IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: The Office of Registrar General of India (ORGI) recently said, that the Census exercise in the country may not take place in 2024.
Background:-
- The Office of Registrar General of India (ORGI) said this replying to an RTI query received.
- The ORGI’s response said, “It is very difficult to conduct the Census and general elections simultaneously.”
About the Office of Registrar General of India (ORGI):-
- Establishment:1961.
- Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Current ORGI: Shri Mritunjay Kumar Narayan.
- Role: Arranging, conducting and analyzing the results of the demographic surveys of India including the Census of India and Linguistic Survey of India.(Census – Challenges & Importance)
- It provides information on size, distribution and socio-economic, demographic and other characteristics of the country’s population.
- The decennial Census of India has been conducted 15 times, as of 2011.
- Beginning of Census: 1872; under British Viceroy Lord Mayo.
- First complete census: 1881.
- Post-1949: it has been conducted by the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India under the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. ( Census 2021)
- The Census Commissioner, India is the statutory authority vested with the responsibility of conducting the Housing & Population Census in India under the Census Act, of 1948 and the Rules framed thereunder.
- The Census Commissioner, India is also designated as Registrar General, India under the Registration of Births & Deaths (RBD) Act, 1969, which provides for the compulsory registration of births and deaths. (UPSC CSE: Registrar-General and Census Commissioner of India)
Functions of ORGI:-
- Housing & Population Census: Planning, coordination and supervision of the field activities; data processing; compilation, tabulation and dissemination of Census results are the primary duties of this office.
- Civil Registration System (CRS): In the role of the Registrar General, India the Census Commissioner coordinates the functioning of the civil registration and vital statistics system in the country through all States and UTs.
- Sample Registration System (SRS): Implementation of a Sample Registration System, wherein a large-scale sample survey of vital events is conducted on a half-yearly basis, is also the responsibility of the ORG&CCI.
- SRS is an important source of vital rates like Birth Rate, Death Rate, Infant Mortality Rate and Maternal Mortality Rate at the State level in the country.
- National Population Register (NPR): In pursuance to provisions contained in Citizenship Rules, 2003 framed under the Citizenship Act, 1955.
- The National Population Register is prepared by collecting information relating to all persons who are usually residing in the country.
- Mother Tongue Survey: The project surveys the mother tongues, which are returned consistently across two and more Census decades.
- The research programme documents the linguistic features of the selected mother tongues.
MUST READ: Caste Census
SOURCE: TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following: (2023)
- Demographic performance
- Forest and ecology
- Governance reforms
- Stable government
- Tax and fiscal efforts
For the horizontal tax devolution, the Fifteenth Finance Commission used how many of the above as criteria other than population area and income distance?
- Only two
- Only three
- Only four
- All five
Q.2) In essence, what does ‘Due Process of Law’ mean? (2023)
- The principle of natural justice
- The procedure established by law
- Fair application of law
- Equality before law
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the new Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS) held its first meeting.
Background:-
- The newly-formed Standing Committee on Statistics held its first meeting recently and discussed the yet-to-be-released results of the Annual Survey of Industries and Annual Survey of Unincorporated Enterprises in detail.
- The Annual Survey of Industries (ASI): it covers all factories registered under the Factories Act across the country, and is considered an important source of industrial statistics of the registered organized manufacturing sector of the economy.
- The survey results for 2020-21 are expected to be released in 2023.
About Standing Committee on Statistics (Sos):-
- Formation: 2023.
- It was constituted on July 13, 2023.
- Historical background: The government renamed and expanded the scope of coverage of the Standing Committee on Economic Statistics (SCES) formed in December 2019 as the Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS).
- The SCoS has a broader mandate to review the framework and results of all surveys conducted under the aegis of the National Statistical Office (NSO).
- NSO: It is the Statistics Wing of the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MOSPI).
- It was created in 2019 by merging the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) and the Central Statistical Office (CSO).
- Objective: it will provide a new internal oversight mechanism for official data, revamping a SCES set up in 2019.
- Headed by: Pronab Sen (former Chief Statistician and former Chairman of the National Statistical Commission).
- Ministry: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MOSPI).
Members of the Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS):-
- The Standing Committee on Economic Statistics had 28 members which made reaching consensus difficult. ( Standing committee)
- Currently, the Standing Committee on Statistics is composed of 14 members.
- It includes four non-official members, 9 official members, and a member secretary.
- The committee can have a total of 16 members, with the possibility of extending this number based on future requirements.
The mandate of the Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS):-
- To provide a new internal oversight mechanism for official data.
- To review the framework and results of all surveys conducted under the aegis of the NSO.
- While the panel will help finalize survey results.
- The National Statistical Commission (NSC) will have the ultimate authority to approve the publication of those results. (NSC)
Terms of reference (ToR) of the Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS):-
- To review the extant framework.
- To address the issues raised from time to time on the subject/ results/ methodology, etc. related to all surveys as brought before the SCoS by MoSPI.
- To advise on survey methodology including sampling frame, sampling design, survey instruments, etc.
- To finalize the tabulation plan of surveys.
- Finalization of survey results.
Need for the new Standing Committee on Statistics (SCoS):-
- Survey design: The members of the Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister have critiqued India’s statistical machinery.
- Its chairperson Bibek Debroy has highlighted the lack of expertise in survey design within the Indian Statistical Service.
- Data quality: In recent years, there have been concerns about the credibility of certain data from the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO), particularly regarding the various household surveys.
- Data divorced from ground realities: Due to the lack of updated data from a recent Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES), India is currently using the 2011-12 figures.
- These do not accurately reflect the present-day ground realities.
MUST READ: (Parliamentary Committees)
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best reflects the Chief purpose of the ‘Constitution’ of a country? (2023)
- It determines the objective for the making of necessary laws.
- It enables the creation of political offices and a government.
- It defines and limits the powers of the government.
- It secures social justice, social equality and social security.
Q.2) Consider the following organizations/bodies in India: (2023)
- The National Commission for Backward Classes
- The National Human Rights Commission
- The National Law Commission
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
How many of the above are constitutional bodies?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: The IMF has projected the Indian economy to grow at 6.1% in 2023 in its World Economic Outlook report.
Key Highlights of Report:-
- India’s Growth projection: The IMF projected a growth rate of 6.1% for India in 2023, which is a 2 percentage point upward revision compared with the April 2023 projection.
- This is reflective of the “momentum” from stronger-than-expected growth in the fourth quarter of 2022 as a result of stronger domestic investment,
- Global Economy: Global growth is projected to fall from an estimated 5% in 2022 to 3% in both 2023 and 2024.
- Inflation:-
- Global headline inflation: expected to fall from 8.7% in 2022 to 6.8% in 2023 and 5.2% in 2024.
- Underlying (core) inflation: is projected to decline more gradually, and forecasts for inflation in 2024 have been revised upward.
- Financial sector: the turbulence could resume as markets adjust to further policy tightening by central banks.
- USA and China:-
- The United States economy has slowed down considerably and faces uncertainty amid global and domestic headwinds.
- China’s recovery could slow, in part as a result of unresolved real estate problems, with negative cross-border spillovers.
- Debt Vulnerabilities in Frontier Economies:-
- There is a need for a global debt resolution initiative to address debt vulnerabilities in frontier economies.
- Sovereign debt distress could spread to a wider group of economies.
- Central Banks’ policy measures: The central banks in economies with elevated and persistent core inflation should continue to clearly signal their commitment to reducing inflation.
- A restrictive stance, with real rates above neutral is needed until there are clear signs that underlying inflation is cooling.
About World Economic Outlook:
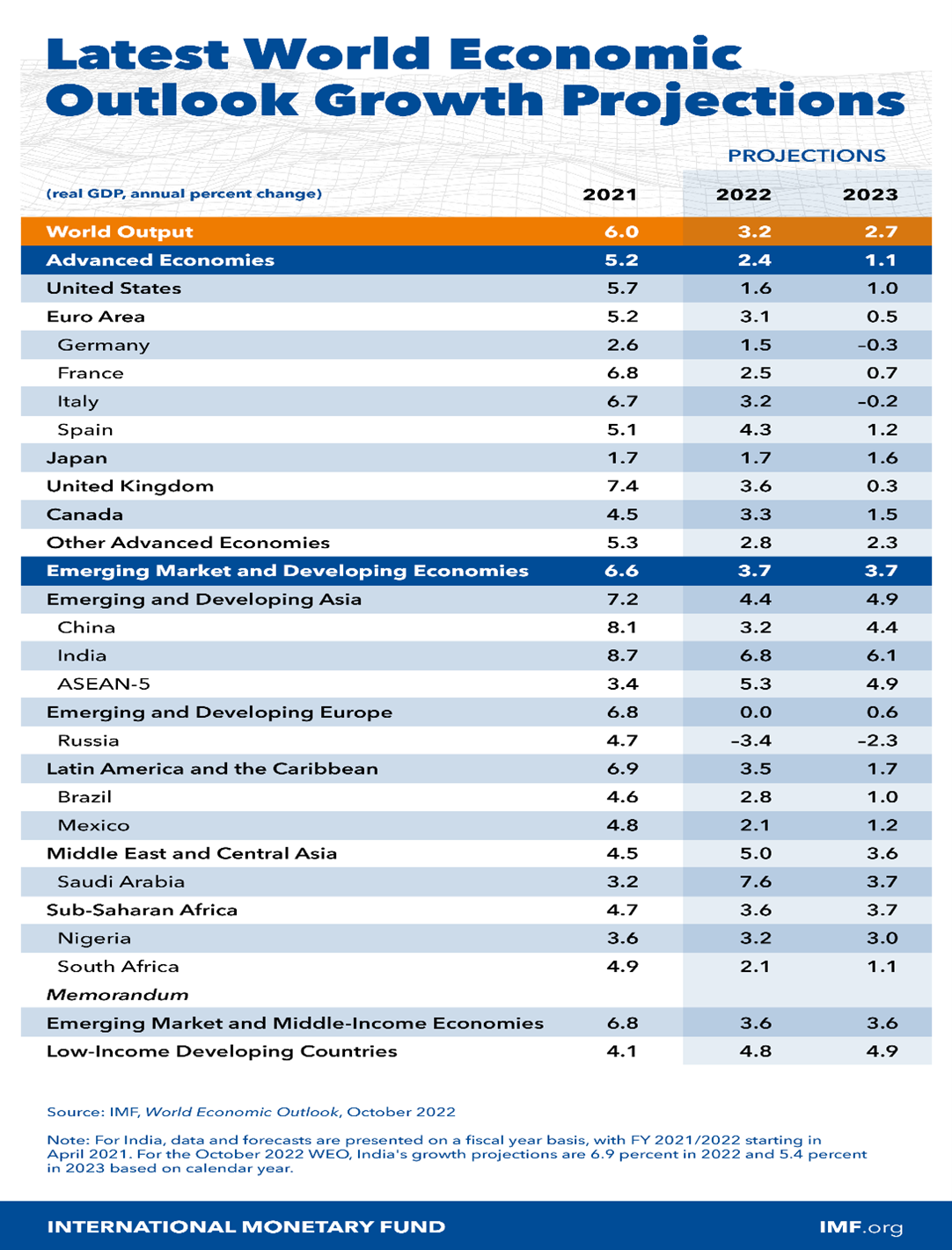
IMAGE SOURCE: IMF.ORG
- Published by: (IMF). WEO)
- It is a survey by the IMF that is usually published twice a year in the months of April and October.
- Objective: It analyzes and predicts global economic developments during the near and medium term.
Significance of the World Economic Outlook:-
The reports provide-
- Analysis and forecasts of economic developments and policies in its member countries.
- Encapsulates the state of the global economy.
- Highlight risks and uncertainty that could threaten growth.
- This report is the main instrument for disseminating the findings and analysis of their global surveillance activities to the world.
About IMF:-
- Established in 1944.
- HQ: Washington, D.C. (United States of America).
- It is an international organization that works to achieve sustainable growth and prosperity for all of its member countries.
- Members: 190
- India is a member.
- Any other state, whether or not a member of the UN, may become a member of the IMF.
- Funding: the IMF’s resources mainly come from the money that countries pay as their capital subscription (quotas) when they become members.
Objectives of IMF:-
- Foster global monetary cooperation.
- Secure financial stability.
- Facilitate international trade.
- Promote high employment and sustainable economic growth.
- Reduce poverty around the world.
- Macroeconomic growth.
- Policy advice & financing for developing countries.
- Promotion of exchange rate stability, and an international payment system.
Structure of IMF:–
- At the top of its organization is the Board of Governors.
- The day-to-day work of the IMF is overseen by its 24-member Executive Board.
- The Managing Director is the head of the IMF staff and Chair of the Executive Board.
Functions of IMF:-
Lending
- The IMF provides loans including emergency loans to member countries experiencing actual or potential balance of payments problems.
Surveillance
- The IMF monitors the international monetary system and global economic developments.
- It identifies risks and recommends policies for growth and financial stability.
Capacity Development
- The IMF provides technical assistance and training to governments, including central banks, finance ministries, revenue administrations, and financial sector supervisory agencies.
FLAGSHIP PUBLICATIONS of IMF:-
- World Economic Outlook (IMF and World Economic Outlook)
- Global Financial Stability Report
- Fiscal Monitor
MUST READ: IMF bailout
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Central Bank digital currencies, consider the following statements: (2023)
- It is possible to make payments in a digital currency without using the US dollar or the SWIFT system.
- A digital currency can be distributed with a condition programmed into it such as a timeframe for spending it.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) “Rapid Financing Instrument” and “Rapid Credit Facility” are related to the provisions of lending by which of the following: (2022)
- Asian Development Bank
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
- World Bank
Syllabus
- Prelims –Economy
Context: Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) permitted non-bank companies to set up, own and operate White Label ATMs (WLAs) in the country.
Background:-
- This has been done in order to drive ATM penetration in the country with a greater focus on Tier III to VI centers.
About White Label ATMs (WLAs):-
- These are the Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) set up, owned and operated by non-bank entities. ( Non-Bank PSPs to Join Centralized Payment System)
- Non-bank entities incorporated in India under the Companies Act 1956 are allowed to operate WLAs.
- 2015: The government permitted Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), up to 100%, under the automatic route.
- Non-bank entities are permitted to set up WLAs in India, after obtaining authorization from RBI under the Payment and Settlement Systems (PSS) Act 2007.
- Such non-bank entities should have a minimum net worth of Rs 100 crore.
- Tata Communications Payment Solutions Limited (TCPSL) was the first company authorized by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to open White Label ATMs in the country.
- Role of WLA: enabling the transactions of all bank customers by establishing technical connectivity with the existing authorized, shared ATM Network Operators or Card Payment Network Operators.
- The operators are entitled to receive a fee from the banks for the use of ATM resources by the bank’s customers and are not permitted to charge bank customers directly.
- Cash in ATMs is provided by the sponsored bank while the ATM machine does not have any branding of the Bank.
Services Provided by WLA:-
- Dispensing cash ( Cardless cash withdrawals at ATMs)
- Account Information
- Cash Deposit
- Regular Bill Payment
- Mini / Short Statement Generation
- PIN Change
- Request for Cheque Book
MUST READ: UPI and NPCI Regulation
SOURCE: PIB
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) In the context of finance, the term ‘beta’ refers to (2023)
- the process of simultaneous buying and selling of an asset from different platforms
- an investment strategy of a portfolio manager to balance risk versus reward
- a type of systemic risk that arises where perfect hedging is not possible
- a numeric value that measures the fluctuations. of stock to changes in the overall stock market.
Q.2) With reference to Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), consider the following statements: (2022)
- They enable the digital representation of physical assets.
- They are unique cryptographic tokens that exist on a blockchain.
- They can be traded or exchanged at equivalency and therefore can be used as a medium transaction. of commercial
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, studies were done on the status of the lost tiger’s population of the Kawal Tiger Reserve (KTR).
Background:-
- Tigers were locally extirpated from Kawal Tiger Reserve (KTR).
- However, the Chief wildlife warden of Telangana, Lokesh Jayaswal, said that though NTCA figures for the core Kawal reserve say there are no tigers there, there are 10 tigers still present in the Kawal tiger corridor.
About Kawal Tiger Reserve (KTR):-
- Location: North Eastern part of Telangana (Old Adilabad district).
- It has the Godavari River on one side and the Maharashtra border on the other side.
- Govt of India declared Kawal wildlife sanctuary as Tiger Reserve in 2012. (Amrabad Tiger Reserve)
- Rivers: This sanctuary is the catchment for the rivers Godavari and Kadam, which flow towards the south of the sanctuary.
- Total Area: 2015.44 Sq Km out of which core Area is 893 Sq.Km.
- The Kawal Tiger Reserve (KTR) extends into the districts of Nirmal, Mancherial, Adilabad and KB Asifabad Districts. ( Indravati Tiger Reserve)
MUST READ: Anamalai Tiger Reserve
SOURCE: TIMES OF INDIA
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”? (2020)
- Corbett
- Ranthambore
- Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam
- Sunderbans
Q.2) Which of the following are in Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve? (2019)
- Neyyar, Peppara and Shendurney Wildlife sanctuaries; and Kalakad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve
- Mudumalai, Sathyamangalam and Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuaries; and Silent Valley National Park
- Kaundinya, Gundla Brahmeswaram and Papikonda Wildlife Sanctuaries; and Mukurthi National Park
- Kawal and Sri Venkateswara Wildlife Sanctuaries; and Nagarjunasagar Srisailam Tiger Reserve
The ‘free movement regime’ along the India-Myanmar border
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Security Issues)
Context: Amid tensions in Manipur, questions have been raised on the Free Movement Regime (FMR) that facilitates migration across the Indo-Myanmar Border (IMB).
About the Free Movement Regime
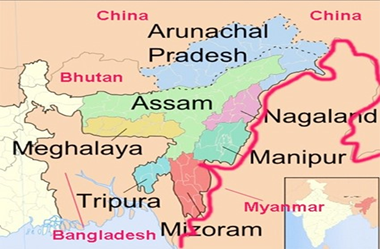
- The border between India and Myanmar runs for 1,643 km in the four states of Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- The FMR is a mutually agreed arrangement between the two countries that allows tribes living along the border on either side to travel up to 16 km inside the other country without a visa.
- The FMR was implemented in 2018.
Significance of FMR:
- The agreement will facilitate movement of people on basis of valid passports and visas, which will enhance economic and social interaction between two countries.
- It will facilitate regulation and harmonization of already existing free movement rights for people ordinarily residing in border areas of both countries.
- It will also give boost to economy of North East and leverage geographical connections with Myanmar to boost trade and people-to-people ties.
- It will also safeguard traditional rights of largely tribal communities residing along border, which are accustomed, to free movement across land border.
Challenges:
Insurgency and drug trafficking:
- A number of insurgent groups have built camps in nearby regions.
- According to the Centre for Land Warfare Studies (CLAWS), a number of insurgent groups such as the United National Liberation Front (UNLF), People’s Liberation Army (PLA), the United Liberation Front of Assam (ULFA), National Socialist Council of Nagaland (NSCN), and small groups of Kukis and Zomis have built camps in Sagaing Division, Kachin State and Chin State in Myanmar.
- They took shelter there, obtained arms, trained cadres and engaged in illegal activities such as smuggling drugs and selling weapons to raise funds.
- This is possible because of the porous borders and frequent misuse of FMR.
- Therefore, managing and administering the border areas effectively is pertinent for reducing drug trafficking and illegal cross-border movement on unfenced borders,” the paper said. (Revisiting Free Movement Regime (FMR): Challenges and Implications, November 2022)
Suggestive measures: Way Forward
- The focus should be on revising FMR and transforming informal to formal trade by focusing on infrastructural development, regulatory mechanisms.
- Designated multiple entry points, within reasonable distance along the India-Myanmar Border, and strict vigilance by deploying the border guards as per requirement, must be initiated.
- Through these designated entry points, people should be strictly informed to use the designated point for going and coming across the border.
- Deployment of manpower 24/7 and increasing their number, is a must to check the frequency of traders’ movement, locals and people with local head loads.
- Strict checking or frisking of women should be done in a separate compartment, especially for women by deploying more women in uniform.
- Strict vigilance at entry points by deploying sufficient security guards. Selective fencing in specific regions is required.
- It is imperative that India strengthens the security of the border and redoubles its efforts to meaningfully engage Myanmar to effectively manage this border.
- To begin with, it should give the Assam Rifles the sole responsibility of guarding the India-Myanmar border and strengthen it with adequate manpower and equipment.
- At the same time, through sustained community interaction programmes, the border community should be sensitised to participate in the nation-building project.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 1 (Society) and GS 2 (Governance)
Context: The Union government has told the Supreme Court that transgender persons can avail of any of the existing 50% reservation in admissions and government jobs already available to Scheduled Caste, Scheduled Tribe and Socially and Educationally Backward Communities (SEBC) across the country.
About reservation for Transgender:
- Transgender persons are those whose gender identity or expression does not match their assigned sex at birth.
- They face discrimination, stigma, violence and exclusion from various spheres of life.
- To address these issues and ensure their rights and dignity, some countries have introduced reservation policies for transgender persons in education, employment, health care and political representation.
- In India, reservation is granted to certain castes, tribes, and religious minorities that are classified as socially and educationally backward classes (SEBCs).
- One such group that has been recognized as SEBCs by the Supreme Court of India is the transgender community.
Demand for horizontal reservation for transgender community:
- Transgender individuals have faced long-term marginalization in society, warranting specific provisions and recognition of their social identity.
- The NALSA judgment has been interpreted as directing reservations for transgender individuals in the OBC category due to their identification as a socially and educationally backward class.
- The demand for horizontal reservation raises concerns that Dalit, Bahujan, and Adivasi transgender individuals may have to choose between availing reservation based on caste and gender identities, leading to competition and exclusion.
NALSA judgement:
- A study conducted by the National Human Rights Commission revealed that in 2017, only 6% of transgender people were formally employed.
- In the National Legal Services Authority of India (NALSA) vs Union of India (2014) case, the Supreme Court ruled that transgender persons have a right to reservation.
- It also directed the Centre and the State Governments to take steps to treat them as socially and educationally backward classes of citizens and extend all kinds of reservation in education and employment.
Horizontal and Vertical Reservations in India
- Reservation in education and employment can be divided into two broad categories, namely, vertical and horizontal.
- Vertical reservations are provisions aimed at addressing social asymmetry arising out of caste hierarchy, and in the case of OBCs, social and educational “backwardness”.
- These include reservations for Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST) and Other Backward Classes (OBC).
- Horizontal reservation, on the other hand, cuts across all vertical groups to provide affirmative policies for disadvantaged groups within categories.
- For example, disabled persons are guaranteed horizontal reservation in all the aforementioned vertical categories, general and reserved (vertical) alike, by the Central government.
Challenges faced by Transgender Community
- Social Stigma: They often face difficulty in property inheritance or child adoption.
- Because of being socially ostracized, they are compelled to take up menial jobs despite good qualifications or forced into sex work.
- Identity crisis: They are often forced to identify with a gender with which they are not associated at the workplace despite the government passing the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019 that allows the community the right to self-perceived gender identity.
- Discrimination and ostracisation: They face discrimination in employment, educational institutes, and within families which severely affects their overall wellbeing.
- Unemployment: The community has limited avenues of employment and faces severe discrimination at work because of the associated social stigma.
- Lack of public amenities: They face issues with the accessibility of public toilets and public spaces.
- They often face problems in prisons, hospitals and schools.
Transgender initiatives in India
- Transgender (Protection of Rights) Act 2019: The Act, passed by Parliament, aims to end discrimination against Transgender people in access to education, employment and healthcare and to recognize the right to their self-perceived gender identity.
- Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Rules, 2020: To carry out the provisions of the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019 of the Government.
- National Transgender Council: The Transgender (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019 established the National Transgender Council to advise the Central Government on the formulation and evaluation of policies, programmes, legislation and projects for the welfare of the Transgender community.
- National Transgender Portal: It is a portal of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment that helps transgender people to apply for certificates and identity cards digitally from anywhere in the country.
- Garima Greh: The aim of the scheme is to provide refuge to Transgender people with basic amenities like shelter, food, medical care and recreational facilities.
Way Forward:
By implementing these measures, we can create a more inclusive and equitable society for transgender persons and other marginalized groups. The establishment of National Council for Transgender Persons has been a welcome step to mainstream the community in the society and increase sense of respect for transgender community. Reservation policies are not a panacea, but they are a necessary and effective tool to address the historical injustices and systemic barriers that transgender persons face.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Tiger Reserve | Location |
| 1.Kawal Tiger Reserve (KTR) | Andhra Pradesh |
| 2.Kali Tiger Reserve | Chhattisgarh |
| 3.Indravati Tiger Reserve | Karnataka |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
Tata Communications Payment Solutions Limited (TCPSL) was the first company authorized by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to open White Label ATMs in the country.
Statement-II:
White Label ATMs cannot provide PIN Change service.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
World Economic Outlook is usually published twice a year in the months of April and October.
Statement-II:
The report highlights the risk and uncertainty that could threaten growth.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Mains Practice Questions
Q.1) Although beneficial to local people and helpful in improving Indo-Myanmar ties, the Free Movement Regime has been criticized for unintentionally aiding illegal immigration, drug trafficking, and gun running. Should the FMR be removed? Discuss. (250 words)
Q.2) Reservation for transgender people in government jobs and educational institutions is a contentious issue that has been debated for a long time. What are the significances of providing equal opportunities and representation to the transgender community? How can the government and society address these challenges faced by the transgender community? (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 31st July 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 29th July – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – c














