IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA)
Part of: Prelims and GS – II – Civil society
Context The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has extended the deadline till December 31 for NGOs to apply for renewal of their Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA) registration certificates.
- The registration is mandatory for associations and NGOs to receive foreign funds.
What is Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA)?
- Foreign funding of persons in India is regulated under FCRA Act and is implemented by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The Act ensures that the recipients of foreign contributions adhere to the stated purpose for which such contribution has been obtained.
- Under the Act, organisations are required to register/renew themselves every five years.
- Registered NGOs can receive foreign contributions for five purposes — social, educational, religious, economic and cultural.
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Amendment Act, 2020
- Prohibition to accept foreign contribution: The Act bars public servants from receiving foreign contributions.
- Transfer of foreign contribution: The Act prohibits the transfer of foreign contribution to any other person not registered to accept foreign contributions.
- Aadhaar for registration: The Act makes Aadhaar number mandatory for all office bearers, directors or key functionaries of a person receiving foreign contribution, as an identification document.
- FCRA account: Foreign contribution must be received only in an account designated by the bank as FCRA account in such branches of the State Bank of India, New Delhi.
- Reduction in use of foreign contribution for administrative purposes: Not more than 20% of the total foreign funds received could be defrayed for administrative expenses. In FCRA 2010 the limit was 50%.
- Surrender of certificate: The Act allows the central government to permit a person to surrender their registration certificate.
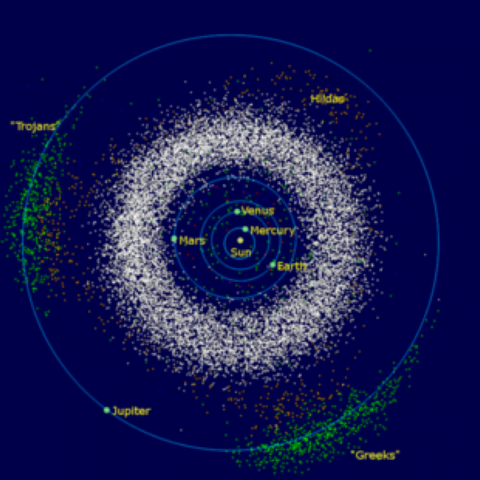
NASA’s Lucy mission to probe Jupiter’s mysterious Trojan asteroids
Part of: Prelims and GS III – Sci and Tech
Context NASA is poised to send its first spacecraft to study Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids to glean new insights into the solar system’s formation 4.5 billion years ago.
- The Jupiter trojans, commonly called Trojan asteroids or simply Trojans, are a large group of asteroids that share the planet Jupiter’s orbit around the Sun.
Key takeaways
- The probe, called Lucy after an ancient fossil that provided insights into the evolution of human species, will launch on October 16 from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
- Mission: To investigate the group of rocky bodies circling the Sun in two swarms, one preceding Jupiter in its orbital path and the other trailing behind it.
- After receiving boosts from Earth’s gravity, Lucy will embark on a 12-year journey to eight different asteroids — one in the Main Belt between Mars and Jupiter and then seven Trojans.
- Trojans are present in a very small region of space and are very physically different from one another. The differences indicate how far away from the Sun they might have formed before assuming their present trajectory.
- Trojan asteroids number more than 7,000 in total.
- It will be the first solar-powered spaceship to venture this far from the Sun, and will observe more asteroids than any other spacecraft before it.
OCI candidates can appear in general category
Part of: Prelims and GS-II – Education
Context The Supreme Court has permitted Overseas Citizens of India (OCI) candidates to participate in the NEET-UG 2021 counselling in the general category.
The court clarified that the order allowing the OCIs to compete in the general category was confined to the 2021-2022 academic year alone.
Background
- Ministry of Home Affairs had directed OCI candidates to be treated on a par with Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) for the purpose of NEET.
- This would have meant that successful OCI candidates would have to pay the higher fee paid by NRIs for medical seats in India.
What is the difference between NRI and OCI?
- NRI is given to provide a residential status to a citizen of India with an Indian Passport who resides in a foreign country for the purpose of work/business, or education.
- OCI is an immigration status which is provided to a foreign citizen of Indian origin as an alternative for dual citizenship which is not allowed by the Indian Constitution.
China can join Quad initiatives
Part of: Prelims and GS II – International Relations
Context Recently Australian Prime Minister said that China is welcome to contribute to the objective of ensuring a free and open Indo-Pacific through QUAD initiatives.
QUAD
- Full form: Quadrilateral Security Dialogue
- Countries: USA, Japan, Australia and India
- Location/Headquarter: –
- Aims: The main aim is to enable a regional security architecture for the maintenance of a rules- based order. It seeks to contain a ‘rising China’ and work against its predatory trade and economic policiesThe main
Right to seek bail implicit in Constitution: Supreme Court
Part of: Prelims and GS II – Rights And duties
Context The Supreme Court has held that the right to apply for bail is an “individual right” implicit in the Constitution.
- The right of an accused, an undertrial prisoner or a convicted person awaiting appeal court’s verdict to seek bail on suspension of sentence is recognised in Sections 439, 438 and 389 of the Code of Criminal Procedure.
- If there is a blanket ban on listing of these applications, even for offences with lesser degree of punishment, it would effectively block access for seekers of liberty to apply for bail and suspend the fundamental rights of individuals in or apprehending detention.
- Such an order also has the effect of temporarily eclipsing statutory provisions.
Background
- A Single Judge of the Rajasthan High Court had in March passed an order to not to list bails, appeals, applications for suspension of sentence in appeals and revisions in the category of extreme urgent matters.
Meghalaya Enterprise Architecture Project (MeghEA)
Part of: Prelims and GS II – Policies and interventions
Context Recently, Meghalaya Enterprise Architecture Project (MeghEA) was launched.
- The project aims to improve service delivery and governance for the people using the power of Digital technologies.
- Enterprise Architecture (EA) is the process by which organizations standardize and organize IT (Information Technology) infrastructure to align with business goals.
Key takeaways
- The initiative is spread across 6 pillars i.e. Governance, Human Resources, Entrepreneurship, Primary Sector, Infrastructure and Environment, and envision to make Meghalaya a high income state by 2030.
- It is envisioned to make Meghalaya a high income state by 2030.
- MeghEA is conceived to support the following digital government goals:
- A planned state government transformation initiative which demands efficient coordination between strategies, policies, processes, services and organizational capacity
- Coordinate all ICT initiatives under one umbrella to get a better holistic perspective
- Implement and ICT enable state government process reengineering to provide multi-channel service delivery
- Ensure that state government applications and systems provide end-users with information they need
- Craft an ecosystem for the digital economy to boost shared prosperity, by leveraging ICT for employment and growth.
India Enterprise Architecture (IndEA)
- It is a framework that enables the development and implementation of Enterprise Architectures independently and in parallel by all governments and their agencies across India, conforming to the same models and standards.
- It was notified as an e-Governance standard by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in October 2018.
- The primary purpose of IndEA is to help state governments, ministries and departments in the governments at various levels to adopt a structured approach for developing their enterprise architecture.
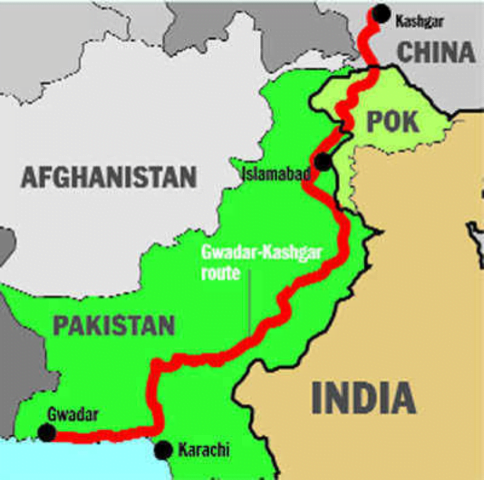
Extension of CPEC to Afghanistan
Part of: Prelims and GS II – International Relations
Context Recently, Pakistan has discussed Taliban-led Afghanistan joining the multibillion-dollar China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) infrastructure project.
- China has proposed construction of the Peshawar-Kabul motorway as an extension of CPEC in Afghanistan.
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor
- The CPEC is a bilateral project between Pakistan and China.
- It is intended to promote connectivity across Pakistan with a network of highways, railways, and pipelines accompanied by energy, industrial, and other infrastructure development projects.
- It aims to link the Western part of China (Xinjiang province) to the Gwadar Port in Balochistan, Pakistan via Khunjerab Pass in the Northern Parts of Pakistan.
- It will pave the way for China to access the Middle East and Africa from Gwadar Port, enabling China to access the Indian Ocean.
- CPEC is a part of the Belt and Road Initiative. The BRI, launched in 2013, aims to link Southeast Asia, Central Asia, the Gulf region, Africa and Europe with a network of land and sea routes.
- India has been severely critical of the CPEC, as it passes through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, which is a disputed territory between India and Pakistan.
(News from PIB)
International Day of Older Persons: 1st October
By: Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- Dedicate the Elderly Line 14567 to the Nation
- Launch the Senior Able Citizens Reemployment in Dignity (SACRED) portal
- Launch the Senior Care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE) Portal
About the Senior Able Citizens Reemployment in Dignity (SACRED) portal
- An IT portal to be developed to bring the employment seeker senior citizens and employment providers on one platform
- The aim is to devise ways to ensure Senior Citizens live healthy, happy, empowered, dignified and self-reliant life
About the Senior Care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE) Portal
- Aimed at promoting private enterprises to bring out innovation in products to benefit elders
- Shaped on the recommendations of the empowered expert committee (EEC) report on startups for the elderly
- SAGE to select, support and create a ‘one-stop access’ of elderly care products and services
News Source: PIB
Launch of DigiSaksham
Part of: GS-Prelims
Context: DigiSaksham is a digital skills programme to enhance the employability of youth by imparting digital skills that are required in an increasingly technology driven era.
- This joint initiative with Microsoft India is an extension of the Government’s ongoing programs to support the youth from rural and semi-urban areas.
- Through DigiSaksham initiative, free of cost training in digital skills including basic skills as well as advance computing, will be provided to more than 3 lakh youths in the first year.
- There will be basically three types of training viz. Digital Skills – Self paced learning, VILT mode training (Virtual Instructor led) and ILT mode training (Instructor led).
News Source: PIB
India extends support for protecting the Antarctic environment
Part of: GS-Prelims and Mains GS-III: Environment, Conservation
In News: India has extended support for protecting the Antarctic environment and for co-sponsoring the proposal of the European Union for designating East Antarctica and the Weddell Sea as Marine Protected Areas (MPAs).
- Essential to regulate illegal unreported and unregulated fishing
- India’s decision to consider extending support and co-sponsoring the MPA proposals is driven by conservation and sustainable utilization principles and adhering to the global cooperation frameworks (such as Sustainable Development Goals, UN Decade of Oceans, Convention on Biodiversity, etc.) to which India is a signatory.
India had embarked on Antarctic expedition in 1981, through the Southern Indian Ocean sector. Till date, India had completed 40 expeditions with plans for the 41st expedition in 2021-22. India has solidified its interests in upholding its Antarctic vision.
About Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR)
- CCAMLR is an international treaty to manage Antarctic fisheries to preserve species diversity and stability of the entire Antarctic marine ecosystem.
- CCAMLR came into force in April 1982.
- India has been a permanent member of the CCAMLR since 1986.
About Marine Protected Areas (MPAs)
- An MPA is a marine protected area that provides protection for all or part of its natural resources.
- Certain activities within an MPA are limited or prohibited to meet specific conservation, habitat protection, ecosystem monitoring, or fisheries management objectives.
About Weddell Sea: Part of the Southern Ocean and contains the Weddell Gyre. Its land boundaries are defined by the bay formed from the coasts of Coats Land and the Antarctic Peninsula
Do you know?
- The Indian Antarctic expeditions began in 1981.
- The Indian Antarctic programme has now been credited to have built three permanent research base stations in Antarctica—named Dakshin Gangotri, Maitri, and Bharati.
- As of today, India has two operational research stations in Antarctica named Maitri and Bharati.
- The National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Goa, manages the entire Indian Antarctic program.
News Source: PIB
Launch of Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0 and AMRUT 2.0
Part of: GS-Prelims and Mains GS-I- Urbanisation
Context: SBM-U 2.0 and AMRUT 2.0 have been designed to realize the aspiration to make all our cities ‘Garbage Free’ and ‘Water Secure’. These flagship Missions signify a step forward in our march towards effectively addressing the challenges of rapidly urbanizing India and will also help contribute towards achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals 2030.
About Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0 envisions to
- Make all cities ‘Garbage Free’ and ensure grey and black water management in all cities other than those covered under AMRUT,
- Make all urban local bodies as ODF+ and those with a population of less than 1 lakh as ODF++
- The Mission will focus on source segregation of solid waste, utilizing the principles of 3Rs (reduce, reuse, recycle), scientific processing of all types of municipal solid waste and remediation of legacy dumpsites for effective solid waste management.
About AMRUT 2.0
- Aims to provide 100% coverage of water supply to all households in around 4,700 urban local bodies by providing about 2.68 crore tap connections and 100% coverage of sewerage and septage in 500 AMRUT cities by providing around 2.64 crore sewer/ septage connections, which will benefit more than 10.5 crore people in urban areas.
- AMRUT 2.0 will adopt the principles of circular economy and promote conservation and rejuvenation of surface and groundwater bodies.
- The Mission will promote data led governance in water management and Technology Sub-Mission to leverage latest global technologies and skills.
- ‘Pey Jal Survekshan’ will be conducted to promote progressive competition among cities.
News Source: PIB
(Mains Focus)
POLITY/ GOVERNANCE
- GS-2: Structure, organization and functioning of the Legislature; Issues and challenges pertaining to elections
Making Parties constitutional
What is a Political Party?
- A political party is an organised group of citizens who hold common views on governance. They act as a political unit that seeks to obtain control of government with a view to further the agenda and policy they profess.
- They are indispensable links between the people and the representative machinery of government.
- Political parties maintain a continuous connection between the people and those who represent them either in government or in the opposition.
Do You Know?
- The Indian Constitution, one of the longest Constitutions in the world, elaborately deals with the co-operative societies but not on Political Parties.
- The right to form co-operative societies is a fundamental right under Article 19 (1)(c), but the right to form political parties is not.
What is the legal status of Political Parties?
- Political parties have extralegal growth in almost every democratic country.
- The American Constitution does not presume the existence of political parties. In Britain too, political parties are still unknown to the law.
- Similarly, political parties in India are extra-constitutional, but they are the breathing air of the political system.
- Section 29A(5) of the Representation of the People Act, 1951 is the only major statutory provision dealing with political parties in India.
- It orders that a political party shall bear true faith and allegiance to the Constitution of India as by law established, and to the principles of socialism, secularism and democracy, and would uphold the sovereignty, unity and integrity of India.
What is German Model?
- The Basic Law of the Federal Republic of Germany (1949) gives constitutional status to political parties.
- Article 21 of the Basic Law of Germany deals with their status, rights, duties and functions. It provides:
- Political parties shall participate in the formation of the political will of the people. They may be freely established. Their internal organisation must conform to democratic principles. They must publicly account for their assets and for the sources and use of their funds.
- Parties that seek to undermine or abolish the free democratic basic order or to endanger the existence of the Federal Republic of Germany shall be unconstitutional. The Federal Constitutional Court shall rule on the question of unconstitutionality
- Details of regulation of Political Parties shall be regulated by federal laws.
- The German model of constitutionalising political parties is more desirable for India than the U.S. and the U.K. models.
What are the problems facing Indian Political Parties?
- Political parties in developed nations maintain high levels of internal democracy but this is lacking in India.
- There are no periodical in-party elections in majority of Indian parties.
- Majority of political parties are family fiefdoms, where internal Democracy is lacking.
- Most of the parties are openly caste- or religious-based.
- The finances of almost all political parties are dubious and opaque.
What is the way ahead?
- Political parties are the agents of democracy and safety valves in the political system. They desperately need reform.
- Hence, it is high time to constitutionalise political parties to ensure in-party democracy, to impart transparency in their finances, and to de-communalise them.
Connecting the dots:
- Electoral Reforms (NOTA, VVPAT)
- Electoral Bonds Scheme
- Presidential System vs Parliamentary System
- First Past the Post vs Proportionate Representation
GOVERNANCE/ HEALTH
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in Health and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Failing on food: on child malnutrition and mid-day meals
Context: PM POSHAN scheme was approved by the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs until 2025-26.
- This comes at a critical time when real income declines and the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic have affected the ability of families to ensure good nutrition.
Malnutrition Issue
- The findings in Phase I of the NFHS-5 for 22 States and UT in December 2020 were shocking:
- Childhood stunting rose in 13 States
- High prevalence of anaemia among children and women
- Wasting was a serious concern in 12 States.
- The slippage over the previous survey period exposes the worsening case of malnutrition, threatening to deprive millions of children of a fully productive adult life.
Significance of nutrition schemes (POSHAN, Mid-Day Meals) at this juncture
- To address this hidden malnutrition crisis that has been accentuated by COVID-19 pandemic, mid day meals scheme becomes important.
- The centrally supported hot meal programme in Government and Government-aided schools, covering 11.8 crore children, will be supplemented with nutritional elements in identified aspirational districts and areas with high anaemia.
- The revamped scheme, which is proposed to be extended to pre-primary children, provides for
- social audit
- creation of school nutritional gardens to source fresh produce
- involvement of farmer-producer organisations as providers
- lays emphasis on local food traditions
- The new features of the scheme clearly shows that government is trying to address malnutrition in comprehensive manner that provides benefits to other stakeholders(ex: farmers & local) involved in the food chain.
Way Ahead
- Momentum towards eradicating malnutrition depends on annual budgetary outlays and government has to ensure that any malnutrition programme doesn’t face funding constraints.
- The Government must demonstrate that Saksham Anganwadi-Mission POSHAN 2.0, which merges the POSHAN Abhiyan and schemes covering anganwadis, crèches and adolescent girls, is funded financially better than its previous component parts.
- Government has to monitor the progress of its policies or schemes through measurable outcomes to ensure that they are effective.
- On nutritional planning, the renewed plan should introduce a greater diversity of diets that compensates for micronutrient and protein deficiency.
- Patchy food distribution mechanisms in many States should be rectified on urgent basis.
- Food inflation needs to be addressed by authorities so that it doesn’t hurt poor people’s consumption pattern, which is already under stress due to decline in incomes caused by Pandemic.
Connecting the dots:
- POSHAN Abhiyan
- National Family Health Survey
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
Q.1 Where is Gwadar Port located?
- Pakistan
- India
- Yemen
- Afghanistan
Q.2 Which of the following is/are true regarding Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Amendment Act, 2020:
- The Act bars public servants from receiving foreign contributions.
- It is implemented by the Ministry of External Affairs.
Select the correct statements:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Trojan asteroids share the orbit of which of the following planets?
- Saturn
- Jupiter
- Earth
- Mars
ANSWERS FOR 30th Sept 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | D |
Must Read
On benefits of GI Ecosystem:
On Communalism:
On Gandhi:











