IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, the United Nations announced the creation of the Global Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Infrastructure.
About Global Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Infrastructure :
- The Global Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Infrastructure is endorsed by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Executive Council.
- It will establish an internationally coordinated approach to observing network design, and to the acquisition, international exchange, and use of the resulting observations.
- The focus is to bring back the long-standing auspices of the Integrated Greenhouse Gas Information System, also called IG3IS launched by Global Atmosphere Watch established in 1989.
Objectives :-
- It aims to fill critical information gaps and support action to reduce heat-trapping gases which are fuelling temperature increases.
- It seeks international collaboration in weather prediction and climate analysis.
- The Global Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Infrastructure seeks to clarify uncertainties about where greenhouse gas emissions end up.
- It will offer faster and more precise data on changes in the planet’s atmosphere.
The Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Infrastructure will consist of four main components in its initial phase :-
- A comprehensive sustained, global set of surface-based and satellite-based observations of CO2, CH4, and N2O concentrations, total column amounts, partial column amounts, vertical profiles, and fluxes and of supporting meteorological, oceanic, and terrestrial variables, internationally exchanged as rapidly as possible, pending capabilities and agreements with the system operators;
- Prior estimates of the GHG emissions based on activity data and process-based models;
- A set of global high-resolution Earth System models representing GHG cycles;
- Associated with the models, data assimilation systems optimally combine the observations with model calculations to generate products of higher accuracy.
- The infrastructure is expected to provide essential information and support for implementing the Paris Agreement on climate change.
MUST READ : Paris Climate Deal, Emissions Gap Report 2022.
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Climate Action Tracker” which monitors the emission reduction pledges of different countries is a : (2022 )
- Database created by a coalition of research organizations
- Wing of “International Panel of Climate Change”
- Committee under “United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change”
- Agency promoted and financed by United Nations Environment Programme and World Bank
Q.2) The “Common Carbon Metric” supported by UNEP, has been developed for (2021)
- Assessing the carbon footprint of building operations around the world
- Enabling commercial farming entities around the world to enter carbon emission trading
- Enabling governments to assess the overall carbon footprint caused by their countries
- Assessing the overall carbon footprint caused by the use of fossil fuels by the world in a unit of time
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: Recently, the RBI launched the Mission ‘Har Payment Digital’ on the occasion of Digital Payments Awareness Week (DPAW) 2023.
About Har Payment Digital mission:
- The Har Payment Digital campaign by RBI .
- It aims at reinforcing the ease and convenience of digital payments and facilitating the onboarding of new consumers into the digital fold.
- Objective: Under the mission Payment System Operators (PSOs) will adopt 75 villages across the country and conduct camps in each of these villages with an aim to improve awareness and onboard merchants for digital payments.
- The mission “Har Payment Digital” is aimed at reinforcing the ease and convenience of digital payments and facilitating the onboarding of new consumers into the digital fold.
- This will further encourage and support the adoption of digital payments in the country.
- The message of “Digital Payment Apnao, Auron ko bhi Sikhao” or “Adopt digital payments and Also teach others”, under the mission Har Payment Digital is very relevant and expected to create greater awareness and usage among the people.
MUST READ : UPI , DIGITAL INDIA
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places, and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) 12. With reference to digital payments, consider the following statements: (2018)
- BHIM app allows the user to transfer money to anyone with a UPI-enabled bank account.
- While a chip-pin debit card has four factors of authentication, the BHIM app has only two factors of authentication.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science, and Technology
Context: ISRO successfully carried out the controlled re-entry for the decommissioned Megha-Tropiques-1 (MT-1) satellite recently.
About Megha-Tropiques-1 (MT1) satellite :-
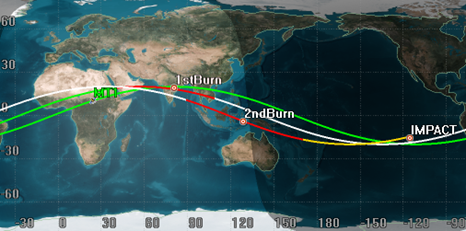
Source: ISRO
Background :-
- The Megha Tropiques was launched in 2011.
- Megha-Tropiques is an Indo-French Joint Satellite Mission for studying the water cycle and energy exchanges in the tropics.
Objective: The main objective of the satellite mission was to study the water cycle in the tropical atmosphere and how climate change will affect the water cycle.
- It provides scientific data on the contribution of the water cycle to the tropical atmosphere, with information on condensed water in clouds, water vapour in the atmosphere, precipitation, and evaporation.
- The Megha-Tropiques was designed based on the GEWEX(Global Energy and Water Exchanges project.)
- It was a research project of the World Climate Research Programme.
- GEWEX did a wide analysis of aerosols in the atmosphere.
The payloads of Megha-Tropiques-1:-
- MADRAS: Microwave Analysis and Detection of Rain and Atmospheric Structures: It was a microwave imager.
- SAPHIR: Sounder for Probing Vertical Profiles of Humidity: It was a sounding instrument to study the absorption band of water vapour.
- SCARAB: Scanner for Radiation Budget: It was based on the Russian satellite models of measuring longwave radiances
MUST READ : Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV)
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media? (2022)
- A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
- A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
- A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
- A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same surface. speed and places a probe on its
Q.2) The experiment will employ a trio of spacecraft flying in formation in the shape of an equilateral triangle that has sides one million kilometres long, with lasers shining between the craft.” The experiment in question refers to (2020)
- Voyager-2
- New Horizons
- LISA Pathfinder
- Evolved LISA
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity
Context: A recent judgement of the Orissa High Court held that abusing someone with a caste name during an argument won’t lead to the SC/ST Act case.
About Scheduled Castes and Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989:-
- Ministry of Social Justice is the nodal ministry to enforce the provisions of the Act.
- Objective: This legislation aims at preventing the commission of offences by persons other than Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes against Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- Offender: Any person who is not a member of a scheduled caste or a scheduled tribe and commits an offence listed in the Act against a member of a scheduled caste or a scheduled tribe is an offender.
Salient features of the Act: –
- It punishes crimes against people belonging to Scheduled Castes and Tribes.
- It vests special protections and rights with the victims.
- It creates Special Courts and special public prosecutors for speedier completion of cases.
- It gives compensation, relief, and rehabilitation for victims of atrocities or their legal heirs.
- Mandatory and periodic monitoring systems at District, State, and National levels are constituted.
Cognizable offence:
- All offences listed in the Act are cognizable.
- The police can arrest the offender without a warrant and start an investigation into the case without taking any orders from the court.
Punishments:
- The minimum in most cases is six months imprisonment while the maximum is five years sentence with a fine.
- In some cases, the minimum is enhanced to one year while the maximum goes up to life imprisonment or even a death sentence.
Constitutional provisions related to Scheduled Castes and Tribes:
- Article 17 -of the constitution prohibits the practice of untouchability.
- Article 15 –Prohibition of discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth.
- Article 16 – Equality of opportunity in matters of public employment.
- Article 46 promotes the educational and economic interests of SCs, STs, and other weaker sections of society and protects them from social injustice and exploitation.
- Article 244 – Administration of Scheduled Areas and Tribal Areas.
- Article 244A
- Article 330- Reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes in the House of the People
- Article 332- Reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes in the Legislative Assemblies of the States.
- Article 335- Claims of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes to services and posts.
- Article 338- Special Officer for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes etc.
- Article 339 – Control of the Union over the administration of Scheduled Areas and the welfare of Scheduled Tribes.
- Article 340 – Appointment of a Commission to investigate the conditions of backward classes.
- Article 341: provides certain privileges and concessions to the members of Scheduled Castes
- Article 342: Scheduled Tribes are notified under Article 342 of Constitution by the President of India
- Article 338 – National Commission for Scheduled Castes
- 338-A – National Commission for Scheduled Tribes
- Schedule 5: deals with the administration and control of certain areas called Scheduled and Tribal Areas in ten Indian states, which come under the category of 5th schedule states.
- Schedule 6: To protect the rights of tribal people
MUST READ : 104 Amendment Act , Manual Scavenging
Source: THE HINDU
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) If a particular area is brought under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the consequence of it? (2022)
- This would prevent the transfer of land from tribal people to non-tribal people.
- This would create a local self-governing body in that area.
- This would convert that area into a Union Territory.
- The State having such areas would be declared a Special Category State.
Q.2) At the national level, which ministry is the nodal agency to ensure effective implementation of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006? (2021)
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climatic change.
- Ministry of Panchayat Raj
- Ministry of Rural Development
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs
Syllabus
- Prelims – Government Schemes (Polity)
Context: Recently, the Union Health Minister, launched NaMo Free Dialysis Centre and 100th Janaushadhi Kendra on the occasion of 5th Jan Aushadhi Diwas.
About Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana:
Background:–
- In 2015, the ‘Jan Aushadhi Scheme’ was revamped as ‘Pradhan Mantri Jan Aushadhi Yojana’ (PMJAY).
- In, 2016, to give further impetus to the scheme, it was again renamed “Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana” (PMBJP).
- Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP) is a campaign launched by the Department of Pharmaceuticals.
- Objective: to provide quality medicines at affordable prices to the masses.
- PMBJP stores have been set up to provide generic drugs, which are available at lesser prices but are equivalent in quality and efficacy to expensive branded drugs.
- Vision: to bring down the healthcare budget of every citizen of India by providing Quality generic Medicines at Affordable Prices.
BENEFITS OF THE JAN AUSHADHI CAMPAIGN:-
- It will make available quality drugs at affordable prices through dedicated stores selling generic medicines.
- Promote greater awareness about cost-effective drugs and their prescription.
- Make available unbranded quality generic medicines at affordable prices through a public-private partnership.
- Encourage doctors, more specifically in government hospitals to prescribe generic medicines.
- Enable substantial savings in health care more particularly in the case of poor patients and those suffering from chronic ailments requiring long periods of drug use.
Quality measures:-
- To ensure high quality, medicines are procured from WHO Good manufacturing practice (GMP), Current Good Manufacturing Practice, and CPSUs manufacturers.
- Each batch of drugs procured is tested randomly at BPPI’s empanelled National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL) accredited laboratories thereby ensuring quality, safety, and efficacy of medicines and conformance with required standards.
- Only after being certified by these laboratories, medicines are dispatched to C&F agents, Distributors, and JAKs.
MUST READ : Ayushman Bharat PMJAY, AB-PMJAY and COVID treatment.
Source: NEWSONAIR
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which of the following are the objectives of the ‘National Nutrition Mission?(2017)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls, and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals, and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs. Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2, and 3 only
- 1, 2, and 4 only
- 3 and 4 only
Q.2) With reference to the National Rural Health Mission, which of the following are the jobs of ‘ASHA”, trained community health workers? (2012)
- Accompanying women to the health facility for antenatal care check-ups
- Using pregnancy test kits for early detection of pregnancy
- Providing information on nutrition and immunization
- Conducting the delivery of a baby.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
- 1, 2, and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance (Polity)
Context: NAAC’s top official’s resignation recently has brought to light the flaws in the system to grade colleges, and universities.
About National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC):-
- It’s an autonomous body under the University Grants Commission (UGC).
- It functions under the Ministry of Education.
- It conducts assessment and accreditation of Higher Educational Institutions (HEI) such as colleges, universities, or other recognized institutions to derive an understanding of the ‘Quality Status’ of the institution.
- It evaluates the institutions for their conformance to the standards of quality.
- It assesses performance related to the educational processes and outcomes, curriculum coverage, teaching-learning processes, faculty, research, infrastructure, learning resources, organization, governance, financial well-being, and student services.
VISION: To make quality the defining element of higher education in India through a combination of self and external quality evaluation, promotion, and sustenance initiatives
Mission:
- To arrange for periodic assessment and accreditation of institutions of higher education.
- To stimulate the academic environment for the promotion of quality of teaching-learning and research in higher education institutions.
- To encourage self-evaluation, accountability, autonomy, and innovations in higher education.
- To undertake quality-related research studies, consultancy, and training programmes.
- To collaborate with other stakeholders of higher education for quality evaluation, promotion, and sustenance.
MUST READ : Higher-level Educational Institutions (HEIs) , Vaibhav fellowship
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) What is the purpose of ‘Vidyanjali Yojana’? (2017)
- To enable famous foreign educational institutions to open their campuses in India.
- To increase the quality of education provided in government schools by taking help from the private sector and the community.
- To encourage voluntary monetary contributions from private individuals and organizations so as to improve the infrastructure facilities for primary and secondary schools.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
Q.2) Regarding Digi Locker’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- It is a digital locker system offered by the Government under Digital India Programme.
- It allows you to access your e-documents irrespective of your physical location.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- (a)1 only
- (b)2 only
- (c)Both 1 and 2
- (d)Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context : Recently , NASA announced that its IBEX spacecraft is back to studying edge of solar system after glitch.
About NASA’s IBEX spacecraft :-
- The Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX) was Launched in 2008.
- Launch Vehicle: Pegasus XL Rocket
- It is a small explorer NASA mission tasked with mapping the boundary where winds from the sun interact with winds from other stars. IBEX.
- The purpose of IBEX is to study the interaction between the solar wind and the interstellar medium and to map the boundary of the solar system.
- It uses instruments that look toward the interstellar boundary from a nine-day orbit around Earth.
Scientific Instruments:-
- It has two Very Large Aperture Single Pixel “Cameras”:- IBEX–Hi and IBEX–Lo
- The cameras are mounted on a spinning spacecraft, allowing them to scan the sky and build up a map of the boundary.
Discoveries:-
- The first direct measurements of the interstellar wind, which flows into the solar system from the direction of the constellation Scorpius.
- The discovery of a “ribbon” of energetic neutral atoms that stretches across the sky, may be caused by the interaction between the solar wind and the interstellar medium.
MUST READ : Gaganyaan , IN-SPACe
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Recently, scientists observed the merger of giant ‘blackholes’ billions of light-years away from the earth. What is the significance of this observation? (2019)
- ‘Higgs boson particles’ were detected.
- ‘Gravitational waves’ were detected.
- Possibility of intergalactic space travel through a ‘wormhole’ was confirmed.
- It enabled the scientists to understand ‘singularity’.
Q.2) Consider the following phenomena
- Light is affected by gravity.
- The Universe is constantly expanding.
- Matter warps its surrounding space-time.
Which of the above is/are the prediction/predictions of Albert Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity, often discussed in media? (2018)
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (Governance)
Context: Rumours of migrant workers being assaulted in Tamil Nadu have triggered concern among manufacturers in the state.
About Migrant Worker:
- A migrant worker is a person who migrates within a home country or outside it to pursue work.
- Migrant workers usually do not have the intention to stay permanently in the country or region in which they work.
- In India, Migrant workers usually refer to those who engage in internal migration within the country, often for the purpose of seeking employment.
- Internal migration refers to the movement of people from one place to another within the same country.
Migrant Workers in India:
Report of Working Group on Migration, 2017:
- As per the Report of the Working Group on Migration, 2017 under the Ministry of Housing and Urban Poverty Alleviation, 17 districts accounted for the top 25% of India’s total male out-migration.
- Ten of these districts are in UP, six in Bihar, and one in Odisha.
- Relatively less developed states such as Bihar and Uttar Pradesh have high net out-migration.
- Relatively more developed states take positive CMM (Cohort-based Migration Metric) values reflecting net immigration such as: Goa, Delhi, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka.
- The largest recipient was the Delhi region, which accounted for more than half of migration in 2015-16.
- Uttar Pradesh and Bihar taken together account for half of total out-migrants.
Reasons for internal migration and size of migrant labour force:
- Economic migration: Moving to find work or pursue a particular career, e.g., Indian workers in UAE constitute the largest part of the population of UAE (27%).
- Social migration: Moving to be closer to family or friends or for a better quality of life. E.g., Indian diaspora in USA going for higher education and better paying jobs
- Political migration: Moving to escape war or political persecution, e.g., the recent Rohingya migration to Bangladesh and India from Myanmar and the Syrian refugee crisis with 6 million leaving the country and 10 million internally displaced.
- Environmental causes of migration: It includes natural disasters such as an earthquake. Many are forced to move during annual floods and cyclones in India.
- Citizens of island countries Kiribati, Tuvalu and Nauru are moving out due to sea level rise.
- Push and pull factors driving migration: People migrate when the perceived interaction of push and pull factors overcome the friction of moving.
- Push factors are elements of the place of origin that are perceived negatively leading to a desire to leave.
- These include drought, famine, lack of jobs, over-population, civil war etc. Agrarian distress is a major push factor for economic migrants in India.
- Pull factors are elements of the destination that are perceived positively leading to place-attraction.
- These include a chance of a better job, education, standard of living or even better climate.
Problems faced by Migrant Workers in India:
- Social exclusion: Migrant workers are often stigmatized and discriminated against due to their ethnicity, language, and cultural differences.
- Lack of job security: Migrant workers often work in unorganized and informal sectors with low wages and no job security.
- They are vulnerable to exploitation, including being paid less than minimum wages, being forced to work long hours, and being subjected to unsafe working conditions.
- Inadequate living conditions: Migrant workers often live in crowded and unhygienic living conditions, with limited access to sanitation facilities. This makes them vulnerable to diseases and illnesses.
- Lack of legal protection: They often face difficulties in accessing justice when their rights are violated. They are not covered by most labour laws and do not have access to social security benefits.
- Lack of access to education: Migrant children often face challenges in accessing education due to language barriers and discrimination. Many of them drop out of school to support their families.
- Lack of coordination among states: There is inadequate coordination among states on a formal exchange of information on migrant workers. In the absence of data, it is difficult to track labourers during times of crisis.
- Exploitation by middlemen: Migrant workers often rely on middlemen or labour contractors to find work, who take advantage of their vulnerable position by charging high fees and forcing them to work in unsafe and exploitative conditions.
Challenges and issues associated with migration:
Multiple vulnerabilities
- The major factors that create multiple vulnerabilities are: economic and food insecurity, harsh living conditions, health hazards, social prejudice, political exclusion and economic hardship.
- The informal nature of their employment compels migrant workers to work for very low wages under extremely harsh conditions for long working hours.
Food insecurity
- As the migrant workers’ ration cards remain with their families in their native villages, they are not entitled to subsidised food in their work cities.
- So, unlike the local poor, the migrants had to spend a substantial portion of their income on buying food.
- Job losses, negligible savings, and lack of documentation for accessing free food created unprecedented challenges for poor migrants in the cities.
Victim of prejudice and exclusion
- Deep-rooted social prejudices against the ‘outsider’ image of the ‘migrant’ labour is prevalent in the local city dwellers.
- Migrants were often perceived as ‘dirty’, ‘job usurpers’, ‘criminals’ and ‘anti-socials’.
- They are subjected to harsh treatment from city administration and police for lack of documents.
- As the workers are not voters of the city in which they work, the political class of the city seem indifferent to their hardship.
States reserve jobs for own residents
- In March 2021, the Haryana government notified a law to reserve 75% of private jobs for local people.
- Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh already have, or have proposed, similar provisions.
Way Forward:
- Addressing Governance Deficit: Better law and order system should be enforced in source regions.
- Increasing Developmental Opportunities: When job and education opportunities are fulfilled in the native place, migration rates start declining.
- Other Measures should be taken up for providing basic amenities like health, education, residence.g. PM Awas Yojna.
- Skill Creation and Employment Generation: Skill development to make the youth employable in place of domicile.
- Eliminating effect of Push and Pull factors: The broad based and effective implementation of schemes like Provision of Urban Amenities to Rural Areas (PURA) will not only reduce migration but also establish Gandhian “village republics” in the long run.
- Promote agriculture as primary occupation through schemes like:
- Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay Unnat Krishi Shiksha Scheme: Started in 2016, it promotes agricultural education in India.
- Attracting and Retaining Youth in Agriculture (ARYA) project: It is implemented at Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVKs) and sanctioned by Indian Council of Agricultural Research.
- Industry-friendly policies: To promote business and job opportunities in rural areas, e.g. MUDRA scheme, Make in India programme etc.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Security Issues)
Context: The Ministry of Defence emphasizes the need to maintain constant vigil on northern and western borders, coastline.
- At the Naval Commanders Conference aboard INS Vikrant, Indian defence minister stressed the need to re-strategies due to the constantly evolving world order.
- The meeting emphasized that future conflicts will be unpredictable and that constant vigilance on the northern and western borders and entire coastline is necessary.
- The defence sector is expected to transform India’s economy, and orders worth over USD 100 billion are expected to be placed through the defence sector in the next 5-10 years.
About India’s Border Disputes:
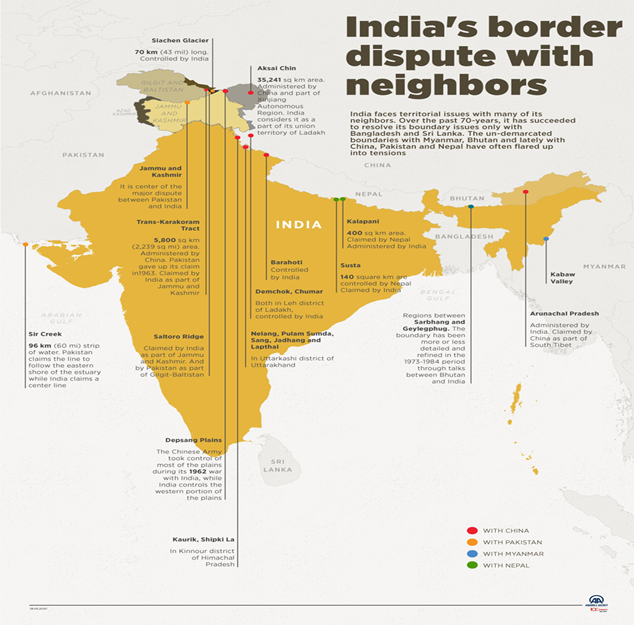
Importance of border vigilance:
- National security: India shares borders with several countries, some of which have a history of hostile relations.
- Constant vigilance in these areas helps to ensure national security and prevent any security threats.
- Protecting sovereignty: Borders and coastline areas are the first line of defense for the country, and maintaining vigilance helps to protect India’s sovereignty.
- Preventing illegal activities: Border and coastline areas are often used for illegal activities such as smuggling, human trafficking, and drug trafficking.
- Vigilance helps to prevent such illegal activities and ensure the safety and security of citizens.
- Disaster management: Natural disasters such as cyclones and tsunamis can cause widespread damage and loss of life in coastal areas.
- Vigilance helps to ensure timely evacuation and disaster management in such situations.
- Economic growth: India’s ports and coastal areas are important for economic growth and development, and vigilance helps to ensure the safety and security of these areas.
Challenges of border vigilance:
- Geographic barriers: The northern and western borders of India are characterized by difficult terrain such as mountains, deserts, and forests, which makes it challenging to maintain constant vigilance.
- Lack of infrastructure: The lack of infrastructure in remote border areas makes it challenging to monitor and secure the borders effectively.
- Infiltration attempts: The borders are porous, making them vulnerable to infiltration attempts by terrorists, smugglers, and other illegal activities.
- Coordination with multiple agencies: Vigilance in border and coastline areas requires coordination between multiple agencies, including the military, paramilitary forces, and local law enforcement agencies.
- Climate and weather conditions: Harsh climate and weather conditions, such as extreme temperatures, heavy rains, and snowfall, pose challenges to border and coastline surveillance.
- Technology and equipment: The deployment of modern technology and equipment, such as unmanned aerial vehicles, radars, and sensors, is necessary for effective border and coastline surveillance.
Government steps to secure Indian borders:
- Use of modern technology: The government has deployed modern technology such as unmanned aerial vehicles, radars, and sensors for effective surveillance along the border.
- Strengthening border infrastructure: The government has allocated significant funds for the construction of roads, border outposts, and fencing along the border helping in improving the mobility of security forces and better surveillance.
- Strengthening border forces: The government has increased the strength of border forces such as the Border Security Force (BSF) and the Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) and provided them with better equipment and training.
- Cross-border connectivity: The government is also focusing on improving cross-border connectivity through road, rail, and air networks to improve the security of the border regions.
- Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS): CIBMS is a high-tech surveillance system that uses modern technology such as thermal imagers, underground sensors, and laser barriers to secure the border.
- Smart fencing: The government is also working on the development of smart fencing along the border, which will have a network of surveillance devices to detect any intrusions.
- Border Area Development Programme (BADP): This scheme aims to promote the development of the border areas by providing basic infrastructure such as roads, schools, health centers, and promoting economic activities.
- Coastal Security Scheme: It aims to enhance the surveillance capabilities of coastal states and Union Territories to prevent any threats from the sea.
- Scheme for Protection and Empowerment of Women in Border Areas (SPARSH): It aims to provide education and vocational training to women in border areas and to empower them to become self-reliant.
Way Forward:
Thus, the vigilance in border and coastline areas is crucial for maintaining national security, preventing illegal activities, protecting sovereignty, promoting economic growth, and ensuring effective disaster management.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Consider the following statements regarding Global Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Infrastructure (GGGMI):
- It is endorsed by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Executive Council.
- It will establish an internationally coordinated approach to observing network design, and to the acquisition, international exchange, and use of the resulting observations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements regarding National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC):
- It’s an autonomous body under the University Grants Commission (UGC).
- It functions under the Ministry of Skill Development.
- It conducts assessment and accreditation of Higher Educational Institutions (HEI) in India
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana:
- It is a campaign launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- It will make available quality drugs at affordable prices through dedicated stores selling generic medicines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 10th March 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 9th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – b














