland.
- Russia defended its position by saying that the restrictions were permissible under treaty rules, and gave the example of the US imposing similar limits on flights over Alaska.
- After the US left the OST, Russia sought assurances from NATO allies who continued to remain on the treaty that they would not transfer data collected by their flights over Russia to Washington. In its statement, Russia said that these requests were not backed by the NATO members, prompting it to leave the treaty.
Critical Analysis of the recent development (Russia’s withdrawal from OST)
- Growing mistrust between global powers: The failure of the Open Skies Treaty follows the demise of another significant arms control accord, the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces (INF) Treaty, after both the US and Russia left it in 2019.
- Weakens EU’ capabilities to track Russia: Russia’s departure could adversely impact Washington’s European allies, which rely on OST data to track Russian troop movements in the Baltic region
- Larger Nuclear Arms Control Treaty in Jeopardy: Experts are now contemplating the fate of the much larger US-Russia ‘New START’ nuclear arms control agreement, which is slated to expire in February 2021. Trump has already said that his administration would not renew the treaty unless China joins. Despite new President Elect Joe Biden’s willingness to renegotiate, there are apprehensions that it would not be completed before Feb deadline.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Gavi Gangadhareshwara Temple is located in:
- Andhra Pradesh
- Telangana
- Tamil Nadu
- Karnataka
Q.2 Which of the following is IUCN’s Satus for Red Panda is:
- Endangered
- Critically endangered
- Vulnerable
- Least concern
ANSWERS FOR 16th January 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | D |
| 4 | A |
Must Read
On Whatsapp and Privacy:
On rise of shadow entrepreneurship:











