IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs Analysis
Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Affairs
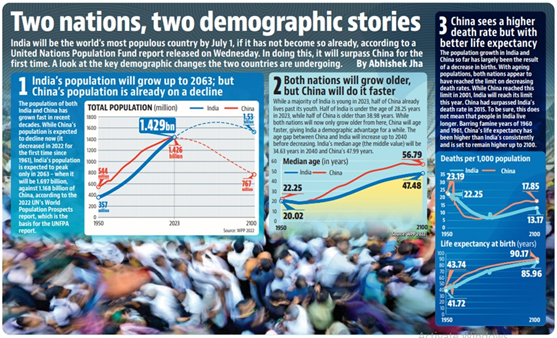
Context: The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) has recently released its report- State of World Population (SOWP).
Key highlights of the report:
Source: Hindustan Times
- The population of the world is 8,045 million.
- The largest share in population has age between 15- 64 years (65%), followed by the 10-24 years (24%) and above 65 years of age (10 %).
- China and India accounts for the largest populations in Asia, with more than 1.4 billion each in 2022.
- India is now the most populous country in the world, outstripping China’s population.
- The rate of global population growth has fallen and is less than 1 % since 2020.
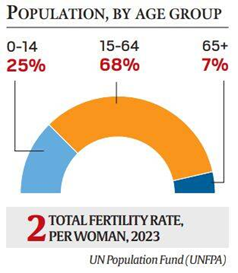
India’s demography:
Age group:
Source: Indian Express
- 68% belongs to the 15-64 years and 26% belongs to the 10-24 years.
- Result: India is one of the youngest countries in the world with 50% of its population below the age of 25.
- The fertility rate in India has been steadily dropping and is lower than 2.1 children per woman.
- Reason of decline: use of contraceptive methods, spacing of pregnancies, access to health care, impetus to family planning, increasing wealth and education.
- Life expectancy for men is 71 years, while it is lower for women at 74 years.
Key projections:
- The global population could grow to around 8.5 billion in 2030, 9.7 billion in 2050 and 10.4 billion in 2100.
- Maximum increase till 2050 will be concentrated in: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines and the United Republic of Tanzania.
- If India’s population continues to grow at the current pace, it would double from the present value in the next 75 years.
Outlook for population growth
- Latest projections suggest that the rate of global population growth has fallen, and has been at less than 1 per cent since 2020.
- This is largely due to declining fertility.
- Around two thirds of people live in a country or area with a total fertility rate at or below 2.1 children per woman (also called “replacement fertility” rate or “zero-growth fertility” rate).
- In 1950 the global fertility rate stood at 5.
- Already 60% of the world’s population lives in a region where the fertility rate is below replacement level, up from 40% in 1990.
Migration as driver of growth:
- It is international migration that is now the driver of growth in many countries, with 281 million people living outside their country of birth in 2020.
- Migration has also occurred due to war, famines, and other catastrophes.
- South Asia clocks some of the highest emigration trends, with India seeing an estimated net outflow of 3.5 million between 2010 and 2021.
- Pakistan has the highest net flow of migrants of 16.5 million during the same period.
Birth rate:
- Despite the continuing decline in the average number of births per woman, the total annual number of births has remained stable at around 140 million since the late 1980s.
- It is due to the youthful age distribution of the global population.
- In 2021, 134 million babies were born worldwide.
- In the future, the number of new-borns is expected to slightly increase to reach 138 million annually between 2040 and 2045, despite the continuous decline in the average number of births per woman.
- In 2021, most births worldwide occurred in the two most populous regions—Asia and sub-Saharan Africa.
Life Expectancy:
- One of the reasons for population growth globally flagged by the UNFPA has been that of increasing life expectancy.
- Fertility rates and mortality rates have been dropping in various parts of the world with better access to health care and improving standards of living.
- Life expectancy among men now stands at 71 years while among women it stands at 76 years.
- Globally, life expectancy reached 72.8 years in 2019, an increase of almost 9 years since 1990.
Source: Hindustan Times
Must Read: Demographic Dividend
Syllabus
- Prelims: Science and Technology
In News: After Ghana, Nigeria’s approval of malaria vaccine will help world achieve WHO goal of reducing malaria cases, deaths by 90% by 2030.
About R21 / Matrix-M Malaria Vaccine:
- The R21, otherwise referred to as Matrix-M malaria vaccine, is the second vaccine ever developed for a disease.
- The first-ever malaria vaccine, RTS, S or Mosquirix was approved by the WHO in 2021.
- Since 2015, 9 countries have been certified by the WHO Director-General as malaria-free, including Maldives, Sri Lanka , Kyrgyzstan, Paraguay, Uzbekistan, Argentina, Algeria, China (2021) and El Salvador (2021).
Initiatives to Curb Malaria
Global Initiatives:
- The WHO has also identified 25 countries with the potential to eradicate malaria by 2025 under its ‘E-2025 Initiative’.
- WHO has initiated the High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) initiative in 11 high malaria burden countries, including India.
- Implementation of “High Burden to High Impact (HBHI)” initiative has been started in four states i.e. West Bengal and Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh.
Indian Initiatives:
- The Government of India set a target to eliminate malaria in India by 2027.
- It developed a National Framework for Malaria Elimination (2016-2030)
- National Strategic Plan for Malaria Elimination for 5 years.
- Launched in 2017
- It provided a roadmap to end malaria in 571 districts out of India’s 678 districts by 2022.
- Malaria Elimination Research Alliance-India (MERA-India)
- Established by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
Source: DTE
MUST READ: CRISPR Biotechnology
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements:
- The Serum Institute of India produced COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using mRNA platform.
- Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using vector based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to recent developments regarding ‘Recombinant vector Vaccines’, consider the following statements:
- Genetic engineering is applied in the development of these vaccines.
- Bacteria and viruses are used as vectors.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (2021)
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
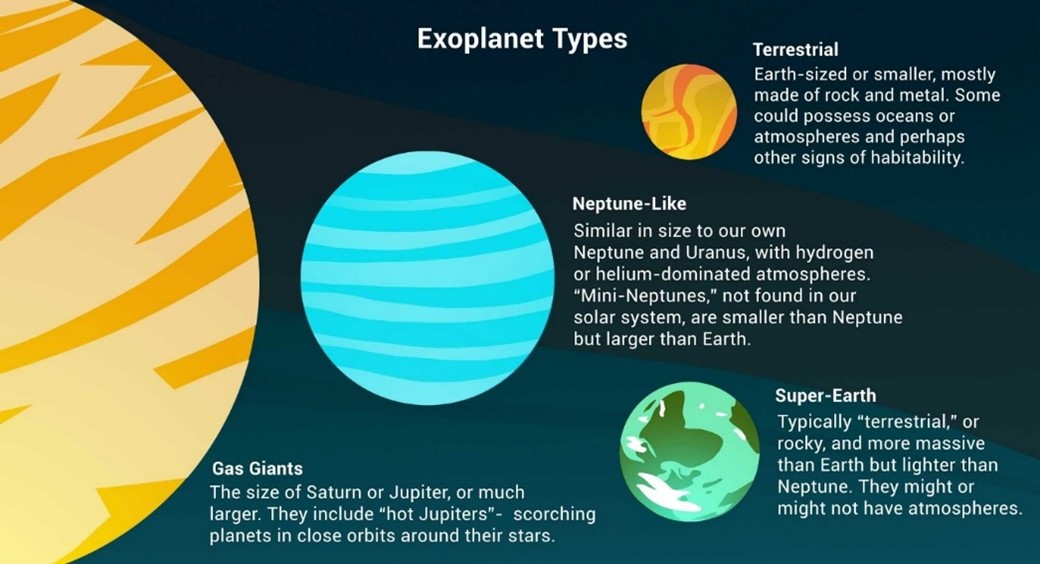
Context: Astronomers have detected a repeating radio signal from an exoplanet, YZ Ceti b, suggesting the presence of a magnetic field — one of the prerequisites for a habitable planet — around it.
About YZ Ceti b:
Source: NASA
- It is a rocky, earth-sized exoplanet.
- It is a terrestrial exoplanet that orbits an M-type star.
- Its discovery was announced in 2017.
- Its mass is 0.7 Earths.
- It takes 2 days to complete one orbit of its star.
- It is 12 light-years from Earth.
Source: The Hindu
Previous year Questions
Q.1) If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth? (2022)
- GPS and navigation systems could fail.
- Tsunamis could occur at equatorial regions.
- Power grids could be damaged.
- Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth.
- Forest fires could take place over much of the planet.
- Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed.
- Shortwave radio communication of the aircraft flying over polar regions could be interrupted.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 4 and 5 only
- 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 only
- 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Q.2) Which one of the following is a reason why astronomical distances are measured in light-years? (2021)
- Distance among stellar bodies do not change
- Gravity of stellar bodies does not change
- Light always travels in straight line
- Speed of light is always same
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: The Central Government recently appointed former Special Protection Group (SPG) chief as the Chairman of the National Technical Research Organisation (NTRO).
About National Technical Research Organisation (NTRO):
- It is a technical intelligence Agency under the National Security Advisor in the Prime Minister’s Office, India.
- It was formed in 2004 to strengthen the country’s national security apparatus.
- It is under the direct control of the Prime Minister’s Office and operates as an autonomous organization.
- Primary Objective: Gather technical intelligence, which involves intercepting and analyzing communications signals, imagery intelligence, and cyber intelligence.
- It also provides technical assistance to other intelligence agencies in the country, including the Intelligence Bureau and Research and Analysis Wing.
- It is responsible for maintaining a database of information related to technology and developing advanced tools and techniques for intelligence gathering.
- It also conducts research and development activities in the field of technical intelligence.
- NTRO is headed by a Chairman who reports directly to the Prime Minister of India.
- HQ: New Delhi,
About Special Protection Group (SPG):
- It was formed in 1985 after the assassination of Prime Minister Indira Gandhi as an executive body on the recommendation of the Birbal Nath committee.
- Later on, it became a statutory body under Special Protection Group Act 1988.
- It is governed by the Cabinet secretariat of India.
- SPG chief is an officer of the rank of inspector-general.
- It is entrusted with the task of providing proximate security to the Prime Minister of India, the former Prime Minister and their immediate family members.
Source: India Today
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science and Technology
Context: The Union Cabinet recently approved the ₹6,003 crore National Quantum Mission (NQM).
About National Quantum Mission (NQM):
- NQM will fund research and development of quantum computing technology and associated applications.
- Led by: Department of Science and Technology
- The mission will have defined milestones that are expected to be achieved over the course of eight years (2023-24 to 2030-31).
- India is the sixth country to have a dedicated quantum mission after the US, Austria, Finland, France and China.
- Four thematic hubs, or T-Hubs, with a focus on quantum computing, communication, sensing and metrology, and materials and devices will be established in India’s leading academic and national R&D institutes.
Objectives:
- Create intermediate-scale quantum computers with 50-1000 qubits in the next eight years.
- Establish satellite-based secure quantum communications between ground stations within India, as well as with other countries, covering a range of 2000 km.
- It will look to provide inter-city quantum key distribution over 2000 km.
- Multi-node quantum network with quantum memories.
- Help to advance atomic technology with highly sensitive magnetometers and precision atomic clocks that serve communication, navigation, and timing.
- Aid in designing and synthesising quantum materials, including superconductors, novel semiconductor structures, and topological materials for the fabrication of quantum devices.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to “Software as a Service (SaaS)”, consider the following statements:
- SaaS buyers can customise the user interface and can change data fields.
- SaaS users can access their data through their mobile devices.
- Outlook, Hotmail and Yahoo! Mail are forms of SaaS.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) Which one of the following is the context in which the term “qubit” is mentioned? (2022)
- Cloud Services
- Quantum Computing
- Visible Light Communication Technologies
- Wireless Communication Technologies
Syllabus
- Prelims – Economy
Context: The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) recently launched the Audit Quality Maturity Model (AQMM) with the aim of enhancing the quality of audits and improving transparency.
About Audit Quality Maturity Model (AQMM):
- It is a tool for the self-evaluation of audit firms & sole proprietors towards technologically driven mechanisms to increase operational efficiency.
- AQMM is an amalgamation of a well-researched set of Audit Quality Indicators (AQIs).
- It includes operations of the firm, viz. revenue budgeting and pricing, audit practice manual, budgeting of engagements, timesheet, use of technology adoption, quality control for engagements, Human Resource Management including resource planning and monitoring, performance evaluation and compensation, physical and IT infrastructure.
- The AQMM model is structured into 3 sections with a total score of 600 points,
- Practice Management (Operation);
- Human Resource Management;
- Practice Management -Strategic/Functional;
- Based on the score(s) obtained under each of the sections, the firm shall arrive at a level ranging from Level 1 to 4.
- While Level 1 depicts that the firm is very nascent, Level 4 indicates that the firm has made significant adoption of standards and procedures.
About Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI):
- It is a statutory body established by an Act of Parliament, viz. The Chartered Accountants Act, 1949.
- Mandate: Regulating the profession of Chartered Accountancy in the country; Formulation of Accounting Standards; and Prescription of Standard Auditing Procedures.
- It functions under the administrative control of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India.
- The affairs of the ICAI are managed by a Council which comprises of 40 members, of whom 32 are elected by the Chartered Accountants and the remaining 8 are nominated by the Central Government.
Source: Financial Express
MUST READ: NFRA
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) With reference to the ‘Banks Board Bureau (BBB)’, which of the following statements are correct? (2022)
- The Governor of RBI is the Chairman of BBB.
- BBB recommends for the selection of heads for Public Sector Banks.
- BBB helps the Public Sector Banks in developing strategies and capital raising plans.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.2) What was the purpose of the Inter Creditor Agreement signed by Indian banks and financial institutions recently? (2019)
- To lessen the Government of India’s perennial burden of fiscal deficit and current account deficit
- To support the infrastructure projects of Central and State Governments
- To act as independent regulator in case of applications for loans of Rs. 50 crore or more
- To aim at faster resolution of stressed assets of Rs. 50 crore or more which are-under consortium lending
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: Recently, Sri Lanka confirmed China’s request for importing 1,00,000 Toque macaques.
About Toque Macaque:

Source: https://neprimateconservancy.org/toque-macaque/
- It is a golden brown-coloured monkey.
- The toque macaque monkey is endemic to Sri Lanka .
- It spends a large amount of time in trees and lives in all types of forests
- Threats: habitat loss owing to the encroachment of plantations, and fuel wood collection.
- Other threats include shooting, snaring, and poisoning of the animals, as they are considered to be crop pests.
- Protection Status:
- It is protected internationally under CITES Appendix II.
- It is classified as Endangered on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) red list.
Source: The Hindu
Previous Year Questions
Q.1) Which one of the following has been constituted under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 ? (2022)
- Central Water Commission
- Central Ground Water Board
- Central Ground Water Authority
- National Water Development Agency
Q.2) Which of the following is not a bird? (2022)
- Golden Mahseer
- Indian Nightjar
- Spoonbill
- White Ibis
Syllabus
- Prelims – Governance
Context: Recently, the Indian scientists working in the Garbh-Ini programme have identified 19 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), or genetic markers, that are associated with preterm or premature birth.
About Garbh-Ini programme:

Source: garbhinicohort.in
- It promotes Maternal and Child Health and develops prediction tools for preterm birth.
- Garbh-Ini is a cohort study of pregnant women initiated in May 2015 at the civil hospital in Gurugram, Haryana, India.
- It is an initiative under the Department of Biotechnology of the Union Ministry of Science and Technology as a collaborative interdisciplinary programme.
- This program is led by the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), NCR Biotech cluster, Faridabad.
- It is part of the Atal Jai Anusandhan Biotech Mission – Undertaking Nationally Relevant Technology Innovation (UNaTI).
About single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP):
- It is the most common type of genetic variation among people.
- Each SNP represents a difference in a single DNA building block, called a nucleotide.
- For example, an SNP may replace the nucleotide cytosine (C) with the nucleotide thymine (T) in a certain stretch of DNA.
- Most commonly these are found in the DNA between genes.
Significance:
- These help in predicting an individual’s response to certain drugs, susceptibility to environmental factors such as toxins, and risk of developing diseases.
- These can also be used to track the inheritance of disease-associated genetic variants within families.
- They can act as biological markers which help scientists locate genes that are associated with the disease.
Source: Indian Express
MUST READ: consequences-of-declining-fertility
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: Recently, the Inter-governmental Commission on Trade, Economic, Scientific, Technological and Cultural Cooperation meet was held between India and Russia.
India-Russia Relations:
Historical relationship:
- During that, Russia has mentioned the support of the Soviet Union for India’s sovereignty over the disputed territories of Kashmir and Portuguese coastal enclaves such as Goa. Even after the abrogation of Article 370 Russia still supports India’s claim over Kashmir.
- The USSR agreed to transfer technology to co-produce the Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 jet fighter in India in 1962. But the USSR rejected a similar move to China.
- India signed the Indo-Soviet Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation in 1971 during the Bangladesh liberation war.
Political Relations:
- The Annual Summit meeting between the Prime Minister of India and the President of the Russian Federation is the highest institutionalized dialogue mechanism in the strategic partnership between India and Russia.
- So far 20 Annual Summit meetings have taken place alternatively in India and Russia.
Intergovernmental Commissions:
- There is regular high-level interaction between the two countries.
- The IRIGC (India-Russia Intergovernmental Commission):
- It is the main body that conducts affairs at the governmental level between both countries. Both countries are members of international bodies including the UN, BRICS, G20 and SCO.
- Two Inter-Governmental Commissions:
- One on Trade, Economic, Scientific, Technological and Cultural Cooperation (IRIGC-TEC), co-chaired by EAM and the Russian DPM, and
- Another on Military-Technical Cooperation (IRIGC- MTC) co-chaired by Russian and Indian Defence Ministers, meet annually.
Trade and Economic Relations:
- It is clear by the revised targets of increasing bilateral investment to US $ 50 billion and bilateral trade to US $ 30 billion by 2025.
- Bilateral trade during April 2020-March 2021 amounted USD 8.1 billion. Indian exports amounted USD 2.6 billion while imports from Russia amounted USD 5.48 billion.
- India Russia Intergovernmental Commission for Trade, Economic, Scientific & Cultural Cooperation (IRIGC-TEC).
- India-Russia Strategic Economic Dialogue (IRSED) has been established for cooperation in the field of development of economic policy and to encourage regular interactions and cooperation between the two countries.
- India is contemplating an FTA/ CECA with the Eurasian Economic Union.
- India is keen to engage more closely with Russia and the CIS countries to further intensify our trade and economic cooperation with this region.
- Bilateral trade in services: Bilateral trade in services has remained stable during the last 5 years with trade balance in Russia’s favour.
- While in 2017, trade in services was USD 1095.4 million, it reduced slightly in 2018 to USD 999 million. The figure stands at USD 973.645 million for the year 2020.
- Investment: Russian investment in India in 2017 has reached 18bn USD and India’s total investment in Russia so far is 13 bn USD.
- The overall investment target of 30 bn USD that was set for 2025 has been already crossed. Investment cooperation has been envisaged in some priority sectors such as hydrocarbons, power, coal, nuclear power, fertilizers, IT, mineral and metallurgy, steel, pharmaceuticals, infrastructure projects amongst others.
Defence and Security Relations:
- India-Russia military-technical cooperation has evolved from a buyer-seller framework to one involving joint research, development and production of advanced defence technologies and systems
- Joint Tri-Services Exercise ‘INDRA 2019’ between India and Russia was carried out simultaneously in Babina, Pune, and Goa in 2019.
- The joint military programmes between India and Russia include:
- BrahMos cruise missile programme
- 5th generation fighter jet programme
- Sukhoi Su-30MKI programme
- Ilyushin/HAL Tactical Transport Aircraft
- KA-226T twin-engine utility helicopters
- The military hardware purchased/leased by India from Russia includes:
- S-400 TRIUMF
- Kamov Ka-226 200 to be made in India under the Make in India initiative
- T-90S Bhishma
- INS Vikramaditya aircraft carrier programme
- S-400 air defence system
Energy Security
- In Energy sector Russia has built nuclear reactors in India (Kudankulam reactors), adopted strategic vision in nuclear energy, offered oil, gas and investment opportunities in the fuel sector of Russia e.g. Sakhalin I etc.
- Both are extending civil nuclear cooperation to 3rd countries, e.g. Bangladesh.
Science & Technology
- The Working Group on Science and Technology, the Integrated Long Term Programme (ILTP) and the Basic Science Cooperation Programme are the three main institutional mechanisms for bilateral Science and Technology cooperation.
- Science Academies of the two countries promote inter-academy exchanges.
Space Exploration:
- Both sides cooperate in the peaceful uses of outer space, including satellite launches, GLONASS navigation system, remote sensing and other societal applications of outer space.
- An MoU ISRO and ROSCOSMOS on Joint Activities in the field of Human Spaceflight Programme was signed during the 19th Bilateral Summit.
Significance of relationship for India:
- Balancing China:
- Russia organised a trilateral meeting among the foreign ministers of Russia, India and China following deadly clashes in Galwan valley.
- This shows that Russia can contribute in defusing tensions with China whose relations with India have come to an inflection point.
- Emerging New Sectors of Economic Engagement:
- mining, agro-industrial, and high technology, including robotics, nanotech, and biotech.
- India’s footprint in the Russian Far East and in the Arctic is set to expand.
- Connectivity projects may get a boost too.
- Combating Terrorism:
- India and Russia are working on Afghanistan.
- Similarly, both are calling for early formalisation of Comprehensive Convention on International terrorism.
- Support At Multilateral Forums:
- Russia has been a long standing supporter of India’s membership of the Nuclear Suppliers Group and Permanent Membership in an expanded UNSC.
Way Forward:
It is in the vital interest of both countries to ensure that the area which relates to the security and defence, civil nuclear energy and space among, is insulated from mutual differences in outlook on some geo-political issues and the pressures of other powers.
India-Russia economic relations carry a lot of potential, but they need to be scaled up. Finding a new logic for the ‘special relationship’ remains a task in progress, and the leadership on both sides should pursue this with energy and enthusiasm.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) The State of World Population (SOWP) 2022 report recently released by
- The United Nations Population Fund
- United Nations Development Programme
- NITI Aayog
- World Economic Forum
Q.2) ‘E-2025 Initiative’ and High Burden to High Impact (HBHI) are the Initiatives of WHOs launched to eliminate
- Tuberculosis
- Malaria
- Dengue
- Polio
Q.3) Consider the following statements regarding the National Technical Research Organisation (NTRO):
- It is a technical intelligence Agency under the National Security Advisor in the Prime Minister’s Office, India.
- It was formed in 1985 after the assassination of Prime Minister Indira Gandhi on the recommendation of the Birbal Nath committee.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 21st April 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 20th April – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – b











