IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: According to a new study two alien planets about 218 light years away from Earth have found a twin in the ocean worlds of Europa and Enceladus — moons orbiting Jupiter and Saturn.
Highlights of the study:
- The exoplanets, Kepler-138 c and Kepler-138 d, are likely water worlds — a feature that scientists have theorised for a long time, the study published in the journal Nature Astronomy noted.
- They are also larger-scale versions of Enceladus (Saturn’s moon) and Europa (Jupiter’s moon), the findings predicted.
- The study reported that the Kepler- 138 c and d are made up of ingredients lighter than rock (rocky planets like Earth) but heavier than hydrogen or helium (gas-giant planets like Jupiter).
- The researchers also discovered a fourth planet in the Kepler planetary system: Kepler-138 e.
About Saturn:
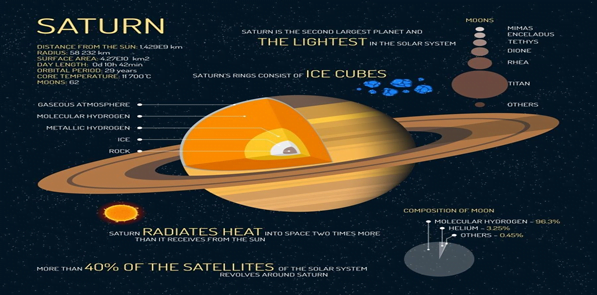
- Saturn is the second largest planet of the solar system in mass and size and the sixth nearest planet in distance to the Sun.
- Saturn has an overall hazy yellow-brown appearance.
- Saturn’s atmosphere is composed mostly of molecular hydrogen and helium.
- Saturn has 83 moons with confirmed orbits that are not embedded in its rings.
- The moons of Saturn are numerous and diverse, ranging from tiny moonlets only tens of metres across to enormous Titan, which is larger than the planet Mercury.
- Saturn got its tilt due to gravitational interactions with its neighbour Neptune according to a well-known theory.
- But the new study argues that Saturn is no longer under Neptune’s gravitational influence.
- Titan, which is Saturn’s largest satellite, may have been responsible, suggested observations from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, which orbited Saturn from 2004-2017.
- Titan’s fast migration caused the planet to tilt further, reducing Neptune’s gravitational influence on Saturn.
About Jupiter:

- Jupiter is the biggest planet in our solar system. It has big storms like the Great Red Spot, which has been going for hundreds of years.
- Jupiter is a gas giant and doesn’t have a solid surface, but it may have a solid inner core about the size of Earth. Jupiter also has rings, but they’re too faint to see very well.
- It is made mostly of hydrogen and helium.
- Jupiter has a very thick atmosphere.
- Jupiter has 79 confirmed moons.
- Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun. That means Mars and Saturn are Jupiter’s neighboring planets.
- Jupiter has been known since ancient times because it can be seen without advanced telescopes.
- Jupiter has been visited or passed by several spacecraft, orbiters and probes, such as Pioneer 10 and 11, Voyager 1 and 2, Cassini, New Horizons, and Juno.
Source: DownToEarth
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which one of the following is a reason why astronomical distances are measured in light-years? (2021)
- Distance among stellar bodies do not change
- Gravity of stellar bodies does not change
- Light always travels in straight line
- Speed of light is always same
Q.2) Recently, scientists observed the merger of giant ‘blackholes’ billions of light-years away from the earth. What is the significance of this observation? (2019)
- ‘Higgs boson particles’ were detected.
- ‘Gravitational waves’ were detected.
- Possibility of intergalactic space travel through ‘wormhole’ was confirmed.
- It enabled the scientists to understand ‘singularity’.
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: According to new research published recently, Mammals may have evolved in Gondwana, the southern landmass formed from the supercontinent Pangaea millions of years, rather than its northern counterpart Laurasia.
- Modern mammals consist of three sub groups: Montremes, marsupials and placentals.
About Monotremes (The Egg-laying Mammals):

- Monotremes or Prototherians are egg laying (oviparous) mammals. They are the most primitive mammals. Currently, only three species of Monotremes are extant viz. Duckbilled Platypus and two species of Echidnas. Monotremes are found only in Australia and New Guinea.
- The word “monotreme” means “one opening” which denotes that Monotremes have only one cloaca that is used as anus, unitary tract as well as for reproduction.
- They lay egg which has leathery shell.
- The young ones get their milk from mammary glands found on mother’s belly. No nipples are found in Monotremes.
- While platypus lays eggs on bank of stream; echidnas lay a single egg in a temporary protective pouch on mother’s belly.
- Monotremes don’t have a placenta also.
About Marsupials (Metatheria):

- Marsupials include kangaroos, wallabies, koala, possums, opossums, wombats, numbat
- There are around 330 species of Marsupials distributed in three continents viz. Australia South America and North America (only two species are found north of Mexico).
- Most (70%) are found Australia continent which includes Australia, New Zealand, New Guinea and neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. Remaining is mostly found in South America and Central America.
Key Features:
- The term marsupium means a pouch. Marsupials give birth to a relatively undeveloped young, which often resides in the pouch with the mother for a certain time after birth. This also implies that they have a relatively short gestation.
- Marsupials have different ecological niches, ranging from moles to insect eaters to plant eaters.
- They first evolved in South America some 100 million years ago when Australia, South America and Antarctica were joined together.
- Gradually, these three continents separated and the marsupials got isolated. They freely evolved in isolation.
- Most Marsupials are nocturnal and they have best sense of smell and hearing.
- Small Kangaroos are called wallabies. Red Kangaroo is largest Marsupial of the world. Further, Kangaroos are able to move more efficiently at high speed in comparison to low speed because of tendons in their hind legs and tail acts as pendulum.
- Kangaroos are able to withstand dry periods and little rainfall and can survive without water for many months.
- A male kangaroo is called a boomer, a female kangaroo a flyer, and a baby kangaroo a joey.
About Placentals (Eutheria):

- There are nearly 4000 described species in Placental mammals, of which most are rodents and bats.
- The Placental mammals give birth to live young. Before birth, the embryo is nourished in mother’s uterus via a specialized organ connected to uterus called placenta.
- We note that Marsupials also have a placenta but it is very short lived and does not make any substantial contribution in the nourishment of the foetus.
The placental animals have been divided into several orders as enumerated below:
- Artiodactyls are mammals with an even number of fingers in claws or paws like. These include cows, sheep and giraffes.
- Perissodactyls or ungulates (hooved), are large animals with an odd number of fingers on each paw, such as horses and rhinos.
- Carnivorous mammals are predators with canine teeth such as dogs, lions and tigers.
- Cetaceans are aquatic mammals without posterior limbs, such as whales and dolphins.
- Edentates are mammals with rare or absent teeth, such as sloths, armadillos and anteaters.
- Lagomorphs are small-sized mammals with three pairs of continuously growing incisor teeth specialized in gnawing, such as rabbits and hares.
- Primates are characterized by their large cranium and well-developed brain, such as humans and apes.
- Proboscideans are large animals whose nose and upper lip form a trunk (snout), such as
- Chiropterans are flying nocturnal mammals; this group includes bats.
- Rodents are animals with two pairs of continuously growing incisor teeth, such as mice, rats, beavers and squirrels.
- Sirenians are freshwater aquatic mammals lacking of posterior limbs, such as dugongs (Sea Cows) and manatees.
Source:DownToEarth
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following animals
- Hedgehog
- Marmot
- Pangolin
To reduce the chance of being captured by predators, which of the above organisms rolls up/roll up and protects/protect its/their vulnerable parts? (2021)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
Q.2) With reference to India’s biodiversity, Ceylon Frogmouth, Coppersmith Barbet, Gray Chinned Minivet and White-throated Redstart are (2020)
- Birds
- Primates
- Reptiles
- Amphibians
Syllabus
- Prelims: Government policies and interventions
Objectives:
- Development of infrastructure for the leather sector
- Address environmental concerns specific to the leather sector: affordable and clean energy and other environmental benefits
- Facilitate additional investments
- Employment generation for women – economic growth, reduction in poverty, quality education/skills, gender equality, good health and well-being, infrastructure development,
- Increase in production.
The six sub-schemes:
- Sustainable Technology and Environmental Promotion(STEP):- Assistance for each Common Effluent Treatment Plant (CETP)
- Integrated Development of Leather Sector (IDLS):- Assistance to be provided to the sectoral units for their modernization/capacity expansion/technology upgradation (Financial assistance, domestic manufactured machinery)
- Mega Leather Footwear and Accessories Cluster Development (MLFACD): Assistance is provided for land development, core infrastructure, social infrastructure, production facilities including ready to use sheds with plug and play facility, R&D support and export services
- Establishment of Institutional Facilities (EIF):- Assistance would be provided for establishment/upgradation of the institutional infrastructure of Footwear Design and Development Institute (FDDI).
- Brand Promotion of Indian Brands in Footwear and Leather Sector
- Development of Design Studios in Footwear and Leather Sector: A one-stop- shop providing a wide range of services: design, technical support, quality control, etc. to promote marketing/export linkages, facilitate buyer- seller meets, display designs to international buyers and work as an interface for the trade fairs.
Leather industry in India
- India is the second largest producer of footwear and leather garments after China in the world
- It is the second largest exporter (after China) of leather garments in the world.
- The industry is known for its consistency in high export earnings and it is among the top ten foreign exchange earners for the country.
- India has an abundance of raw materials with access to 20% of world’s cattle and buffalo and 11% of the world’s goat and sheep population.
- The Leather industry is an employment-intensive industry providing job to more than 4 mn people, mostly from the weaker sections of the society.
- With 30% share, women employment is predominant in Leather products industry
- Has one of the youngest workforces with 55% of the workforce below 35 years of age.
- Major Markets: USA, Germany, UK, Italy, France, Spain, Netherlands, UAE, etc.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims: Governance and Environment and Climate Change
In News: National Action Plan for Climate Change (NAPCC) is a Government of India’s programme launched in 2008 to mitigate and adapt to the adverse impact of climate change.
- Aims at fulfilling India’s developmental objectives with focus on reducing emission intensity of its economy.
- The plan will rely on the support from the developed countries with the prime focus of keeping its carbon emissions below the developed economies at any point of time.
The 8 missions under NAPCC are as follows:
Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission: Aims to establish India as a global leader in solar energy by creating the policy conditions for its deployment across the country.
- Under: Ministry of New and Renewable Energy
- The initial target of NSM was to install 280 GW solar power by 2022. This was upscaled to 100 GW in early 2015.
- Immediate Aim: Focus on setting up an enabling environment for solar technology penetration in the country both at a centralized and decentralized level.
- Also reduce the cost of Solar Power Generation in the country through
- Long term policy
- Large Scale deployment goals
- Aggressive R&D- Tie local research with international efforts
- Domestic production of critical raw materials, components, and products, as a result, to achieve grid tariff by 2022.
National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Aims to strengthen the market for energy efficiency by creating a conducive regulatory and policy regime and has envisaged fostering innovative and sustainable business models for the energy efficiency sector.
- Under: Ministry of Power
- Based on the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- NMEEE consists of four initiatives to enhance energy efficiency in energy-intensive industries:
- Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT): Assigns targets to energy-intensive industries and also allots energy saving certificates (Escerts). These certificates are tradable amongst the candidates who have either breached their targets or remained unsuccessful in achieving them.
- Market Transformation for Energy Efficiency (MTEE) promotes the use and adoption of energy-efficient equipment.
- Energy Efficiency Financing Platform (EEFP) encourages financial institutions and investors to support energy efficiency initiatives.
- Framework for Energy Efficient Economic Development (FEEED) promotes energy-efficient initiatives by hedging against investment risks.
In order to hedge the financial institutions providing loans for the energy efficiency projects against credit risks, the Bureau of Energy Efficiency has also institutionalised two funds namely “Partial Risk Guarantee Fund for Energy Efficiency” and “Venture Capital Fund for Energy Efficiency”. Both these funds have been launched under “Framework for Energy Efficient Economic Development” component of the NMEEE.
- NMEEE calls for:
- Mandating specific energy consumption decreases in large energy consuming industries and creating a framework to certify excess energy savings along with market based mechanisms to trade these savings.
- Innovative measures to make energy efficient appliances/products in certain sectors more affordable.
- Creation of mechanisms to help finance demand side management pro-grammes by capturing future energy savings and enabling public-private-partnerships for this.
- Developing fiscal measures to promote energy efficiency such as tax incentives for including differential taxation on energy efficient certified appliances.
National Mission on Sustainable Habitat:
- Under Ministry of Urban Development
- Objectives:
- To reduce the energy consumption and hence the risk of climate change due to the urban settlement pattern.
- The mission envisages a shift to Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) in the design of new commercial buildings as well as solid and liquid waste management.
- The mission also covers under its ambit, the water resource management as well as drinking water management.
- One of the most important plan under the mission is to pave the way for a shift to public transport.
- The research and development is an important component of the mission to promote the wastewater use and sewage utilisation along with waste management.
- The aim of the Mission is to make habitats more sustainable through a threefold approach that includes:
- Improvements in energy efficiency of buildings in residential and commercial sector
- Management of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)
- Promote urban public transport
- 4 flagship missions or programmes of the Ministry of Urban Development
- Atal Mission on Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) – Focus is on:
- Water supply
- Sewerage and septage management
- Stormwater drainage to reduce flooding
- Non-motorized urban transport, an example would be cycling.
- Green space/parks
- Swachh Bharat Mission
- Smart Cities Mission: To promote cities that provide core infrastructure and give a decent quality of life to its citizens, a clean and sustainable environment and application of Smart Solutions.
- Urban Transport Programme
- Atal Mission on Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) – Focus is on:
National Water Mission: A comprehensive programme for equitable distribution of water across the country as well as for enhancing the capacity-building process for the management of over-exploited blocs.
- Under: Ministry of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation
- Focused upon tackling the issues related to water availability and pollution which is owed to global warming and climate change.
- The mission promotes research and development
- Timely review of National Water Policy is also proposed.
- The mission while promoting the traditional water conservation system, also promotes the expeditious implementation of multipurpose water projects. It has a target of increasing water use efficiency by 20%.
- The convergence of various water conservation schemes for a better outcome and implementation of water resource management programs via the MNREGA route with the participation of the elected representatives of the over-exploited water blocs is central theme of the mission.
- The program has focused on decentralised approach which is reflected in its plan of “basin level” integrated water resource management and sensitization of the urban local youths. The National Water Mission also has an identified goal of putting a comprehensive water resource database in the public domain. The onus of implementation lies on the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
National Mission for Sustaining Himalayan Ecosystem:
- Under: Department of Science and Technology.
- Created to protect the Himalayan ecosystem.
- Mandate: To evolve measures to sustain and safeguard the Himalayan glaciers, mountain ecosystems, biodiversity and wildlife conservation & protection.
Green India Mission
- Under Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
- GIM puts ―greening in the context of climate change adaptation and mitigation. Greening is meant to enhance ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration and storage (in forests and other ecosystems), hydrological services and biodiversity; as well as other provisioning services such as fuel, fodder, small timber and non-timber forest products (NTFPs).
- The Mission aims at responding to climate change by a combination of adaptation and mitigation measures, which would help:
- Enhancing carbon sinks in sustainably managed forests and other ecosystems
- Adaptation of vulnerable species/ecosystems to the changing climate
- Adaptation of forest-dependent communities
- The objectives of the Mission are:
- Increased forest/tree cover on 5 m ha of forest/non-forest lands and improved quality of forest cover on another 5 m ha (a total of 10 m ha)
- Improved ecosystem services including biodiversity, hydrological services and carbon sequestration as a result of treatment of 10 m ha
- Increased forest-based livelihood income of about 3 million households living in and around the forests
- Enhanced annual CO2 sequestration by 50 to 60 million tonnes in the year 2020
National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture: Seeks to transform Indian agriculture into a climate-resilient production system through suitable adaptation and mitigation measures in domains of both crops and animal husbandry.
- Under: Ministry of Agriculture
- To achieve objective to fight against climate change, NMSA have the following multi-pronged strategy:
- Promoting integrated farming system covering crops, livestock & fishery, plantation and pasture based composite farming for enhancing livelihood opportunities, ensuring food security and minimizing risks from crop failure through supplementary/ residual production systems;
- Popularizing resource conservation technologies (both on-farm and off-farm) and introducing practices that will support mitigation efforts in times of extreme climatic events or disasters like prolonged dry spells, floods etc.
- Promoting effective management of available water resources and enhancing water use efficiency through application of technologies coupled with demand and supply side management solutions;
- Involving knowledge institutions and professionals in developing climate change adaptation and mitigation strategies for specific agro climatic situations and promoting them through appropriate farming systems.
National Mission on Strategic Knowledge for Climate Change
- Under: Department of Science and Technology
- Seeks to build a vibrant and dynamic knowledge system that would inform and support national action for responding effectively to the objective of ecologically sustainable development
- This Mission strives to work with the global community in research and technology development and collaboration through a variety of mechanisms and, in addition, will also have its own research agenda supported by a network of dedicated climate change-related institutions and universities and a Climate Research Fund.
- The Mission will also encourage private sector initiatives for developing innovative technologies for adaptation and mitigation.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: In the United States, wildlife officials declared a Nevada wildflower endangered at the only place it’s known to exist – on a high-desert ridge where a lithium mine is planned to help meet the growing demand for electric car batteries.
About Nevada Wildflowers:




- Sierra Nevada meadows explode in the spring and summer with beautiful wildflowers.
- In English Meadow, the orange-red Indian paintbrush (genus Castilleja) grows amid tall, yellow-flowered arrowleaf ragwort (Senecio triangularis).
- Meadow wildflowers play an important role in the larger ecosystems of the Sierra Nevada.
- The flowers are a primary food source for insects, and insects are an important food source for bats and birds.
About Sierra Nevada:
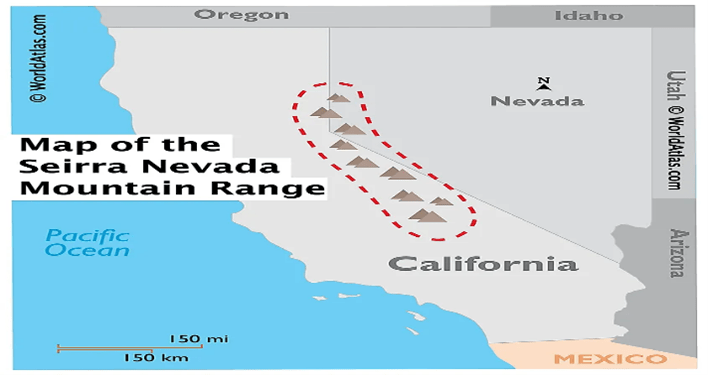
- Sierra Nevada, also called Sierra Nevadas, major mountain range of western North America, running along the eastern edge of the U.S. state of California.
- Its great mass lies between the large Central Valley depression to the west and the Basin and Range Province to the east.
- Extending more than 250 miles (400 kilometres) northward from the Mojave Desert to the Cascade Range of northern California and Oregon, the Sierra Nevada varies from about 80 miles wide at Lake Tahoe to about 50 miles wide in the south.
- Its magnificent skyline and spectacular landscapes make it one of the most beautiful physical features of the United States. Biologically, it is home to the largest trees in the world—the giant sequoias.
- The Sierra Nevada range is an excellent example of how the human occupation and use of an area can modify its landscape.
Source: NewsOnAir
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which one of the lakes of West Africa has become dry and turned into a desert? (2022)
- Lake Victoria
- Lake Faguibine
- Lake Oguta
- Lake Volta
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: Recently Delhi Police recovered bones from the Mehrauli forest area in connection with the Shraddha Walkar murder investigation. DNA testing conducted on the bones — parts of the jaw, pelvis and lower limb — has now confirmed a positive match with Shraddha’s father.
About DNA fingerprinting:
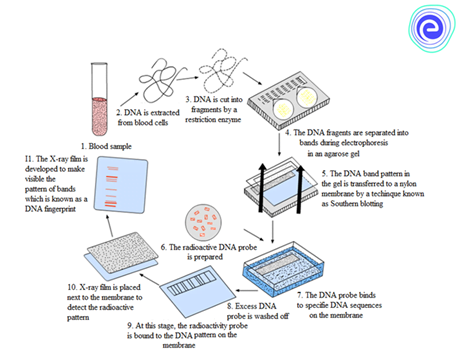
- “DNA fingerprinting is a procedure that shows the hereditary cosmetics of living things. It is a strategy for finding the distinction between the satellite DNA areas in the genome.”
- DNA profiling, DNA testing, DNA examination, Genetic profile, DNA distinguishing proof, genetic fingerprinting, and genetic investigation are a portion of the mainstream names utilized for DNA fingerprinting. This technique was invented by Alec Jeffreys in 1984.
- Sources of DNA:
- hair,
- bone,
- teeth,
- saliva,
- blood, etc.
- Because there is DNA in most cells in the human body, even a minuscule amount of bodily fluid or tissue can yield useful information.
- DNA evidence is used to solve crimes in two ways:
- If a suspect is known, that person’s DNA sample can be compared to biological evidence found at a crime scene to establish whether the suspect was at the crime scene or whether they committed the crime.
- If a suspect is not known, biological evidence from the crime scene can be analysed and compared to offender profiles in existing DNA databases to assist in identifying a suspect.
Uses of DNA Fingerprinting:
- Forensic analysis: It can be used in the identification of a (1) person involved in criminal activities, (2) for settling paternity or maternity disputes, and (3) in determining relationships for immigration purposes.
- Pedigree analysis: It can be used for inheritance pattern of genes through generations and for detecting inherited diseases such as Cystic Fibrosis, Haemophilia, Huntington’s Disease, Sickle Cell Anaemia etc.
- Personal Identification: DNA fingerprints can be used as a genetic bar code to identify individuals.
- Anthropological studies: It is useful in determining the origin and migration of human populations and genetic diversities.
- DNA Barcoding: A technique for specifying the organisms’ species using a short sequence of DNA situated in the genome is termed DNA bar-coding. The barcode DNA sequences are too short in respect to the complete genome and hence cheaper.
DNA Fingerprinting in India:
- Pioneering work was done by Lalji Singh at the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB), Hyderabad
Other centres are :
- Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (Hyderabad)
- Centre for DNA Fingerprinting & Diagnostics (Hyderabad)
- Central Forensic Science Laboratory, Kolkata
- National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resource (NBPGR), New Delhi
- National Institute of Plant and Genetic Research (NIPGR), New Delhi
Source: Indian Express
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements: DNA Barcoding can be a tool to:
- assess the age of a plant or animal.
- distinguish among species that look alike.
- identify undesirable animal or plant materials in processed foods.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the recent developments in science, which one of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
- Functional chromosomes can be created by joining segments of DNA taken from cells of different species.
- Pieces of artificial functional DNA can be created in laboratories.
- A piece of DNA taken out from an animal cell can be made to replicate outside a living cell in a laboratory.
- Cells taken out from plants and animals can be made to undergo cell division in laboratory petri dishes.
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance and Security Issues)
Context: The National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) has formulated a draft National Cyber Security Strategy which looks at addressing the issue of security of national cyberspace.
About National Security Council:
- The National Security Council (NSC) of India is an executive government agency tasked with advising the Prime Minister’s Office on matters of national security and strategic interest.
- It was established by the former Prime Minister of India Atal Bihari Vajpayee on 19 November 1998, with Brajesh Mishra as the first National Security Advisor.
- Prior to the formation of the NSC, these activities were overseen by the Principal Secretary to the preceding Prime Minister.
Members:
- Besides the National Security Advisor (NSA), the Deputy National Security Advisors, the Ministers of Defence, External Affairs, Home, Finance of the Government of India, and the Vice Chairman of the NITI Aayog are members of the National Security Council.
- Prime Minister can chair the meeting of NSC (for e.g. – PM chaired the meeting of NSC Post Pulwama to discuss heightened tension with Pakistan). Other members may be invited to attend its monthly meetings, as and when it is required.
Organisational structure
- The NSC is the apex body of the three-tiered structure of the national security management system in India.
- The three tiers are the Strategic Policy Group, the National Security Advisory Board and a secretariat from the Joint Intelligence Committee.
About National Cyber Security Strategy:
- Aim: It proposes a separate legislative framework for cyberspace and the creation of an apex body to address threats, responses and complaints.
- The policy will focus on both threat assessment and response.
- Need: The existing legal and regulatory frameworks do not address the evolving threat scenarios or processes to combat the cyber incidents.
- There is no dedicated body to look after cyber security at present and no one that you can hold accountable.
- Currently, the response to cyber security threats can be taken under the information technology act and the Indian Penal Code.
- Other provisions:
- It aims to create a comprehensive system with both state-owned and private companies having to comply with cybersecurity standards.
- It provides for a periodic cyber audit and recommends annual reviews by the apex body that will be created.
- A centre of excellence will also be set up in Bangalore to further innovations in the area.
Key facts:
- Till November 2022, a total of 12,67,564 cyber security incidents were reported.
- In 2021, the authorities had recorded 14,02,809 such events compared to 11,58,208 in 2020 and 3,94,499 in 2019.
- Ransomware attacks jumped 51% in 2022. Maharashtra was the most targeted state in India facing 42% of all ransomware attacks.
- Cyber thieves also exploited legitimate tools like “AnyDesk” used for remote administration.
Reasons for increasing Cyber Attacks:
- Adverse relations with China: China is considered one of the world leaders in information technology.
- Therefore, it is expected to have capabilities to disable or partially interrupt the information technology services in another country.
- Combined with the recent border standoff and violent incidents between the armies of the two countries, the adversity in relations is expected to spill over to attacking each other’s critical information infrastructure.
- Asymmetric and covert warfare: Unlike conventional warfare with loss of lives and eyeball to eyeball situations, cyber warfare is covert warfare with the scope of plausible deniability, i.e., the governments can deny their involvement even when they are caught.
- Similarly, even a small nation with advanced systems and skilled resources can launch an attack on a bigger power, without the fear of heavy losses.
- Increasing dependency on technology: As we grow faster, more and more systems are being shifted to virtual space to promote access and ease of use.
- However, the downside to this trend is the increased vulnerability of such systems to cyber-attacks.
Issues with Cyber Security:
- Vulnerable points in the system: sometimes the third-party apps have built-in back door entry or may have malware attached to their installation file. Such issues can be addressed by effective user account control and careful monitoring of the system.
- State-sponsored Cyber Attacks: The problem with such state-sponsored attacks is the unlimited funding received by the hackers to break into the foreign systems.
- Low digital literacy among the public: While India is considered the world leader in the technology industry, the general level of awareness in India about internet etiquette is low.
- It is a continuous process: Cyber-attacks, by their very nature, are innovative and creative. They continue to evolve, and the next attack is more advanced than its previous version.
- Novel issues: Because of the ever-changing and fast evolving nature of technology, new issues keep creeping up in the IT sector.
Steps taken by the Government: The government aims at ensuring an open, safe, trusted and accountable Internet for the users.
- The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) issues alerts and advisories regarding latest cyber threats/vulnerabilities and countermeasures to protect computers and networks on an ongoing basis.
- CERT-In operates the Cyber Swachhta Kendra (Botnet Cleaning and Malware Analysis Centre) to detect malicious programmes and free tools to remove the same, and to provide cyber security tips and best practices for citizens and organisations.
- Security tips have been published for users to secure their desktops and mobile phones and to prevent phishing attacks.
- CERT-In and the Reserve Bank of India [RBI] jointly carry out a cyber security awareness campaign on ‘Beware and be aware of financial frauds’ through the Digital India Platform.
- The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has been designated as the nodal point in the fight against cybercrime.
- Pursuant to the United Nations General Assembly resolution 75/282: an ad-hoc committee to elaborate a ‘Comprehensive International Convention on Countering the Use of Information and Communications Technologies for Criminal Purposes’ was established with all the member states.
- India being the member of the committee has proposed criminalisation of cyber terrorism under the said Convention.
- The MHA has issued National Information Security Policy and Guidelines to the Central Ministries as well as State governments and Union Territories with the aim of preventing information security breaches and cyber intrusions in the information and communication technology infrastructure.
Way Forward:
- The need of the hour is to come up with a futuristic National Cyber-Security Policy which allocates adequate resources and addresses the concerns of the stakeholders.
- Similarly, there is a need for quicker up-gradation of the existing infrastructure as information technology is a fast-evolving field and there is a need to stay ahead of the competition.
- There is a need to enhance the general awareness levels of the government installations as well as the general public to counter such threats.
- Often the private sector is seen as a key innovator and their help can be crucial in securing cyberspace.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Women Empowerment) and GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Recently, on the occasion of the 75th year of India’s independence, the Prime Minister articulated a bold vision that in the coming 25 years, “Nari Shakti” would play a vital role in India’s socio-economic developmental journey.
- The PM said that Culturally and mythologically, women have enjoyed an elevated status in India. For example, it is mentioned in the Kena Upanishad that it was the goddess Uma who enlightened the three powerful but ignorant gods, Indra, Vayu, and Agni, to the profound mystery of Brahman.
Significance of silent revolution by Women
Women Centric policy making :
- Silent revolution has compelled political entrepreneurs and grounded leaders to design women centric policies.
- Some of the most dramatic pro-women policy changes concerning poverty reduction through amenities such as cooking fuel, sanitation, water, and electricity are classic examples of the impact of silent revolution.
- Such Inclusive policies are also the key drivers of long-term economic growth.
Political Empowerment:
- A research on women voters using historical data has revealed that since 2010, the gender gap in voter turnout has diminished significantly and the recent trends show women voter turnout often exceeds male voter turnout.
- Massive increase of women voters is a nationwide phenomenon and is also observed in less developed regions of the country where traditionally, the status of women has been significantly lower.
- Due to this women voters can no longer be marginalised or neglected; they demand respect and command attention.
Rule of Law garnering political attention:
- In less developed regions women and children have been the biggest victims of lawlessness, the silent revolution of rising women voters has compelled political parties to make law and order a critical political issue.
New breed of confident women leaders:
- Since 2010, many women have been contesting elections. For instance in the 1950s, in the state assembly elections, women contested approximately 7 percent of the constituencies, but by the 2010s, women were competing in 54 per cent of the constituencies.
- However, this dramatic increase is yet to translate into more women winning the elections.
- Certainly at panchayat level where 50 per cent seats have been reserved for women helping in developing a new breed of women leaders.
- Women’s political empowerment has been a bottom-up revolution in India and holds lessons for other countries.
Case study of developed world
- In advanced countries, where increased participation of women in the labour force has come at the expense of family structure.
- Fertility rates have declined dramatically below the replacement rate, the share of the ageing population has increased, and there is an alarming increase in the percentage of kinless elderly.
- Subsequently, the economies spend a large share of the GDP on providing care.
- The care industry is labour-intensive and, therefore, subject to Baumol Cost Disease, implying that the cost of providing care would keep rising over time.
Challenges of strengthening of silent revolution:
- Women Unemployment issue: According to World Bank data, the female labour force participation rate has declined from 32 per cent in 2005 to 19 per cent in 2022.
- However, labour force participation only accounts for marketable employment opportunities and does not consider unpaid domestic services.
- Dual burden issues: Women work approximately six hours daily in marketable employment and spend around four hours additionally on unpaid household services.
- The double burden of working women perhaps is one of the critical reasons for the decline in the women’s labour force participation rate.
- In sharp contrast, working or non-working men in the same age group spend less than 45 minutes on unpaid domestic or caregiving services.
- Unpaid domestic work issues: A new research reveals that women in the age group of 25 to 59 years spend approximately seven hours daily in unpaid domestic services.
- On adding unpaid domestic services in GDP, the level of India’s GDP would be significantly higher, and a truer picture of women’s economic contribution would emerge.
Learnings for India:
- The dynamics of the care industry and the breakdown of the family structure in advanced economies give important lessons to India.
- If India wants more women to participate in the labour force, and at the same time preserve the family structure, then men would have to share the burden of unpaid domestic services.
- This would require a break from tradition and the creation of new modern narratives and myths based on gender equality.
Way Forward:
As India takes over the presidency of G20, it is an occasion to celebrate “Nari Shakti” and political empowerment — a stupendous increase in women voter turnout in the decade has strengthened and made Indian democracy more progressive.
Political parties and leaders are now responding to this silent revolution by improving access and affordability to basic needs of women like amenities and securities rather than focusing on the rhetoric of caste and communalism. Thus, Indian experience is in sharp contrast to the “democratic recession” that is being experienced in the rest of the world.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q.1) With reference to solar system, consider the following statements:
- Saturn’s atmosphere is composed mostly of molecular hydrogen and helium.
- Jupiter is the biggest planet in our solar system.
- Saturn has 79 confirmed moons.
- Titan is the Jupiter’s largest satellite.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
Q.2) With reference to mammals, consider the following statements:
- Monotremes or Prototherians are egg laying (oviparous) mammals.
- Kangaroos, wallabies, koala, possums, opossums, wombats are examples of Marsupials.
- Whales and dolphins are examples of cetaceans are aquatic mammals without posterior limbs.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Q.3) With reference to leather industry in India, consider the following statements:
- India is the largest producer of footwear and leather garments in the world.
- It is the second largest exporter of leather garments in the world.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 17th December 2022 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 16th December – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – a













