IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Recent Reforms in Defence Sector
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -III – Security
In news
Recently, the Defence Minister released an E-booklet titled ‘20 Reforms in 2020’ highlighting the major reforms undertaken by the Ministry of Defence (MoD) in 2020.
- Structural Reforms: The post of Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) was created to increase efficiency & coordination among the Armed Forces and reduce duplication, while Department of Military affairs (DMA) was established to ensure improved civil-military integration.
- Boost to Indigenisation: To promote ‘Make in India’ in the defence sector, a list of 101 defence items for which there would be an embargo on the import was notified in August 2020, while Defence Acquisition Procedure 2020 was unveiled in September 2020. The increased partnership with the private sector has led to a substantial rise in defence exports.
- Funding: There was a 10% budget increase in 2020-21 over the previous year.
- Promoting Innovation: To promote innovation by young minds, five Young Scientists Laboratories of Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) were launched in 2020.
- Digitising Tribunals: The Armed Forces Tribunal began digital hearing for the first time in August 2020.
- Strategic Connectivity: World’s longest Atal tunnel above 10,000 feet, at Rohtang on the Leh-Manali Highway was inaugurated.
- Women Participation: Ten streams of Indian Army were opened for giving Permanent Commission to Short Service Commission (SSC) Women officers. All Sainik Schools were thrown open for girl students from academic session 2020-21.
- NCC: Expanding the reach of the National Cadet Corps (NCC) to remote locations was a major announcement.
Related Articles
- Challenges in India’s defence trade
- Grasping the Defence Self-reliance
Swachh Bharat Mission Grameen Phase-II
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Governance
In news
- Swachh Bharat Mission (Grameen) [SBM (G)] Phase-II is making steady progress amidst Covid-19 with 1249 villages declared ODF(Open Defecation Free) Plus.
About SBM(G) Phase-II:
- SBM (G) Phase-II was approved in February 2020 by the Ministry of Jal Shakti and will be implemented from 2020-21 to 2024-25 with total outlay of Rs. 1,40,881 crores.
- It emphasizes the sustainability of achievements under phase I and to provide adequate facilities for Solid/Liquid & plastic Waste Management (SLWM) in rural India.
- The fund sharing pattern between Centre and States will be 90:10 for North-Eastern States and Himalayan States and UT of J&K; 60:40 for other States; and 100% for other Union Territories.
Other Schemes as part of SBM:
- Individual Household Latrines (IHHL) initiative whereby individuals get around 15,000 Rs for the construction of toilets.
- GOBAR-DHAN (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources) Scheme launched by the Ministry of Jal Shakti in 2018.The scheme aims to augment income of farmers by converting biodegradable waste into compressed biogas (CBG).
- Swachh Vidyalaya Abhiyan launched by the Ministry of Education with an objective to provide separate toilets for boys and girls in all government schools.
World Food Safety Day
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Health; International
In news
- The Union Minister for Health and Family Welfare virtually attended the World Food Safety Day (7th June) celebrations organized by Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI).
- Access to sufficient amounts of safe food is key to sustaining life and promoting good health
- Global food waste accounts for 6.7% of global greenhouse gas emissions, directly leading to climate change.
About World Food Safety Day
- WHO and FAO jointly facilitate the observance of World Food Safety Day.
- It was first celebrated in 2019, to strengthen the commitment to scale up food safety made by the Addis Ababa Conference and the Geneva Forum in 2019 under the umbrella of “The Future of Food Safety”.
- Aim: To draw attention and inspire action to help prevent, detect and manage foodborne risks, contributing to food security, human health, economic prosperity, agriculture, market access, tourism and sustainable development.
- 2021 Theme: Safe Food for a Healthy Tomorrow.
Value Addition
Indian Initiatives for Food Safety:
- State Food Safety Index, released by FSSAI to measure the performance of States on five parameters of food safety namely Human Resources and Institutional Data, Compliance, Food Testing – Infrastructure and Surveillance, Training & Capacity Building and Consumer Empowerment.
- Eat Right India Movement: Initiative of the Government of India and FSSAI to transform the country’s food system in order to ensure safe, healthy and sustainable food for all Indians.
- Eat Right Awards: Instituted by FSSAI to recognize the contribution of food companies and individuals to empower citizens to choose safe and healthy food options,
- Eat Right Mela: Organised by FSSAI, it is an outreach activity for citizens to nudge them towards eating right
Also Read: COVID-19 and Food Security
I-Familia: Global Database to Identify Missing Persons
Part of: GS Prelims and GS –II- International
In news
- Recently, the Interpol has launched a new global database named “I-Familia” to identify missing persons through family DNA and help the police solve cold cases in member countries
About I-Familia:
- There is growing international concern about the number of missing persons and unidentified victims around the world due to increased international travel, the prevalence of organized crime and human trafficking, the rise in global migration, conflicts and natural disasters.
- The first of its kind, I-Familia is a global database for identifying missing persons based on international DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) kinship matching.
- The database seeks to identify missing persons or unidentified human remains when direct comparison is not possible, by using DNA samples from family members instead.
- Family members must give their consent for their data to be used for international searching.
Value Addition
International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- Interpol is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Lyon, France that helps coordinate the police force of 194 member countries.
- Each of the member countries hosts an Interpol National Central Bureau (NCB) which connects their national law enforcement with other countries and with the General Secretariat.
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) is designated as the National Central Bureau of India.
- Interpol Notices are international requests for cooperation or alerts allowing police in member countries to share critical crime-related information.
RBI’s Bimonthly Monetary Policy – June 2021
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy; Monetary policy
Various decisions were announced by RBI while unveiling Bimonthly Monetary Policy
- Policy Rate Unchanged: The Policy rate was unchanged at 4% for the sixth time in a row and reverse repo rate at 3.35%
- Growth Prospects downsized: India’s GDP growth rate projection was slashed to 9.5% due to uncertainties caused by second wave of COVID-19
- Liquidity Boost: Rs. 15,000-crore liquidity window to be launched by banks for contact intensive sectors like Hotel and tourism. Also, fresh Rs 16000-crore liquidity line to Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) for on-lending/ refinancing through novel models and structures.
- Upper limit for MSMEs revised: The maximum limit for borrowers is enhanced from Rs. 25 crore to Rs. 50 crore for MSMEs, small businesses and business loans to individuals
Value Addition
Monetary Policy Committee
- Urjit Patel committee in 2014 recommended the establishment of the Monetary Policy Committee.
- It is a statutory and institutionalized framework under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, for maintaining price stability, while keeping in mind the objective of growth.
- Composition: Six members (including the Chairman) – three officials of the RBI and three external members nominated by the Government of India. The Governor of RBI is ex-officio Chairman of the committee
- Functions: The MPC determines the policy interest rate (repo rate) required to achieve the inflation target (presently 4%). Decisions are taken by majority with the RBI Governor having the casting vote in case of a tie.
Miscellaneous

Pic Source: Al Jazeera
Sea Snot outbreak in Turkey
- Recently, Turkey’s Sea of Marmara, which connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea, has witnessed the largest outbreak of ‘sea snot’.
- Sea Snot, which looks like a viscous, brown and foamy substance, are huge mass of marine mucilage – a thick, slimy substance made up of compounds released by marine organisms.
- It is formed when algae are overloaded with nutrients as a result of water pollution combined with the effects of climate change.
- The nutrient overload occurs when algae feast on warm weather caused by global warming.
- Impact: Several species are under threat, livelihoods of fishermen are getting affected due to mass deaths among the fish population.
(Mains Focus)
EDUCATION/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Education, Human Resources
- GS-2: Federalism
Performance Grading Index
Context: The Education Ministry released the latest edition of the Performance Grading Index or PGI.
The Education Ministry released the first PGI in 2019 for the reference year 2017-18.
How is PGI worked out?
- Objective: This relatively new index measures the performance of states in school education. The objective is to help the states prioritise areas for intervention in school education
- Multiple Data Sources: It assesses states’ performance in school education based on data drawn from several sources, including the Unified District Information System for Education Plus, National Achievement Survey, and Mid-Day Meal.
- Parameters: States are scored on a total of 1,000 points across 70 parameters, which are grouped under five broad categories:
- Access (eg. enrolment ratio, transition rate and retention rate);
- Governance and management;
- Infrastructure
- Equity (difference in performance between scheduled caste students and general category students)
- Learning outcomes (average score in mathematics, science, languages and social science).
- Grading & not ranking: States are graded and not ranked to discourage the practice of one improving only at the cost of others, “thereby casting a stigma of underperformance on the latter”.
What does the grading system reflect?
The PGI grading system has 10 levels.
- Level 1 indicates top-notch performance and a score between 951 and 1,000 points.
- Level II, also known as Grade 1++, indicates a score between 901 and 950.
- Those with Grade 1+ (or Level III) have scored between 851 and 900.
- The lowest is Grade VII, and it means a score between 0 and 550 points.
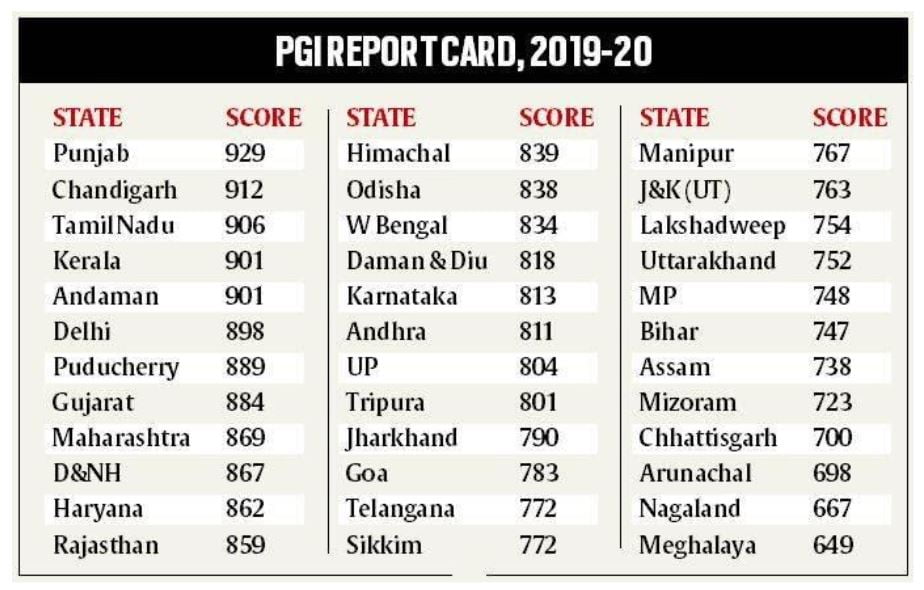
Source: Indian Express
How have states performed this time?
- None in first level: In PGI 2019-20, no state or Union Territory could achieve the highest grade, that is Level I. Even in the 2017-18 and 2018-19 editions, no state had reached Level 1 and Grade 1++.
- General Upward Shift: A total of 33 States and UTs have improved their total PGI score in 2019-20 as compared to 2018-19, indicating a general upward shift. For some this improvement has been improvements in their data reporting mechanisms while for some others, the improvements have been in specific domains
- Best Performing States: Chandigarh, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Andaman and Nicobar and Kerala have scored more than 90% and obtained Grade 1++ (or Level II), which makes them the best performing states. This is the first time that any state has reached Level II.
- Biggest Improvements: The biggest improvement in PGI this year has been shown by Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Punjab, and Arunachal Pradesh. All three have improved their score by 20%.
- Areas of Concern: However, there are still 31 states and UTs placed in Level III (Grade 1) or lower, showing that they still have a lot of ground to cover
- Only the UT of Ladakh has been placed in the lowest grade, that is Grade VII, but that’s because it was the first time it was assessed after it was carved out of Jammu and Kashmir in 2019.
What are the areas where the states still have to improve?
- The PGI accords the highest importance to Governance Domain because compliance with the indicators here will lead to critical structural reforms
- According to the report, states and UTs mainly need to improve their performance in terms of governance processes. This domain carries several parameters, including
- Teacher availability: monitoring the attendance of teachers
- Teachers training
- Regular inspection
- Availability of finances.
- In the domain Governance Processes, there are 24 States/UTs which have scored less than 288 (80% of the maximum possible score)
- The second area that requires attention is the Domain for Infrastructure and facilities. This is a cause for concern as a proper school building with adequate facilities is a must to improve the overall quality of school education
Connecting the dots:
- ASER Survey & COVID-19 impact
- ASER 2019 report: Fix early learning in government schools
- New Educational Policy, 2020
- Right to Education Act
ENVIRONMENT/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- GS-3: Environmental Conservation
Green future for Indian cities
Context: A progressive track of urban development while keeping sustainability, disaster risk resilience and community building at its core has been the guiding principle for urban development in India.
The following national programmes and missions of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs has contributed to the mitigation of Climate Change and helping India progress towards greener cities
The Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban)
- This scheme focuses on achieving an open-defecation-free India, building solid waste management capacity and bringing about behavioural change.
- Through the annual Swachh Survekshan, cooperative and competitive federalism have become the driving force behind this citizen-led jan andolan.
- It is estimated that the various initiatives under SBM-U can mitigate 17.42 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2022.
- It was, in effect, the harbinger of a total transformation of our urban landscape.
The Smart Cities Mission
- This mission has been the one taking charge of the technological advancements of our cities to improve governance, sustainability and disaster risk resilience.
- Smart solutions are being implemented to improve energy efficiency and non-motorised transport capacity in urban centres.
- The Climate Smart Cities Assessment Framework has been adopted which aims to help cities adapt, collaborate and exchange best practices to achieve international standards for green, sustainable and resilient urban habitats.
- So far, the infrastructure for 417.5 km of smart roads, solar panels generating 30 MW of energy and 253.5 MLD of wastewater treatment capacity has been completed.
- The overall reduction in GHG emissions from projects implemented under SCM is expected to reach 4.93 million tonnes of CO2 by 2022.
Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
- Under AMRUT, water supply and management, energy efficiency and increased green spaces have been part of the goal in 500 target cities.
- As of June 2021, 1,831 parks over 3,700 acres have been developed, 85 lakh street lights have been replaced, resulting in energy saving of 185.33 crore units (kWh), and 106 water bodies have been rejuvenated.
- The mission is likely to result in the mitigation of 48.52 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent of GHG emissions by 2022.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Urban)
- With 1.12 crore houses sanctioned, PMAY(U) has focused on new construction technologies that are innovative, environmentally friendly and disaster-resilient.
- The Global Housing Technology Challenge was launched, and 54 new technologies identified & incorporated in construction.
- About 43.3 lakh houses are being constructed where fly ash bricks/blocks and concrete blocks are being used.
- Overall, the mission has the potential to mitigate around 12 million tonnes CO2 equivalent of GHG emissions by 2022.
Public Transport- Metro
- Lastly, the metro rail, an energy-efficient mass rapid transit system, is operational in 18 cities with over 720 km of line constructed.
- Another 1,055 km of new lines is under construction in 27 cities.
- This network is expected to mitigate around 21.58 million tonnes of CO2 eq GHG from 2015-2022.
Conclusion
Cumulatively, the national missions under the MoHUA are projected to mitigate GHG emissions equivalent to more than 93 million tonnes of CO2 by 2022. This number is bound to increase.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Consider the following statements:
- There has been10% budget increase in 2020-21 over the previous year for the defence sector
- Atal tunnel was constructed by National Highways Authority of India
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding GOBAR-DHAN (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources) Scheme:
- It was launched by the Ministry of Agriculture
- It aims to augment income of farmers by converting biodegradable waste into compressed biogas (CBG).
Which of the above is or are correct ?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 8th June 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | B |
Must Read
On centralised procurement of vaccines:
On preparing for third wave:
About Human Rights in Digital Era:











