IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis

Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Intermediate-Mass Black Hole
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Space
In news
- Analyses of signals from gravitational waves detected in 2019 at the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO), the USA and the detector Virgo at Italy have indicated a black hole with unusual mass.
Key takeaways
- These waves were a result of a collision between two black holes billions of years ago.
- The signal has been named GW190521.
- It likely represented the instant that the two black holes merged.
- It lasted less than one-tenth of a second.
- It was calculated to have come from roughly 17 billion light-years away.
Do you know?
- Out of the two, the larger black hole was of 85 solar masses and the smaller black hole was of 66 solar masses
- In the merger leading to the GW190521 signal, the larger black hole was well within the unexpected range, known as the pair-instability mass gap.
- The researchers suggest that the larger 85-solar-mass black hole was not the product of a collapsing star but was itself the result of a previous merger.
Important value additions
About LIGO
- It is a large scale physics experiment observatory established in 2002 to detect gravitational waves.
- The present telescopes could detect objects which emit electromagnetic radiations like X-ray, gamma rays etc. However, merger of black holes and many other cataclysmic events do not emit electromagnetic waves rather gravitational waves.
- Thus, LIGO was established to unfold the many unknown phenomenon in universe through the gravitational waves detection.
- Indian participation in the LIGO Scientific Collaboration, was done under the umbrella Initiative –IndIGO, which is a consortium of Indian gravitational-wave physicists.
Draft Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture: NITI Aayog
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- IT; Cybersecurity
In news
- Recently, the NITI Aayog has released draft Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture (DEPA).
- Aim: To promote greater user control on data sharing.
- Implemented by: RBI, SEBI, IRDAI, PFRDA and the Ministry of Finance
Key takeaways
- DEPA will be empowering individuals with control over their personal data, by operationalising a regulatory, institutional, and technology design for secure data sharing.
- It is designed as an evolvable and agile framework for good data governance.
- It empowers people to seamlessly and securely access their data and share it with third party institutions.
- The consent given under DEPA will be free, informed, specific, clear, and revocable.
Do you know?
- Using DEPA, individuals and Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) can use their digital footprints to access not just affordable loans, but also insurance, savings, and better financial management products.
- The framework is expected to become functional for the financial sector starting fall 2020.
- It will help in greater financial inclusion and economic growth.
- Opening up an API-based data sharing framework would bring significant innovation by new fintech entities.
- This architecture replaces costly and cumbersome data access and sharing practices that disempower individuals.
Rogan Art: Gujarat
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I- Art and Culture
In news
- Rogan art (hand painting on cloth) was recently in news because it is facing an unprecedented challenge due to pandemic.
Important value additions
- With origins in Persia, it came to Kutch around 300 years ago.
- This rare craft is practised by a lone Muslim family, the Khatris of Nirona Village, Gujarat.
- Rogan is a form of textile painting which uses a rich, brightly coloured paint made from castor oil and natural colors.
- The intricate motifs – geometric flowers, peacocks, the tree of life, etc. – are drawn from the history and folk culture of the Kutch region.
- The ‘Tree of Life’ design is the most famous design in Rogan painting.

Image source: Click here
Flying V Aircraft
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III- Defence
In news
- The first real test flight of the scaled model of the ‘Flying V’ aircraft was successfully conducted.
Key takeaways
- Flying V is a futuristic and fuel-efficient long-distance aircraft that could one day carry passengers in its wings.
- The Flying-V design integrates the passenger cabin, the cargo hold and the fuel tanks in the wings.
- Computer calculations have predicted that the aircraft’s improved aerodynamic shape and reduced weight will reduce fuel consumption by 20% compared to today’s advanced aircrafts.
Do you know?
- The original plan for the Flying-V aircraft design came from TU Berlin student Justus Benad.
- The ‘Flying V’ project was first presented at the 100th anniversary of the Dutch airlines KLM, which has also been a partner in the project since its beginning in 2019.
- Various business partners including Airbus (an aerospace company), are now involved in the project.
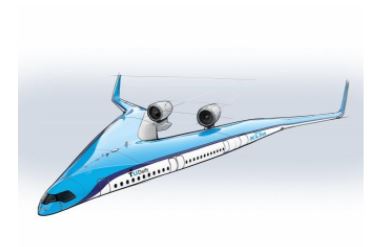
Image source: Click here
Kiran: Mental Health Rehabilitation Helpline launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II- Health
In news
- 24/7 toll-free helpline ‘Kiran’ was recently launched.
- Launched by: The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- Objective: To provide support to people facing anxiety, stress, depression, suicidal thoughts and other mental health concerns.
- Coordinated by: The National Institute for the Empowerment of Persons with Multiple Disabilities (NIEPMD), Chennai (Tamil Nadu) and National Institute of Mental Health Rehabilitation (NIMHR), Sehore (Madhya Pradesh).
Key takeaways
- It will cater to – People in Distress, pandemic induced psychological issues and Mental Health Emergency.
- It will offer mental health rehabilitation services with the objective of early screening, first-aid, psychological support, distress management, promoting positive behaviours, etc.
- It will be available in 13 languages and has 660 clinical/rehabilitation psychologists and 668 psychiatrists as volunteers.
- Helpline operators had been sensitised not to ask the caller for name or any identification details.
Do you know?
- Earlier, the Ministry of Education had launched the ‘Manodarpan’ initiative to provide psycho-social support and counselling to students for their mental health and well-being.
Extension of Tenure of Standing Committees may be extended
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Parliament
In news
- The Rajya Sabha Secretariat is considering changing the rules governing the Departmentally-Related Standing Committees’ (DRSC) tenure to make it to two years from the present one year.
- Objective: The panels should have enough time to work on the subjects selected by them. A significant amount of the tenure of the committees was lost due to the Covid-19 pandemic. Many of the panels have not been able to complete reports on the subjects they were working on.
Options that are being considered
- To extend the term of the panels for a year.
- To form new committees with a fixed tenure of two years.
Important value additions
Parliamentary Committees
- The Constitution of India makes a mention of these committees at different places, but without making any specific provisions regarding their composition, tenure, functions, etc.
- Two kinds of parliamentary committees — Standing Committees and Ad Hoc Committees.
- Standing Committees: Permanent (constituted every year or periodically) and work on a continuous basis. Term: one year from the date of its constitution.
- Ad Hoc Committees: Temporary and cease to exist on completion of the task assigned.
- Role: (1) Through Committees, Parliament exercises its control and influence over administration and keeps vigilance over the executive; (2) They aid and assist the Legislature in discharging its duties; (3) They also provide the expertise on a matter which is referred to them.
Ease of Doing Business Rankings of the States: DPIIT
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Ease of Doing Business
In news
- 4th edition of Ease of Doing Business Rankings based on the State Business Reform Action Plan (State BRAP) was recently released.
- Released by: The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Top Performers: (1) Andhra Pradesh; (2) Uttar Pradesh; (3) Telangana; (4) Madhya Pradesh; (5) Jharkhand.
- Worst performers: (1) Tripura; (2) Sikkim; (3) Odisha
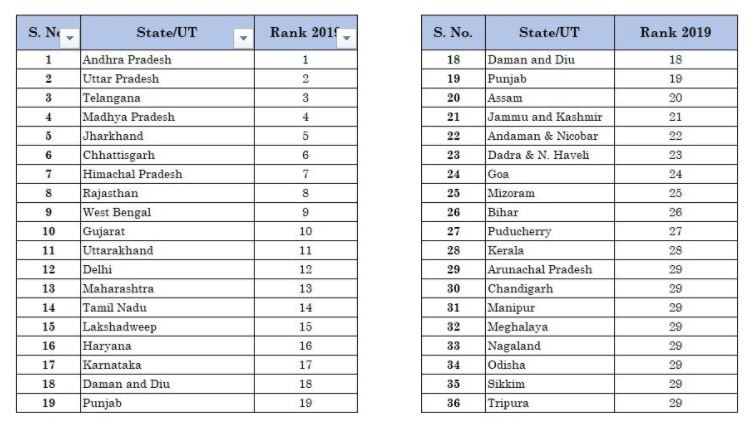
Important value additions
Ease of Doing Business (EODB)
- Joint initiative by: The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) and the World Bank
- Objective: To improve the overall business environment in the States.
Business Reform Action Plan
- Launched in: 2015.
- BRAP 2019 contains a list of 80 reforms (187 reform action points) to be implemented by 19 State departments.
- These reforms cover 12 business regulatory areas such as Access to Information, Single Window System, Labour, Environment, etc.
- Objective: To encourage a healthy competition between states.
- This would help in attracting investments and increasing Ease of Doing Business in each State.
SAROD-Ports: Dispute Resolution Mechanism launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Ease of Doing Business
In news
- ‘SAROD-Ports’ (Society for Affordable Redressal of Disputes – Ports) through virtual ceremony in New Delhi was recently launched.
- Launched by: The Union Ministry of Shipping
Key takeaways
- Established under: Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- ‘SAROD-Ports’ is similar to provision available in Highway Sector in the form of SAROD-Roads constituted by National Highways Authority of India (NHAI).
- Composition: Members from Indian Ports Association (IPA) and Indian Private Ports and Terminals Association (IPTTA).
- Functions: (1) SAROD-Ports will advise and assist in settlement of disputes through arbitrations in the maritime sector.
- Benefits: (1) SAROD-Ports will become the pivotal mechanism of ummeed (hope), vishwas (trust) and nyaya (justice) in the Port sector of India; (2) It will lead to saving huge amounts of legal expenditure and time; (3) Enforcement of concession agreements in the letter and spirit.
Do you know?
- A concession agreement is a contract that gives a company the right to operate a specific business within a government’s jurisdiction or on another firm’s property, subject to particular terms.
- It will promote ease of doing business in the maritime sector because of the fast, timely, cost effective and robust dispute resolution mechanism.
- It will inspire confidence in the private players.
Miscellaneous
Real Mango: Illegal Software
-
In a nationwide investigation, Railway Protection Force (RPF) has disrupted the operation of illegal software called “Real Mango” – used for cornering confirmed Railway reservation.
- Real Mango software is illegal software developed for booking Tatkal tickets.
- It bypasses captcha.
- It synchronises bank OTP with help of a mobile app and feeds it to the requisite form automatically.
- The software auto-fills the passenger details and payment details in the forms.
- The software logs in to the IRCTC website through multiple IRCTC Ids.
- Following these steps multiple tickets can be booked. And it leads to swift online tickets booking by agents whereas common people may not get the tickets booked on their own. This creates the possibility of ticket hoarding and black marketing of tickets.
- Significance: The information supplied by RPF will help the Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS) to strengthen security features in the Passenger Reservation System (PRS).
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNATIONAL / SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) | A counter-coalition of Eurasian power
Context: External Affairs Minister (EAM) S. Jaishankar’s visit to Russia to participate at the SCO foreign ministers’ meet during which India and China agreed to de-escalate the tension which was flared up along Indo-China border in recent months.
For a brief background on the border tension issue: click here and here
What was SCO founded and what is its historical background?
- Built on Shanghai Five: Russia, China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan (Kyrgyz Republic) and Tajikistan popularly known as Shanghai Five had come together in the post-Soviet era in 1996, in order to work on regional security, reduction of border troops, and terrorism.
- Initial Success in resolving Boundary Disputes: The 1996 meeting of the Shanghai Five resulted in an ‘Agreement on Confidence-Building in the Military Field Along the Border Areas’ between China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan, which led to an agreement on the mutual reduction of military forces on their common borders in 1997.
- Inclusion of Uzbekistan: Subsequently, Shanghai Five helped resolve disputes between Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan on border issues and the Ferghana Valley enclaves.
- Institutionalisation: Subsequently a permanent intergovernmental international organisation called SCO was founded in June 2001. It is Eurasian political, economic, and security alliance of China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
- Expansion: Its membership was expanded to include India and Pakistan in 2017.
- Observer States: The SCO also has four observer states — Afghanistan, Iran, Belarus and Mongolia — which may be inducted at a later date.
What is the Organisational Structure of SCO?
- The organisation has two permanent bodies — the SCO Secretariat based in Beijing and the Executive Committee of the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS) based in Tashkent.
- The SCO Secretary-General and the Director of the Executive Committee of the SCO RATS are appointed by the Council of Heads of State for a term of three years.
- However, the venue of the SCO council meetings moves between the eight members
How does West perceive SCO?
- The SCO describes one of its main goals as moving towards the establishment of a democratic, fair and rational new international political and economic order.
- In 2005, the Astana declaration called for SCO countries to work on a “joint SCO response to situations that threaten peace, security and stability in the region”, indicating the group’s strategic ambitions
- As a result, the SCO was eyed with some misgivings by the U.S. and Europe. It was even dubbed the “Anti-NATO” for proposing military cooperation.
- Western and NATO concerns were heightened when they placed heavy sanctions against Russia for its actions in Crimea, but China came to Russia’s aid, signing a 30-year, $400 billion gas pipeline framework agreement.
What are the Contradictions with India joining SCO?
- Not aligned with QUAD: India joining the SCO has been seen as puzzling foreign policy move, as it has come at a time when New Delhi is looking more keenly at the West, and in particular at the maritime ‘Quadrilateral’ with the U.S., Japan and Australia.
- On the issue of Pakistan: Since 2014, India and Pakistan have cut all ties, talks and trade with each other, and India has refused to attend the SAARC summit due to tensions with Pakistan, but both their leaderships have consistently attended all meetings of the SCO.
- On the issue of Terrorism: Despite the fact that India accuses Pakistan of perpetrating cross-border terrorism at every other multilateral forum, at the SCO, Indian and Pakistani armed forces even take part in military and anti-terrorism exercises together
How does SCO deal with bilateral tensions?
- The SCO Charter doesn’t allow any bilateral dispute to be taken up, but it provides a comfortable platform for finding common ground and eventually, creating conditions for dialogue between countries.
- In 2009, India and Pakistan held the first talks after the Mumbai attacks on the sidelines of the SCO summit in Astana, where then Prime Minister Manmohan Singh and former Pakistani President Asif Ali Zardari met and tried to resolve tension through talks
- In 2015, Prime Minister Narendra Modi met then Pakistani PM Nawaz Sharif at the SCO summit in Ufa, for a meeting that even resulted in a joint statement.
- In 2020, SCO host, Russia, encouraged and facilitated meetings between between India and China to discuss the stand-off at the LAC
Conclusion
- SCO seeks to build a continental coalition that, its founders hope, may one day be as strong as some of the other coalitions that exist to its west and south.
Connecting the dots:
- Future of SAARC and BIMSTEC
- India’s Non-Alignment Policy in the times of increasing Polarisation in world
SOCIETY / GOVERNANCE/ SECURITY
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Formal/informal associations and their role in the Polity.
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, and how does it control donations
Context: The licences of 13 non-governmental organisations (NGOs) have been suspended under the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 2010, this year. Their FCRA certificates were suspended and bank accounts frozen.
What is the FCRA?
- Objective: First enacted in 1976 FCRA regulates foreign donations and ensures that such contributions do not adversely affect internal security.
- Applicability: The FCRA is applicable to all associations, groups and NGOs which intend to receive foreign donations. It is mandatory for all such NGOs to register themselves under the FCRA
- Accountability: Registered associations can receive foreign contribution for social, educational, religious, economic and cultural purposes. Filing of annual returns, on the lines of Income Tax, is compulsory.
- Modified rules in 2015: New rules by Ministry of Home Affairs said all such NGOs would have to operate accounts in either nationalised or private banks which have core banking facilities to allow security agencies access on a real time basis.
Who cannot receive foreign donations?
- Members of the legislature and political parties, government officials, judges and media persons are prohibited from receiving any foreign contribution.
- Political Funding: However, in 2017 the MHA, through the Finance Bill route, amended the FCRA law retrospectively paving the way for political parties to receive funds from the Indian subsidiary of a foreign company or a foreign company in which an Indian holds 50% or more shares
How else can one receive foreign funding?
- The other way to receive foreign contributions is by applying for prior permission.
- It is granted for receipt of a specific amount from a specific donor for carrying out specific activities or projects.
- But the association should be registered under statutes such as the Societies Registration Act, 1860, the Indian Trusts Act, 1882, or Section 25 of the Companies Act, 1956.
- A letter of commitment from the foreign donor specifying the amount and purpose is also required.
When is a registration suspended or cancelled?
- Financial Irregularities of NGO: The MHA on inspection of accounts and on receiving any adverse input against the functioning of an association can suspend the FCRA registration initially for 180 days.
- Restriction on Functioning of NGO: Until a decision is taken, the association cannot receive any fresh donation and cannot utilise more than 25% of the amount available in the designated bank account without permission of the MHA
- Public Interest Violation: The government can refuse permission if it believes that the donation to the NGO will adversely affect “public interest” or the “economic interest of the state”.
- Recent Example: In 2017, the MHA suspended the FCRA of the Public Health Foundation of India (PHFI), one of India’s largest public health advocacy groups, on grounds of using “foreign funds” to lobby with parliamentarians on tobacco control activities.
- After several representations by the PHFI to the government, it was placed in the ‘prior permission’ category.
Do You Know?
- According to MHA data, since 2011, the registration of 20,664 associations was cancelled for violations such as misutilisation of foreign contribution, non-submission of mandatory annual returns and diversion of foreign funds for other purposes.
- As on September 11,2020 there are 49,843 FCRA-registered associations.
What are the Criticism of FCRA?
- Affects Fundamental Rights: The FCRA restrictions have serious consequences on both the rights to free speech and freedom of association under Articles 19(1)(a) and 19(1)(c) of the Constitution.
- Democratic Functioning: NGOs perform vital role of interest aggregation and interest articulation in Democratic process. Disproportionately restricting their functioning will hamper Democracy in long run.
- Liable to misuse due to Vagueness in law: The Act gave the government the power to frame rules whereby an organisation can be declared to have political objectives — without defining what a ‘political objective’ is.
Conclusion
Regulation of NGOs is very much required but it should be ‘light’ and consistent with the fundamental rights, so as to give effect to the objects for which voluntarism is being promoted.
Connecting the dots:
- Importance of NGOs in Democracy
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Recently, 4th edition of Ease of Doing Business Rankings for the states was announced. Consider the following statements:
- The results were based on the State Business Reform Action Plan (State BRAP).
- It was released by The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- Andhra Pradesh is the top state in Ease of Doing Business.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2 Real Mango was in news recently. It is associated with which of the following?
- A spy satellite launched by China
- Illegal software used by agents to book tatkal tickets
- A malware
- New breed of Mango cultivated in Uttar Pradesh
Q.3 Consider the following regarding SAROD-Ports:
- It was launched by the Union Ministry of Shipping.
- It was established under Societies Registration Act, 1860.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4 Recently, Kiran: Mental Health Rehabilitation Helpline was launched by which of the following Ministry?
- Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- Ministry of Education
- Ministry of Home Affairs
- Ministry of Finance
ANSWERS FOR 12th September 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | D |
Must Read
About Lok Sabha Deputy Speaker:
About demand supportive fiscal policies:
About Pandemic and Pregnancy:












