IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, Oil hypocrisy of countries imposing sanctions on Russia came to the surface.
About the Oil hypocrisy:-
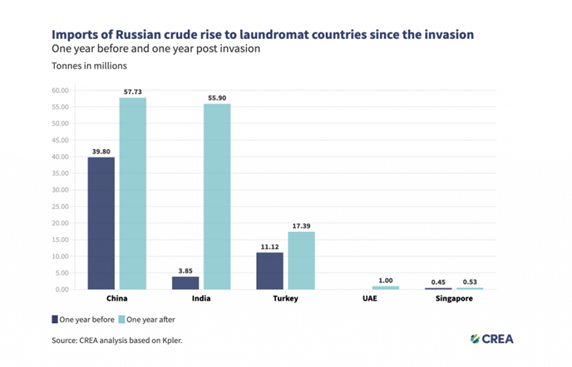
IMAGE SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
- Recent reports show that the countries that banned Russian oil imports(UPSCPrelims: Understanding EU ban on Russia’s Oil) instead imported oil commodities worth €42 billion from India, China, United Arab Emirates, Singapore and Turkey after the war started 2022.
- These five countries were thus identified as ‘laundromats’.
- The five countries are responsible for 70 per cent of Russia’s crude oil exports.
- India emerged as the leading exporter of refined oil products at 3.7 million tonnes to Price Cap Coalition countries in 2022.
- This is an increase of 0.3 million tonnes from the previous year.
- This was followed by China at three million tonnes and the United Arab Emirates at 2.9 million tonnes.
- The Price Cap Coalition comprising Australia, Canada, the European Union, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States imposed a maximum price of $60 a barrel of oil transported by vessels owned or insured by some countries in the alliance to third-party countries, with the intention to dent Russia’s financing of the war(UPSCPrelims: Russia-Ukraine War impact, beyond oil).
- Since the beginning of the invasion, demand for Russian crude oil has increased significantly by China, India, Turkey, UAE and Singapore.
- The EU was the largest importer of oil products from these laundromat countries worth €17.7 billion, despite partially banning crude oil imports from Russia last year.
- This was followed by Australia (€17.7 billion), the USA (€6.6 billion), the UK (€5 billion) and Japan (€4.8 billion).
MUST READ: The new energy disorder
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The term ‘West Taxes Intermediate’, sometimes found in news to a grade of (2020)
- Crude oil
- Bullion
- Rare earth elements
- Uranium
Q.2) In the Indian context, what is the implication of ratifying the ‘Additional Protocol’ with the ‘International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’? (2018)
- Civilian nuclear reactors come under IAEA safeguards.
- The military nuclear installations come under the inspection of the IAEA
- The country will have the privilege to buy uranium from the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
- The country automatically becomes a member of the NSG.
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: The Union Minister for Women and Child Development and Minority Affairs opened a Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC) account recently.
About Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC):-

IMAGE SOURCE: Mahila Samman Saving Certificate Form Interest Calculator – Sarkari Yojana – TheHowPedia
- Mahila Samman Savings Certificate Scheme was announced in the 2023-24 Union Budget (UPSCPrelims: Union Budget Summary 2023-24 ) to commemorate ‘Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav’.
- It is a one-time savings scheme(UPSCPrelims: Understanding Small savings schemes) for women.
- Objective: to empower women by increasing their participation in investments.
- It is a significant step towards financial inclusion and empowerment of women including girls.
- The two-year tenure scheme offers an attractive interest rate of 7.5 per cent compounded quarterly
- It will have flexible investment and partial withdrawal options with a maximum ceiling of Rs two lakh.
- The scheme is valid for a two-year period up to 31st March 2025.
- The scheme has been made available in all 1.59 lakh post offices from April 01, 2023.
Deposit limits:-
- One can start investing in this scheme with a minimum amount of Rs. 1,000 or any other amount in multiples of Rs. 100.
- But one cannot make additional deposits after that.
- Under this scheme, one can open multiple accounts, but the maximum total investment should be Rs 2 lakh only.
- And each account opened should have a three-month gap between the opening date of the existing account and the new account.
Eligibility Criteria:-
- The scheme is exclusively available to women.
- Any woman above 18 years of age can invest in this scheme by herself.
- Also, in the case of minors, the guardian can open the account on behalf of the girl.
Tax Benefits of the Mahila Samman Savings Certificate:-
- No information has been provided by the government related to its taxability.
- Unless more details emerge, normal taxation as per the slab rate can be assumed for this scheme.
MUST READ: Mission Shakti
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Maternity Benefit Amendment Act, 2017? (2019)
- Pregnant women are entitled to three months of pre-delivery and three months of post-delivery paid leave.
- Enterprises with creches must allow the mother minimum of six creche visits daily.
- Women with two children get reduced entitlements.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to the ‘stand up India scheme’, which of the following statement is/are correct? (2016)
- Its purpose is to promote entrepreneurship among SC/ST and women entrepreneurs.
- It provides for refinancing through SIDBI.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: The issues regarding India’s nuclear liability law came to continue to hold up the plan to build six nuclear power reactors in Maharashtra’s Jaitapur.
About Nuclear liability law:-
IMAGE SOURCE: jaitapur nuclear power plant map – Brainly.in
- The laws on civil nuclear liability ensure that compensation is available to the victims for nuclear damage caused by a nuclear incident or disaster and set out who will be liable for those damages.
- The international nuclear liability regime consists of multiple treaties and was strengthened after the 1986 Chornobyl nuclear accident(UPSC Prelims: Place in news-Chornobyl).
- Convention on Supplementary Compensation (CSC): it is an umbrella convention adopted in 1997.
- Objective: Establish a minimum national compensation amount.
- India was a signatory to the CSC, Parliament ratified the convention in 2016.
- To keep in line with the international convention, India enacted the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act (CLNDA) in 2010, to put in place a speedy compensation mechanism for victims of a nuclear accident(UPSC CSE: Understanding India’s Nuclear Doctrine).
- The CLNDA provides for strict and no-fault liability on the operator of the nuclear plant, where it will be held liable for damage regardless of any fault on its part.
-
- It establishes legal liability for nuclear harm as well as rapid compensation for victims of nuclear disasters.
- It specifies the experts who will assess claims of nuclear injury, sanction compensation, and provide financial assurance.
-
- It also specifies the amount the operator will have to shell out in case of damage caused by an accident and requires the operator to cover liability through insurance or other financial security.
- The operator’s maximum liability under Section 6(2) of the Act is Rs. 1500 crore.
- In case the damage claims exceed ₹1,500 crore, the CLNDA expects the government to step in, in accordance with Section 7(1)(a) of the CLND Act.
- However, it has limited the government liability amount to the rupee equivalent of 300 million Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) or about ₹2,100 to ₹2,300 crores.
-
- It specifies the limitations on the amount and time when an action for compensation can be brought against the operator.
- Section 7 (2) of the CLND Act provides that the Central Government may establish a “Nuclear Liability Fund” by charging such amount of levy from the operators, in such manner, as may be prescribed.
- Any violations of the terms of the act could result in fines.
- India currently has 22 nuclear reactors(UPSC CSE: Understanding India’s Nuclear Energy).
- All the existing reactors are operated by the state-owned Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL).
- Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) is a Public Sector Enterprise.
- It is under the administrative control of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), Government of India.
- The Company was registered as a Public Limited Company under the Companies Act, 1956.
- Objective: operating atomic power plants and implementing atomic power projects for generation of electricity in pursuance of the schemes and programmes of the Government of India under the Atomic Energy Act, 1962.
- NPCIL is responsible for design, construction, commissioning and operation of nuclear power reactors.
- Mission: To develop nuclear power technology and to produce nuclear power as a safe, environmentally benign and economically viable source of electrical energy to meet the increasing electricity needs of the country’.
- Objectives:-
- To maximise the power generation and profitability from nuclear power stations with the motto ‘safety first and production next’.
- To increase nuclear power generation capacity in the country, consistent with the available resources in a safe, economical and rapid manner, in keeping with the growth of energy demand in the country.
- To continue and strengthen QA activities relating to nuclear power programme.
- To develop personnel at all levels to further improve their skills and performance consistent with the high technology.
- To strengthen the environmental protection measures relating to nuclear power generation.
MUST READ: Zaporizhzhia nuclear plant
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
- Japan
- Russia
- The United Kingdom
- The United States of America
Q.2) What is/are the consequence /consequences of a country becoming a member of the ‘Nuclear Suppliers Group’? (2018)
- It will have access to the latest and most efficient nuclear technologies.
- It automatically becomes a member of “The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT)”.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: The Union Minister of Science and Technology recently launched the SUPREME initiative.
About Support for Up-gradation Preventive Repair and Maintenance of Equipment (SUPREME):-
- The Support for Up-gradation Preventive Repair and Maintenance of Equipment (SUPREME), is an initiative of the Ministry of Science and Technology. (UPSC CSE: Science and Technology and Indian culture )
- It extends financial support for repair, upgradation, maintenance, retrofitting, or acquiring additional attachments to increase the functional capabilities of existing analytical instrumentation facilities.
- Eligibility: Different facilities created under the projects/ Analytical instrumentation facilities (AIFs) with the support of DST only will be considered for funding support under this Scheme.
- UGC recognized Central Universities/ State Funded Universities/Deemed Universities /Private Universities among others are also eligible to apply under this scheme(UPSC Mains: Analyzing India’s Higher Education sector).
- Duration: The duration of support will be for a period not exceeding 3 years.
- Funding Pattern: The funding pattern in the scheme would be 75:25 for all private and government-owned institutions (except for state-funded institutions for which 100% funding would be considered).
MUST READ: Foreign Universities in India
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- Other than those made by humans, nanoparticles do not exist in nature.
- Nanoparticles of some metallic oxides are used in the manufacture of some cosmetics.
- Nanoparticles of some commercial products which enter the environment are unsafe for humans.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to street lighting, how do sodium lamps differ from LED lamps? (2021)
- Sodium lamps produce light at 360 degrees but it is not so in the case of LED lamps.
- As street lights, sodium lamps have a longer life span than LED lamps.
- The spectrum of visible light from sodium lamps is almost monochromatic while LED lamps offer significant colour advantages in street lighting.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 3 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, India appealed to SCO Interbank Consortium members to increase cooperation among themselves.
About SCO Interbank Consortium:-
IMAGE SOURCE: SCO 2019: Opportunities and challenges for India | bilaterals.org
- The SCO Interbank Consortium was established by the member countries of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation in 2005. (UPSC Prelims: Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) )
- It provides funding and bank services for investment projects sponsored by the governments of the SCO member states. (UPSC Mains: Significance of SCO for India)
- Objective: to provide financial services, promote trade, and facilitate investment among the member states.
- The SCO IBC Council meets ad hoc upon the consensus of all of the parties at least once per year.
- The Presidency of the Council is carried out on a rotational basis.
- It consists of major banks from the member countries, such as the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, the National Bank of Kazakhstan, and the Bank of Russia.
- The first meeting of the SCO Interbank Association was held in Beijing on 21–22 February 2006.
MUST READ: 21st SCO Council Meet
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) “Rapid Financing Instrument” and “Rapid Credit Facility” are related to the provisions of lending by which of the following: (2022)
- Asian Development Bank
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
- World Bank
Q.2) With reference to Trade-Related Investment Measures (TRIMS), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2020)
- Quantitative restrictions on imports by foreign investors are prohibited.
- They apply to investment measures related to trade in both goods and services.
- They are not concerned with the regulation of foreign investment.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, nine European countries signed a declaration at the North Sea Summit.
About North Sea Summit:-
IMAGE SOURCE: North Sea – Kids | Britannica Kids | Homework Help
- The second edition of the North Sea Summit was held in the city of Ostend in Belgium.
- Participant countries included: Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Ireland, Luxembourg, Netherlands Norway, and the United Kingdom
- Objective: to make the North Sea the largest green energy (UPSC CSE: Green Energy as a driving force) centre in Europe by accelerating the deployment of offshore wind turbines.
- The summit set ambitious targets including the production of at least 120 gigawatts (GW) of offshore wind energy(UPCS CSE: Understanding Wind Energy) in the North Sea by 2030
- The first summit was held in 2022 in Denmark.
- It resulted in the Esbjerg Declaration
MUST READ: Black Sea Security ties
SOURCE: THE ECONOMIC TIMES
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2020)
International agreement set-up Subject
- Alma-Ata Declaration – Healthcare of the people
- Hague Convention – Biological and Chemical Weapons
- Talanoa Dialogue – Global Climate Change
- Under2 Coalition – Child Rights
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2,3 and 4 only
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Climate Group is an international non-profit organisation that drives climate action by building large networks and running them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the “Under2 Coalition”.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1,2, 4 and 5
- 1,3 and 4 only
- 2,3 and 5 only
- 1,2, 3, 4 and 5
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, India and EFTA countries discussed the resumption of talks for a trade pact.
About European Free Trade Association (EFTA):-
- European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is an intergovernmental organisation established in 1960 by the Stockholm Convention.
- Objective: Promotes free trade and economic integration between its members within Europe and globally.
- EFTA currently has 4 member countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland.
- The EFTA countries have developed one of the largest networks of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs). (UPSC Prelims: Understanding Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) )
- These FTAs span over 60 countries and territories, including the European Union (EU).
- In contrast to the EU(UPSC CSE: India-EU trade relations), EFTA is not a customs union.
- This means that the individual EFTA States are free to set their own customs tariffs and arrange other foreign trade measures vis-à-vis the non-EFTA States.
Governance Structure:-
- EFTA’s highest governing body is the EFTA Council.
- The headquarters of the EFTA Secretariat is located in Geneva.
- EFTA Surveillance Authority (ESA): monitors compliance with European Economic Area (EEA) rules in Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway.
- EFTA Court: is based in Luxembourg and has the competence and authority to settle internal and external disputes regarding the implementation, application or interpretation of the EEA agreement.
MUST READ: India-EU: Trade talks
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which of the following adopted a law on data protection and privacy for its citizens known as the ‘General Data Protection Regulation’ in April 2016 and started implementation of its form
25th May 2018? (2019)
- Australia
- Canada
- The European Union
- The United States of America
Q.2) ‘Broad-based Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA)’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of negotiations held between India and (2017)
- European Union
- Gulf Cooperation Council
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
- Shanghai Cooperation Organization
Syllabus
- Prelims –Governance
Context: Recently, the government launched a new e-commerce portal ‘Indiahandmade’.
About Indiahandmade:-
- Indiahandmade Portal is an e-commerce portal(UPSC CSE: Understanding e-commerce) launched by the Indian Government.
- Objective: Empower artisans and weavers by providing them with a platform to sell their products directly to customers.
- This initiative is part of the government’s efforts to promote local artisans and craftsmanship and support the “Vocal for Local” movement. (UPSC Mains: understanding ‘vocal for local’ strategy)
- It provides a platform for artisans and weavers to showcase their products to a wide customer base.
- It connects artisans and weavers directly to buyers through a common platform.
- Indiahandmade Portal offers an opportunity for weavers and artisans to become future e-entrepreneurs.
- The portal provides free handholding to sellers from registration to order fulfilment, helping them with logistics, payments, and other aspects of online selling.
- This empowers weavers and artisans with the necessary tools and support to become successful e-entrepreneurs and grow their businesses.
- The portal does not charge any commission from sellers, ensuring that artisans and weavers receive the full value of their products.
- Free shipping is provided to customers, making it convenient and cost-effective for them to purchase products from the portal.
- It also provides a return option to customers, ensuring a seamless buying experience.
- Multiple payment gateways are available for customers to pay online, providing flexibility and convenience in payment options.
- The portal complements the PM-VIKAS initiative by providing a platform for artisans and weavers to showcase their products and sell them directly to customers.
- PM Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman Yojana (PM-VIKAS): aims to provide small artisans and craftsmen with training on quality, scale, and reach, as well as access to advanced skill training, modern digital techniques, brand promotion, linkage with local and global markets, digital payments, and social security.
MUST READ: Empowering MSMEs digitally
SOURCE: FINANCIAL EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
- Department of Science and Technology
- Ministry of Labour and Employment
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Q.2) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Universal Health Care can help to address the current health disparities that exist in India, as it would ensure that everyone, regardless of their social status, has access to essential health services.
About Universal Health Coverage/Care:
- The United Nations defines UHC as “everyone, everywhere should have access to the health services they need without risk of financial hardship.”
- Sustainable Development Goals target 3.8 also focuses on achieving universal health coverage.
- In the context of India, this includes health promotion, prevention, treatment, rehabilitation, and palliative care, without experiencing any financial hardship or risk of impoverishment.
The Evolution of Universal Health Care:
- In 1977, the World Health Assembly endorsed the slogan “Health for All by 2000,” implying universalization.
- Thus, nobody is denied this and everybody is eligible without being discriminated against on the basis of financial status, gender, race, place of residence, affordability to pay, or any other factors.
- India committed itself to this goal through its National Health Policy in 1983.
India’s Initiatives for UHC:
- National Health Mission (NHM): NHM was launched by the Union Government in 2013 subsuming the National Rural Health Mission (2005) and the National Urban Health Mission (2013).
- Main components:
- Health System Strengthening
- Reproductive-Maternal- Neonatal-Child and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A)
- Communicable and Non-Communicable Diseases
- NHM envisages achievement of universal access to equitable, affordable & quality health care services that are accountable and responsive to people’s needs.
- Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0: Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 is an Integrated Nutrition Support Programme.
- It seeks to address the challenges of malnutrition in children, adolescent girls, pregnant women and lactating mothers through a strategic shift in nutrition content and delivery and by creation of a convergent eco-system to develop and promote practices that nurture health, wellness and immunity.
- Components:
- Nutrition Support for POSHAN through Supplementary Nutrition Programme (SNP);
- Early Childhood Care and Education [3-6 years] and early stimulation for (0-3 years);
- Anganwadi Infrastructure including modern, upgraded Saksham Anganwadi; and
- Poshan Abhiyaan aims to reduce stunting, undernutrition, anaemia and reduce low birth weight by 2%, 2%, 3% and 2% per annum r
- National Food Security Act (NFSA): The Union Government provides food grains at low cost under the NFSA.
- The act aims to ensure people’s food and nutritional security by assuring access to enough high-quality food at reasonable prices.
Advantages of Universal health coverage in India:
- Improved access to health services: UHC would ensure that all Indians have access to necessary healthcare services, including preventive care, treatment, and rehabilitation, regardless of their financial status or geographic location.
- Better health outcomes: Access to healthcare services will improve health outcomes and reduce mortality rates by diagnosing and treating illnesses and diseases at an earlier stage.
- Reduced financial burden: UHC would protect individuals and families from catastrophic healthcare expenses, reducing the financial burden on households and preventing them from falling into poverty due to healthcare costs.
- Increased government accountability: UHC would increase government accountability in healthcare, as the government would be responsible for ensuring that all citizens have access to essential health services.
- Increased productivity: Improved health outcomes would lead to increased productivity and economic growth as a healthy workforce is more productive.
Challenges in Implementing UHC in India:
Inequitable Access to Health Insurance:
- The lowest coverage of health insurance is among households with the lowest wealth quintile and underprivileged sections, indicating a lack of equitable access to health insurance.
- The NFHS-5 results paint a different picture for India, where insurance coverage is lowest (36.1%) among households with the lowest wealth quintile.
Lack of Financial Protection:
- Despite the existence of schemes like Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram, the average out-of-pocket expenditure per delivery in public health facilities is still high, particularly in urban areas.
- The latest report of NFHS revealed that the average out-of-pocket expenditure per delivery in a public health facility is Rs. 2,916, which in the case of urban and rural stands at Rs. 3,385 and Rs. 2,770.
Inclusion and Exclusion Errors in Health Insurance Policies:
- Recent studies have shown that like earlier health insurance policies, the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) is also not free from inclusion and exclusion errors, which could lead to the inclusion of ineligible households and exclusion of eligible households.
Availability of Services:
- Although 56% of empanelled hospitals under the PMJAY are in the public sector, 40% are in the private for-profit sector, indicating that the availability of services may be concentrated in areas with previous experience implementing publicly funded health insurance schemes.
Inadequate Infrastructure:
- In many low- and middle-income countries, the lack of proper infrastructure is a significant challenge to achieving UHC.
- This includes inadequate health facilities, inadequate equipment, and inadequate medical supplies.
- There is a shortfall of 79.5% of specialists at the Community Health Centers (CHCs) as compared to the requirement.
Poor Health Education:
- Lack of education and awareness regarding healthy lifestyles and preventive health measures can lead to an increase in preventable illnesses and conditions.
Way Forward:
India’s National Health Mission, with concurrent intersectoral thrusts on Poshan Abhiyan, National Food Security, Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, etc., is a better model of fully tax-funded Universal Health Care.
Thus, moving forward with a newer concept of Universal Health Care is necessary to encompass primary, secondary, and tertiary care for all who need it at an affordable cost without discrimination.
Source: The Hindu
MUST READ: India’s Healthcare Sector
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Economy)
Context: emergence of brain economy in recent times, that is Technology driven knowledge based economy, which will change the way we look at labour, capital and skills.
About Brain Economy:
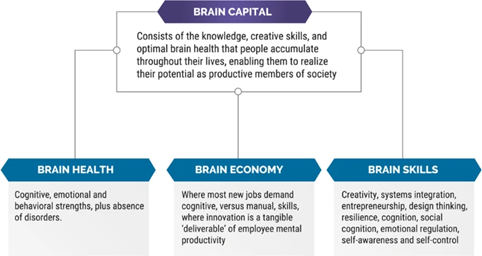
Source: https://www.nature.com
- The Brain Economy refers to the shift towards a knowledge-based economy where the primary source of economic growth is driven by innovation and creativity, and the ability to generate, process, and use knowledge effectively.
Advantages of the brain economy
- Higher Productivity: With advancements in technology and automation, the brain economy has the potential to significantly increase productivity and efficiency.
- Improved Quality of Life: Brain-based work can create jobs that are less physically demanding and more intellectually stimulating.
- This can lead to an improved quality of life for those who work in the brain economy.
- Increased Innovation: Brain-based work is about rapid innovation and creation, driven by technology.
- This can lead to new products, services, and technologies that can enhance people’s lives.
- Amazon, for example, has brains that create new offerings, skills that maintain their vast data centres and bodies that deliver packages to homes.
- Increased Collaboration: The brain economy requires collaboration across different fields, disciplines, and cultures.
- This can lead to increased cooperation and understanding among people from diverse backgrounds.
- Consistency in Social Progress: Technology and brain power can be used to address social and environmental challenges, such as poverty, inequality, climate change, and healthcare.
- Much Flexibility: With technology, brain-based work can be done from anywhere, at any time, providing greater flexibility for workers and businesses.
- Easy Access to Information: Technology has made it easier than ever to access information and knowledge, which can help to create a more informed and educated society.
- Personal Development: Brain-based work requires continuous learning and personal development, which can lead to increased self-awareness, creativity, and adaptability.
Challenges for the brain economy:
- Inequality: The brain economy has the potential to exacerbate inequality by assigning exponentially differential values to body, skill, and brain.
- This can lead to a widening gap between those who have access to education and training in advanced technology and those who do not.
- Ethical dilemmas: As technology continues to evolve and become more integrated into the brain economy, ethical dilemmas around privacy, inclusivity, fairness, and the impact on social issues such as gender parity and wealth sharing may arise.
- Regulatory challenges: The fast-paced nature of technology development in the brain economy may pose regulatory challenges for policymakers and regulators.
- There may be a need for more agile and responsive regulatory frameworks to keep pace with technological developments.
- Access to technology: Not everyone may have access to the technology required to participate in the brain economy, leading to a digital divide and further exacerbating inequality.
- Job displacement: The rise of the brain economy may result in the displacement of jobs that require physical labor or lower levels of skill, leading to job losses in certain sectors.
- This may also require significant retraining and upskilling of workers in order to adapt to the new demands of the economy.
- Societal impacts: The widespread adoption of technology in the brain economy may have significant societal impacts, such as changes to the nature of work, social relationships, and human behavior.
- It will be important to monitor these impacts and take steps to mitigate any negative effects.
- Environmental impact: The growth of the brain economy may lead to increased energy consumption and environmental impact, particularly as new technologies such as quantum computing and genetic engineering become more prevalent.
- It will be important to consider the environmental impact of these technologies and take steps to mitigate any negative effects.
Way Forward:
There is a need to abandon outdated stereotypes of evil corporations, sinful profits and inhuman technology. The myth of man vs machine needs to be ended. Technology doesn’t destroy jobs, instead It creates jobs, liberates people and drives social progress.
The education architecture of the country needs to be revamped. Students and teachers in primary and secondary education need to be equipped with technology. Failures in experimentation and creation in schools should be celebrated.
Multidisciplinary research universities should be created on a war footing. Courses in different aspects of technology must be made mandatory for all liberal arts programmes, just like liberal arts courses should be made mandatory in all science and technology departments.
Source: Indian Express
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following countries:
- Belgium
- Sweden
- France
- Finland
- the United Kingdom
which of the above countries borders with the North Sea?
- 1 3 and 4 only
- 2 4 and 5 only
- 1 3 and 5 only
- All of the above
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding the Support for Up-gradation Preventive Repair and Maintenance of Equipment (SUPREME) Initiative:
- It extends financial support for repair, upgradation, maintenance, retrofitting, or acquiring additional attachments to increase the functional capabilities of existing analytical instrumentation facilities.
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) With reference to India’s Nuclear Energy, which of the following statements is not correct?
- India is signatory to the Convention on Supplementary Compensation which ensures compensation is available to the victims for nuclear damage caused by a nuclear incident or disaster
- India currently has 25 nuclear reactors
- All the existing reactors are operated by the state-owned Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL)
- NPCIL works under the administrative control of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), Government of India.
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 28th April 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 27th April – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – c











