IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
CAFE Regulations
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy
In news
- Carmakers from the Society of India Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM) recently requested Ministry for Road Transport to postpone implementation of BS VI CAFÉ Phase II regulations since the industry is still recovering from the impact of COVID.
Important value additions
- CAFE (Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency) regulations are similar norms to BS VI.
- However, it has a different approach towards reducing the carbon footprint in the exhaust gasses of the vehicle.
- CAFE majorly focuses on COx emissions.
- While, BS VI focuses on overall emissions which include NOx (Nitrogen Oxides), SOx (Sulphur Oxides).
- Aim of CAFE regulations: To reduce the overall COx (Carbon Oxides) from the exhaust of the vehicle.
- The reduced carbon footprint leads to increased fuel economy.
- These regulations were first implemented in India on 1st April 2017 with the introduction of BS4 exhaust emission norms.
Merchant Digitization Summit 2021: Towards AatmaNir bhar Bharat
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy; IT
In news
- Merchant Digitization Summit 2021: Towards AatmaNirbhar (Self Reliance) Bharat was recently held.
- Hosts: The Government of India, Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI), and UN-based Better Than Cash Alliance
- Special focus: Himalayan Regions, North East Regions and Aspirational Districts of India.
Important value additions
Better Than Cash Alliance
- Based at the United Nations.
- It is a partnership of governments, companies and international organizations.
- It accelerates the transition from cash to responsible digital payments.
- It has 75 members.
- The Alliance Secretariat works with members to digitize payments by:
- Providing advisory services based on their priorities.
- Sharing action-oriented research and fostering peer learning on responsible practices.
- Conducting advocacy at national, regional and global level.
- It was created in 2012.
- Launched by: United Nations Capital Development Fund, the United States Agency for International Development, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Citigroup, the Ford Foundation, the Omidyar Network, and Visa Inc.
Related articles:
Maritime India Summit 2021
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Defence and Security
In news
- Indian Prime Minister recently inaugurated the ‘Maritime India Summit 2021’.
Key highlights of the summit
- The Maritime India Vision 2030 outlines the priorities of the Government.
- Capacity of major ports has increased from 870 million tonnes (2014) to 1550 million tonnes.
- Mega ports with world class infrastructure are being developed in Vadhavan, Paradip and Deendayal Port in Kandla.
- India aims to operationalise 23 waterways by 2030.
- India has 189 lighthouses across its vast coastline.
- It has formulated a programme for developing tourism in the land adjacent to 78 lighthouses.
- Steps are being taken to introduce urban water transport systems in key states and cities such as Kochi, Mumbai, Gujarat and Goa.
- To encourage domestic shipbuilding, approval has been given to the Shipbuilding Financial Assistance Policy for Indian Shipyards.
- The Ministry of Port Shipping and Waterways has created a list of 400 investable projects having investment potential of $ 31 billion.
- The Sagar-Manthan: Mercantile Marine Domain Awareness Centre has been launched.
- It is an information system for enhancing maritime safety, search and rescue capabilities, security and marine environment protection.
- Government is in the process of installing solar and wind-based power systems at all the major ports across the country.
- It aims to increase usage of renewable energy to more than 60% of total energy by 2030 in three phases across Indian ports.
Karnataka’s Engineering Research Policy
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Sci & tech; economy
In news
- India’s first Engineering Research & Development (ER&D) Policy was launched recently by Karnataka.
- Objective: To raise Karnataka’s contribution to the sector to 45% in the next five years.
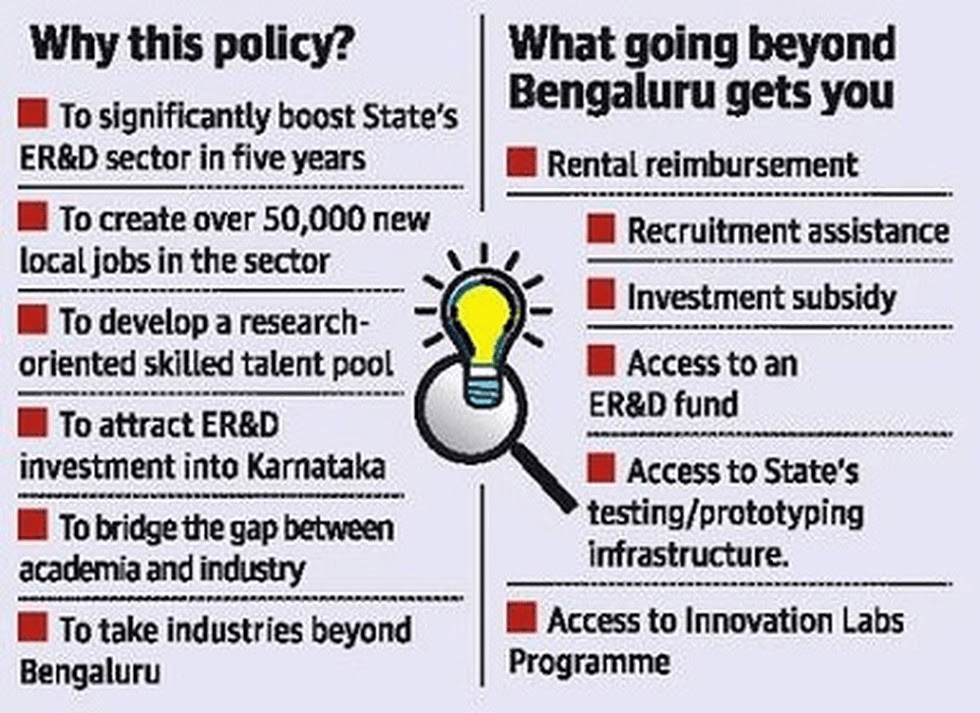
Key takeaways
- The policy has the potential to create over 50,000 jobs in the ER&D space in five years.
- ER&D has the potential to become a $100-billion industry in India in the next five years.
- The sector is the fastest growing industry in India with a CAGR of 12.8%.
- The global engineering research and development industry is also expected to reach $2 trillion by 2025.
- Five key focus sectors: Aerospace and defence; auto, auto components and EV; biotechnology, pharma and medical devices; semiconductors, telecom, ESDM; and software products.
“Freedom in the World 2021: Democracy under Siege” report
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – Fundamental rights
In news
- “Freedom in the World 2021: Democracy under Siege” report was recently released.
- Released by: U.S. think tank, Freedom House
- It has classified India as ‘partly free’.
Key takeaways
- India’s score was 67
- Last year, its score was 71/100 (free category )
- According to the report, the Indian government and its State-level allies continued to crack down on critics during the year.
- The report also highlighted that many outfits encouraged the scapegoating of Muslims, who were disproportionately blamed for the spread of the COVID-19 virus.
- The U.S. dropped three points over one year, down to 83/100.
- China, classified as ‘not free’, dropped a point from last year going down to 9/100.
(Mains Focus)
RIGHTS/ JUDICIARY
Topic:
- GS-2: Fundamental Rights
- GS-2: Structure, organization and functioning of the Judiciary
Rape and Marriage
Context: Recently, Supreme Court bench headed by CJI asked a State government employee whether he would marry a girl he was accused of raping repeatedly while she was a minor.
The accused had also forced her mother to not lodge a police complaint on the promise that he would marry the victim when she turned 18.
The man refused by Supreme Courts proposal saying he was already married.
Implication of remarks(proposal) made by SC
- Impact on Society: Words uttered in the highest, most pre-eminent court of the land ripple out into the larger society. SC should have been more cautious before making such proposals.
- Criticised as Retrograde proposal: The SC’s remarks, unfortunately, risk perpetuating the offensive and retrograde idea of marriage as a payoff for the trauma and violation of rape.
- Dilution of Offence: Under the law of the land, rape is a “non-compoundable” crime. That is, the offence cannot be diluted or mitigated by any settlement reached outside court. Making such compromises is considered as dilution of offence.
- Against SC’s own precedence: In a 2015 judgment in State of MP vs Madanlal, the court had unambiguously stated, “In a case of rape or attempt of rape, the conception of compromise under no circumstances can really be thought of”. In an earlier judgment in Shimbhu v State of Haryana, the SC had said, “Rape is not a matter to be left for the parties to compromise and settle.”
- Perpetuating Patriarchy: Such type of compromises is making violation of women(rape) a matter to be settled between families so to preserve the reputation and honour of male assailants.
- Against Article 21: By offering marriage as a solution to a rape victim, the judiciary failed to protect the rights of a girl. Such obscene matchmaking and settlements devalues a woman’s worth and her dignity of life.
- Against Article 14: Such type of remarks is considered as assault on the autonomy of Indian women as equal citizens. Equal rights activists have always worked hard against misogyny, patriarchal mindsets and other failings such as blaming the victim for rape. This arduous battle for equality becomes even more difficult when people in high offices make offensive remarks
- Increases Vulnerability: Such type of compromises exposes the victim to more violence from her husband/assailant
- Existing Practice: It is pertinent to note here that marital rape is not a crime under the Indian Penal Code. Such compromises are routinely peddled by police, village councils and lower courts. But CJI’s remarks in open court could perpetuate this inglorious tradition and derail the progress made towards empowerment of women.
Conclusion
When the scars of the Nirbhaya case are still raw, and a series of rape and murders are being reported against minors, especially Dalits, the judiciary’s shocking remarks echo a deep-set prejudice against gender equality
Connecting the dots:
GEOGRAPHY/ ENVIRONMENT
Topic:
- GS-1: Geographical phenomena
- GS-3: Environment and Ecology, Bio diversity – Conservation, environmental degradation, environmental impact assessment, Environment versus Development
- GS-3: Issues relating to deforestation, land use pattern and use of fossil fuel.
Simlipal Forest Fires
Context: The Simlipal forest reserve area frequently witnesses forest fires during dry weather conditions. A fire which started in the biosphere reserve area in February 2021 was raging for nearly a week that was finally brought under control.
About Simlipal Reserve
- Location: Similipal, which derives its name from ‘Simul’ (silk cotton) tree and is situated in the northern part of Odisha’s Mayurbhanj district.
- Protection: It is a national park and a tiger reserve. Also, Similipal and the adjoining areas, comprising 5,569 sq km, was declared a biosphere reserve by the Government of India on June 22, 1994, and lies in the eastern end of the eastern ghats
- Rich in Biodiversity: Similipal is the abode of 94 species of orchids and about 3,000 species of plants, 12 species of amphibians, 29 species of reptiles, 264 species of birds and 42 species of mammals. Sal is the dominant tree species.
- Human Settlements: The transition zone of the reserve has 1,200 villages with a total population of about 4.5 lakh. Tribals constitute about 73 per cent of the population.
How fire prone is Simlipal forest?
- Generally, with the onset of summers and towards the end of autumn, the forest area remains vulnerable to forest fires.
- They are a recurrent annual phenomenon, but are also brought under control due to short span of precipitation. The months of January and February witness rainfall of 10.8 and 21 mm, respectively.
- This duration coincides with the shedding of deciduous forests in the forest areas. The fallen leaves are more vulnerable to catching fire and facilitate the spreading of these forest fires quickly over the entire forest area.
Causes of forest fires
- Natural causes such as lighting or even soaring temperatures can sometimes result in these fires. With dried leaves and tree trunks, even a spark can lead to a raging fire.
- Poaching: Most of the fires can be attributed to man-made factors. Instances of poaching and hunting wherein the poachers set a small patch of forest on fire to divert the wild animals can lead to such fires.
- Collection of mahua flowers: jungle areas are also set on fire by villagers to clear the dry leaves on the ground for easy collection of mahua flowers. These flowers are used to prepare a drink which is addictive in nature.
- Traditional Practices: Villagers also believe burning patches of sal trees will lead to better growth when planted again.
- Climate Change: This year, along with man-made factors, an advanced heat wave with the early onset of summer further deteriorated the condition.
How are these forest fires controlled and prevented?
Such fires are generally brought under control by natural rains. some of the methods to prevent fires include
- Forecasting fire-prone days
- Creating fire lines: The forest fire lines which are strips kept clear of vegetation, help break the forest into compartments to prevent fires from spreading.
- Clearing sites of dried biomass
- Crackdown on poachers
- Including community members to mitigate incidents of fire
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements regarding BS-VI:
- The BS-VI grade fuel has 10 ppm sulphur.
- BS VI can bring Particulate Matter in diesel cars down by 80%.
- On-board diagnostics (OBD) is mandatory for all vehicles under BS-VI.
Which of the above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2 India’s first Engineering Research & Development (ER&D) Policy was launched recently by:
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
- Karnataka
- Telangana
ANSWERS FOR 3rd March 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | C |
Must Read
On criticism of government’s disinvestment plans:
On perils facing Britain:
On India’s migrant workers:











