IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Nutrient Loss in Wheat & Rice: ICAR Study
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Health and GS -III – Agriculture
In news
- Recently, researchers from various institutes under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) and Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya found depleting trends in grain density of zinc and iron in rice and wheat cultivated in India.
- Zinc and iron deficiency affects billions of people globally and the countries with this deficiency have diets composed mainly of rice, wheat, corn, and barley.
Findings of the study
- Zinc Concentrations in Rice and Wheat:
- For rice:Zinc concentrations in grains of rice cultivars depleted to 20.6 mg/kg (2000s) from 27.1 mg/kg (1960s)
- For wheat: The concentrations of zinc dropped to 23.5 mg/kg during the 2010s from 33.3 mg/kg (1960s)
- Iron Concentrations in Rice and Wheat:
- For rice: Iron concentrations in grains of rice cultivars depleted to 43.1 mg/kg within the 2000s from 59.8 mg/kg (1960s).
- For wheat: The concentrations of iron dropped to 46.4 mg/kg (2010s) from 57.6 mg/kg (1960s).
- A cultivar is a plant variety that has been produced in cultivation by selective breeding.
Reason for the Decrease
- ‘Dilution effect’ which is caused by decreased nutrient concentration in response to higher grain yield.
- This means the rate of yield increase is not compensated by the rate of nutrient take-up by the plants.
- Also, the soils supporting plants could be low in plant-available nutrients.
Suggestions
- Improving the grain ionome (that is, nutritional make-up) while releasing cultivars in future breeding programmes.
- There is a need to concentrate on other options like biofortification, where we breed food crops that are rich in micronutrients.
- Biofortification is the process by which the nutritional quality of food crops is improved through agronomic practices, conventional plant breeding, or modern biotechnology.
Initiatives Taken by India
- Recently, the Prime Minister dedicated 17 biofortified varieties of 8 crops to the nation.
- Some examples:
- Rice- CR DHAN 315 has excess zinc.
- Wheat- HI 1633 rich in protein, iron and zinc.
- Maize- Hybrid varieties 1, 2 and 3 are enriched with lysine and tryptophan.
- Madhuban Gajar, a biofortified carrot variety higher β-carotene and iron content.
- ICAR has started Nutri-Sensitive Agricultural Resources and Innovations (NARI) programme for promoting family farming linking agriculture to nutrition.
Biotech-KISAN Programme for North East region
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Sci and tech; Agriculture
In news
- The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has issued a Special Call for North East Region as a part of its Mission Programme “Biotech-Krishi Innovation Science Application Network (Biotech-KISAN)”.
- Aim: To understand the local problems of the NER farmers and provide scientific solutions to those problems.
Reason for the Special Call:
- The present call specifically focuses on the North East Region as it is predominantly agrarian with70% of its workforce engaged in agriculture and allied sector for livelihood.
- The region produces merely 1.5% of India’s food grain and continues to be a net importer of food grains even for its domestic consumption.
- The NE region has untapped potential to enhance the income of the farming population by promotion of location specific crops, horticultural and plantation crops, fisheries and livestock production.
About the Special Call:
- Objective: Linking available innovative agriculture technologies to the farm with the small and marginal farmers, specially women farmers of the region.
- The Hubs in NER will collaborate with the top scientific institutions across the country as well as State Agricultural Universities (SAUs) and other Farmers’ organizations in the NER for demonstrations of technologies and training of farmers.
About Biotech-KISAN
- It is a scientist-farmer partnership scheme launched in 2017 for agriculture innovation.
- Objective: To connect science laboratories with the farmers to find out innovative solutions and technologies to be applied at farm level.
- Progress:
- So far 146 Biotech-KISAN Hubs have been established covering all 15 agroclimatic zones and 110 Aspirational Districts
- The scheme has benefitted over two lakhs farmers so far by increasing their agriculture output and income.
- Over 200 entrepreneurships have also been developed in rural areas.
- Ministry: Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology.
Black Softshell Turtle
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Biodiversity
In news
- Recently, the Assam forest department has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with two NGOs and adopted a Vision Document to raise at least 1,000 black softshell turtles by 2030.
About Black Softshell Turtle
- Scientific Name: Nilssonia nigricans
- Habitat:
- They are found in ponds of temples in northeastern India and Bangladesh.
- Its distribution range also includes the Brahmaputra River and its tributaries.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Critically Endangered
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: No legal protection
- Threats:
- Consumption of turtle meat and eggs,
- Silt mining
- Encroachment of wetlands
- Change in flooding pattern.
Turtle Conservation
- National Marine Turtle Action Plan:
- It contains ways and means to not only promote inter-sectoral action for conservation but also guide improved coordination amongst the government, civil society and all relevant stakeholders.
- Indian Ocean Sea Turtle Agreement (IOSEA)
-
- India is a signatory to the Indian Ocean Sea Turtle Agreement (IOSEA) of the Convention on Migratory Species (CMS).
- It puts in place a framework through which States of the Indian Ocean and South-East Asian region and other concerned States can work together to conserve and replenish depleted marine turtle populations for which they share responsibility.
- KURMA App:
- It has a built-in digital field guide covering 29 species of freshwater turtles and tortoises of India.
- Developed by: Indian Turtle Conservation Action Network (ITCAN) in collaboration with the Turtle Survival Alliance-India and Wildlife Conservation Society-India.
Related articles:
Integrated Power Development Scheme (IPDS)
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Power resources
In news
- A 50 kWp Solar roof top was inaugurated in Solan, Himachal Pradesh under the Integrated power development scheme (IPDS) of Ministry of Power ,Government of India.
About Integrated power development scheme
- It was launched in the year 2014
- Launched by: Ministry of Power
- Eligible Utilities: All Discoms will be eligible for financial assistance under the scheme.
- It has following components:
-
- Strengthening of sub-transmission and distribution networks in the urban areas.
- Metering of distribution transformers in the urban areas.
- IT enablement of the distribution sector and strengthening of distribution network.
- Schemes for Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and IT enablement of balance urban towns.
- Underground cabling to include additional demand of States and smart metering solution for performing UDAY States and Solar panels on Govt. buildings with net-metering are also permissible under the scheme.
Maiden IN-EUNAVFOR Exercise
Part of: GS Prelims and GS II – International Relations
In news
- Indian Naval Ship Trikand, mission deployed for Anti-Piracy Operations, participated in the maiden IN – EUNAVFOR Joint Naval Exercise in the Gulf of Aden.
- Coordinated by: European Union Naval Force (EU NAVFOR).
-
- Along with Indian Navy, other naval forces are from Italy, Spain and France.
- The naval exercise included advanced air defence and anti-submarine exercises, tactical manoeuvres, Search & Rescue, and other maritime security operations.
- EUNAVFOR and the Indian Navy converge on multiple issues including counter piracy operations and protection of vessels deployed under the charter of World Food Programme (UN WFP).
- The two navies also have regular interaction through SHADE (Shared Awareness and Deconfliction) meetings held annually at Bahrain.
ABout Gulf of Aden
- The Gulf of Aden is also known as the Gulf of Berbera.
- It is a deepwater gulf between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, Socotra (Yemen), and Somalia to the south. (See the map)
- In the northwest, it connects with the Red Sea through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait, and it connects with the Arabian Sea to the east.
- To the west, it narrows into the Gulf of Tadjoura in Djibouti.
- The waterway is part of the important Suez Canal shipping route between the Mediterranean Sea and the Arabian Sea in the Indian Ocean.
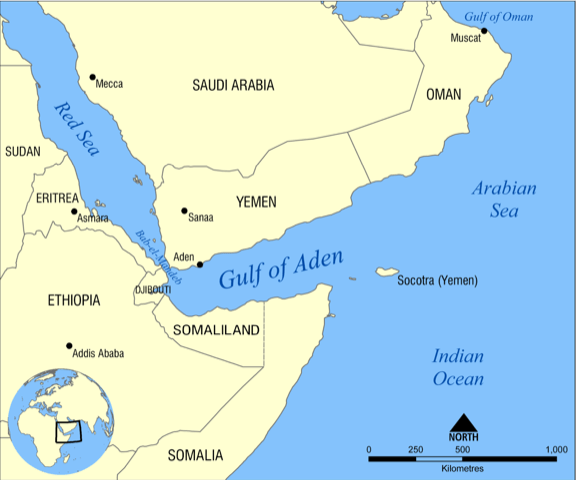
Pic courtesy: Wikipedia
Miscellaneous
Summer Solstice: 21st June
- 21st June is the longest day in the Northern Hemisphere, technically this day is referred to as Summer solstice.
- It is a natural phenomenon that occurs twice every year, once in the summer and again during winter, in each hemisphere of the earth – Summer and Winter Solstice.
- It is the longest day and shortest night of the year in the Northern Hemisphere.
- During this, countries in the Northern Hemisphere are nearest to the Sun and the Sun shines overhead on the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° North).
- During the solstice, the Earth’s axis — around which the planet spins, completing one turn each day — is tilted in a way that the North Pole is tipped towards the sun and the South Pole is away from it.
- Typically, this imaginary axis passes right through the middle of the Earth from top to bottom and is always tilted at 23.5 degrees with respect to the sun.
- At the Arctic Circle, the sun never sets during the solstice.
- 21st June is also observed as the International Yoga Day.
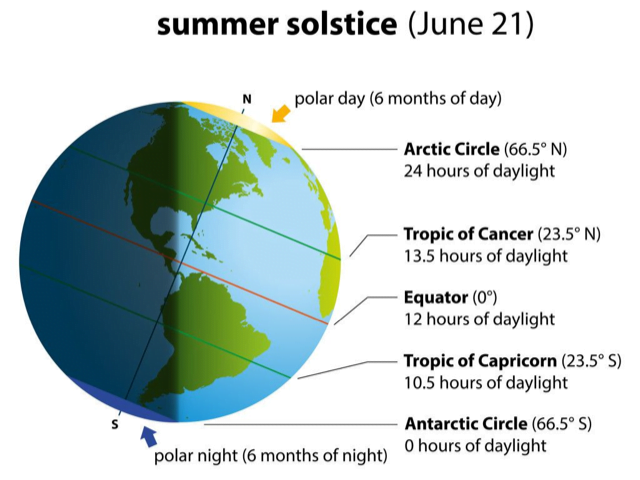
Pic courtesy: Pinterest
(Mains Focus)
POLITY/ ECONOMY
Topic:
- GS-3: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
- GS-3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Democracy & Social Media
Context: The Covid-19 pandemic has shown how social media, by connecting with various stakeholders, can help average citizens and complement the efforts of the governments in dealing with the crisis.
Positive Impacts of Social Media
- Sustains Democracy: Social media is an instrument that can question the seemingly invincible governments, make them accountable and bring sustained change driven by people beyond one vote in years.
- Direct connect between Politicians & Citizens: Social media provides unadulterated access for political leaders to connect with their own citizens
- Civic Engagement: Social media provides the platform for people tend to discuss & debate news over any topics. This interaction of people from varied backgrounds strengthens civil engagement in society.
Challenges
- Political Misuse: Data shows that political parties mostly in the last two years have spent around $800 million (Rs 5,900 crore) on election ad. Micro-targeting through social media can enable half-baked information to alter the agenda of elections & cause faultlines in society.
- Fake News: The anonymous nature provided by social media platforms can help people to spread fake news and misinformation. Since there is no editorial board in these companies, unlike traditional media, which makes the spread of fake news easy
- Intolerance to Contrary views: One of the most common criticisms of social media is that it creates echo chambers where people only see viewpoints they agree with — further driving us apart.
Conclusion
If there’s one fundamental truth about social media’s impact on democracy it’s that it amplifies human intent — both good and bad.
Connecting the dots:
- Twitter Controversy during Farmers protest
- Dominance of Big tech
- Australia’s News Media Bargaining Code
INTERNATIONAL/ SECURITY
Topic:
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
US-Russia: Biden-Putin Meet
Context: In March 2021, after assuming the White House, Mr. Biden described Mr. Putin as a “killer” and criticised Russia’s interference in US elections. Three months later, Biden met Putin and sought a more predictable relationship between the “two great powers”.
West & China
- Focus Shifted to China: Earlier NATO’s main focus was Russia now it is China. NATO members warned against the “systemic challenges to the rules-based international order” emanating from China’s rise.
- Criticism of China’s HR record: The G7 industrialised nations has recently issued a communique slamming China’s human rights records. Issues such as the detention of Uighurs in Xinjiang, the crackdown on dissent in Hong Kong, growing tensions with Taiwan was highlighted
- Collaboration to compete better: US and EU has decided to set up a high-level trade and technology council, which would boost innovation and investment, so as to better compete with China.
Changing US- Russia dynamics
- Ties between the US & Russia are at the lowest point since the end of the Cold War. There were allegations of Russian cyberattacks and election interference in the U.S., while Moscow is reeling under Western sanctions.
- When Mr. Biden moves forward, focusing on China, Russia remains a distraction.
- As a result, US wants to reset its ties with Russia and is looking for a détente (easing of hostility). With some predictability in ties with Russia, Mr. Biden can strengthen his China-focussed foreign policy
- The détente is also pragmatic for Russia. With a less hostile America, Mr. Putin can retain Russian influence in the country’s backyard and get relaxation from sanctions.
Conclusion
- It’s too early to see any meaningful change in Russia-U.S. relations. But the Geneva summit suggests that policymakers in Washington have at least started thinking of Russia as a secondary challenge that needs to be tackled diplomatically, not only through coercion,
Connecting the dots:
- China’s Belt and Road Initiative
- Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)
- Reviving SAARC to deal with China
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 In summer solstice, the season in the south of the equator is?
- Summer
- Winter
- Autumn
- Spring
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Indian Ocean Sea Turtle Agreement (IOSEA)
- India is not a signatory to the Indian Ocean Sea Turtle Agreement (IOSEA).
- It puts in place a framework through which States of the Indian Ocean and South-East Asian region can work together to conserve and replenish depleted marine turtle populations.
Which of the above is or are correct
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 21st June 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | C |
Must Read
On need for estimating poverty:
On Tax and Federalism:
On Green Hydrogen:












