IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –GOVERNMENT SCHEMES
Context: Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI 5.0), a campaign of the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare will conclude all 3 rounds on 14th October 2023.
About Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI 5.0):-
- Launch:2023.
- Ministry: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Objective: to enhance immunization coverage for all vaccines provided under the Universal Immunization Programme (UIP) as per the National Immunization Schedule (NIS).
- It is the flagship routine immunization campaign of the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. (Mission Indradhanush)
Salient Features:-
- The campaign will be conducted across the country during the months of August, September and October this year.
- During these three rounds, children of the 0-5 years age group and pregnant women, who have missed any dose of vaccine as per the National Immunization Schedule ( NIS), will be vaccinated.
- This year, for the first time the campaign is being conducted across all the districts in the country and includes children up to 5 years of age (Previous campaigns included children up to 2 years of age).
- Government of India is committed to achieving the target of Measles-Rubella Elimination ( MR Elimination) by December 2023 and the Intensified Mission Indradhanush 5.0 program is a major step toward achieving this goal. (India’s plan to eradicate measles, rubella)
- Every state/ UT, has been given a target of 95% for both MR doses (MR1, MR2) and 2 per lac population for Non Measles Non Rubella ( NMNR) Discard Rate, by GOI.
- Chandigarh has already achieved 103% ( MR1) , 95%(MR2) and 6 per Lac( NMNR Discard Rate).
- IMI 5.0 is being conducted in three rounds i.e., 7 -12 August, 11-16 September, and 9-14 October 2023 i.e., 6 days in a month with the inclusion of a Routine Immunization Day.
- All States/UTs except Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Punjab will conclude all three rounds of the IMI 5.0 campaign by 14 October 2023.
- As of 30th September 2023, over 34,69,705 children and 6,55,480 pregnant women were administered vaccine doses during the first 2 rounds of the IMI 5.0 campaign across the country.
Significance:-
- IMI 5.0 ensures that routine immunization services reach the missed-out and dropped-out children and pregnant women across the country.
MUST READ: mRNA Vaccine
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under the Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy: (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for preschool children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming. to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with a special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) ‘Wolbachia method’ is sometimes talked about with reference to which one of the following? (2023)
- Controlling the viral diseases spread by mosquitoes
- Converting crop residues into packing material
- Producing biodegradable plastics
- Producing biochar from. thermochemical conversion of biomass
Syllabus
- Prelims –DEFENSE
Context: The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) conducted the 21st National Maritime Search and Rescue Board (NMSAR) meeting recently.
Key highlights of the 21st NMSAR meeting:-
- Date: 12 October 2023.
- Venue: Kolkata.
- The meeting was chaired by Director General Rakesh Pal, ICG in his capacity as Chairman, of the NMSAR Board.
- ICG is the coordinating and executing agency for Maritime Search and Rescue in the Indian Search and Rescue Region.
- NMSAR Board:-
- It was formed in 2002 and since the Board meeting is being held annually.
- To discuss policy issues, formulate guidelines/ procedures and consider recommendations for reviewing the National Search and Rescue plan.
- During the meeting, National Search and Rescue (SAR) awards for the year 2022-23 were also presented.
- The United Kingdom Flag vessel MV Furious was awarded in the merchant vessel category.
- Indian Fishing Boat New Aparajita from West Bengal was awarded in the fishing boat category.
- ICG Ship Sujeet & ICG Air Squadron 835 Sqn(CG) in Govt owned SAR unit category.
- Gujrat Maritime Board and INMCC received the award in the ashore unit category.
About the Indian Coast Guard (ICG):-
- Establishment: 1978.
- Ministry: Ministry Of Defence.
- HQ: New Delhi, Delhi
- It was established in August 1978 by the Coast Guard Act, 1978 as an independent armed force of India.
- It is the fourth largest Coast Guard in the world.
- For effective command and control, the Maritime Zones of India are divided into five Coast Guard Regions, namely, North-West, West, East, North-East and Andaman & Nicobar, with the respective Regional Headquarters located at Gandhinagar, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata and Port Blair.
Historical Background:-
- The concept of forming ICG came into being after the 1971 war.
- The blueprint for a multidimensional Coast Guard was conceived by the visionary Rustamji Committee.
Objectives and Functions:-
- To protect our ocean and offshore wealth including oil, fish and minerals.
- To assist mariners in distress and safeguard life and property at sea. (Indian Coast Guard Ships (ICGS))
- To enforce maritime laws with respect to sea, poaching, smuggling and narcotics.
- To preserve marine environment and ecology and protect rare species.
- To collect scientific data and back up the Navy during war.
- To Prevent and Control of Marine Pollution.
- To ensure the safety and Protection of Artificial Islands and Offshore Terminals
MUST READ: Defence Acquisition Council
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Home Guards, consider the following statements: (2023)
- Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards Act and Rules of the Central Government.
- The role of the Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary force to the police in the maintenance of internal security.
- To prevent infiltration on the international border/ coastal areas, the Border Wing Home Guards Battalions have been raised in some states.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
- Japan
- Russia
- The United Kingdom
- The United States of America
Syllabus
- Prelims –SPORTS
Context: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi will inaugurate the 141st International Olympic Committee (IOC) Session on 14th October 2023.
Background:-
- The 141st International Olympic Committee (IOC) Session, will be held at the Jio World Centre in Mumbai.
- IOC session is being held in India after a gap of about 40 years.
- India is hosting the IOC Session for the second time. (Mission Olympic Cell)
About the International Olympic Committee (IOC):-
- Establishment: 1894.
- HQ: Lausanne, Switzerland.
- Objective: to promote the Olympic movement and uphold the Olympic values, which include friendship, respect, and excellence, globally.
- They are responsible for organizing and managing the Summer and Winter Olympic Games.
- IOC Session discusses and decides on the key activities of the global Olympics movement including:-
- Adoption or amendment of the Olympic Charter
- The election of IOC members and office-bearers
- Election of the host city of the Olympics
Functions:-
- Olympic Games Organization: They select the cities for the Games and ensure smooth operations.
- The IOC chooses which cities will host the Olympic Games.
- The IOC supports and develops sports globally.
- It provides financial assistance and Aid to National Olympic Committees (NOCs).
- The IOC perform such activities in order to assist them with sports development.
- The IOC collaborates with sports organizations to ensure their efficient management.
- It also plays a significant role in the fight against doping in sports, working with organizations like the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) to maintain the integrity of Olympic competitions.
MUST READ: Indian Olympic Association
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements in respect of the 44th Chess Olympiad, 2022: (2023)
- It was the first time that the Chess Olympiad was held in India.
- The official mascot was named Thambi.
- The trophy for the winning team in the open section is the Vera Menchik Cup.
- The trophy for the winning team in the women’s section is the Hamilton-Russell Cup.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following statements in respect of the Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards. (2021)
- Bharat Ratna and Padma Awards are titled under Article 18(1) of the Constitution of India.
- Padma Awards, which were instituted in the year 1954, were suspended only once.
- The number of Bharat Ratna Awards is restricted to a maximum of five in a particular year.
Which of the above statements is not correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
Context: A recent study states that cutting down on Methane emission by Targeted methane mitigation can avoid 0.1°C warming in 2050.
Key Highlights of the report:-
- The report was released jointly by the International Energy Agency, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the UNEP-convened Climate and Clean Air Coalition.
- Around 580 million tonnes (Mt) of methane is emitted every year globally, 60 per cent of which comes from human activities, according to the latest assessment.
- Under current trajectories, total anthropogenic methane emissions could rise by up to 13 per cent between 2020 and 2030.
- The report called for rapid cuts in methane emissions from fossil fuels as it will prevent global warming to an extent greater than the emissions impact of immediately taking all cars and trucks in the world off the road.
- It urged that methane abatement measures should be above and beyond the decarbonization efforts for the energy sector.
- Without targeted action on methane, even with deep reductions in fossil fuel use, the increase in the global average surface temperature will likely exceed 1.6°C by 2050.
- The fossil fuel sector likely holds the largest potential for rapid and low-cost reductions in methane emissions.
- More than 80 Mt of annual methane emissions from fossil fuels can be avoided by 2030 using existing technologies, often at low – or even negative – costs.
- Around $75 billion is required by 2030 for all methane abatement measures in the oil and gas sector in the Net Zero scenario, according to the findings. “This is equivalent to less than 2 per cent of the income generated by the oil and gas industry in 2022,”.
- Controlling methane emissions will also provide health benefits and enhance food security.
About Methane Emission:-
- Methane (CH4) is the simplest hydrocarbon, consisting of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
- It is a colorless, odorless, and highly flammable gas, and the main component in natural gas.
- It is such a potent heat absorber.
- It is the primary component of natural gas.
- It is a powerful greenhouse gas.
- It warms the planet more than 80 times as quickly as a comparable volume of atmospheric CO2 over a comparable amount of time.
- It is estimated to have been responsible for 30 per cent of global warming since the Industrial Revolution.
- Methane pollution, which is a primary component of ground-level ozone.
- It has been linked to heart disease, birth defects, asthma and other adverse health impacts.
Sources of Methane:-
- Biological Sources: it is made from some organic compounds by methane-generating microbes known as
- Agriculture: Livestock emissions from manure and gastroenteric releases account for roughly 32% of human-caused methane emissions.
- Cows also belch out methane.
- Emissions from Fuel and Industries.
Initiatives to reduce methane emission:-
- COP 26 Pledges: At COP26 in Glasgow, over 100 countries signed an agreement to cut methane emissions by 30% by 2030 as methane might be easier to deal with than carbon dioxide.
- MethaneSAT: a planned American-New Zealand space mission scheduled for launch later in 2022.
- It will be an Earth observation satellite that will monitor and study global methane emissions in order to combat climate change.
- UN Initiatives: The UN Food Systems Summit in September 2021 was also aimed at helping make farming and food production more environmentally friendly.
- India’s Initiative: Central Salt & Marine Chemical Research Institute (CSMCRI) in collaboration with the country’s three leading institutes developed a seaweed-based animal feed additive formulation that aims to reduce methane emissions from cattle.
MUST READ: Methane Alert and Response System (MARS)
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) “Climate Action Tracker” which monitors the emission reduction pledges of different countries is a: (2022)
- Database created by a coalition of research organizations
- Wing of “International Panel of Climate Change”
- Committee under “United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change”
- Agency promoted and financed by the United Nations Environment Programme and World Bank
Q.2) ) In the Indian context, what is the implication of ratifying the ‘Additional Protocol’ with the ‘International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’? (2018)
- Civilian nuclear reactors come under IAEA safeguards.
- The military nuclear installations come under the inspection of the IAEA
- The country will have the privilege to buy uranium from the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
- The country automatically becomes a member of the NSG.
Syllabus
- Prelims –SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: Recent reports show that the samples collected from the 4.5-billion-year-old asteroid Bennu could indicate the building blocks of life on Earth.
Background:-
- The sample return capsule from NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission is seen shortly after touching down in Utah, on September 24, 2023.
- The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020. (NASA’s OSIRIS-REx)
About Asteroid Bennu:-
- Discovered: 1999.
- Discovered by: NASA.
- The asteroid was discovered by a team from the NASA-funded Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research team in 1999.
- It was originally named as 1999 RQ36.
- The name Bennu comes from an Egyptian deity related to the Sun, often depicted as a grey heron.
- It is a 500-meter-wide asteroid in an elliptical orbit around the sun.
- It is currently more than 200 million miles from Earth.
- Bennu’s orbit is close in proximity to Earth’s, even crossing it.
- The asteroid makes its closest approach to Earth every 6 years.
- It is one of the most potentially hazardous asteroids currently known to Earth.
- It has a 1‐in‐2,700 chance of impacting Earth during one of its close approaches to Earth in the late 22nd century.
- OSIRIS-REx – short for Origins-Spectral Interpretation-Resource Identification-Security-Regolith Explorer was the first U.S. mission to collect a sample from an asteroid.
About OSIRIS-Rex:-
- Launched on: Sept. 8, 2016.
- Launched y: NASA.
- OSIRIS-REx – short for Origins-Spectral Interpretation-Resource Identification-Security-Regolith Explorer.
- It was the first U.S. mission to collect a sample from an asteroid.
- The OSIRIS-REx mission is essentially a seven-year-long voyage.
- It was meant to explore asteroid Bennu.
- The spacecraft contains five instruments including cameras, a spectrometer, and a laser altimeter.
- The spacecraft arrived at Bennu in December 2018.
- It Surveyed the asteroid for more than two years.
- Bennu is an ancient asteroid, currently more than 200 million miles from Earth.
- The asteroid was discovered by a team from the NASA-funded Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research team in 1999.
- It offers scientists a window into the early solar system as it was first taking shape billions of years ago and tossing ingredients that could have helped seed life on Earth.
- On 20, 2020, the spacecraft collected a sample from the asteroid and stowed it in its sample return capsule.
- The pristine material from Bennu – rocks and dust collected from the asteroid’s surface will offer generations of scientists a window into the time when the Sun and planets were forming about 4.5 billion years ago.
MUST READ: Exoplanets
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media? (2022)
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same surface. speed and places a probe on its
Q.2) With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-stage launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors, and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 3 only
Syllabus
- Prelims –POLITY
Context: Recently, the Central Information Commission (CIC) commemorated the 18th anniversary of the enactment of the RTI Act.
About Central Information Commission (CIC):-
- Establishment: 2005.
- The CIC was constituted in 2005 under the Right to Information Act, 2005.
- The RTI Act 2005 provides for the constitution of a Central Information Commission and State Information Commissions in each state.
- Jurisdiction: the Commission extends over all Central Public Authorities.
- The Right to Information (Amendment) Act, of 2019 amended the Right to Information Act, of 2005.
- The RTI Act, of 2005 specified the tenure, terms of service, and salaries of the Chief Information Commissioner (CIC) and Information Commissioners (ICs) at the central and state levels, in the parent law.
Structure:-
- The Central Information Commission shall consist of:
- The Chief Information Commissioner (CIC).
- Members: Such numbers of Central Information Commissioners (ICs), not exceeding ten, as may be deemed necessary.
- The members shall be persons of eminence in public life with wide knowledge and experience in law, science and technology, social service, management, journalism, mass media or administration and Governance.
- The CIC or IC shall not be an MP or MLA or hold any other office of profit connected with any political party carrying on any business or pursuing any profession.
- Appointment: The members of the commission are appointed by a committee consisting of the PM (as Chair), the Leader of Opposition (LoP) in Lok Sabha and a Union Cabinet Minister appointed by the Prime Minister.
- Tenure: The CIC and ICs (at the central and state level) will hold office for a term of three years.
- Resignation: The CIC or an IC may, at any time, by writing under his hand addressed to the President, resign from his office.
- Removal: The CIC or an IC may be removed from office only by order of the President on the grounds of proven misbehaviour or incapacity after the
- Supreme Court, on a reference made to it by the President, reports that he/she should be removed on the grounds mentioned.
- The President may also remove them from office if such a person is adjudged insolvent, convicted for certain offences etc.
- They are not eligible for reappointment.
Power and Functions:-
- To receive and inquire into a complaint from any person regarding information requested under the RTI act.
- It can order an inquiry into any matter if there are reasonable grounds (suo-moto power).
- While inquiring, the Commission has the powers of a civil court in respect of summoning, requiring documents, etc.
- Adjudication in the second appeal for giving information;
- Direction for record-keeping
- Imposition of penalties and Monitoring and Reporting including preparation of an Annual
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) If a particular area is brought under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the consequence of it? (2022)
- This would prevent the transfer of land from tribal people to non-tribal people.
- This would create a local self-governing body in that area.
- This would convert that area into a Union Territory.
- The State having such areas would be declared a Special Category State.
Q.2) With reference to India, consider the following statements (2021)
- Judicial custody means an accused is in the custody of the concerned magistrate and such accused is locked up in a police station, not in jail.
- During judicial custody, the police officer in charge of the case is not allowed to interrogate the suspect without the approval of the court.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –POLITY
Context: The National Human Rights Commission celebrated its 30th Foundation Day recently.
About the National Human Rights Commission:-
- Established: 1993.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- NHRC is a statutory body established under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993.
- The Act also provides for the creation of the State Human Rights Commission (SHRC) as well.
Historical Background:-
- NHRC was established in conformity with the Paris Principles.
- Paris Principles: adopted for the promotion and protection of human rights in Paris in 1991. It was endorsed by the General Assembly of the United Nations in 1993.
Composition of NHRC:-
- It is a multi-member body. (NHRC)
- It consists of a chairperson, five full-time Members, and seven deemed Members.
- Chairperson: a retired chief justice of India or a judge of the Supreme Court.
- Appointments:-
- The chairman and members are appointed by the President on the recommendations of a six-member committee consisting of:-
- Prime Minister (head)
- Speaker of the Lok Sabha
- Deputy Chairman of the Rajya Sabha
- Leaders of the Opposition in both Houses of Parliament
- Union Home Minister.
- Term: three years or until they attain the age of 70 years, whichever is earlier.
- Removal: The president can remove them from office under specific circumstances.
- They can be removed only on the charges of proven misbehaviour or incapacity if proved by an inquiry conducted by a Supreme Court Judge.
Functions of NHRC:-
- To investigate the violation of human rights.
- To prevent a human rights violation.
- To conduct research about human rights.
- To create awareness campaigns through various mediums, and encourage the work of non-governmental organizations (NGOs).
- NGO: a group that functions independently of any government.
- It is the watchdog of human rights in the country.
MUST READ: Giving Human Rights Commissions more teeth
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following organizations/ bodies in India: (2023)
- The National Commission for Backward Classes
- The National Human Rights Commission
- The National Law Commission
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
How many of the above are constitutional bodies?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- The Self-Help Group (SHG) programme was originally initiated by the State Bank of India by providing microcredit to the financially deprived.
- In an SHG, all members of a group take responsibility for a loan that an individual member takes.
- The Regional Rural Banks and Scheduled Commercial Banks support SHGs.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
United Nations Security Council (UNSC) reforms
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International relations)
Context: The longstanding debate on fundamental reforms at the United Nations (UN) has resurfaced once again, more than thirty years after it first began.
About United Nations Security Council (UNSC):

- It is one of the UN’s six main organs and is aimed at maintaining international peace and security.
- EST: 1945
- HQ: New York City.
- Membership: The Council is composed of 15 Members including 10 non-permanent members.
- P5 with veto power: China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom and the United States.
UNSC elections:
- Each year the General Assembly elects five non-permanent members (out of 10 in total) for a two-year term.
- The 10 non-permanent seats are distributed on a regional basis as follows:
- Five for African and Asian States.
- One for the Eastern European States.
- Two for the Latin American and Caribbean States;
- Two for Western European and other States
- To be elected to the Council, candidate countries need a two-thirds majority of ballots of the Member States that are present and voting in the Assembly.
- The UNSC elections were traditionally held in the General Assembly hall with each of the 193 member states casting its vote in a secret ballot.
Need for United Nations Reforms:
- Inadequate Council Representation: Presently, with 193 UN member-states, only 15 Council members exist, accounting for less than 8%.
- Consequently, a significant number of nations do not feel fairly represented within the Council.
- Imbalanced Powers and privileges: The current privilege enjoyed by the five permanent members and based on historical precedence is politically untenable.
- Europe, comprising just 5% of the global population, controls 33% of Council seats, not including Russia, another European power.
- Financial Disparities: Some countries contribute more financially to the UN than four of the five permanent members.
- For example, Japan and Germany have consistently ranked as the second and third largest UN budget contributors.
- Unresolved conflicts: Conflicts in regions like Sudan, Syria, Afghanistan, Palestine and Myanmar often remain unaddressed, allowing certain countries and non-state actors to exploit these situations economically.
- Failure in basic functions: The Security Council struggles to fulfill its fundamental role, especially when a permanent member attacks its neighbour.
- For example, when Russia attacked Ukraine in February 2022, its veto power obstructed UNSC resolutions addressing the situation.
- Denied Opportunities for Contributions and Representation: Prominent nations like India, with significant population, economic influence, and substantial contributions to the UN, find their opportunities curtailed.
- Despite their active roles in shaping global affairs, these states remain underrepresented, highlighting the pressing need for reforms within the UN framework.
Way Forward: Suggestive measures
- Expansion of UNSC: The changing needs of global governance for peace and security require significant reforms in the UNSC, including expanding its permanent and non-permanent seats to better address the complex and evolving challenges to international peace and security.
- Democratization: The power imbalance between the P5 and other countries in the UNSC needs to be addressed urgently to make the council more democratic and increase its legitimacy in governing international peace, security and order.
- Equitable Representation: Equitable representation of all the regions in the UNSC is critical to decentralizing its governing power and authority over nations.
- The decentralization of the UNSC’s decision-making processes will enable its transformation to a more representative, participatory body.
- India and UNSC: India as the current one of the non-permanent members of the UNSC can start by drafting a resolution containing a comprehensive set of proposals for reforming the UNSC.
- India urged for UNSC reform hosting a meeting of two separate groupings G-4 and L-69 in New York on the sidelines of the UN General Assembly in September 2022.
Source: TH
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Geography)
Context: A study just published in the journal Climate and Atmospheric Science reported a sharp change in the potential for cyclones to form over the Arabian Sea during the late 1990s.
- Climate scientists employ a range of terms to describe observed changes in climate variables. These include;
- Trend: A trend implies that a climate variable is consistently changing in one direction, such as a continuous increase in temperature.
- The term “anthropogenic trend” suggests that these changes are occurring within human lifetimes, although the specific timeframe for a variable to be considered a trend is not always clear.
- Secular Trend: This term is used when a variable has been increasing or decreasing for a certain period within a longer timeframe.
- For instance, a variable may exhibit a secular trend if it has been steadily increasing for 30 years within a 100-year period.
- Decadal Variability: Decadal variability refers to oscillations from a positive to a negative phase that occur over the span of decades.
- It is somewhat similar to the concept of a shift, but decadal variability is often cyclic in nature.
- Shift: A shift represents a rapid transition from one state to another, such as a sudden change in the amount of rainfall or temperature.
- It can be an irreversible jump or a temporary change that later reverts to a previous state.
About Cyclones:
- The word Cyclone is derived from the Greek word Cyclos meaning the coils of a snake.
- It was coined by Henry Peddington because the tropical storms in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea appear like coiled serpents of the sea.
- They are caused by atmospheric disturbances around a low-pressure area distinguished by swift and often destructive air circulation.
- They are usually accompanied by violent storms and bad weather.
- The air circulates inward in an anticlockwise direction in the Northern hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern hemisphere.
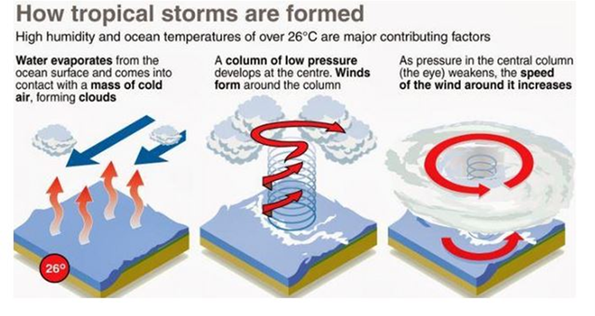
Highlights of Recent study:
- Climate scientists are examining whether observed changes in climate variables, such as decreasing monsoon rainfall, increasing extreme rainfall, droughts, heatwaves, and cyclones, are trends, shifts, or decadal cycles.
- These distinctions are important for how we plan for resources, such as water, crops, and energy.
- A new study suggests a shift in the Arabian Sea’s cyclogenesis potential, which may be linked to a shift in the Warm Arctic, Cold Eurasian pattern. Global warming and regime shifts may also be involved.
- To better understand climate risks and plan for adaptation, scientists must investigate natural variability and how it is modulated by global warming.
Impacts of Climate Change on Cyclone Formation:
- Augmented Precipitation: A warmer atmosphere can accommodate a greater amount of moisture, resulting in increased rainfall.
- More rainfall leads to the release of more heat, ultimately fuelling stronger winds within the cyclone.
- Recent studies have revealed that hurricane rainfall rates rise by at least 7% for every degree of warming.
- Intensification of Cyclones: A warming climate is anticipated to boost wind speeds, leading to a higher proportion of storms intensifying into formidable Category 4 or 5 hurricanes/ Cyclones.
- Temperature Elevation: The temperature of both the ocean and the atmosphere plays a pivotal role in the genesis of tropical cyclones.
- cyclonic storms draw strength from the release of heat generated when ocean surface water evaporates and subsequently condenses into rainfall within the storm.
- In a warming climate, a warmer ocean leads to increased evaporation, which, in turn, means more moisture available in the atmosphere.
- Sea-Level Surge: Elevated temperatures contribute to rising sea levels, increasing the depth of stormwater.
- As sea levels rise, the storm’s inundation reaches further inland.
- Reduced Storm Speed: The velocity of a cyclone can significantly impact the total amount of rainfall at a particular location.
- Slower-moving storms offer a more extended timeframe for rainfall accumulation.
- Although studies indicate a slowdown in storm speed, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear.
- Fusion of Storms: In an increasingly warming world, the convergence of two sizable tropical storms over any of the world’s oceans could result in the formation of a colossal super-cyclone.
Implications of changing landscape of cyclones and its impacts:
- Increased destructions: More powerful storms can inflict significantly greater harm to both people and economies.
- The eastern part of India and Bangladesh were struck by Cyclone Amphan in May of 2020.
- The storm killed 98 people in India, and required the evacuation of more than 5,00,000 people from Bengal and Odisha.
- Unpredictable Predictions: The rapidly evolving nature of storms has rendered conventional forecasting methods unreliable.
- This unpredictability has had a direct impact on the ability to take adequate precautionary measures.
- Rising Storm Frequency: The number of hurricanes forming each year may undergo alterations in the future.
- However, there is no universally accepted theory that comprehensively explains the current quantity of storms in the existing climate or forecasts how this might change in the future.
- Shifting Impact Zones: Recent research suggests that the areas where storms reach their maximum intensity are gradually shifting toward the Earth’s poles.
- This shift holds significant implications for the primary areas affected by these storms.
- In 2021, Gujarat was faced with Cyclone Tauktae, the deadliest cyclone to hit the Arabian Sea in a decade.
- Reports said that the tempestuous winds and rain killed approximately 70 people and more than 8,000 cattle, and damaged as many as 88,000 homes. 2,80,000 people were evacuated from the coastal areas.
Way Forward:
Therefore the study highlighting the shift in cyclone-genesis potential over the Arabian Sea in the late 1990s serves as a compelling example of the complex interplay between climate patterns and regional climate phenomena. It underscores the importance of distinguishing between trends, shifts, and decadal cycles in climate research and their impact on resource planning and climate adaptation.
Source:TH
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| SPCAE MISSIONS | AGENCY |
| 1.Cassini–Huygens | JAXA |
| 2.Prarambh Mission | ISRO |
| 3.PUNCH & TRACERS MISSION | NASA |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
OSIRIS-Rex was the first U.S. mission to collect a sample from an asteroid.
Statement-II:
Bennu is an ancient discovered by a team from the NASA-funded Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research team in 1999.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) With reference to the NHRC, consider the following statements:
- Chairperson is a retired chief justice of India or a judge of the Supreme Court.
- It is a single-member body.
- It conducts research about human rights.
How many of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 3 only
Mains Practice Question
Q.1) Examine the hurdles in amending the UN Charter for UNSC reforms. What strategies can enhance the UNSC’s effectiveness in addressing these challenges today? (250 words)
Q.2) what do you meant by tropical cyclones? Explain how shift in cyclone-genesis potential over the Arabian Sea in the late 1990s happening and how does it relate to the ‘Warm Arctic, Cold Eurasian’ (WACE) pattern and global warming? (250 Words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 13th October 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 12th October – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – a











