IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Major Global energy companies ask Indian Government to bring natural gas under the GST regime
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Energy; GST; Taxation
In news
- Major Global energy companies have called on the Government of India to bring natural gas under the GST regime at the India energy Forum held recently.
- Currently petrol, diesel, aviation turbine fuel, natural gas and crude oil fall outside India’s GST regime.
- Government officials have also indicated that the government is considering bringing natural gas under the ambit of the GST regime.
Benefits of bringing Natural gas under GST regime
- It would lead to a reduction in the cascading impact of taxes on industries such as power and steel, which use natural gas as an input.
- It would do away with the central excise duty and different value added taxes imposed by states.
- This would lead to an increase in the adoption of natural gas which would be in line with the government’s goal to increase the share of natural gas in the country’s energy basket from 6.3% to 15%.
Guidelines unveiled for Awarding Bodies and Assessment Agencies under Skill India Mission
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and interventions
In news
- Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE) in collaboration with their unified regulator— National Council for Vocational Education and Training (NCVET) unveiled guidelines for the Awarding Bodies (AB) and Assessment Agencies (AA) over a digital conference.
- The guidelines aim at establishing quality, improved outcomes and standardizing the processes under Skill India Mission.
Important value additions
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) was formed on November 9, 2014 by the Government of India to focus on enhancing employability of skills.
- Under its flagship programme, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) 2016-2020, the Ministry has trained more than 92 lakh candidates so far.
- The National Council for Vocational Education and Training (NCVET) was notified by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) on 5th December 2018.
- The NCVET acts as an overarching skills regulator which regulates the functioning of entities engaged in vocational education and training.
CCEA approves Mandatory Packaging In Jute Materials
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Economy
In news
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved that 100% of the food-grains and 20% of the sugar shall be mandatorily packed in diversified jute bags.
Key takeaways
- The decision also mandates that initially 10% of jute bags for packing food grains would be placed through reverse auction on the Gem portal.
- The Government has expanded the scope of mandatory packaging norms under the Jute Packaging Material (JPM) Act, 1987.
- The approval will benefit farmers and workers located in the Eastern and North Eastern regions of the country particularly in West Bengal, Bihar, Odisha, Assam, Andhra Pradesh, Meghalaya and Tripura.
Important value additions
Other Support provided to the Jute Sector
- The National Jute Board has collaborated with National Institute of Design and a Jute Design Cell has been opened at Gandhinagar.
- In order to boost demand in the jute sector, Government of India has imposed Definitive Anti-Dumping Duty on import of jute goods from Bangladesh and Nepal with effect from 5th January, 2017.
- In order to promote transparency in jute sector, Jute SMART, an e-govt initiative was launched in December, 2016 which provides an integrated platform for procurement of Jute sacking by Government agencies.
Jute
- Jute is a rainy season crop.
- Jute requires a warm and humid climate with temperature between 24° C to 37° C.
- Constant rain or water-logging is harmful.
- The new gray alluvial soil of good depth, receiving salt from annual floods, is best for jute.
- Jute is harvested any time between 120 days to 150 days when the flowers have been shed, early harvesting gives good healthy fibers.
- The jute plant’s fibres lie beneath the bark and surrounded the woody central part of the stem.
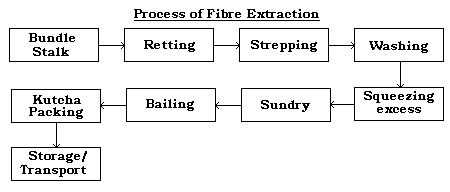
- To extract the fibres from the stem, the process is carried out in the following stages :
Dam Rehabilitation And Improvement Project (DRIP) approved
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Infrastructure
In news
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved the Dam Rehabilitation and Improvement Project (DRIP) Phase II & Phase III with the financial assistance of the World Bank (WB) and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB).
Key takeaways
- Objective: To improve the safety and operational performance of selected dams across the whole country, along with institutional strengthening.
- The Scheme envisions comprehensive rehabilitation of 736 existing dams located across India.
- The Project will be implemented over a period of 10 years duration in two Phases.
- DRIP Phase II & Phase III has following components: (1) Rehabilitation and improvement of dams and associated appurtenances; (2) Dam safety institutional strengthening in participating States and Central agencies; (3) Exploration of alternative incidental means to generate the incidental revenue for sustainable operation and maintenance of dams; (4) Project management.
Meri Saheli launched
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I – Social issues
In news
- Indian Railways has launched “Meri Saheli” initiative for focused action on security of women across all zones.
- Objective: To provide safety and security to lady passengers travelling by trains for their entire journey from starting station to destination station.
Key takeaways
- It is an initiative of Railway Protection Force (RPF).
- It entails interaction with lady passengers especially those travelling alone by a team of young lady RPF personnel at the originating station.
- These lady passengers are briefed about all precautions to be taken during the journey and told to dial 182 in case they face or see any problem in the coach.
- The platform duty RPF personnel at the stopping stations en-route keep unobtrusive watch over the concerned coaches and berths and if need arises, interact with the lady passengers.
Do you know?
- The “Meri Saheli” initiative was started as a pilot project in South Eastern Railway in September 2020 and after getting encouraging response from lady passengers, it was extended to all zones
SERB – Power scheme for women scientists
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Science and Technology
In news
- A Scheme titled “SERB-POWER (Promoting Opportunities for Women in Exploratory Research)” was recently launched exclusively for women scientists.
- Ministry: Ministry of Science & Technology
- Launched by: The Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), a Statutory body of the Department of Science and Technology (DST)
Key takeaways
- Objective: To mitigate gender disparity in science and engineering research in various S&T programs.
- It will have two components namely: (1) SERB-POWER Fellowship; (2) SERB- POWER Research Grants.
Features of the SERB-POWER Fellowship
- Target: Women researchers in 35-55 years of age. Up-to 25 Fellowships per year and not more than 75 at any point in time.
- Components of support: Fellowship of Rs. 15,000/- per month in addition to regular income; Research grant of Rs. 10 lakh per annum; and Overhead of Rs. 90,000/- per annum.
- Duration: Three years, without the possibility of extension. Once in a career.
Features of the SERB – POWER Research Grants
- POWER Grants will empower women researchers by funding them under following two categories: (1) Level I (Applicants from IITs, IISERs, IISc, NITs, Central Universities, and National Labs of Central Government Institutions): The scale of funding is up to 60 lakhs for three years; (2) Level II (Applicants from State Universities / Colleges and Private Academic Institutions): The scale of funding is up to 30 lakhs for three years.
- POWER Grant will be regulated through terms of reference conforming to SERB-CRG (Science and Engineering Research Board-Core Research Grant) guidelines.
PLI Schemes For Promoting Domestic Manufacturing Of Bulk Drugs & Medical Devices revised
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-III – Science and Technology
In news
- Chemicals and Fertilizers Ministry has revised the Production Linked Incentive Schemes for promoting domestic manufacturing of bulk drugs and medical devices.
Key takeaways
- In the revised guidelines, the ‘Minimum Threshold’ investment requirement has been replaced by ‘committed investment’ taking into account availability of technology choices which varies from product to product.
- The change has been made to encourage efficient use of productive capital.
- The Department of Pharmaceuticals earlier come out with the two Production Linked Incentive Schemes: (1) Production Linked Incentive scheme for promotion of domestic manufacturing of critical Key Starting Materials, Drug Intermediates and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients in India; (2) Production Linked Incentive Scheme for Promoting Domestic Manufacturing of Medical Devices.
Do you know?
- Globally, the Indian pharmaceutical industry is the third largest in terms of volume.
(MAINS FOCUS)
EDUCATION/ GOVERNANCE/ SCIENCE & TECH
Topic: General Studies 2, 3:
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Education, Human Resources
- Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
ASER Survey: COVID-19 impact and Gaps in Learning
Context: Although the Centre has now permitted States to start reopening schools if they can follow COVID-19 safety protocols, the vast majority of the country’s 25 crore students are still at home after seven straight months.
What is Annual Status of Education Report?
- It is the largest citizen-led survey in India facilitated by Pratham NGO. It is also the only annual source of information on children’s learning outcomes available in India today
- ASER is a household-based rather than school-based survey. This design enables all children to be included – those who have never been to school or have dropped out, as well as those who are in government schools, private schools, religious schools or anywhere else.
- ASER 2020 was conducted in 26 states and four Union Territories.
- The phone-based survey was done in September 2020, the sixth month of national school closures. A total of 52,227 rural households and 59,251 children in the 5-16 age group were surveyed.
- ASER 2020 explored whether this unprecedented situation has caused shifts in children’s enrollment patterns in rural India
Key Finding of 2020 report (rural) are:
- Shift in enrolments from private schools to government institutions: 69.55 per cent children in the 6-14 age group are enrolled in government schools, up from 66.42 per cent in 2018.
- Decrease in Enrolment: ASER 2020 shows that 5.5 per cent children are not currently enrolled for the 2020-21 school year, up from 4 per cent in 2018. This difference is the sharpest among the youngest children (ages 6 to 10), possibly because they have not yet secured admission to school. While 1.8 per cent children in this age group were not enrolled in 2018, that has spiked to 5.3 per cent.
- Digital Divide: The survey found 43.6% of students in government schools without access to a smartphone, while 67.3% of those who received learning materials in these institutions got them over WhatsApp, underscoring the role played by gadgets and connectivity
- Increased Smartphone penetration not translated into access to Education: The levels of smartphone ownership have almost doubled – from 36.5% in 2018 to 61.8% in 2020, but a third of children with smartphone access still did not receive any learning materials.
- Parental/community involvement: Almost 75 per cent of children said they received some form of learning support from family members, with older siblings playing a key role.
- Government worked to respond to crisis: More than 80 per cent children said they had textbooks for their current grade, this proportion was higher among students enrolled in government schools (84.1 per cent) than in private ones (72.2 per cent).
- Parental levels of education and resources played a key role in whether children studied at home: About 20% of children whose parents had less than five years of education got learning materials, compared to 46% among parents who had studied beyond Class IX themselves
- Regional imbalance: In Bihar, less than 8% got such materials from their schools, along with 20% in West Bengal, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh. On the other hand, more than 80% of rural children in Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Kerala and Gujarat received such input.
Important Takeaways from the report
- Evidence based policy making: The data collected could facilitate intervention by the education system in some respects, even if, going forward, schools opt for a hybrid solution of partial reopening and online learning.
- Expanding availability of textbooks to all, including those who dropped out or are waiting to be formally admitted, will help parents and siblings aid learning.
- Bridging the divide on educational aids, now including smartphones, will enable transmission of learning materials, and personal tutorial sessions.
- Opportunity for Observational Learning: The education system could creatively use opportunities during the current year to broaden learning. Students could use the safety of the open countryside to learn, under guidance from teachers, a host of topics by doing things themselves which helps create strong foundations.
- Need for Monitoring: When schools re-open, it will be important to continue to monitor who goes back to school, and very importantly to understand whether there is learning loss as compared to previous years,
- Leveraging Home Support to improve learning: Schools should find ways to build on the home support going forward, given that families provided learning support to children during pandemic, either from parents or elder siblings.
Connecting the dots:
- ASER 2019 report: Fix early learning in government schools
AGRICULTURE/ SCIENCE & TECH
Topic: General Studies 2,3:
- Different types of irrigation and irrigation systems
- Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
Precision Agriculture
About
- It is an approach to farm management that uses information technology (IT) to ensure that the crops and soil receive exactly what they need for optimum health and productivity.
- It is an approach where inputs are utilised in precise amounts to get increased average yields, compared to traditional cultivation techniques.
- The goal of PA is to ensure profitability, sustainability and protection of the environment.
- PA is also known as satellite agriculture, as-needed farming and site-specific crop management (SSCM).
- Precision agriculture relies upon specialized equipment, software and IT services.
- The approach includes accessing real-time data about the conditions of the crops, soil and ambient air, along with other relevant information such as hyper-local weather predictions, labor costs and equipment availability.
Advantages precision farming
- Helps increase agriculture productivity in sustainable manner
- Prevents soil degradation
- Reduction of chemical application in crop production
- Efficient use of water resources
- Dissemination of modern farm practices to improve quality, quantity and reduced cost of production
- Developing favourable attitudes
- Precision farming changing the socio-economic status of farmers
Precision farming in India
- Some of the schemes like PMKSY’s (Per Drop More Crop) involve Precision Agriculture practices.
- The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) and the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) has formulated a project entitled “SENSAGRI: SENsor based Smart AGRIculture”.
- The major objective is to develop indigenous prototype for drone based crop and soil health monitoring system using hyperspectral remote sensing (HRS) sensors.
- Drone technology is also being used. It has ability for smooth scouting over farm fields, gathering precise information and transmitting the data on real time basis.
- Mobile apps are being used to provide farmers with weather information and provide early warning.
Drawbacks of precision farming
- High cost
- Lack of technical expertise knowledge and technology
- Not applicable or difficult/costly for small land holdings
- Heterogeneity of cropping systems and market imperfections
Conclusion
- The need of the hour is to adopt state of the art technology to make agriculture sustainable and profitable.
- Agricultural renaissance can take shape on a strong digital foundation.
- Adoption of technology will help in sustaining food security and enhanced livelihood opportunities.
- In addition, the farming community needs to diversify and take up allied activities like fisheries, dairy and poultry as well to double the on-farm incomes.
Connecting the dots:
- New Farm Bills and Opposition to it
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Which of the following is/are outside India’s GST regime?
- Petrol
- Diesel
- Aviation turbine fuel
- Natural gas
Select the correct code:
- 1 and 4 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Jute cultivation:
- Jute requires a warm and humid climate with temperature between 24° C to 37° C.
- Constant rain or water-logging is helpful for its growth.
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
ANSWERS FOR 29th October 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | D |
Must Read
About Farm bills and critical analysis:
About deepening of Indo-US defence partnership:
About declining US power:














