IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Local sales by SEZ units without import tag
Part of: Prelims and GS – III – Economy
Context The government is considering a proposal to allow producers in Special Economic Zones (SEZs) to sell their output to the domestic market without treating them as imports. It is also reviewing the exclusion of export-oriented units (EOUs) and SEZs from the recently notified tax refund scheme for exports.
- It was also emphasised recently that despite the rise in freight rates and input costs, SEZ and EOU units had not been given benefits under the Remission of Taxes and Duties on Export Products (RoDTEP) scheme.
What is the RoDTEP Scheme?
- The Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) Scheme was announced in 2019 by the Government of India and it became effective on 1 January 2021.
- It allows exporters to receive refunds on taxes and duties that are not exempted or refunded under any other scheme.
- Aim: To boost the export of goods that were poor in volume.
- It replaces the Merchandise Export from India Scheme (MEIS).
- It is a combination of the MEIS and the Rebate of State and Central Taxes and Levies (RoSCTL).
- Under this scheme, refund would be claimed as a percentage of the Freight On Board (FOB) value of exports.
What are Special Economic Zones (SEZ)?
- It is a specifically delineated duty-free enclave, deemed to be foreign territory for the purposes of trade operations and duties and tariffs.
- Goods and services going into the SEZ area from Domestic Tariff Area (whole India except SEZ) shall be treated as exports and goods coming from the SEZ area into DTA shall be treated as imports.
- SEZ units may be set up for manufacture of goods and rendering of services.
- The business and trade laws are different from the rest of the country.
- SEZs are located within a country’s national borders.
- Their aims include increasing trade balance, employment, increased investment, job creation and effective administration
- The present rule governing SEZ units is that SEZ units may import/procure goods and services from DTA without payment of import duty. But when SEZs are selling goods into DTA then Import/Customs Duty is imposed.
News Source: TH
Cairn Energy to end tax dispute with India
Part of: Prelims and GS – III – Economy
Context The U.K.-based Cairn Energy is working with the Government of India to expedite “documentation and payment of refund” of $1.06 billion of retrospective taxes.
- In its half-yearly report, Cairn said it plans to return $700 million to the shareholders through special dividends and buybacks, out of the expected tax refund from the Indian government.
Recent Amendment to I-T laws by the Indian government
- The government recently amended the income tax laws to scrap the retrospective tax provisions introduced in 2012-13, under which Cairn was taxed in 2014 for a corporate restructuring undertaken in 2006-07.
- The tax department subsequently froze the firm’s shares as part of the proceedings and sold them off to recover the claimed tax dues.
- The changes propose to refund the taxes levied retrospectively if the affected taxpayers drop all pending litigation and forego any interest and damages claims.
Tribunal verdict
- An international arbitration tribunal, scrutinising the tax dispute, last year ruled in Cairn’s favour and awarded $1.2 billion in damages to the company. While the government has filed an appeal against the verdict, Cairn has filed lawsuits in several overseas jurisdictions to enforce the tribunal’s award.
Background
- The year in reference, 2006-07, was one in which big corporate changes and developments took place in Cairn Energy.
- It was the year in which it not only undertook a corporate reorganisation, but also floated an Indian subsidiary, Cairn India, which in early 2007 got listed on the Indian bourses.
- Through the corporate reorganisation process, Cairn Energy had transferred all of its India assets, which were until then held by nine subsidiaries in various countries, to the newly-formed Cairn India.
- But the tax authorities claimed that in the process of this reorganisation, Cairn Energy had made capital gains worth ₹24,500 crore. This, the department asserted, was the basis of the tax demand of 1.6 billions USD.
- In 2011, the U.K.-based Vedanta Resources bought a nearly 60% stake in Cairn India. In fact, four years after this, Cairn India received a tax notice for not withholding tax for the gains ascribed to its former parent company.
News source: TH
CSCs and Passport Services
Part of: Prelims and GS – II – Policies and interventions
Context The Common Services Centres (CSC) has received approvals to manage and operate Passport Seva Kendra kiosks in rural areas.
Key takeaways
- The village-level entrepreneurs (VLEs), who operate the CSCs, will be entrusted with collecting documents, photographs and other details necessary for the passport process as well as the initial non-police verification.
- A nominal fee of up to Rs 100 could be charged for the same.
- The pilot for the programme was launched at a few CSCs in Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
- Full-fledged services will be rolled out nationwide soon
What is CSC?
- The CSC is a special purpose vehicle of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- CSCs are physical facilities for delivering Government of India e-Services to rural and remote locations where availability of computers and Internet was negligible or mostly absent.
- They are multiple-services-single-point models for providing facilities for multiple transactions at a single geographical location.
- Current function of CSCs
-
- At present, CSCs are allowed only to fill and upload application forms for others, pay an applicable fee on an applicant’s behalf, and schedule an appointment for them.
- It has over the past three years tied up with partners, both in the public and private sector, across domains by leveraging their presence across the country.
- They have done tie-ups with domestic and multinational corporations as well such as Tata, PepsiCo, Unibic foods, etc.
- During lockdown, VLEs also opened up Grameen e-store for easy delivery of essential and non-essential items in villages, gram panchayats and other rural areas.
News source: IE
UAE’s Green Visa
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- II – International Relations
Context The United Arab Emirates has announced a new class of visas intended to ease the restrictions faced by foreigners in pursuing employment opportunities in the country, referred to as “green visa”.
Key features of the new visa
- Under the green visa, foreigners will be allowed to work in the UAE without being sponsored by an employer.
- The green visa will enable visa holders to sponsor their parents.
- It will increase the cap on the age of children who can be sponsored by the holder from 18 to 25.
- The program will also allow the holder a grace period of up to three months to look for a new job if they lose their old one.
News source: IE
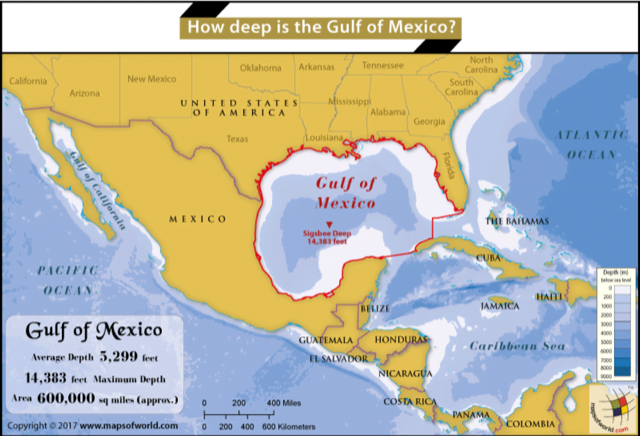
Oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico
Part of: GS Prelims and GS- III – Environment
Context Clean-up crews and the US Coast Guard are trying to locate the source of an oil spill spotted in the Gulf of Mexico after deadly Hurricane Ida.
- Recent satellite photos by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) showed the slick about two miles (3km) off Port Fourchon, Louisiana.
What is the source of the spill?
- The source of the miles-long oil spill was believed to be in the Bay Marchand area of the Gulf of Mexico.
- It appears to be coming from a source underwater at an offshore drilling site
- Damaged pipelines in the Bay are possible reasons for the spill.
Gulf of Mexico
- The Gulf of Mexico is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent.
What is an oil spill?
- An oil spill refers to any uncontrolled release of crude oil, gasoline, fuels, or other oil by-products into the environment.
- Harmful effects of oil spill
- Oil spills can pollute land, air, or water.
- It prevents sufficient amounts of sunlight from penetrating the surface.
- It also reduces the level of dissolved oxygen.
- Oil-coated birds and marine mammals may die from hypothermia
- Ingested oil can be toxic to affected animals, and damage their habitat and reproductive rate.
Cleanup of Oil Spill:
- Containment Booms: Floating barriers, called booms are used to restrict the spread of oil and to allow for its recovery, removal, or dispersal.
- Skimmers: They are devices used for physically separating spilled oil from the water’s surface.
- Sorbents: Various sorbents (e.g., straw, volcanic ash, and shavings of polyester-derived plastic) that absorb the oil from the water are used.
- Dispersing agents: These are chemicals that contain surfactants, or compounds that act to break liquid substances such as oil into small droplets.
- Biological agents: Nutrients, enzymes, or microorganisms such as Alcanivorax bacteria or Methylocella silvestris that increase the rate at which natural biodegradation of oil occurs are added
News source: IE
(News from PIB)
Poshan Vatika for alleviation of malnutrition
Part of: GS Prelims and GS -II – Health
In News: The Ministry of Ayush and Ministry of Women and Child Development jointly organised a webinar on the importance of ‘Poshan Vatika’ (Nutri Garden) for alleviation of malnutrition.
About POSHAN Vatika
- Rural areas have ample space and establishing a Nutri garden/Poshan Vatikas is far simpler as farm families are involved in agriculture.
- Plantation of nutritional and herbal trees under PoshanVatika would reduce external dependency and make communities Atmanirbhar for their nutritional security.
- The Ministry of Ayush will collaborate with 3,000 Aanganwadis to take forward the campaign of establishing Nutri Garden and will also decide the nutritional and herbal trees that will be planted there.
- Plants such as Moringa, Guava, Banana and Tulsi are great candidates to plant in a Poshan Vatika as they deal with problems of malnutrition in women and children.
Significance of Poshan Vatika
- Poshan Abhiyaan aims to encourage convergence among various Ministries to tackle the problem of malnutrition. Aanganwaadi covers 50% of the people who are poor and don’t get proper nutrition while Poshan Abhiyaan covers the other 50% who might not be poor but need information about proper nutrition
- Can play an important role in enhancing dietary diversity by providing micronutrients through constant supply of fruits and vegetables sufficient to meet the family’s requirements, which can prove to be a sustainable model for providing food security and diversity to combat malnutrition at the household or community level.
The Ministry of Ayush:
- AYUSH is the acronym for Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha and Sowa, Rigpa and Homeopathy, (Sowa and Rigpa added later).
- The Ministry aims to develop education and research in the above fields.
- Originally formed in 1995 as Department of Indian Medicines and Homeopathy (IM&H), it was renamed to AYUSH in 2003 and given a separate ministry in Nov’ 2014.
POSHAN Abhiyaan: POSHAN (Prime Minister’s Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nutrition) Abhiyaan
- It is Government of India’s flagship programme to improve nutritional outcomes for children, adolescent girls, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- Ministry: Ministry of Women & Child Development
- Mission Poshan 2.0 (Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0) has been announced in the Budget 2021-2022 as an integrated nutrition support programme.
- Objectives: To strengthen nutritional content, delivery, outreach and outcomes, with a focus on developing practices that nurture health, wellness and immunity to disease and malnutrition.
- Target: Reducing stunting, under-nutrition, anemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls) and low birth weight by 2%, 2%, 3% and 2% per annum respectively.
- Poshan Gyan: A national digital repository on health and nutrition
Must Read:Important Portals in the Ayush sector
News Source: PIB
Parkash Purab of Sri Guru Granth Sahib Ji
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-1
In News: The Prime Minister has greeted the people on the sacred occasion of the Parkash Purab of Sri Guru Granth Sahib Ji.
- The occasion marks the completion of the holy book of Sikhs, Sri Guru Granth Sahib Ji, under the supervision of the fifth Guru Arjan Dev Ji in 1604 at Gurdwara Ramsar Sahib.
About Parkash Purab of Sri Guru Granth Sahib Ji
- The first Prakash Purab Utsav marked the installation of Guru Granth Sahib in Harmandir Sahib, also known as the Golden temple, in 1604.
- After the death of Guru Gobind Singh, his hymns and other writings were compiled into a book known as the Dasam Granth.
Kartarpur Sahib Corridor: Most celebrated project of Sikhs of India and Pakistan in recent times
- Facilitates pilgrims from India to visit the Gurdwara Kartarpur Sahib in Pakistan. The corridor is being built to connect Dera Baba Nanak in Gurdaspur with Gurdwara Darbar Sahib in Kartarpur, the final resting place of Sikhism founder Guru Nanak.
- Indian pilgrims of all faiths and persons of Indian origin can use the corridor.
- The travel will be Visa Free; Pilgrims need to carry only a valid passport
- Pilgrims would be allowed to carry kirpans (dagger), one of the five articles of faith worn by Sikhs.
Gatka: A traditional Sikh martial art
News Source: PIB
Coal based Hydrogen
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III-Energy
In News: Ministry of Coal has constituted two Committees, one to oversee the program and another of experts to give guidance to the Ministry. This is aimed for contributing to PM’s agenda of a hydrogen-based economy in a clean manner.
Producing Hydrogen through Coal
- Coal is one of the important sources of hydrogen making (Brown Hydrogen) apart from Natural Gas (Grey hydrogen) and renewable energy (Green Hydrogen) through electrolysis. In case of renewable energy (Green Hydrogen) surplus solar power is used to electrolyze water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- The global emphasis is on substituting liquid fuels with hydrogen (as fuel in vehicles), storage of surplus renewable power as hydrogen (as power cannot be stored at a cost effective price), and cutting down emission.
- However, Coal has not been encouraged elsewhere because of the fear that while extracting hydrogen via coal (from the moisture embedded in coal) there may be carbon emission.
- Almost 100% of Hydrogen produced in India is through Natural Gas.
The Challenges
Production of hydrogen from coal will have challenges in terms of high emissions and ‘carbon capture, utilisation and storage’ (CCUS) will play an important role. However, when the carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide formed during coal to hydrogen process are trapped and stored in an environmentally sustainable manner (CCUS), then, Indian coal reserves could become a great source of hydrogen.
- For every tonne of brown hydrogen produced, we get – at a minimum – between 10 and 12 tonnes of CO2. That’s not even including the CO2 produced by the energy source driving the process, or the CO2 produced in transporting the hydrogen to the customer. In all, production and transport of brown hydrogen is very bad for the environment.
- In steel making, lots of work has been done on production of steel by use of Hydrogen. However, iron reduction through hydrogen is an endothermic reaction and will require lot of heat. This heat can be generated in DRI plants due to presence of CO in syn Gas being produced from coal gasification process.
News Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
AGRICULTURE/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-3: Major crops-cropping patterns in various parts of the country,
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Significance of Millet Farming
Context: UN General Assembly adopted a resolution declaring 2023 the International Year of Millets, as proposed by India to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
About Millets
- Millets are coarse grains and a repository of protein, fibre, vitamins and minerals.
- They include jowar (sorghum), ragi (finger millet), korra (foxtail millet), arke (kodo millet), sama (little millet), bajra (pearl millet), chena/barr (proso millet) and sanwa (barnyard millet).
- Millets were one of the oldest foods known to humans. But they were discarded in favour of wheat and rice with urbanization and industrialization
- India is their largest global producer, with a 41% market share, and a compound annual growth rate of 4.5% is projected for the global millet market in the coming decade.
What are the advantages with Millets?
- Climate Resilience
- Being hardy crops, they can withstand extreme temperatures, floods and droughts.
- They also help mitigate the effects of climate change through their low carbon footprint of 3,218-kg CO2 equivalent per hectare, as compared to wheat and rice, with 3,968kg and 3,401kg, respectively, on the same measure.
- Restoration of ecosystems and sustainability:
- Land degradation has been a major problem in India, causing massive economic losses year after year. Drought-tolerant crops, like millets, with low dependence on chemical inputs would put far less pressure on ecosystems.
- The inter-cropping of millets with other crops is especially beneficial because the fibrous roots of millet plants help in improving soil quality, keep water run-off in check and aid soil conservation in erosion-prone areas, thereby restoring natural ecosystems.
- Biofuel and Ethanol Blending
- In June 2021, government set a target of achieving 20% ethanol blending with petrol by 2025.
- Most bio-ethanol in India is produced using sugar molasses and maize.
- However, a study conducted among farmers in Madhya Pradesh showed that bio-ethanol can be created using sorghum (jowar) and pearl millet (bajra), and that this fuel could bring down carbon emissions by about half.
- Estimates also suggest that millets can deliver greater returns than maize, while using 40% less energy in processing. Millets also offer a significant cost advantage over maize as a feedstock for bio-ethanol production.
- A cultural connection:
- The cultivation of millets is deep-rooted in Indian culture.
- Organizations like Deccan Development Society have formed women’s collectives in Telangana and are promoting millets through a culture-centric approach.
- Such crop sensitization has filtered into urban settings too. In 2018, the #LetsMilletCampaign in Bengaluru saw the use of millets in dishes such as risotto and pizza by restaurateurs.
- Helps address Sustainable DGs:
- Millets can play a role in India’s sustainability policy interventions. Contemporary research developments have shed light on the influence of millets on energy optimization, climate resilience and ecosystem restoration.
- Millet farming has led to women’s empowerment, too. The Odisha Millet Mission, for example, saw 7.2 million women emerge as ‘agri-preneurs’.
What are the concerns with Millets growth?
- A rise in incomes and urbanization has reduced the demand for millets
- Inadequate government policies.
- Unjust pricing for farmers due to intermediaries.
- Lack of input subsidies and price incentives.
- Procurement and subsidised supply of rice & wheat through the PDS has made farmers shift from millets to these crops.
- Millets being used for various purposes other than for consumption.
Way Forward
- Incentivizing the adoption of inter-cropping with millets (two or more crops planted side by side) and providing crop insurance and support for storage facilities will foster income and food security.
- Brimming with potential, millets can act as a vital cog in the country’s sustainable development wheel if backed by policies that promote their production, incentivize farmers and strengthen market linkages.
Connecting the dots:
INTERNATIONAL/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-2: Indian Neighbourhood
- GS-2: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
Taliban and China
Context: China is filling the power vacuum created by abrupt US withdrawal from Afghanistan & Taliban taking over the country.
Do You Know?
- Since 2001, the U.S. has spent $2.26 trillion in Afghanistan, out of which $1.53 trillion was spent on defence.
- The Afghan economy did not flourish, with 90% of its population still living below poverty line, with less than $2 a day.
China and Taliban
- The return of the Taliban is seen as a victory of Chinese diplomacy and a failure for the USA. China (also, Russia) have kept their embassies running in Kabul while the western embassies have disappeared.
- Afghanistan has rare-earth metals and huge deposits of copper. The Chinese are interested in these resources as they have the technology to excavate them.
- Also, China is engaging with the Taliban, to ensure success of Belt & Road Initiative (BRI). This being a huge investment requires many years of successful operation to yield profit. Therefore, Taliban support is necessary for China.
What are the intentions of China’s investment strategy in BRI (more particularly in CPEC)?
- The cost of production is lower in this region and therefore Chinese firms could gain by shifting their production bases from China to these regions.
- Investing in these regions meant access to bigger markets for Chinese firms
- It also enables more uniform regional development for China (western underdeveloped part of China can emerge as economic hub)
- Chinese firms could evade high-tariff & non-tariff measures targeted at Chinese goods when they begin exporting from here.
- Investing in Africa and Asia has also reduced some of China’s energy requirements, enabling China to access cheaper foreign energy (oil and power) and minerals.
Challenges for China
- No businesses can flourish in the presence of terrorism. With Taliban gaining power, there is concern of resurgence of terrorist groups such as al Qaeda, Daesh, and the Islamic State.
- Taliban is also known to have a soft corner for the East Turkestan Islamic Movement — a militant group active in the Uighur province of China (Muslim majority province).
- There are doubts on the economic capability to repay Chinese granted loans or projects. Pakistan is unable to repay a China-funded energy project, built under the BRI.
- The Taliban ruling groups are far from united, making it impossible to make any reliable domestic and international policy predictions. This doesn’t fit with the stable autocracy like China.
- Rebellions, factional wars, will be the likely events in Taliban-controlled Afghanistan. These issues will spread to Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Turkey, and other essential rings in the BRI chain. Hence, the cash flow into the BRI will constantly face a risk of interruption
Conclusion
In a game of chess, the U.S. move of vacating Afghanistan may in fact prove costly for China.
Can you answer this question now?
Chinese presence in Afghanistan with an all-weather ally Pakistan may sound trouble for India. Discuss. (250 words, 15 marks).
(AIR Spotlight)
Spotlight Sep 7: Discussion on BRICS Summit 2021: Expectations and Challenges.
GOVERNANCE/ ECONOMY
- GS-2: Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
- GS-2: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
BRICS Summit 2021
Context: As part of India’s ongoing Chairship of BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) in 2021, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi (2nd time) will chair the 13th BRICS Summit on 9 September 2021 in virtual format.
The theme for the Summit is ‘BRICS@15: Intra-BRICS cooperation for continuity, consolidation and consensus’. India had outlined four priority areas for its Chairship. These are –
- Reform of the Multilateral System
- Counter Terrorism: Cooperation for continuity, consolidation and consensus
- Using Digital and Technological Tools for achieving SDGs
- Enhancing People to People exchanges
In addition to these areas, the leaders will also exchange views on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and other current global and regional issues.
India will be hosting the BRICS Summit for the 3rd time.
Expectations from the Summit
- Afghanistan Issue: Apart from business and economic issues, the summit is expected to see extensive discussions on the Afghanistan crisis and BRICS leaders may also issue a joint statement on the latest situation in the country.
- Framework for greater cooperation in services trade: May promise easier movement of professionals across BRICS nations. This is expected to eventually lead to discussions on movement of natural persons, such as independent professionals (called Mode 4 services trade) and Mode 1, the cross- border supply of services, sources said. While broad level consensus has been achieved so far, it is expected to slowly open doors to Indian professionals moving freely within BRICS economies as well as expand on services trade in the region.
- Pledge to establish a common approach towards the multilateral trading system, keeping in mind the upcoming 12th Ministerial Conference of the World Trade Organisation to be held in Geneva in December 2021. This is expected to bring the BRICS countries on an unprecedented common platform on matters of global trade policy. While India and China have often advocated for developmental goals and policies, leading poor and developing nations at the global fora, significant differences exist among BRICS nations with regards to trade policy. A new move towards papering over these differences will prove to be the biggest achievement in India’s trade diplomacy.
- The government has said that despite numerous challenges and constraints, India was successful in building consensus for new areas of work and cooperation among BRICS countries. As a result, for the first time, a common understanding has arisen amongst BRICS countries on a wide range of areas. These include new declarations related to consumer protection, e-commerce, genetic resources and traditional knowledge.
- Trade push: The Commerce Department is currently giving the final touches to its internal reports that pinpoint the areas where trade can be quickly ramped up. This comes after a push by the Prime Minister’s Office on the issue. Barring trade with China, India’s trade with the 15-year-old grouping has not expanded nearly as much as New Delhi had earlier hoped for. India hopes to fix this through a combination of targeted exports, based on demand in these markets, easing of rules of customs, trade and standards and a greater political will.
India’s total trade with the BRICS countries in 2020-21 stood at $110 billion in 2019-20, which rose to $113.3 billion in 2020-21, despite COVID-19. India’s trade figures for the grouping is heavily dictated by its trade with China ($86.4 billion in FY21). The latest rise was also majorly due to a rise in trade with China.
Conclusion
- The idea of BRICS – a common pursuit of shared interests by the five emerging economies from four continents – is fundamentally sound and relevant.
- It is still possible that the BRIC grouping could become as large as the G7 within the next generation. The governments have invested huge political capital in pushing the BRICS experiment forward. Therefore, the strains in the grouping needs to be addressed to keep alive the relevance of it.
Can you answer this question now?
The grouping succeeded up to a point but it now confronts multiple challenges. Do you agree? Discuss.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 Which of the following are correctly matched?
- Typhoons: China Sea and Pacific Ocean.
- Hurricanes: Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean.
- Willy-willies: In north-western Australia
- Tropical Cyclones: In the Indian Ocean Region.
Select the correct answers:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Common Service Centers:
- The CSC is a special purpose vehicle of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- CSCs are physical facilities for delivering Government of India e-Services to rural and remote locations where availability of computers and Internet was negligible or mostly absent.
Select the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Which of the following countries has recently launched Green visa for its workers?
- USA
- Japan
- UAE
- Israel
ANSWERS FOR 8th Sept 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | B |
Must Read
On Economic Reforms:
On Reservation Policy:
On Tribunals:











