IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
About Court martial :
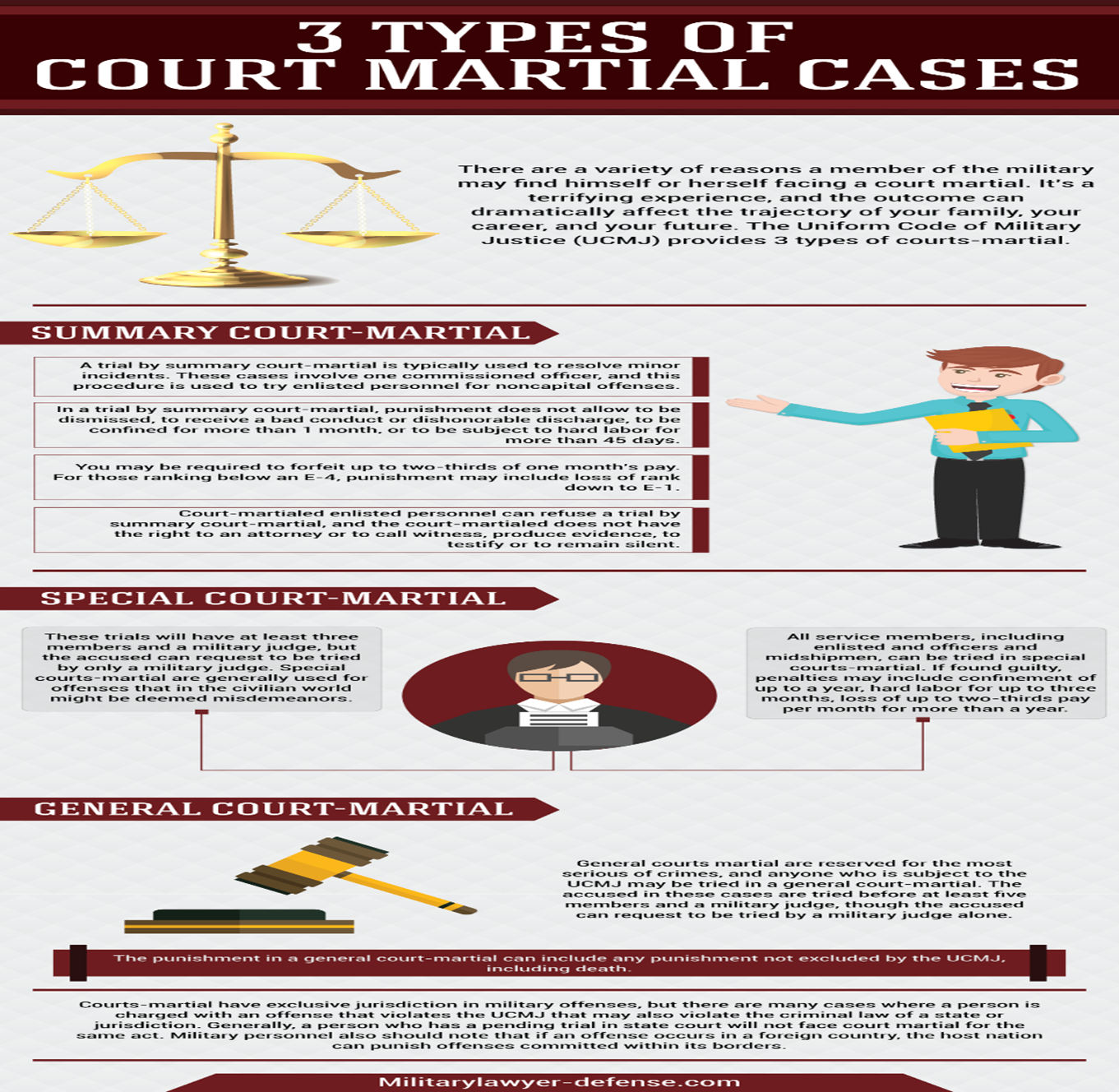
- Court-martial is a procedure for trials of military personnel for violating military laws or making any military offences.
- It is similar to civilian criminal trial proceedings but conducted in a military court.
- This is separately designed for the military personnel only (army, navy, marine, air force and at times coast guards),
- Purpose: It tries them for the violation of military discipline and other misconduct.
- There are twelve groups of people who can be trialed under court-martial namely the military personnel, members of a quasi-military organisation (public sectors working with the armed force), prisoners of the military and war and even some specific civilians can be trailed under court martial despite the place of occurrence of the offence.
- Court-martial cannot trial civil proceedings.
- When a person (in service) is accused to be an offender, the charges are investigated by his commander to find out the information regarding the offence, and the culpability (severity) of the offence.
- Post-investigation the commander can let go of the accused, take action against him, give him non-judicial punishment, form charges against him or refer the case to the higher authority to form the charges.
Legal recourse , available to the accused:-
- Under the Army Act, the accused can file a pre-confirmation petition as well as post- confirmation petition.
- A pre-confirmation petition will go to the Army Commander, who may look into its merits.
- A post-confirmation petition must be filed with the government since the officer is cashiered and his ranks are removed and he is dismissed from service after the confirmation of sentence by the Army commander.
- After these options have been exhausted, the accused can approach the Armed Forces Tribunal, which can suspend the sentence.
- The president of India, under Article 72 of the Constitution, can use his/her powers to pardon, reprieve, respite or remission of punishment or sentence given by a court martial.
Legal provisions related to court martial in India:-
The legal provisions related to court martial in India are primarily governed by three laws:
- The Army Act, of 1950: applies to members of the Indian Army.
- The Navy Act, of 1957: applies to members of the Indian Navy.
- The Air Force Act, of 1950: applies to members of the Indian Air Force.
MUST READ: Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act 1958, Death Penalty in India , AFSPA and the Northeast.
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements:
- When a prisoner makes out a sufficient case, parole cannot be denied to a such prisoner because it becomes a matter of his/her right.
State Governments have their own Prisoners Release on Parole Rules.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2021)
- Pursuant to the report of the H.N. Sanyal Committee, the Contempt of Courts Act, 1971 was passed.
- The Constitution of India empowers the Supreme Court and the High Courts to punish for contempt of themselves.
- The Constitution of India defines Civil Contempt and Criminal Contempt.
- In India, the Parliament is vested with the power to make laws on Contempt of Court.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
About the International big cat alliance:-
- The International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) strives to work towards the protection and conservation of the seven major big cats including tiger, lion, leopard, snow leopard, puma, jaguar, and cheetah.
- IBCA will be supported by India’s ‘total grant assistance’ of $100 million.
- There are 7 major big cats in the world – Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Puma, Jaguar, and Cheetah
- India is home to 5 of these big cats – Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, and Cheetah
Membership:-
- It is open to 97 “range” countries, which contain the natural habitat of these big cats, as well as other interested nations, international organizations, etc.
- The alliance’s purpose is to provide a platform for the “dissemination of information IBCA’s governance structure which will comprise a General Assembly .
- It consisting of all member countries, a council of at least seven but not more than 15 member countries elected by the General Assembly for a term of 5 years, and a Secretariat.
- Upon the recommendation of the Council, the General Assembly will appoint the IBCA Secretary General for a specific term.
MUST READ: Importance of Tiger Conservation, Tiger Estimation, Global Conservation Assured|Tiger Standards (CA|TS), Valmiki Tiger Reserve, Amrabad Tiger Reserve, Mudumalai Tiger Reserve, Pakke Tiger Reserve, Project Lion, Status Of Leopards Report , snow leopard, 7 BIG CATS and Cheetah reintroduction
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to Indian laws about wildlife protection, consider the following statements : (2022)
- Wild animals are the sole property of the government.
- When a wild animal is declared protected, the such animal is entitled to equal protection whether it is found in protected areas or outside.
- Apprehension of a protected wild animal becoming a danger to human life is sufficient ground for its capture or killing.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Q.2) With reference to Indian elephants, consider the following statements: (2020)
- The leader of an elephant group is a female
- The maximum gestation period can be 22 months
- An elephant can normally go on calving till the age of 40 years only
- Among the States in India, the highest elephant population is in Kerala
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 3 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
About Lokayuktas : –
- In 1809, the institution of the ombudsman was inaugurated officially in Sweden.
- New Zealand and Norway adopted this system in the year 1962
- In 1967, on the recommendations of the Whyatt Report of 1961, Great Britain adopted the institution of the ombudsman.
- In India, the concept of a constitutional ombudsman was first proposed by the then-law minister Ashok Kumar Sen in the early 1960s.
- The term Lokpal and Lokayuktas were coined by Dr. L. M. Singhvi.
- In 1966, the First Administrative Reforms Commission recommended the setting up of two independent authorities- at the central and state level, to look into complaints against public functionaries, including MPs.
- In 2002, the Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution headed by M.N. Venkatachaliah recommended the appointment of the Lokpal and Lokayuktas, and also recommended that the PM be kept out of the ambit of the authority.
- In 2005, the Second Administrative Reforms Commission chaired by Veerappa Moily recommended that the office of Lokpal should be established without delay.
- The Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013 provided for the establishment of Lokpal for the Union and Lokayuktas for States.
- However, even much before the enactment of the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act (2013) itself, many states had already set up the institution of Lokayuktas.
- The institution of Lokayuktas was established first in Maharashtra in 1971
- These institutions are statutory bodies without any constitutional status.
- They perform the function of an “ombudsman” and inquire into allegations of corruption against certain public functionaries and related matters.
- Till 2013, 21 states and 1 Union Territory (Delhi) have established the institution of Lokayuktas.
- The structure of the Lokayuktas is not uniform in all the states.
- The Lokayuktas and Upalokayukta are appointed by the Governor of the state after consulting the Chief Justice of the HIGH COURT and the leader of the opposition party.
- The Lokayuktas presents a consolidated report, annually to the Governor of the state on his performance.
- He takes the help of the state investigating agencies for conducting inquiries.
- The recommendations made by the Lokayuktas are only advisory and not binding on the state government.
MUST READ : Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) In the context of India, which one of the following is the characteristic appropriate for bureaucracy? (2020)
- An agency for widening the scope of parliamentary democracy
- An agency for strengthening the structure of federalism
- An agency for facilitating political stability and economic growth
- An agency for the implementation of public policy
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The Chief Secretary in a State is appointed by the Governor of that State.
- The Chief Secretary in a State has a fixed tenure
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
About the Asiatic lion :
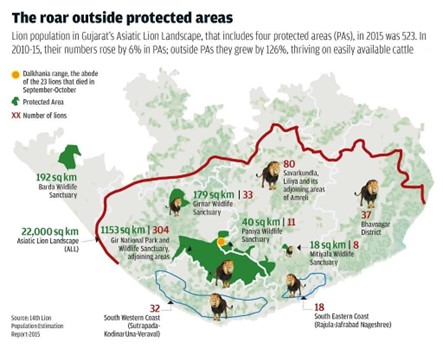
- The Asiatic lion is a population of Panthera leo that today survives in the wild only in India.
- Habitat: Since the turn of the 20th century, its range has been restricted to Gir National Park and the surrounding areas in the Indian state of Gujarat.
- Historically, it inhabited much of the Middle East to northern India.
- The first scientific description of the Asiatic lion was published in 1826 by the Austrian zoologist Johann N. Meyer, who named it Felis leo persicus.
- The lion is one of five pantherine cats native to India, along with the Bengal tiger (P. tigris tigris ), Indian leopard (P. pardus fusca ), snow leopard (P. uncia ), and clouded leopard (Neofelis nebulosa).
- It was also known as the Indian lion and the Persian lion.
Conservation Status:-
- Schedule I of Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972
- Appendix I of CITES
- Endangered on IUCN Red List
MUST READ : Project Lion, Rise in Asiatic Lions’ population reported and Asiatic lions test positive for SARS-CoV2 virus in Hyderabad zoo
Source: DOWN TO EARTH
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which of the following Protected Areas are located in the Cauvery basin? (2020)
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”? (2018)
- Corbett
- Ranthambore
- Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam
- Sunderbans
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy, Science, and Technology
Context: Recently, the government announced that trade in cryptocurrency will be covered under India’s money laundering laws.
About Cryptocurrencies:-
- It is any form of currency that exists digitally or virtually and uses cryptography to secure transactions.
- Cryptocurrencies don’t have a central issuing or regulating authority.
- It uses a decentralized system to record transactions and issue new units.
- It is supported by a decentralized peer-to-peer network called the blockchain.
Types of cryptocurrencies
The most common and valued cryptocurrency is Bitcoin.
All the other cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin are together as a set are known as alternate coins or commonly called “Altcoins”. Most famous alt coins are:-
- Litecoin
- Cardano
- Polkadot
- Stellar(XLM)
- Binance Coin
Advantages:-
- Cryptocurrencies are cheaper to use to execute international transactions because they don’t have to be handled by intermediaries.
- It is faster than other financial instruments.
- With a digital key, access to the currency is protected t.
- Identity Protection: Cryptocurrency can be sent directly to a recipient without any information other than the total amount you want to send.
- Risk-free for sellers: Payments using Cryptocurrency can’t be reversed, which means merchants don’t have to worry about stopped payments.
- Anti-Inflationary Currency: Due to the high demand for cryptocurrency its prices have largely remained on a growing trajectory. In this scenario, people tend to hold more cryptocurrency than spend it.
Disadvantages:-
- Privacy Concerns: All the transaction information is stored in a distributed ledger (called blockchain), which is publicly visible.
- High Volatility
- Destination for black money: The fear among regulators and policymakers is that cryptocurrencies, being an alternative source of value to fiat currency, could be misused to launder black money or finance terrorist activities.
- Cybersecurity Concerns: Cryptocurrencies are prone to cybersecurity breaches and hacks.
- Dark activities: The possibility that the new money will nurture illicit activities and markets like drug selling, weapons, etc. through Darknet is always high using cryptocurrency anonymously.
- Monetary control and economic behavior: It could dramatically change global monetary policymaking.
- Inflation: Governments and policymakers will have a reduced ability to control inflation
MUST READ: Cryptocurrency, Cryptocurrency and RBI , Cryptocurrencies Regulation, Money laundering and fugitive offender issue, Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002
Source: AIR
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which one of the following situations best reflects “Indirect Transfers” often talked about in media recently with reference to India? (2022)
- An Indian company investing in a foreign enterprise and paying taxes to the foreign country on the profits arising out of its investment
- A foreign company investing in India and paying taxes to the country of its base on the profits arising out of its investment
- An Indian company purchases tangible assets in a foreign country and sells such assets after their value increases and transfers the proceeds to India
- A foreign company transfers shares and such shares derive their substantial value from assets located in India
Q.2) With reference to “Blockchain Technology”, consider the following statements: (2020)
- It is a public ledger that everyone can inspect, but which no single user controls.
- The structure and design of the blockchain are such that all the data in it are about cryptocurrency only.
- Applications that depend on the basic features of blockchain can be developed without anybody’s permission.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy and Polity
Context: Recently, the BSE and UN Women India launched a new programme, ‘FinEMPOWER’.
About UN Women :
- UN Women is the UN organization dedicated to gender equality and the empowerment of women.
- UN Women was established to accelerate progress in meeting their needs worldwide.
- Objective: to develop and uphold standards and create an environment in which every woman and girl can exercise her human rights and live up to her full potential.
- Executive leadership: UN Women’s Directorate consists of Executive Director Sima Bahous, Deputy Executive Director Åsa Regnér, and Deputy Executive Director Anita Bhatia.
- Governance: According to UN General Assembly resolution 64/289, which established UN Women, the organization is governed by a multi-tiered intergovernmental governance structure.
MUST READ : Women Issues, Mission Shakti, Women Employment, COVID Impact on Women Workforce , Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
Source: AIR
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- In India, credit rating agencies are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The rating agency popularly known as ICRA is a public limited company.
- Brickwork Ratings is an Indian credit rating agency.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the Indian economy, what are the advantages of “Inflation-Indexed Bonds (IIBs)”? (2022)
- Government can reduce the coupon rates on its borrowing by way of IIBs.
- IIGs provide protection to investors from uncertainty regarding inflation.
- The interest received as well as capital gains on IIBs are not taxable.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Recently, FCI sold 5.40 lakh metric tonnes of wheat in the 4th e-auction.
About Food Corporation of India (FCI):-
- The Food Corporation of India was set up under the Food Corporation Act of 1964.
- It is a statutory body set up in 1965.
- It was established against the backdrop of a major shortage of grains, especially wheat.
- Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) was created simultaneously in 1965 to recommend remunerative prices to farmers.
CACP : –
- It is an attached office of the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- It is mandated to recommend minimum support prices (MSPs) to incentivize cultivators to adopt modern technology and raise productivity and overall grain production in line with the emerging demand patterns in the country.
- As of now, CACP recommends MSPs of 23 commodities.
Objectives of FCI:
- Effective price support operations for safeguarding the interests of the farmers.
- Distribution of food grains throughout the country for the public distribution system.
- Maintaining a satisfactory level of operational and buffer stocks of foodgrains to ensure National Food Security
- To provide farmers with remunerative prices
- To make food grains available at reasonable prices, particularly to the vulnerable sections of the society
- To maintain buffer stocks as a measure of Food Security
- To intervene in the market for price stabilization
MUST READ: Procurement Reforms, MSP
Source: AIR
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which of the following factors/policies were affecting the price of rice in India in the recent past? (2020)
- Minimum Support Price
- Government’s trading
- Government’s stockpiling
- Consumer subsidies
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2) n India, which of the following can be considered as public investment in agriculture? (2020)
- Fixing Minimum Support Price for agricultural produce of all crops
- Computerization of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies
- Social Capital Development
- Free electricity supply to farmers
- Waiver of agricultural loans by the banking system
- Setting up of cold storage facilities by the governments.
In India, which of the following can be considered as public investment in agriculture?
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, and 5 only
- 1, 3, 4, and 5 only
- 2, 3, and 6 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Despite progress in closing the global gender gap overall, women and girls continue to be left behind in the digital world.
About the Digital Gender Gap/Digital Divide:
- Digital divide is a term that refers to the gap between demographics and regions that have access to modern information and communications technology, and those that don’t or have restricted access.
- This technology can include the telephone, television, personal computers and the Internet.
- The term “digital gender gap” was coined by UN Women in 2010.
Digital Equity:
- Digital equity on the other hand is about providing everyone with equal opportunities to use technology to improve their lives.
- It includes making sure that everyone has access to the internet and the skills they need to use it effectively.
UNICEF Report:
- According to a UNICEF report, as many as 90% of the jobs in the world today have a digital component.
- These jobs, however, are available only to the digitally able, and to more men than women.
- According to the report, in developing countries, only 41% of women have access to the internet compared with 53% of men.
- Women are 20% less likely to own a smartphone and are more likely to borrow phones from a male family member.
Significance of bridging the Gender Digital Divide:
Benefits to women and to the Nation:
- India aims to have a $1 trillion digital economy by 2025.
- Already, 40% of global digital transactions take place in India.
- In 2022, a staggering 49 billion digital transactions took place in India.
- As economies digitize further, there is every reason to believe that most jobs will require some knowledge of digital technology.
- There are vast opportunities for girls and women to power India’s digital economy and benefit from it.
Can act as a multiplier effect:
- We have the world’s largest young population, and women and girls constitute almost half of it.
- Access to digital technology for a young woman can be a game changer with multiplier effects.
Acting as a solution:
- Giving women access to the internet and teaching them digital skills can help them overcome many of the obstacles they face.
- With internet access, women can gain new knowledge and skills, connect with others, and find new opportunities.
- Digital knowledge can also play a significant role in women’s safety.
- With digital equity, women can be empowered to reach their full potential.
Challenges leading to Gender Digital Divide
Lack of Infrastructure: Being a densely populated country, India needs well established infrastructure to deliver e-services.
- But still there are some rural disconnected regions which are not connected to Internet.
Population: It is a challenge for a developing country to serve a population of 1.30 billion uniformly.
- Every policy and project that is initiated should be implemented at a large scale keeping the future perspectives in mind.
Geographical Diversity: Rural India is still deprived of the facilities of urban India because of its geographical location.
- It is poorly connected in terms of roads and infrastructural facilities.
Illiteracy and Poverty: A large part of population is fighting for its daily basic needs. They do not bother about high speed devices and digitization.
- They are more worried about food and shelter.
- A large portion is illiterate and cannot operate digital devices. According to census 2011, literary rate in India is 74.04%.
Gender Divide: In India, there is huge discrimination among male and female.
- Only 65.46% of Indian women are literate and it is shocking that only 29 percent of Indian internet users are female. This creates a huge gender divide.
Corruption: Corruption is a termite for government. At each tier of government structure, politicians and stakeholders try to draw illegal benefits for themselves.
- Most of the budget that is decided at higher level cannot reach the general public and a large part of it is lost due to mediators.
Lack of Participation: It is observed that often the rural people are not very much attracted towards the web-based E-Governance services for various reasons.
- Many-a-times they are afraid of the technologies and at times they are even ignorant about the availability of technologies which can help in dealing with their problems.
Govt of India Initiatives to promote gender equality in access to technology
- In 2011, the BharatNet project was launched to connect 0.25 million panchayats through optical fibre and connect India’s villages.
- Its implementation began only in 2014, the deadline was extended to August 2021.
- In 2015, the government launched several schemes under its Digital India campaign to connect the entire country.
- This includes the Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan, launched in 2017, to usher in digital literacy in rural India by covering 60 million households.
- Kisan Call centre: The Department of Agriculture & Cooperation launched Kisan Call Centers to deliver extension services to the farming community.
- The purpose of these call centers is to respond to issues raised by farmers, instantly, in the local language.
- Technology Development for Indian Languages (TDIL): The department of information technology initiated the TDIL with the aim of developing information processing tools and techniques to facilitate human-machine interaction without language barrier.
- Digital library of India is an ambitious project of IISc and Ministry of communication and information technology, Government of India.
Way Forward:
- Addressing the divide: Addressing the digital divide requires special, urgent and focused efforts of the government.
- A large investment needs to be made, year after year, in digital infrastructure.
- Need of policy interventions: Bridging the gender gap will require smart interventions specially designed for girls and women in health, education, employment, banking, skilling and transportation.
- A favourable policy environment to promote the digital empowerment of women is a step in the right direction.
- Skills: Digital skills, required today both for life and for livelihoods, must be imparted on a war footing by transforming government digital literacy programmes into skilling missions, and expanding outreach, including through the private sector.
- Online safety of women: Social media sites can use their “algorithm power” to proactively tackle the issue of safety.
- Governments need to strengthen laws that hold online abusers to account, and the public to speak up whenever they witnessed abuse online.
- Example of ‘Digital Sakhis’:
- Young women known as ‘Digital Sakhis’ from Madhya Pradesh are upturning discriminatory social norms through the use of smartphones.
The digital gender gap is not only a modern social evil but also a huge economic constraint. To leave women out of the digital world would amount to denying what today has become a basic skill for survival.
Prime Minister of India recently has emphasized the need for ‘women-led development’ as India took over the G20 presidency. Women20—the G20’s official engagement platform to promote gender equity—identifies “bridging the gender digital divide” as one of its five priorities that need to be mainstreamed as part of the G20 agenda this year.
Source: LiveMint
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements:
- Food Corporation of India is a statutory body set up in 1965.
- Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) was created simultaneously in 1965 to recommend remunerative prices to farmers.
- CACP is an attached office of the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1 2 and 3
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding Asiatic Lion:
- Its range has been restricted to Gir National Park and the surrounding areas only.
- The species has been listed as Schedule II of Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) The president of India, under which of the following article, can use his/her powers to pardon, reprieve, respite or remission of punishment or sentence given by a court martial?
- Article 32
- Article 72
- Article 76
- Article 123
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 9th March 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 8th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – b











