IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
MoU between Spices Board India and UNDP India
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III – Economy; Supply chains
In news
- Spices Board India and UNDP India’s Accelerator Lab signed a MoU.
- Aim: To build a blockchain based traceability interface for Indian spices to enhance transparency in supply chain and trade.
- It will start with over 3,000 farmers engaged in chilli and turmeric farming in select Districts of Andhra Pradesh.
- Blockchain is a decentralized process of recording transactions on an open and shared electronic ledger.
- This allows for ease and transparency in data management across a complex network, including, farmers, brokers, distributors, retailers and consumers, thus simplifying the supply chain.
Do you know?
- Spices Board is one of the five Commodity Boards functioning under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- It is an autonomous body.
- It is responsible for the export promotion of the 52 scheduled spices and development of Cardamom (Small & Large).
Global Gender Gap Report 2021
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-I – Society
In news
- Global Gender Gap Report 2021 was released recently.
- Released by: World Economic Forum
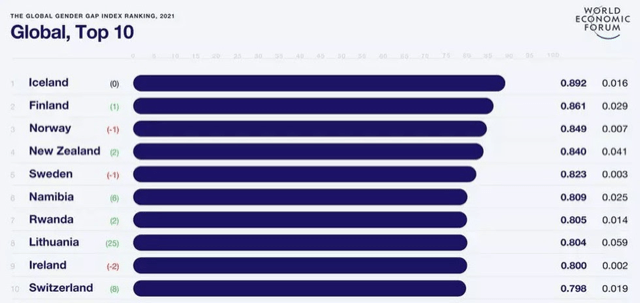
Key takeaways
- India has fallen 28 places
- It is now one of the worst performers in South Asia,
- It is ranked below neighbouring countries – Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka and Myanmar.
- India’s rank: 140 among 156 countries.
- South Asia incidentally is one of the worst performing regions, followed only by the Middle East and northern Africa.
- Overall, many countries have fared worse in this year’s rankings compared to last year’s, on account of economic performance.
- On its current trajectory, it will now take 135.6 years to close the gender gap worldwide.
- Women represent only 26.1% of some 35,500 parliament seats and just 22.6% of over 3,400 ministers worldwide
- In 81 countries, there has never been a woman head of state, as of January 15, 2021.
Launch of Sankalp Se Siddhi
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II – Policies and Interventions
In news
- “Sankalp se Siddhi” – Village and Digital Connect Drive was recently launched.
- Launched by: TRIFED
- Ministry of: Ministry of Tribal Affairs
Key takeaways
- It is a 100 day drive which was started from April 1, 2021.
- It will entail 150 teams visiting ten villages each.
- Aim: To activate the Van Dhan Vikas Kendras in these villages.
- The visiting teams will also identify locations and shortlist potential Van Dhan Vikas Kendras for clustering as TRIFOOD, and Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries- (SFURTI) units as larger enterprises.
- TRIFOOD aims to enhance the income of tribals through better utilization of and value addition to the Minor Forest Produce collected by the tribal forest gatherers.
Phase III of the eCourts Project
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Judiciary
In news
- The eCommittee of the Supreme Court (SC) has prepared the draft vision document for Phase III of the eCourts Project under SC.
Key takeaways
- E-Courts Project is a mission mode project undertaken by the Department of Justice, Government of India.
- Chairperson of eCommittee: Dr Justice Dhananjaya Y Chandrachud, Judge, SC
- The eCommittee has been overseeing the implementation of the eCourts Project, conceptualized under the “National Policy and Action Plan for Implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the Indian Judiciary-2005”.
- Phase III of the eCourts Project in India is rooted in two central facets—access and inclusion.
- Phase III envisions a judicial system that is more easily accessible irrespective of geographical distances, efficient and equitable for every individual who seeks justice, makes more efficient use of human and other resources, and absorbs the latest technology for a positive environmental impact.
All-India Survey Of Migrant Workers
Part of: GS Prelims and GS-II – Policies and Interventions
In news
- Government of India launched the All-India Survey of Migrant Workers and All-India Quarterly Establishment-based Employment Survey.
- Ministry: Labour and Employment Ministry
Key takeaways
- Objective of All-India Survey of Migrant Workers: To study the kind of employment-related migration undertaken by workers.
- The survey will provide the details of working and living conditions faced by Migrant Workers and impact of COVID 19 on their world of work.
- All-India Quarterly Establishment-based Employment Survey will provide the employment estimates for establishments employing ten or more workers and those employing nine or less workers.
- The survey will provide crucial data on the changes in employment situation across the selected sectors on a quarterly basis.
- These surveys will plug-in the data gap on various aspects of labour and employment and will aid evidence-based policy making processes.
Miscellaneous
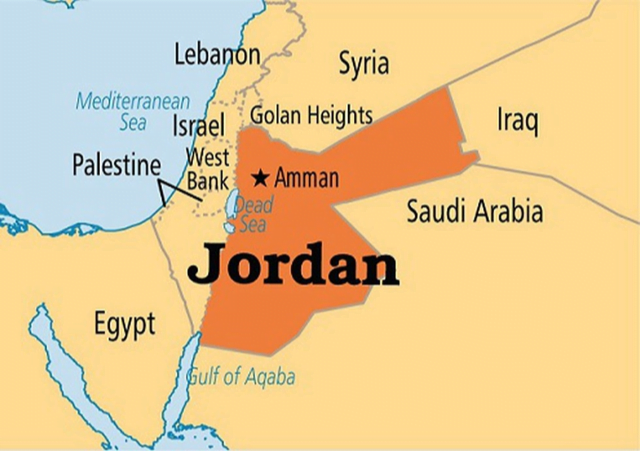
Jordan
-
Jordan was recently in news today.
- Prince Hamzah bin Al Hussein, the former crown prince and half-brother of ruling monarch Abdullah, has reportedly been placed under house arrest as part of a crackdown on critics.
- Jordan is an Arab country in the Levant region of Western Asia, on the East Bank of the Jordan River.
- It is bordered by Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Syria, Israel and Palestine (West Bank).
- The Dead Sea is located along its western borders
- Capital city: Amman.
- It is a constitutional monarchy, but the king holds wide executive and legislative powers.
(Mains Focus)
ENVIRONMENT/ GEOGRAPHY/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-1: Geographical phenomena
- GS-3: Environment and Ecology, Bio diversity – Conservation, environmental degradation, environmental impact assessment, Environment versus Development
- GS-3: Issues relating to deforestation, land use pattern and use of fossil fuel.
Forest Fires
Context: April-May is the season when forest fires take place in various parts of the country. Since the start of 2021, there has been a series of forest fires in Himachal Pradesh, Nagaland-Manipur border, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat, including in wildlife sanctuaries
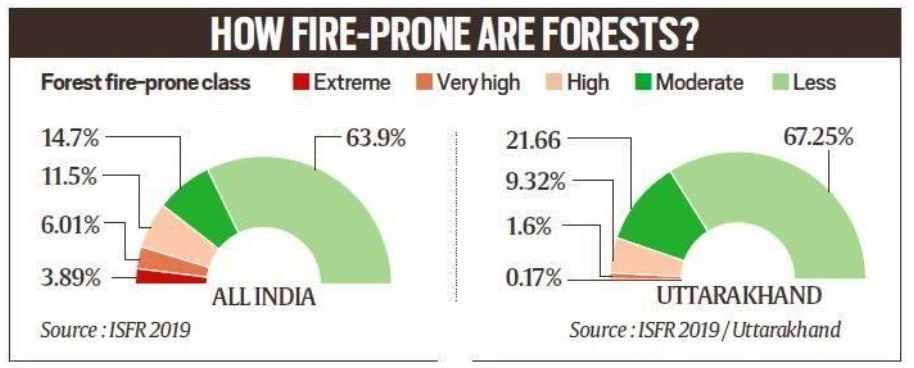
Image Source: Indian Express
How prone to fire are India’s forests?
- As of 2019, about 21.67% (7,12,249 sq km) of the country’s geographical area is identified as forest, according to the India State of Forest Report 2019 (ISFR) released by the Forest Survey of India. Tree cover makes up another 2.89% (95, 027 sq km).
- Based on previous fire incidents and recorded events, forests of the Northeast and central India regions are the most vulnerable areas to forest fires
- Forests in Assam, Mizoram and Tripura have been identified as ‘extremely prone’ to forest fire.
- States with large forest areas under the ‘very highly prone’ category include Andhra Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Odisha, Maharashtra, Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
- Western Maharashtra, Southern Chhattisgarh and areas of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, along with central Odisha, are turning into ‘extremely prone’ forest fire hotspots, the 2020-2021 annual report of the MoEFCC said.
- Areas under the ‘highly prone’ and ‘moderately prone’ categories make up about 26.2% of the total forest cover — a whopping 1,72,374 sq km.
- Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh are the two states that witness the most frequent forest fires annually. In Uttarkhand, 24,303 sq km (over 45 per cent of the geographical area) is under forest cover.
What causes forest fires?
- Forest fires can be caused by a number of natural causes, but officials say many major fires in India are triggered mainly by human activities.
- Emerging studies link climate change to rising instances of fires globally, especially the massive fires of the Amazon forests in Brazil and in Australia in the last two years.
- Fires of longer duration, increasing intensity, higher frequency and highly inflammable nature are all being linked to climate change.
- In India, forest fires are most commonly reported during March and April, when the ground has large quantities of dry wood, logs, dead leaves, stumps, dry grass and weeds that can make forests easily go up in flames if there is a trigger. Under natural circumstances, extreme heat and dryness, friction created by rubbing of branches with each other also have been known to initiate fire.
- In Uttarakhand, the lack of soil moisture too is being seen as a key factor. In two consecutive monsoon seasons (2019 and 2020), rainfall has been deficient by 18% and 20% of the seasonal average, respectively.
- But, forest officials say most fires are man-made, sometimes even deliberately caused. Even a small spark from a cigarette butt, or a carelessly discarded lit matchstick can set the fire going.
- For example, in Odisha, which saw a major fire recently in Simlipal forest, villagers are known to set dry leaves to fire in order to collect mahua flowers, which go into preparation of a local drink
Why are forest fires difficult to control?
- Difficult Terrain: The locality of the forest and access to it pose hurdles in initiating firefighting efforts.
- Manpower Shortage: During peak season, shortage of staff is another challenge in dispatching firefighting teams. Timely mobilisation of forest staff, fuel and equipment, depending on the type of fire, through the thick forests remain challenges.
- Outdated Techniques: As it is impossible to transport heavy vehicles loaded with water into the thick forests, a majority of fire dousing is initiated manually, using blowers and similar devices. But there have been incidents when forest fires were brought under control using helicopter services.
- Weather Factors: Wind speed and direction play a critical role in bringing a forest fire under control. The fire often spreads in the direction of the winds and towards higher elevations
What factors make forest fires a concern?
- Forest’s role in mitigation and adaptation to climate change: They act as a sink, reservoir and source of carbon. A healthy forest stores and sequesters more carbon than any other terrestrial ecosystem.
- Endangers Livelihood of people: In India, with 1.70 lakh villages in close proximity to forests (Census 2011), the livelihood of several crores of people is dependent on fuelwood, bamboo, fodder, and small timber.
- Impacts regeneration capacity of Ecosystem: Forest fires can have multiple adverse effects on the forest cover, soil, tree growth, vegetation, and the overall flora and fauna. Fires render several hectares of forest useless and leave behind ash, making it unfit for any vegetation growth.
- Shrinkage of Forests: Heat generated during the fire destroys animal habitats. Soil quality decreases with the alteration in their compositions. Soil moisture and fertility, too, is affected. Thus forests can shrink in size. The trees that survive fire often remain stunted and growth is severely affected.
What efforts are being taken to protect forests from fire?
- Since 2004, the FSI developed the Forest Fire Alert System to monitor forest fires in real time. In its advanced version launched in January 2019, the system now uses satellite information gathered from NASA and ISRO.
- Real-time fire information from identified fire hotspots is gathered using MODIS sensors (1km by 1km grid) and electronically transmitted to FSI.
- This information is then relayed via email at state, district, circle, division, range, beat levels. Users of this system in the locality are issued SMS alerts. The FSI system in January 2019 had over 66,000 users.
Connecting the dots:
SOCIETY
Topic:
- GS-1: Society and Social Issues
Racism
Racism is a systematic ideology, a complex set of beliefs and practices that, on the presumed basis of biology, divides humanity into the ‘higher’ us and a lower ‘them’.
In a nutshell, it is this: one can tell everything important about a person, his group, its past and future, by noting the colour of his skin.
Issues
- More than HR Violation: Racial discrimination, beyond being a breach of human rights, has harmful effects on human health and well-being, and risks wider disruptions to social cohesion.
- Complex: Current forms of racism and discrimination are complex and often covert. Structural forms of discrimination, including micro-aggressions and everyday indignities, remain widespread.
- Growth of Social Media: Anonymity of the Internet has allowed racist stereotypes and inaccurate information to spread online.
- Techno-Racism: The use of new technologies and artificial intelligence in security raise the spectre of ‘techno-racism’, as facial recognition programmes can misidentify and target racialised communities.
- Aggravates Inequalities: Racial discrimination deepens and fuels inequality in our societies. Prejudiced attitudes and discriminatory acts, whether subtle or overt, aggravate existing inequalities in societies.
- Double Burden on Women: Women and girls also carry a double burden of being exposed to racial and gender-based prejudices.
Way Ahead
- Public attitudes to anti-racism have improved, as expressions of racist ideology have become less socially acceptable.
- Multisectoral effort to tackle the root causes of racism through anti-racist laws, policies and programmes.
- UNESCO’s actions against racism through education, the sciences, culture, and communication offer an example of a way forward.
- UNESCO promotes the role of education in providing the space for young people to understand processes that sustain racism, to learn from the past, and to stand up for human rights.
- Through new approaches to inter-cultural dialogue and learning, youth and communities can be equipped with skills to eradicate harmful stereotypes and foster tolerance.
- Racism will not be overcome with mere professions of good faith but must be combatted with anti-racist action.
- A global culture of tolerance, equality and anti-discrimination is built first and foremost in the minds of women and men.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Jordan is flanked by which of the following river on its western borders?
- Mediterranean Sea
- Dead sea
- Red Sea
- Caspian sea
Q.2 Consider the following statements regarding Spices Board of India:
- It comes under Ministry of Finance.
- It is an autonomous body.
Which of the above is or are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3 Global gender Gap Report is released by which of the following?
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations
- World Economic Forum
- Amnesty International
ANSWERS FOR 5th April 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | A |
| 3 | C |
| 4 | A |
Must Read
On Chhattisgarh’s Sukma district encounter:
On US-China relations:
On India and NATO:











